Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67 as the Prognostic Markers in Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas—A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics and Tumor Samples
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.3. Evalualtion of Immunostaining
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Data
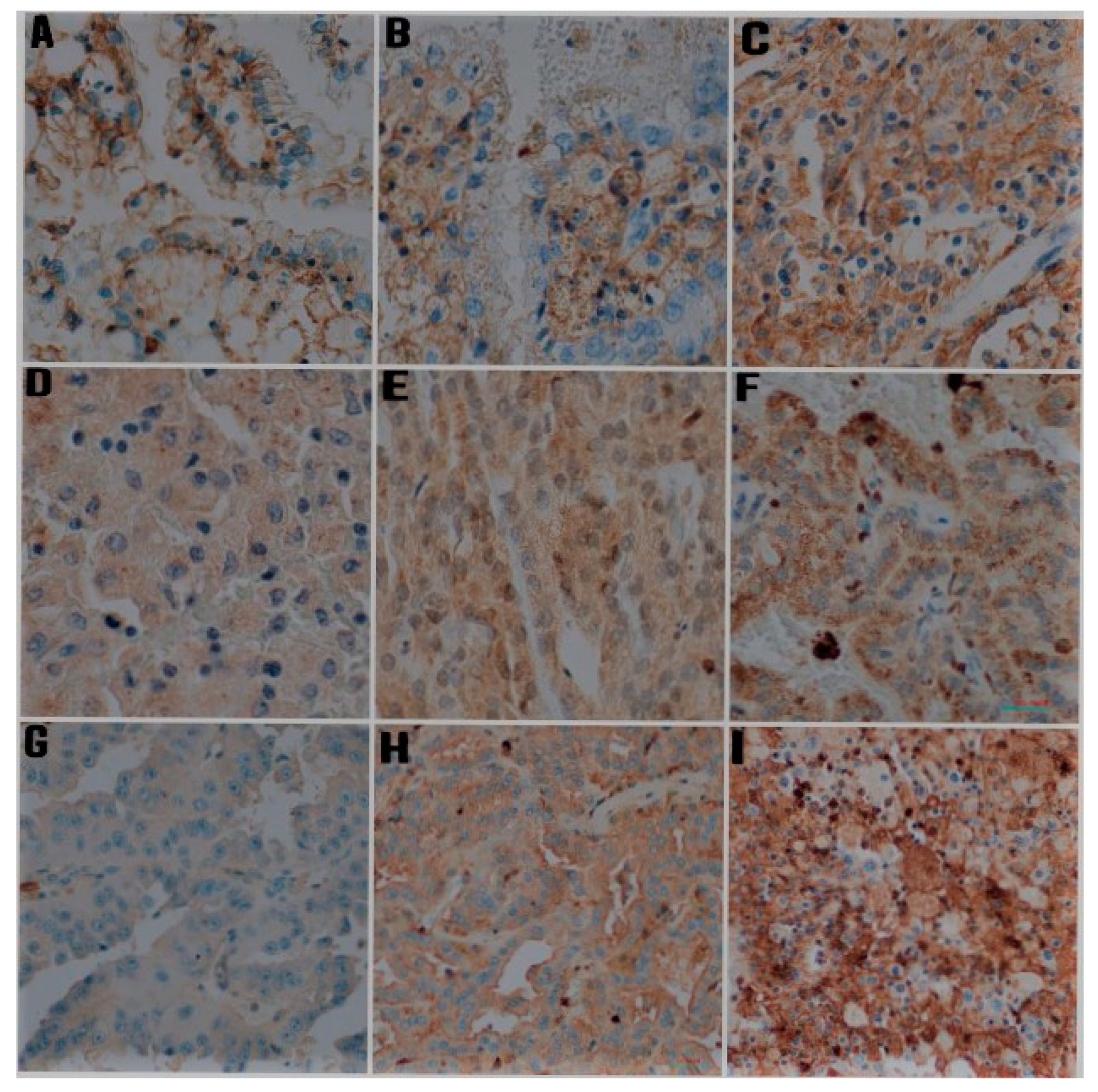
3.2. Immunohistochemical Staining in Papillary RCC
3.3. Immunohistochemical Staining in Chromophobe RCC
3.4. Correlation of Clinicopathological Factors with the Expression of CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67
3.5. The Expression Correlations between CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67
3.6. Prognostic Value of CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67 Expression for Clinical Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Low, G.; Huang, G.; Fu, W.; Moloo, Z.; Girgis, S. Review of renal cell carcinoma and its common subtypes in radiology. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagher, J.; Delahunt, B.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Egevad, L.; Coughlin, G.; Dunglison, N.; Gianduzzo, T.; Kua, B.; Malone, G.; Martin, B.; et al. Assessment of tumour-associated necrosis provides prognostic information additional to World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology grading for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2019, 74, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V.E. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs. In WHO Classification of Tumours, 4th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2016; Volume 8, pp. 11–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Carrasco, J.C.; Cheng, L.; Scarpelli, M.; Kirkali, Z.; Montironi, R. 2009 update on the classification of renal epithelial tumors in adults. Int. J. Urol. 2009, 16, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.D.; Young, A.N.; Paner, G.P.; Amin, M.B. Prognostic role of CD44 cell adhesion molecule expression in primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A clinicopathologic study of 125 cases. Virchows Arch. 2008, 452, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroufim, A.; Messai, Y.; Hasmim, M.; Rioux, N.; Iacovelli, R.; Verhoest, G.; Bensalah, K.; Patard, J.J.; Albiges, L.; Azzarone, B.; et al. Tumoral CD105 is a novel independent prognostic marker for prognosis in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, A.; Fournier, L.; Lassau, N.; Mulders, P.; Nathan, P.; Oyen, W.J.; Powles, T. Assessing the Response to Targeted Therapies in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Technical Insights and Practical Considerations. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.Z.; Nagi, A.H.; Naseem, N. MCM—2 and Ki—67 as proliferation markers in renal cell carcinoma: A quantitative and semi—quantitative analysis. Int. Braz J. Urol. 2016, 42, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, H.J.; Seong, I.O.; Kim, K.H. Immunohistochemical expression of CD44, matrix metalloproteinase2 and matrix metalloproteinase9 in renal cell carcinomas. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCawley, L.J.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinases: Multi-functional contributors to tumor progression. Mol. Med. Today 2000, 6, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauvois, B. New facets of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 as cell surface transducers: Outside-in signaling and relation-ship to tumor progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1825, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, B.C.; Scotti, F.M.; Vieira, D.S.; Biz, M.T.; Castro, R.G.; Modolo, F. Immunohistochemical expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9, myofibroblasts and Ki-67 in actinic cheilitis and lip squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 96, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roomi, M.W.; Monterrey, J.C.; Kalinovsky, T.; Rath, M.; Niedzwiecki, A. Patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in human cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, L.C.; Chi, Q.; Cáceres, R.; Hastie, E.; Schindler, A.J.; Jiang, Y.; Matus, D.Q.; Plastino, J.; Sherwood, D.R. Adaptive F-actin polymerization and localized ATP production drive basement membrane invasion in the absence of MMPs. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Feng, J.; Klocker, H.; Lee, C.; Zhang, J. Type IV collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9) in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostate Dis. 2004, 7, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.V.; Vanner, R.; Dirks, P.; Eaves, C.J. Cancer stem cells: An evolving concept. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucin, K.; Matusan, K.; Dordevic, G.; Stipić, D. Prognostic significance of CD44 molecule in renal cell carcinoma. Croat. Med. J. 2004, 45, 703–708. [Google Scholar]
- Matusan, K.; Dordevic, G.; Stipic, D.; Mozetic, V.; Lucin, K. Osteopontin expression correlates with prognostic variables and survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 94, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, S.; Mizuno, R.; Kosaka, T.; Saya, H.; Oya, M.; Okada, Y. Expression of TNF-alpha and CD44 is implicated in poor prognosis, cancer cell invasion, metastasis and resistance to the sunitinib treatment in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunt, B.; Cheville, J.C.; Martignoni, G.; Humphrey, P.A.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; McKenney, J. The international society of urological pathology (ISUP) grading system for renal cell carcinoma and other prognostic parameters. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 1490–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Ulbright, T.M. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Sullivan, D.C.; Brookland, R.K. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Allred, D.C.; Harvey, J.M.; Berardo, M.; Clark, G.M. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eun, H.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Lee, B.S.; Kim, S.; Song, I.S.; Chun, K.; Oh, C.H.; Yeo, M.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Cytochrome P450 4A11 expression in tumor cells: A favorable prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuschieri, S. The STROBE guidelines. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusan, K.; Dordevic, G.; Mozetic, V.; Lucin, K. Expression of osteopontin and CD44 molecule in papillary renal cell tumors. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2005, 11, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devrim, T.; Balcı, M. Coexistence of CD44 and Ki-67 as the prognostic markers in renal cell carcinoma. Kırıkkale Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Derg. 2020, 22, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, L.S.; Madjd, Z.; Abolhasani, M.; Rasti, A.; Fodstad, O.; Andersson, Y.; Asgari, M. Increased expression of CD44 is associated with more aggressive behavior in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Biomark Med. 2018, 12, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.J.; Liang, Z.L.; Huang, S.M.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, H.J. CD44 is associated with tumor recurrence and is an independent poor prognostic factor for patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Gu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, X. Prognostic value of CD44 expression in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, e13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in the sera and in the urine of human oncocytoma and renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1051–1056. [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Woessner, J.F. Matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21491–21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, M.; Koivunen, E. Gelatinase-mediated migration and invasion of cancer cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1755, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kallakury, B.V.; Karikehalli, S.; Haholu, A.; Sheehan, C.E.; Azumi, N.; Ross, J.S. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 and 2 correlate with poor prognostic variables in renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 3113–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Struckmann, K.; Mertz, K.; Steu, S.; Storz, M.; Staller, P.; Krek, W.; Schraml, P.; Moch, H. pVHL co-ordinately regulates CXCR4/CXCL12 and MMP2/MMP9 expression in human clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.K.; Li, Y.L.; Lu, H.T.; Wang, K.I.; Xu, W.H. Expression of tissue levels of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in renal cell carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shim, H.S.; Rha, S.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, Y.D.; Hong, S.J.; Cho, S.H. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 correlates with poor prognostic variables in renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouian, S.; Farzadnia, M.; Memar, B.; Attaranzadeh, A.; Tayyebi, N. Expression of P53 and Ki67 proteins in renal cell carcinoma and its relationship with nuclear grade. Iranian J. Pathol. 2008, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Gu, L.; Gao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Prognostic and clinicopathological role of high Ki-67 expression in patients with renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijima, S.; Tobe, T.; Suyama, T.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Ito, H. The prognostic value of p53, Ki-67 and matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 in transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis and ureter. Int. J. Urol. 2005, 12, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.S.; Guruvayoorappanb, C.; Sakthivelc, K.M.; Rasmi, R.R. Ki-67 protein as a tumour proliferation marker. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 491, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhu, W.; Tan, J.; Wu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J. Retrospective analysis of a large patient sample to determine p53 and Ki67 expressions in renal cell carcinoma. J. Buon. 2014, 19, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gontero, P.; Ceratti, G.; Guglielmetti, S.; Andorno, A.; Terrone, C.; Bonvini, D.; Faggiano, F.; Tizzani, A.; Frea, B.; Valente, G. Prognostic factors in a prospective series of papillary renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. J. 2008, 102, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunt, B.; Eble, J.N.; McCredie, M.R.; Bethwaite, P.B.; Stewart, J.H.; Bilous, A.M. Morphologic typing of papillary renal cell carcinoma: Comparison of growth kinetics and patient survival in 66 cases. Hum Pathol. 2001, 6, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antibody | Clone | Source | Dilution | Incubation (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD44 | Monoclonal | MRQ-13, Cell Marque, Rocklin, CA, USA | 1:300 | 20 |
| MMP-2 | Monoclonal | CA-4001, Zeta Corporation, Arcadia, CA, USA | 1:50 | 60 |
| MMP-9 | Monoclonal | EP127, Bio SB, Goleta, CA, USA | 1:100 | 60 |
| Ki67 | Monoclonal | MIB-1, Perlan, Beaverton, OR, USA | 1:150 | 20 |
| Histological Subtype of RCC | Papillary RCC | Chromophobe RCC | Total RCC | Power/ Effect Size | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of tumor samples (n (%)) | 41 (69.50%) | 18 (30.50%) | 59 (100.00%) | - | - |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 64.22 ± 9.62 | 60.83 ± 9.87 | 63.19 ± 9.74 | d = 0.35 Power = 0.33 | t = 1.24 p > 0.05 |
| Gender (n (%)) | |||||
| Female | 9 (21.95%) | 7 (38.89%) | 16 (27.10%) | V = 0.18 Power = 0.27 | Chi2 = 1.81 p > 0.05 |
| Male | 32 (78.05%) | 11 (61.11%) | 43 (72.90%) | ||
| Type of operation (n (%)) | |||||
| Radical nephrectomy | 14 (34.15%) | 6 (33.33%) | 20 (33.90%) | V = 0.08 Power = 0.09 | Chi2 = 0.04 p > 0.05 |
| Partial nephrectomy | 27 (67.85%) | 12 (66.67%) | 39 (66.10%) | ||
| Tumor location (n (%)) | |||||
| Right kidney | 24 (41.46%) | 9 (50.00%) | 33 (55.90%) | V = 0.08 Power = 0.09 | Chi2 = 0.37 p > 0.05 |
| Left kidney | 17 (58.54%) | 9 (50.00%) | 26 (44.10%) | ||
| Tumor size, cm (mean ± SD) | 4.9 ± 3.36 | 3.75 ± 2.24 | 4.55 ± 3.07 | d = 0.40 Power = 0.40 | t = 1.68 p > 0.05 |
| Tumor stage (n (%)) | |||||
| pT1 | 26 (63.42%) | 11 (61.11%) | 37 (62.70%) | V = 0.11 Power = 0.10 | Chi2 = 0.69 p > 0.05 |
| pT2 | 7 (17.07%) | 2 (11.11%) | 9 (15.30%) | ||
| pT3 | 8 (19.51%) | 5 (27.78%) | 13 (22.00%) | ||
| pT4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| WHO/ISUP grading | - | - | |||
| G1 | 11 (26.83%) | - | - | ||
| G2 | 24 (58.54%) | - | - | ||
| G3 | 2 (4.88%) | - | - | ||
| G4 | 4 (9.76%) | - | - | ||
| Tumor necrosis area % (mean ± SD) | 14.51 ± 27.15% | 0.56 ± 2.36 | 10.25 ± 23.50 | d = 0.59 Power = 0.64 | U = 404.50 p < 0.05 |
| Sarcomatoid area % (mean ± SD) | 2.46 ± 12.60 | - | - | - | - |
| Rhabdoid area % (mean ± SD) | 0 | - | 0 | - | - |
| Lymphatic invasion present (n (%)) | 3 (7.32%) | 0 (0.00%) | 3 (5.10%) | V = 0.14 Power = 0.19 | Chi2 = 0.28 p > 0.05 |
| Angioinvasion present (n (%)) | 5 (12.20%) | 0 (0.00%) | 5 (8.50%) | V = 0.18 Power = 0.28 | Chi2 = 1.08 p > 0.05 |
| Neuroinvasion present (n (%)) | 2 (4.88%) | 0 (0.00%) | 2 (3.40%) | V = 0.12 Power = 0.15 | Chi2 = 0.02 p > 0.05 |
| Renal fibrous capsule invasion present (n (%)) | 19 (46.34%) | 8 (44.44%) | 27 (45.80%) | V = 0.04 Power = 0.06 | Chi2 = 0.01 p > 0.05 |
| Perinephric fat invasion present (n (%)) | 6 (41.63%) | 4 (22.22%) | 10 (16.90%) | V = 0.09 Power = 0.10 | Chi2 = 0.11 p > 0.05 |
| Renal sinus fat invasion present (n (%)) | 3 (7.32%) | 6 (27.78%) | 9 (15.30%) | V = 0.33 Power = 0.72 | Chi2 = 4.69 p < 0.05 |
| Renal sinus vascular invasion present (n (%)) | 3 (7.32%) | 0 | 3 (5.10%) | V = 0.15 Power = 0.21 | Chi2 = 0.29 p > 0.05 |
| Dead (n (%)) | 6 (14.63%) | 0 | 6 (10.20%) | V = 0.22 Power = 0.39 | Chi2 = 1.55 p > 0.05 |
| Overall Immunohistochemical Score | CD44 | MMP-2 | MMP-9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (low expression) (n (%)) | 28 (68.29%) | 27 (65.85%) | 31 (75.61%) |
| Group 2 (moderate expression) (n (%)) | 8 (19.51%) | 11 (26.83%) | 6 (14.63%) |
| Group 3 (high expression) (n (%)) | 5 (12.20%) | 3 (7.32%) | 4 (9.76%) |
| Overall Immunohistochemical Score | CD44 | MMP-2 | MMP-9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (low expression) (n (%)) | 9 (50.00%) | 7 (38.89%) | 16 (88.89%) |
| Group 2 (moderate expression) (n (%)) | 5 (27.78%) | 5 (27.78%) | 2 (11.11%) |
| Group 3 (high expression) (n (%)) | 4 (22.22%) | 6 (33.33%) | 0 (0.00%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chrabańska, M.; Rynkiewicz, M.; Kiczmer, P.; Drozdzowska, B. Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67 as the Prognostic Markers in Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas—A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175196
Chrabańska M, Rynkiewicz M, Kiczmer P, Drozdzowska B. Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67 as the Prognostic Markers in Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas—A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175196
Chicago/Turabian StyleChrabańska, Magdalena, Magdalena Rynkiewicz, Paweł Kiczmer, and Bogna Drozdzowska. 2022. "Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67 as the Prognostic Markers in Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas—A Prospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175196
APA StyleChrabańska, M., Rynkiewicz, M., Kiczmer, P., & Drozdzowska, B. (2022). Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44, MMP-2, MMP-9, and Ki-67 as the Prognostic Markers in Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas—A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175196








