A Novel Propofol Dosing Regimen for Pediatric Sedation during Radiologic Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Pediatric Sedation Protocol
2.3. Statistical Analysis
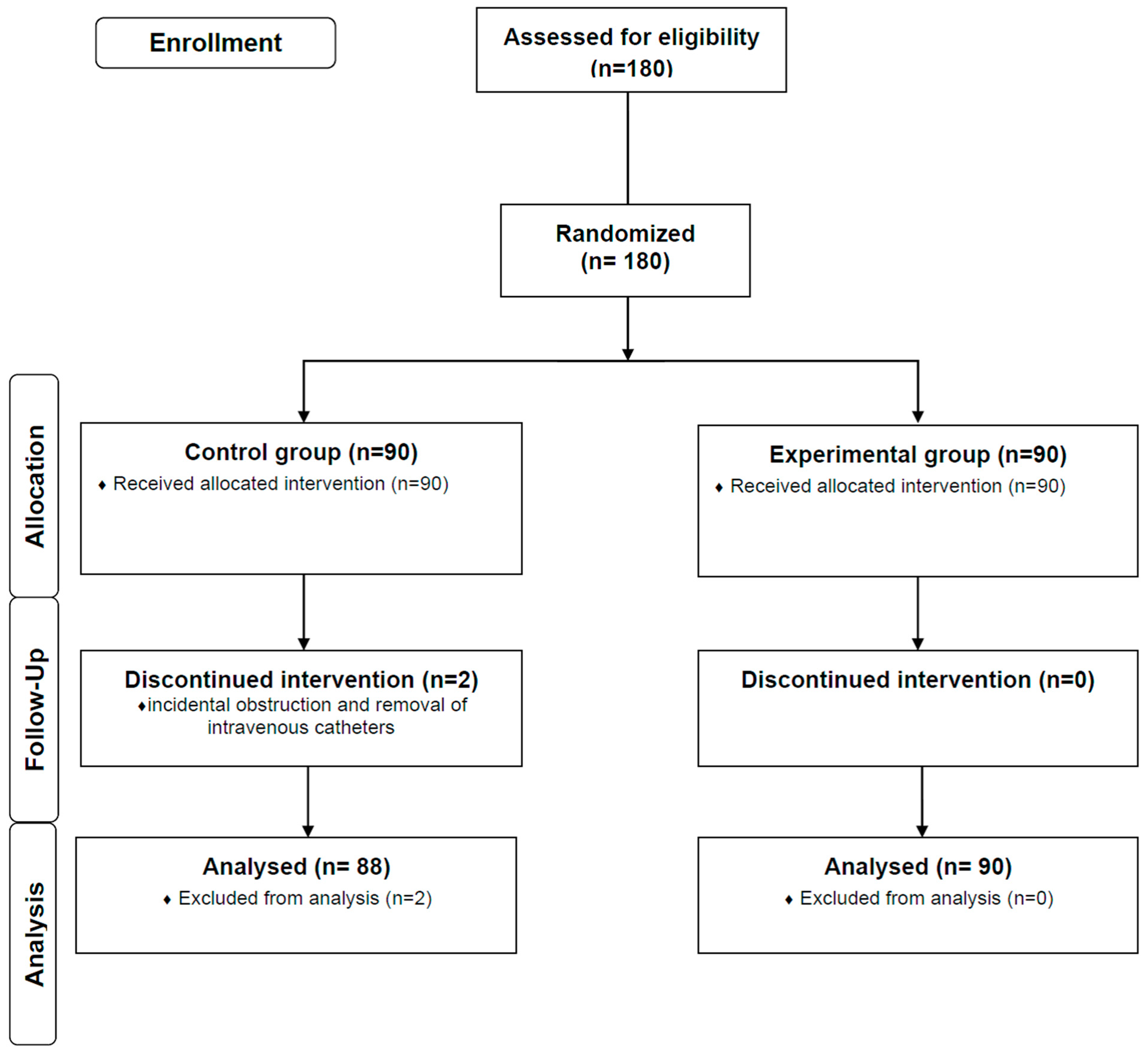
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, H.; Chao, L.; Miao, T.; Ling, L.S.; Ying, P.Y.; Han, P.X.; Bo, X.Y. Serious airway-related adverse events with sevoflurane anesthesia via facemask for magnetic resonance imaging in 7129 pediatric patients: A retrospective study. Pediatr. Anesth. 2019, 29, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongodi, S.; Ottonello, G.; Viggiano, R.; Borrelli, P.; Orcesi, S.; Pichiecchio, A.; Balottin, U.; Mojoli, F.; Iotti, G.A. Ten-year experience with standardized non-operating room anesthesia with Sevoflurane for MRI in children affected by neuropsychiatric disorders. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.M. Drug selection for sedation and general anesthesia in children undergoing ambulatory magnetic resonance imaging. Yeungnam Univ. J. Med. 2020, 37, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravero, J.P.; Blike, G.T. Review of Pediatric Sedation. Anesthesia Analg. 2004, 99, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, J.; Bao, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhu, Q.; Shang, S.; Weiqiang, D.E.; Xia, W. Benefits of Silent DWI MRI in Success Rate, Image Quality, and the Need for Secondary Sedation During Brain Imaging of Children of 3–36 Months of Age. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, A.M.; Markowitz, R.I.; Kimmel, B.; Kroger, M.; Bartko, M.B. Sedation for Pediatric Patients Undergoing CT and MRI. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1992, 16, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, S.; Voepel-Lewis, T.; Eldevik, O.; Rockwell, D.; Wong, J.; Tait, A. Sedation and general anaesthesia in children undergoing MRI and CT: Adverse events and outcomes. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 84, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthurs, O.J.; Sury, M. Anaesthesia or sedation for paediatric MRI: Advantages and disadvantages. Curr. Opin. Anesthesiol. 2013, 26, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, A.; Salem, Y.; Padeh, S.; Paret, G.; Barzilay, Z. Is propofol safe for procedural sedation in children? A prospective evaluation of propofol versus ketamine in pediatric critical care. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machata, A.-M.; Willschke, H.; Kabon, B.; Kettner, S.C.; Marhofer, P. Propofol-based sedation regimen for infants and children undergoing ambulatory magnetic resonance imaging. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chidambaran, V.; Costandi, A.; D’Mello, A. Propofol: A Review of its Role in Pediatric Anesthesia and Sedation. CNS Drugs 2015, 29, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, K.E.; Anderson, J.L.; Pribble, C.G.; Guenther, E. Propofol for procedural sedation in children in the emergency department. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2003, 42, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skokan, E.G.; Pribble, C.; Bassett, K.E.; Nelson, D.S. Use of Propofol Sedation in a Pediatric Emergency Department: A Prospective Study. Clin. Pediatr. 2001, 40, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milius, E.M.; Papademetrious, T.R.; Heitlinger, L.A. Retrospective Review of Propofol Dosing for Procedural Sedation in Pediatric Patients. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 17, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigouzzo, A.; Servin, F.; Constant, I. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Propofol in Children. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2010, 113, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby-Jones, A.E.; Sneyd, J.R. Propofol and children—what we know and what we do not know. Pediatr. Anesth. 2010, 21, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinez, L.H.; Munoz, H.R.; Lopez, R. Pharmacodynamics of propofol in children and adults: Comparison based on the auditory evoked potentials index. Rev. Esp. De Anestesiol. Y Reanim. 2006, 53, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.N. The problems in scaling adult drug doses to children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2008, 93, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, I.; Boddy, A.V.; Wallace, H.; Mycroft, J.; Hollis, R.; Picton, S. Body surface area estimation in children using weight alone: Application in paediatric oncology. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.Y.; Lee, J.-R.; Kang, Y.S.; Ho, J.H.; Byon, H.J. Pediatric characteristics and the dose of propofol for sedation during radiological examinations: A retrospective analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 0300060521990992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangerven, M.; van Hemelrijck, J.; Wouters, P.; Vandermeersch, E.; van Aken, H. Light anaesthesia with propofol for paediatric MRI. Anaesthesia 1992, 47, 706–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlachov, Y.; Ganatra, R.H. Sedation/anaesthesia in paediatric radiology. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e1018–e1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.L.; Lennox, P.H. Sedation and Analgesia in the Interventional Radiology Department. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiak, K.D.; Phan, H.; Christich, A.C.; Edwards, C.J.; Skrepnek, G.H.; Patanwala, A.E. Induction dose of propofol for pediatric patients undergoing procedural sedation in the emergency department. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2012, 28, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravero, J.P.; Beach, M.L.; Blike, G.T.; Gallagher, S.M.; Hertzog, J.H.; Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium. The incidence and nature of adverse events during pediatric sedation/anesthesia with propofol for procedures outside the operating room: A report from the Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, M.D.; Baxter, A.L.; Kost, S.I. Propofol vs. pentobarbital for sedation of children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging: Results from the Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium. Pediatr. Anesth. 2009, 19, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control Group (n = 88) | Experimental Group (n = 90) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (month) | 31.0 (21.0–49.0) | 39.5 (25.0–51.5) | 0.121 |
| Sex (male/female) | 54/34 | 55/35 | 0.972 |
| Weight (kg) | 13.8 (10.4–16.4) | 14.6 (11.9–16.0) | 0.429 |
| Height (cm) | 90.0 (80.0–99.9) | 95.0 (83.0–102.0) | 0.118 |
| BSA (m2) | 0.58 (0.48–0.67) | 0.61 (0.52–0.68) | 0.215 |
| Control Group (n = 88) | Experimental Group (n = 90) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neurologic disorder | 57 (64.8%) | 55 (61.1%) | 0.613 |
| Seizure disorder | 20 | 16 | |
| Anatomical malformation | 16 | 22 | |
| Tumor | 11 | 10 | |
| Vascular disease | 6 | 2 | |
| Shunt related problem | 2 | - | |
| Trauma | 2 | 5 | |
| Genetic disorder | 15 (17.0%) | 9 (10.0%) | 0.169 |
| Delayed development | 11 | 9 | |
| Anorectal anomaly | 2 | - | |
| Down syndrome | 2 | - | |
| Ophthalmologic disorder (Tumor or mass) | 4 (4.5%) | 6 (6.7%) | 0.747 * |
| Orthopedic disease (Fracture or malformation) | 2 (2.5%) | 5 (5.6%) | 0.444 * |
| Others | 10 (11.4%) | 15 (16.7%) | 0.309 |
| Control Group (n = 88) | Experimental Group (n = 90) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total induction dose (mg) | 34.0 (27.5–45.0) | 40.5 (30.8–51.3) | 0.011 |
| Total induction dose (mg/kg) | 3.0 (2.0–3.0) | 2.8 (2.4–3.4) | 0.001 |
| Number of injections for induction | 3.0 (2.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.0–2.0) | 0.0001 |
| Rescue dose (mg) | 14.0 (0.0–24.5) | 0.0 (0.0–17.3) | 0.032 |
| Number of rescue injections | 1.0 (0.0–2.0) | 0.0 (0.0–1.0) | 0.005 |
| Total dose of propofol (mg) | 47.0 (33.5–64.5) | 49.5 (34.8–66.5) | 0.823 |
| Duration of radiologic test (minutes) | 25.0 (20.0–31.0) | 25.0 (20.0–31.0) | 0.908 |
| Duration of sedation (minutes) | 33.0 (27.0–43.0) | 35.0 (28.8–45.0) | 0.450 |
| Recovery time (minutes) | 9.0 (1.0–15.0) | 10.0 (2.0–17.0) | 0.349 |
| Side effects of propofol | 2/86 | 1/89 | 0.619 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-R.; Lee, H.-M.; Nam, H.-J.; Byon, H.-J. A Novel Propofol Dosing Regimen for Pediatric Sedation during Radiologic Tests. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175076
Min J-Y, Lee J-R, Lee H-M, Nam H-J, Byon H-J. A Novel Propofol Dosing Regimen for Pediatric Sedation during Radiologic Tests. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175076
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Ji-Young, Jeong-Rim Lee, Hye-Mi Lee, Ho-Jae Nam, and Hyo-Jin Byon. 2022. "A Novel Propofol Dosing Regimen for Pediatric Sedation during Radiologic Tests" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175076
APA StyleMin, J.-Y., Lee, J.-R., Lee, H.-M., Nam, H.-J., & Byon, H.-J. (2022). A Novel Propofol Dosing Regimen for Pediatric Sedation during Radiologic Tests. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175076





