Cytomegalovirus and Glioblastoma: A Review of the Biological Associations and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Detection of CMV
3. Is CMV Infection Associated with GBM?
4. CMV Infection Is Associated with the Prognosis of GBM
5. Mechanisms of CMV-Related Glioma Tumorigenesis
5.1. Oncomodulation
5.2. Oncogenic Features
5.3. Tumor Microenvironment
5.4. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition
5.5. Overall Immune System
6. CMV-Associated Encephalopathy in Standard Therapy
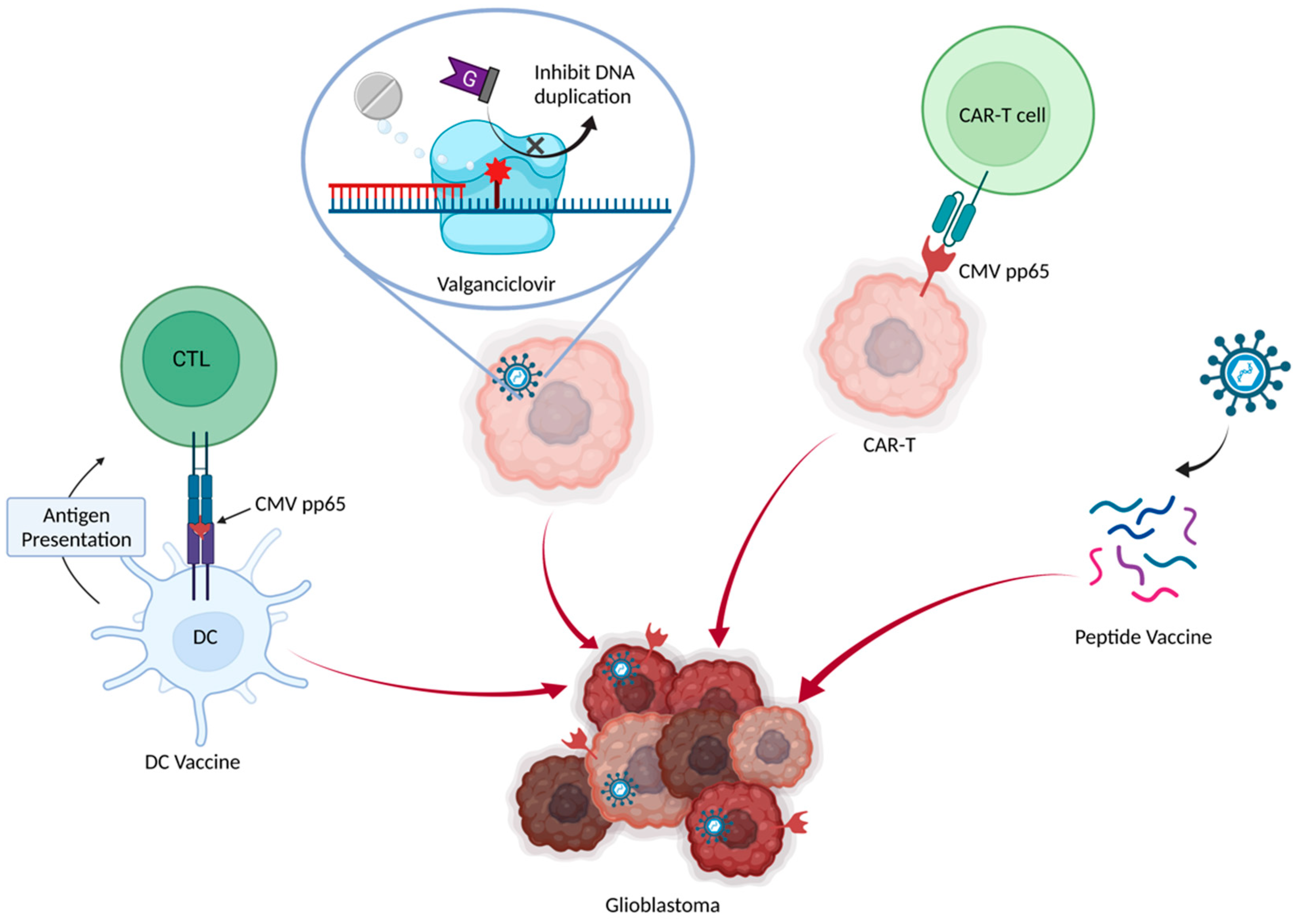
7. Anti-CMV Therapy in GBM
7.1. Valganciclovir
7.2. Dendritic Cell Vaccine
7.3. Adoptive CMV-Specific T Cells
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, T.; Nam, D.-H.; Ram, Z.; Poon, W.-S.; Wang, J.; Boldbaatar, D.; Mao, Y.; Ma, W.; Mao, Q.; You, Y.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of adult diffuse gliomas. Cancer Lett. 2020, 499, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Patil, N.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22 (Suppl. S2), iv1–iv96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolfo, S.; Gariglio, M.; Gribaudo, G.; Lembo, D. The human cytomegalovirus. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 98, 269–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Baraniak, I.; Reeves, M. The pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicklal, S.; Emery, V.C.; Lazzarotto, T.; Boppana, S.B.; Gupta, R.K. The “silent” global burden of congenital cytomegalovirus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picarda, G.; Benedict, C.A. Cytomegalovirus: Shape-Shifting the Immune System. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3881–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razonable, R.R.; Humar, A. Cytomegalovirus in solid organ transplant recipients-Guidelines of the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halwachs-Baumann, G. Recent developments in human cytomegalovirus diagnosis. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2007, 5, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbs, C.S. Cytomegalovirus and brain tumor: Epidemiology, biology and therapeutic aspects. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, S.; Cobbs, L.H.; Minu Samanta, G.; Gillespie, Y.; Bharara, S.; Peter, H.; King, L.; Burt Nabors, C.; Cobbs, G.; William, J.B. Human Cytomegalovirus Infection and Expression in Human Malignant Glioma. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3347–3350. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, K.; Moreli, M.L.; Floriano, V.G.; da Costa, V.G. Evidence based on a meta-analysis of human cytomegalovirus infection in glioma. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullberg-Lindh, C.; Olofsson, S.; Brune, M.; Lindh, M. Comparison of serum and whole blood levels of cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2008, 10, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, M.; Doerr, H.W.; Cinatl, J., Jr. Oncomodulation by human cytomegalovirus: Evidence becomes stronger. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 198, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, L.; Volk, A.L.; Samanta, M.; Mikolaenko, I.; Britt, W.J.; I Bland, K.; Cobbs, C.S. Specific localisation of human cytomegalovirus nucleic acids and proteins in human colorectal cancer. Lancet 2002, 360, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, M.H.L.; Klemm, K.; Britt, W.J.; Cobbs, C.S. High prevalence of human cytomegalovirus in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostatic carcinoma. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, C.; Frisk, G.; Fuentes, S.; Religa, P.; Costa, H.; Assinger, A.; Vetvik, K.K.; Bukholm, I.R.; Yaiw, K.-C.; Smedby, K.E.; et al. High Prevalence of Human Cytomegalovirus in Brain Metastases of Patients with Primary Breast and Colorectal Cancers. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 7, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libard, S.; Popova, S.N.; Amini, R.-M.; Kärjä, V.; Pietiläinen, T.; Hämäläinen, K.M.; Sundström, C.; Hesselager, G.; Bergqvist, M.; Ekman, S.; et al. Human Cytomegalovirus Tegument Protein pp65 Is Detected in All Intra- and Extra-Axial Brain Tumours Independent of the Tumour Type or Grade. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolmer-Solberg, N.; Baryawno, N.; Rahbar, A.; Fuchs, D.; Odeberg, J.; Taher, C.; Wilhelmi, V.; Milosevic, J.; Mohammad, A.A.; Martinsson, T.; et al. Frequent detection of human cytomegalovirus in neuroblastoma: A novel therapeutic target? Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2351–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrensch, M.; Weinberg, A.; Wiencke, J.; Miike, R.; Barger, G.; Kelsey, K. Prevalence of Antibodies to Four Herpesviruses among Adults with Glioma and Controls. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 154, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, A.; Peredo, I.; Solberg, N.W.; Taher, C.; Dzabic, M.; Xu, X.; Skarman, P.; Fornara, O.; Tammik, C.; Yaiw, K.; et al. Discordant humoral and cellular immune responses to Cytomegalovirus (CMV) in glioblastoma patients whose tumors are positive for CMV. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e982391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Söderberg-Nauclér, C.; Stragliotto, G. Valganciclovir in Patients with Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2064–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, P.; Clark, P.A.; Kuo, J.S.; Salamat, M.S.; Kalejta, R.F. Significant association of multiple human cytomegalovirus genomic Loci with glioblastoma multiforme samples. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, F.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Sun, J.Y.; Fang, W.; Rayner, S.; McVoy, M.A.; Jiang, X.J.; Tang, Q.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus DNA and immediate early protein 1/2 are highly associated with glioma and prognosis. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priel, E.; Wohl, A.; Teperberg, M.; Nass, D.; Cohen, Z.R. Human cytomegalovirus viral load in tumor and peripheral blood samples of patients with malignant gliomas. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, I.H.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Milner, D.A., Jr.; Folkerth, R.D. Cytomegalovirus and Glioblastoma: A Review of Evidence for Their Association and Indications for Testing and Treatment. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 73, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, H.; Tavakoli, A.; Faranoush, M.; Naderi, A.; Kiani, S.J.; Sadeghipour, A.; Javanmard, D.; Farahmand, M.; Ghorbani, S.; Sedaghati, F.; et al. Molecular Investigation of Human Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in Glioblastoma Brain Tumor: A Case-Control Study in Iran. Iran. Biomed. J. 2021, 25, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, H.; Piper, K.; Depledge, L.; Li, H.-F.; Scanlan, J.; Jae-Guen, Y.; Boeckh, M.; Cobbs, C.; Yoon, J.-G. Human cytomegalovirus seropositivity is associated with decreased survival in glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2019, 1, vdz020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisyany, N.I.; Klyuchnikova, A.A.; Belskaya, L.N.; Lisyany, A.A.; Gnedkova, I.A. Cytomegaloviruses and malignant brain tumors. Exp. Oncol. 2019, 41, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Li, W. Viral infection and glioma: A meta-analysis of prognosis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbar, A.; Orrego, A.; Peredo, I.; Dzabic, M.; Wolmer-Solberg, N.; Strååt, K.; Stragliotto, G.; Söderberg-Nauclér, C. Human cytomegalovirus infection levels in glioblastoma multiforme are of prognostic value for survival. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbar, A.; Stragliotto, G.; Orrego, A.; Peredo, I.; Taher, C.; Willems, J.; Söderberg-Naucler, C. Low levels of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in Glioblastoma multiforme associates with patient survival—A case-control study. Herpesviridae 2012, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strååt, K.; Liu, C.; Rahbar, A.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, L.; Wolmer-Solberg, N.; Lou, F.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Jia, J.; et al. Activation of Telomerase by Human Cytomegalovirus. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinatl, J., Jr.; Nevels, M.; Paulus, C.; Michaelis, M. Activation of telomerase in glioma cells by human cytomegalovirus: Another piece of the puzzle. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, F.; Sadigh, Z.A.; Sadeghi, F.; Muhammadnejad, A.; Farahmand, M.; Parvin, M.; Shirkoohi, R. Human cytomegalovirus infection in Iranian glioma patients correlates with aging and tumor aggressiveness. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geder, L.S.E.; Rohner, T.J.; Rapp, F. Cytomegalovirus and cancer of the prostate: In vitro transformation of human cells. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1977, 61, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Merchut-Maya, J.M.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Bartkova, J.; Galanos, P.; Pantalone, M.R.; Lee, M.; Cui, H.L.; Shilling, P.J.; Brøchner, C.B.; Broholm, H.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus hijacks host stress response fueling replication stress and genome instability. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, G.P.; McDermott, R.; Baryshnikova, M.A.; Cobbs, C.S.; Ulasov, I.V. Cytomegalovirus as an oncomodulatory agent in the progression of glioma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 384, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderberg-Naucler, C.; Johnsen, J.I. Cytomegalovirus in human brain tumors: Role in pathogenesis and potential treatment options. World J. Exp. Med. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shenk, T. Human cytomagalovirus IE1 and IE2 proteins are mutagenic and mediate "hit-and-run" oncogenic transformation in cooperation with the adenovirus E1A proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3341–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, S.M.Y.K.; Paulus, C.; Nevels, M.; Kalejta, R.F. Human Cytomegalovirus Genomes Survive Mitosis via the IE19 Chromatin-Tethering Domain. mBio 2020, 29, e02410–e02420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slinger, E.; Maussang, D.; Schreiber, A.; Siderius, M.; Rahbar, A.; Fraile-Ramos, A.; Lira, S.A.; Söderberg-Nauclér, C.; Smit, M.J. HCMV-Encoded Chemokine Receptor US28 Mediates Proliferative Signaling Through the IL-6–STAT3 Axis. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenzlin, H.; Behera, P.; Lorenz, V.; Passaro, C.; Zdioruk, M.; Nowicki, M.O.; Grauwet, K.; Zhang, H.; Skubal, M.; Ito, H.; et al. Cytomegalovirus promotes murine glioblastoma growth via pericyte recruitment and angiogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroceanu, L.; Cobbs, C.S. Is HCMV a tumor promoter? Virus Res. 2011, 157, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulasov, I.V.; Kaverina, N.V.; Ghosh, D.; Baryshnikova, M.A.; Kadagidze, Z.G.; Karseladze, A.I.; Baryshnikov, A.Y.; Cobbs, C.S. CMV70-3P miRNA contributes to the CMV mediated glioma stemness and represents a target for glioma experimental therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25989–25999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziurzynski, K.; Chang, S.M.; Heimberger, A.B.; Kalejta, R.F.; Dallas, S.R.M.; Smit, M.; Soroceanu, L.; Cobbs, C.S. The HCMV and Gliomas Symposium. Consensus on the role of human cytomegalovirus in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maussang, D.; Langemeijer, E.; Fitzsimons, C.P.; Walsum, M.S.-V.; Dijkman, R.; Borg, M.K.; Slinger, E.; Schreiber, A.; Michel, D.; Tensen, C.P.; et al. The Human Cytomegalovirus–Encoded Chemokine Receptor US28 Promotes Angiogenesis and Tumor Formation via Cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziurzynski, K.; Wei, J.; Qiao, W.; Hatiboglu, M.A.; Kong, L.-Y.; Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Cahill, D.; Levine, N.; Prabhu, S.; et al. Glioma-Associated Cytomegalovirus Mediates Subversion of the Monocyte Lineage to a Tumor Propagating Phenotype. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, B.; Hu, M.; Qian, D.; Wang, B. Human cytomegalovirus infection enhances invasiveness and migration of glioblastoma cells by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 2637–2647. [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura, M.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.; Britt, W.J. Human cytomegalovirus induces TGF-beta1 activation in renal tubular epithelial cells after epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbs, C. Cytomegalovirus is a tumor-associated virus: Armed and dangerous. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 39, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.-H.; Meng, Q.; Rao, M.; Liu, Z.; Paraschoudi, G.; Dodoo, E.; Maeurer, M. The impact of inflationary cytomegalovirus-specific memory T cells on anti-tumour immune responses in patients with cancer. Immunology 2018, 155, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallemeijn, M.J.; Boots, A.M.H.; Van Der Klift, M.Y.; Brouwer, E.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Verhaar, J.; Van Dongen, J.; Langerak, A.W. Ageing and latent CMV infection impact on maturation, differentiation and exhaustion profiles of T-cell receptor gammadelta T-cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klenerman, P.; Oxenius, A. T cell responses to cytomegalovirus. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Ahluwalia, M.; Baehring, J.; Brem, H.; Brem, S.; Butowski, N.; Campian, J.L.; Clark, S.W.; Fabiano, A.J.; et al. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 1537–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerig, N.; Semrau, S.; Frey, B.; Korn, K.; Fleckenstein, B.; Überla, K.; Dörfler, A.; Putz, F.; Gaipl, U.S.; Fietkau, R. Clinically significant CMV (re)activation during or after radiotherapy/chemotherapy of the brain: Correlation with neurological deterioration and improvement upon antiviral treatment. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2016, 192, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerig, N.L.; Frey, B.; Korn, K.; Fleckenstein, B.; Überla, K.; Schmidt, M.A.; Dörfler, A.; Engelhorn, T.; Eyüpoglu, I.; Rühle, P.F.; et al. Frequent occurrence of therapeutically reversible CMV-associated encephalopathy during radiotherapy of the brain. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Reitter, E.-M.; Kastner, M.-T.; Thannesberger, J.; Rieder, F.J.; Preusser, M.; Marosi, C.; Steininger, C. Absence of CMV viremia in high-grade glioma patients under low dosage glucocorticoid treatment. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerig, N.L.; Frey, B.; Korn, K.; Fleckenstein, B.; Überla, K.; Schmidt, M.A.; Dörfler, A.; Engelhorn, T.; Eyüpoglu, I.; Rühle, P.F.; et al. Early Mortality of Brain Cancer Patients and its Connection to Cytomegalovirus Reactivation During Radiochemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3259–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stragliotto, G.; Rahbar, A.; Solberg, N.W.; Lilja, A.; Taher, C.; Orrego, A.; Bjurman, B.; Tammik, C.; Skarman, P.; Peredo, I.; et al. Effects of valganciclovir as an add-on therapy in patients with cytomegalovirus-positive glioblastoma: A randomized, double-blind, hypothesis-generating study. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderberg-Naucler, C.; Peredo, I.; Rahbar, A.; Hansson, F.; Nordlund, A.; Stragliotto, G. Use of Cox regression with treatment status as a time-dependent covariate to re-analyze survival benefit excludes immortal time bias effect in patients with glioblastoma who received prolonged adjuvant treatment with valganciclovir. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 135, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottenhausen, M.; Bodhinayake, I.; Schaefer, P.M.; Boockvar, J.A. VIGAS and Beyond: The Impact of HCMVInfection and its Treatment in Glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 2014, 74, N23–N24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderberg-Nauclér, C.; Rahbar, A.; Stragliotto, G. Survival in Patients with Glioblastoma Receiving Valganciclovir. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 985–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stragliotto, G.; Pantalone, M.R.; Rahbar, A.; Bartek, J.; Söderberg-Naucler, C. Valganciclovir as Add-on to Standard Therapy in Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4031–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batich, K.A.; Reap, E.A.; Archer, G.E.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Nair, S.K.; Schmittling, R.J.; Norberg, P.; Xie, W.; Herndon, J.E., II; Healy, P.; et al. Long-term Survival in Glioblastoma with Cytomegalovirus pp65-Targeted Vaccination. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1898–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.A.; Batich, K.A.; Gunn, M.D.; Huang, M.-N.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Nair, S.K.; Congdon, K.L.; Reap, E.A.; Archer, G.E.; Desjardins, A.; et al. Tetanus toxoid and CCL3 improve dendritic cell vaccines in mice and glioblastoma patients. Nature 2015, 519, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuessler, A.; Smith, C.; Beagley, L.; Boyle, G.M.; Rehan, S.; Matthews, K.; Jones, L.; Crough, T.; Dasari, V.; Klein, K.; et al. Autologous T-cell Therapy for Cytomegalovirus as a Consolidative Treatment for Recurrent Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3466–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Lineburg, K.E.; Martins, J.P.; Ambalathingal, G.R.; Neller, M.A.; Morrison, B.; Matthews, K.K.; Rehan, S.; Crooks, P.; Panikkar, A.; et al. Autologous CMV-specific T cells are a safe adjuvant immunotherapy for primary glioblastoma multiforme. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6041–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weathers, S.-P.; Penas-Prado, M.; Pei, B.-L.; Ling, X.; Kassab, C.; Banerjee, P.; Bdiwi, M.; Shaim, H.; Alsuliman, A.; Shanley, M.; et al. Glioblastoma-mediated Immune Dysfunction Limits CMV-specific T Cells and Therapeutic Responses: Results from a Phase I/II Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3565–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reap, E.A.; Suryadevara, C.M.; Batich, K.A.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Archer, G.E.; Schmittling, R.J.; Norberg, P.K.; Herndon, J.E.; Healy, P.; Congdon, K.L.; et al. Dendritic Cells Enhance Polyfunctionality of Adoptively Transferred T Cells That Target Cytomegalovirus in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åsberg, A.; Humar, A.; Rollag, H.; Jardine, A.G.; Mouas, H.; Pescovitz, M.D.; Sgarabotto, D.; Tuncer, M.; Noronha, I.L.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Oral Valganciclovir Is Noninferior to Intravenous Ganciclovir for the Treatment of Cytomegalovirus Disease in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderberg-Nauclér, C. Treatment of cytomegalovirus infections beyond acute disease to improve human health. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 12, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baryawno, N.; Rahbar, A.; Wolmer-Solberg, N.; Taher, C.; Odeberg, J.; Darabi, A.; Khan, Z.; Sveinbjörnsson, B.; Fuskevåg, O.-M.; Segerström, L.; et al. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in medulloblastomas reveals a potential therapeutic target. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4043–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wick, W.; Wick, A.; Platten, M. Good maths is needed to understand CMV data in glioblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 134, 2991–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, W.; Wick, A.; Platten, M. Challenging cytomegalovirus data in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Soffietti, R.; Brada, M. The legend of cytomegalovirus and glioblastoma lives on. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Hu, Y.W. Immortal time bias in retrospective analysis: Is there a survival benefit in patients with glioblastoma who received prolonged treatment of adjuvant valganciclovir? Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stragliotto, G.; Pantalone, M.R.; Rahbar, A.; Soderberg-Naucler, C. Valganciclovir as Add-On to Standard Therapy in Secondary Glioblastoma. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantalone, M.R.; Rahbar, A.; Söderberg-Naucler, C.; Stragliotto, G. Valganciclovir as Add-on to Second-Line Therapy in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Tanksley, J.P.; Mobley, B.C.; Ayers, G.D.; Moots, P.L.; Clark, S.W. Valganciclovir and bevacizumab for recurrent glioblastoma: A single-institution experience. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 4, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kane, J.R.; Panek, W.K.; Young, J.S.; Rashidi, A.; Yu, D.; Kanojia, D.; Hasan, T.; Miska, J.; Gómez-Lim, M.A.; et al. A Dendritic Cell-Targeted Adenoviral Vector Facilitates Adaptive Immune Response Against Human Glioma Antigen (CMV-IE) and Prolongs Survival in a Human Glioma Tumor Model. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Hossain, J.; Latif, A.; Ystaas, L.A.R.; Ninzima, S.; Riecken, K.; Muller, A.; Azuaje, F.; Joseph, J.V.; Talasila, K.M.; Ghimire, J.; et al. Long-term treatment with valganciclovir improves lentiviral suicide gene therapy of glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Tetanus shot may improve glioblastoma treatment. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 571. [Google Scholar]
- Batich, K.A.; Mitchell, D.A.; Healy, P.; Herndon, J.E.; Sampson, J.H. Once, Twice, Three Times a Finding: Reproducibility of Dendritic Cell Vaccine Trials Targeting Cytomegalovirus in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5297–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbein, G. The Human Cytomegalovirus, from Oncomodulation to Oncogenesis. Viruses 2018, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Treatment | Year | Trial Registration | Trial Name | Interventions | Patients | N | Phase | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valganciclovir | 2013 | NCT00400322 | VIGAS | Valganciclovir + CRT vs. CRT | ND-GBM | 42 | I/II | No difference in tumor volume, OS, and PFS. OS-24 27.3% in experiment arm vs. 25% in control. Treatment >6 m OS 24.1 m, <6 m OS 13.1 m. Treatment >6 m OS-2 year 67.6%, OS-4 year 27.3% | Soderberg-Naucler, C. [60] |
| 2013 | - | VIGAS re-analysis | Valganciclovir + CRT vs. CRT | ND-GBM | retrospective | Valganciclovir vs. control HR 2.44, treatment >6 m vs. control HR 0.441, treatment >6 m vs. <6 m HR 1.351 | Soderberg-Naucler, C. [61] | ||
| 2014 | - | VIGAS re-analysis | Valganciclovir + CRT vs. CRT | ND-GBM | retrospective | Patients with lower viral load have better prognosis | Malte Ottenhausen [62] | ||
| 2013 | - | VIGAS further study | Valganciclovir + CRT vs. CRT | ND-GBM | 50 | retrospective | OS-24 62% in experiment arm vs. 18% in control; OS 25.0 m vs. 13.5 m. Treatment >6 m OS-24 70%, OS 30.1 m | Soderberg-Naucler, C. [63] | |
| 2020 | - | Valganciclovir + CRT vs. CRT | R-GBM | 8 | retrospective | OS after relapse 19.1 m in experiment arm vs. 12.7 m in control; OS-24 37.5% vs. 2.8% | Soderberg-Naucler, C. [64] | ||
| DC vaccine | 2017 | NCT00639639 | ATTAC-GM | DI-TMZ + GM-CSF + CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC vs. CRT | ND-GBM | 11 | I | PFS 25.3 m, OS 41.1 m, 4 patients survived longer without progression (59–64 m) | John H. Sampson [65] |
| 2015 | NCT00639639 | ATTAC | CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC + Td+ CRT vs. unpulsed DC + Td+ CRT vs. CRT | ND-GBM | 12 | I | PFS, OS no worse than control, 3 patients survived >36.6 m. Td enhances DC vaccine because CCL3 enhances DC migration and inhibits tumor progression | John H. Sampson [66] | |
| CAR-T | 2014 | ACTRN12609000338268 | Autologous CMV pp65-specific T cells | R-GBM | 19 | I | PFS 246 d, OS 403 d, 4 of 10 patients remained progression-free during study | Rajiv Khanna [67] | |
| 2020 | ACTRN12615000656538 | Autologous CMV pp65-specific T cells | ND-GBM | 25 | I | PFS 25 m, PFS-12 20%, OS 21 m, OS-12 52%. Treatment before relapse was significantly longer OS than that after relapse | Rajiv Khanna [68] | ||
| 2020 | NCT02661282 | Autologous CMV pp65-specific T cells | ND + R-GBM | 65 | I/II | Increased circulating CMV-CD8 T cells, but did not improve survival | Amy B Heimberger [69] | ||
| 2017 | NCT00693095. | ATCT | CMV pp65-specific T cells + CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC vs. CMV pp65-specific T cells | ND-GBM | 22 | I | CMV DC vaccine enhanced polyfunctionality of adoptive CMV-specific T cells, correlated with OS. | John H. Sampson [70] |
| Treatment | Research Team | Trial Registration | Year | Trial Name | Study Title | Treatment Plan | Patients | N | Phase | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valganciclovir | Cecilia Soderberg-Naucler | NCT04116411 | September 2019–August 2024 | VIGAS2 | A Clinical Trial Evaluating the Efficacy of Valganciclovir in Glioblastoma Patients | Valganciclovir + CRT vs. placebo + CRT | ND-GBM | 220 | II, Randomized | recruiting |
| DC vaccine | Gary Archer | NCT03615404 | October 2018–July 2020 | ATTAC-P | Cytomegalovirus (CMV) RNA-Pulsed Dendritic Cells for Pediatric Patients and Young Adults With WHO Grade IV Glioma, Recurrent Malignant Glioma, or Recurrent Medulloblastoma | DI-TMZ + GM-CSF + Td + CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC | ND + R-GBM, recurrent medulloblastoma | 11 | I | completed |
| Gary Archer | NCT03927222 | September 2019–December 2023 | I-ATTAC | Immunotherapy Targeted Against Cytomegalovirus in Patients With Newly-Diagnosed WHO Grade IV Unmethylated Glioma | DI-TMZ + GM-CSF + Td+ CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC | ND-GBM | 48 | II | recruiting | |
| Duane Mitchell | NCT02465268 | August 2016–June 2024 | ATTAC-II | Vaccine Therapy for the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Multiforme | GM-CSF + Td + CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC vs. un-pulsed PBMC | ND-GBM | 120 | II, Randomized | recruiting | |
| Gary Archer | NCT02366728 | October 2015–August 2020 | ELEVATE | DC Migration Study for Newly-Diagnosed GBM | DC + CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC + TMZ vs. Td + CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC + TMZ vs. basiliximab + Td+ CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC + TMZ | ND-GBM | 100 | II, Randomized | Active, not recruiting | |
| Gary Archer | NCT03688178 | August 2020–March 2025 | DERIVe | DC Migration Study to Evaluate TReg Depletion In GBM Patients With and Without Varlilumab | DC pre-conditioning vaccine + TMZ vs. Td pre-conditioning + DC vaccine + TMZ vs. DC Vaccine + varlilumab (Td pre-conditioning) + TMZ | ND + R-GBM | 112 | II, Randomized | recruiting | |
| DC vaccine+ CAR-T | John Sampson | NCT00693095 | September 2008–April 2015 | ERaDICATe | Evaluation of Recovery From Drug-Induced Lymphopenia Using Cytomegalovirus-specific T-cell Adoptive Transfer | CMV-autologous lymphocyte transfer (CMV-ALT) vs. CMV-ALT + CMV pp65 RNA-pulsed DC | ND-GBM | 23 | I, Randomized | completed |
| CAR-T | Nabil Ahmed | NCT01109095 | October 2010–March 2018 | HERT-GBM | CMV-specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Expressing CAR Targeting HER2 in Patients With GBM | HER2-CAR CMV-specific CTL | R-GBM | 16 | I | completed |
| Peptide Vaccine | Gary Archer | NCT02864368 | December 2016–September 2021 | PERFORMANCE | Peptide Targets for Glioblastoma Against Novel Cytomegalovirus Antigens | PEP CMV + Td + CRT vs. PEP CMV + Td+ TMZ | ND-GBM | 70 | I, Randomized | Active, not recruiting |
| Observational | Benjamin Frey | NCT02600065 | November 2015–February 2020 | GLIO-CMV-01 | Analysis of CMV Infections in Patients With Brain Tumors or Brain Metastases During and After Radio(Chemo)Therapy | CRT + TMZ | HGG, metastases | 250 | Observation | recruiting |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.; Liu, D.; Fang, S.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y. Cytomegalovirus and Glioblastoma: A Review of the Biological Associations and Therapeutic Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175221
Yang T, Liu D, Fang S, Ma W, Wang Y. Cytomegalovirus and Glioblastoma: A Review of the Biological Associations and Therapeutic Strategies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175221
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tianrui, Delin Liu, Shiyuan Fang, Wenbin Ma, and Yu Wang. 2022. "Cytomegalovirus and Glioblastoma: A Review of the Biological Associations and Therapeutic Strategies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175221
APA StyleYang, T., Liu, D., Fang, S., Ma, W., & Wang, Y. (2022). Cytomegalovirus and Glioblastoma: A Review of the Biological Associations and Therapeutic Strategies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175221