Total Burden of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease on MRI May Predict Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
- (a)
- the presence of atypical, secondary, or hereditary parkinsonian syndromes.
- (b)
- head trauma history.
- (c)
- strokes associated with large vessel diseases (atherothrombotic strokes).
- (d)
- MRI contraindications.
- (e)
- incapable of completing assessments.
- (f)
- evidence of a brain tumor or hydrocephalus on MRI imaging.
2.2. Clinical Assessment of PD
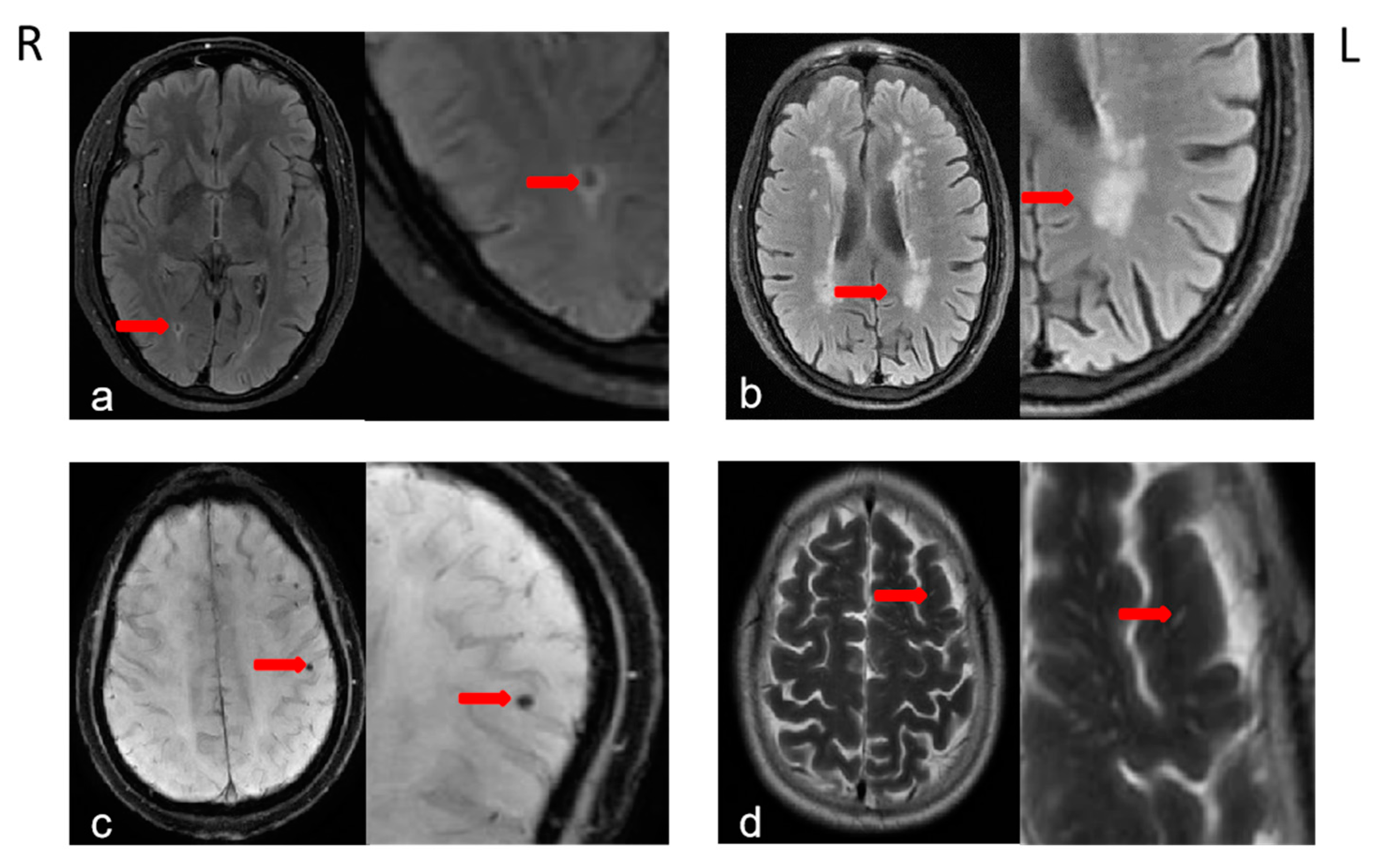
2.3. Brain MRI Acquisition and Definition of CSVDs
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Clinical and Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. CSVDs and Cognitive Impairment
3.3. Cognitive Impairment and Other Influence Factors
3.4. Correlation Analysis of the Total Burden of CSVD and Other Factors
3.5. Accuracy of the Total Burden of CSVD in Detecting Cognitive Impairment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salawu, F.; Danburam, A.; Olokoba, A. Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: Diagnosis and management. Niger. J. Med. 2010, 19, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletti, M.; Emre, M.; Bonuccelli, U. Mild cognitive impairment and cognitive reserve in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarsland, D.; Brønnick, K.; Larsen, J.; Tysnes, O.; Alves, G. Cognitive impairment in incident, untreated Parkinson disease: The Norwegian ParkWest study. Neurology 2009, 72, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigott, K.; Rick, J.; Xie, S.X.; Hurtig, H.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Duda, J.E.; Morley, J.F.; Chahine, L.M.; Dahodwala, N.; Akhtar, R.S. Longitudinal study of normal cognition in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hely, M.A.; Reid, W.G.; Adena, M.A.; Halliday, G.M.; Morris, J.G. The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: The inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, D.; Mamikonyan, E. The Neuropsychiatry of Parkinson Disease: A Perfect Storm. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 998–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reekes, T.H.; Higginson, C.I.; Ledbetter, C.R.; Sathivadivel, N.; Zweig, R.M.; Disbrow, E.A. Sex specific cognitive differences in Parkinson disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempster, P.A.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Holton, J.L.; Revesz, T.; Lees, A.J. Relationships between age and late progression of Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study. Brain 2010, 133, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.; Tang, M.-X.; Louis, E.D.; Cote, L.J.; Alfaro, B.; Mejia, H.; Stern, Y.; Marder, K. The association of incident dementia with mortality in PD. Neurology 2002, 59, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Benveniste, H.; Black, S.E.; Charpak, S.; Dichgans, M.; Joutel, A.; Nedergaard, M.; Smith, K.J.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Wardlaw, J.M. Understanding the role of the perivascular space in cerebral small vessel disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.U.; Lee, J.E.; Kwon, D.Y.; Park, J.H.; Ma, H.I. Parkinson’s disease might increase the risk of cerebral ischemic lesions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wan, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Pan, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y. Cerebral small vessel disease may worsen motor function, cognition, and mood in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 83, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, H.M.; Wolfson, L.; Moscufo, N.; Guttmann, C.R.; Kaplan, R.F.; White, W.B. Cardiovascular risk factors and small vessel disease of the brain: Blood pressure, white matter lesions, and functional decline in older persons. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Guio, F.; Jouvent, E.; Biessels, G.J.; Black, S.E.; Brayne, C.; Chen, C.; Cordonnier, C.; De Leeuw, F.-E.; Dichgans, M.; Doubal, F. Reproducibility and variability of quantitative magnetic resonance imaging markers in cerebral small vessel disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1319–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staals, J.; Booth, T.; Morris, Z.; Bastin, M.E.; Gow, A.J.; Corley, J.; Redmond, P.; Starr, J.M.; Deary, I.J.; Wardlaw, J.M. Total MRI load of cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive ability in older people. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2806–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemoto, C.K.; Ferretti-Rebustini, R.E.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Leite, R.E.; Soterio, L.; Brucki, S.M.; Spera, R.R.; Cippiciani, T.M.; Farfel, J.M.; Chiavegatto Filho, A.; et al. Neuropathological diagnoses and clinical correlates in older adults in Brazil: A cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, N.D.; Van Dijk, E.J.; Den Heijer, T.; Vermeer, S.E.; Jolles, J.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Hofman, A.; Breteler, M.M. Cerebral small-vessel disease and decline in information processing speed, executive function and memory. Brain 2005, 128, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poels, M.M.; Ikram, M.A.; van der Lugt, A.; Hofman, A.; Niessen, W.J.; Krestin, G.P.; Breteler, M.M.; Vernooij, M.W. Cerebral microbleeds are associated with worse cognitive function: The Rotterdam Scan Study. Neurology 2012, 78, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, K.; Tanaka, R.; Okuma, Y.; Shimura, H.; Ueno, Y.; Miyamoto, N.; Urabe, T.; Hattori, N. Cerebral microbleeds are associated with worse cognitive function in the nondemented elderly with small vessel disease. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra 2014, 4, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won Seo, S.; Hwa Lee, B.; Kim, E.-J.; Chin, J.; Sun Cho, Y.; Yoon, U.; Na, D.L. Clinical significance of microbleeds in subcortical vascular dementia. Stroke 2007, 38, 1949–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.H.; Hilal, S.; Schwingenschuh, P.; Wittfeld, K.; van der Lee, S.J.; DeCarli, C.; Vernooij, M.W.; Katschnig-Winter, P.; Habes, M.; Chen, C. A priori collaboration in population imaging: The Uniform Neuro-Imaging of Virchow-Robin Spaces Enlargement consortium. Alzheimers Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2015, 1, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.P.; Cain, J.; Thomas, O.; Jackson, A. Dilated perivascular spaces in the Basal Ganglia are a biomarker of small-vessel disease in a very elderly population with dementia. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol 2015, 36, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.W.; Shin, N.Y.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.M.; Lee, P.H.; Lee, S.K.; Ahn, K.J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Visible Perivascular Spaces in Basal Ganglia Predict Cognitive Decline in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Adler, C.H.; Bloem, B.R.; Chan, P.; Deuschl, G.; Gasser, T.; Goetz, C.G.; Halliday, G.; Joseph, L. The new definition and diagnostic criteria of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, T.; McKinlay, A.; Warren, N.; Stolwyk, R.J. Assessing the sensitivity and specificity of cognitive screening measures for people with Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRehabilitation 2018, 43, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatate, J.; Miwa, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Sasaki, T.; Yagita, Y.; Sakaguchi, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Mochizuki, H. Association between cerebral small vessel diseases and mild parkinsonian signs in the elderly with vascular risk factors. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 26, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Shan, Y.; Cai, W.; Liu, S.; Hu, M.; Liao, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y. Cerebral small vessel disease: Neuroimaging markers and clinical implication. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2347–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1987, 8, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Cordonnier, C.; Viswanathan, A.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Warach, S.; Launer, L.J.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Breteler, M.M.; Group, M.S. Cerebral microbleeds: A guide to detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doubal, F.N.; MacLullich, A.M.; Ferguson, K.J.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Enlarged perivascular spaces on MRI are a feature of cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke 2010, 41, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, G.M.; Doubal, F.N.; Jackson, C.A.; Chappell, F.M.; Sudlow, C.L.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Enlarged perivascular spaces and cerebral small vessel disease. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staals, J.; Makin, S.D.J.; Doubal, F.N.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Stroke subtype, vascular risk factors, and total MRI brain small-vessel disease burden. Neurology 2014, 83, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xiao, X.; Yin, J.; Yang, T.; Zeng, B. An Assessment of the Relationship between Structural and Functional Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease and Cognition-Related Fibers. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 4347676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Fu, Z.; Luo, X.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Vince, C.D. The Influence of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease on Static and Dynamic Functional Network Connectivity in Subjects Along Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijts, M.; Duits, A.; Van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Kroon, A.A.; De Leeuw, P.W.; Staals, J. Accumulation of MRI markers of cerebral small vessel disease is associated with decreased cognitive function. A study in first-ever lacunar stroke and hypertensive patients. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lee, A.; Fan, Y.-H.; Mok, V.C.T.; Shi, L. Magnetic resonance imaging manifestations of cerebral small vessel disease: Automated quantification and clinical application. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Zimmermann, J.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Focke, N.K.; Wicke, T.; Ebentheuer, J.; Schaumburg, M.; Lang, E.; Friede, T.; Trenkwalder, C. Baseline predictors for progression 4 years after Parkinson’s disease diagnosis in the De Novo Parkinson Cohort (DeNoPa). Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, D.; Kvaløy, J.; Andersen, K.; Larsen, J.; Tang, M.; Lolk, A.; Kragh-Sørensen, P.; Marder, K. The effect of age of onset of PD on risk of dementia. J. Neurol. 2007, 254, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, D.; Bronnick, K.; Williams-Gray, C.; Weintraub, D.; Marder, K.; Kulisevsky, J.; Burn, D.; Barone, P.; Pagonabarraga, J.; Allcock, L. Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease: A multicenter pooled analysis. Neurology 2010, 75, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-J.; Baumeister, T.R.; Garg, S.; McKeown, M.J. Cognitive profiles and hub vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Feng, T. Effect of small vessel disease burden and lacunes on gait/posture impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, A.M.; van Dijk, E.; Zwiers, M.P.; van Norden, A.G.; de Laat, K.F.; Shumskaya, E.; Norris, D.G.; de Leeuw, F.E. Structural network connectivity and cognition in cerebral small vessel disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, A.M.; van Norden, A.G.; de Laat, K.F.; Zwiers, M.P.; van Dijk, E.J.; Norris, D.G.; de Leeuw, F.-E. White matter integrity in small vessel disease is related to cognition. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 7, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, A.M.; Lawrence, A.; Norris, D.G.; Barrick, T.R.; Markus, H.S.; de Leeuw, F.E. Disruption of rich club organisation in cerebral small vessel disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuladhar, A.M.; van Uden, I.W.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.C.; Lawrence, A.; van der Holst, H.; van Norden, A.; de Laat, K.; van Dijk, E.; Claassen, J.A.; Kessels, R.P. Structural network efficiency predicts conversion to dementia. Neurology 2016, 86, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, A.J.; Chung, A.W.; Morris, R.G.; Markus, H.S.; Barrick, T.R. Structural network efficiency is associated with cognitive impairment in small-vessel disease. Neurology 2014, 83, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwoo, M.; Jeon, S.; Ham, J.; Hong, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.M.; Sohn, Y.; Lee, P. The burden of white matter hyperintensities is a predictor of progressive mild cognitive impairment in patients with P arkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 922-e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, P.; Pavese, N.; Canapicchi, R.; Paoli, C.; Del Dotto, P.; Puglioli, M.; Rossi, G.; Bonuccelli, U. White matter hyperintensities in Parkinson’s disease: Clinical correlations. Arch. Neurol. 1995, 52, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yue, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Tian, J.; Lv, W.; Lo, C.Z.; Hsu, Y.C.; Kober, T.; et al. The role of brain perivascular space burden in early-stage Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, P.; Lawrence, A.J.; Lambert, C.; Patel, B.; Chung, A.W.; MacKinnon, A.D.; Morris, R.G.; Barrick, T.R.; Markus, H.S. Strategic lacunes and their relationship to cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 4, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wu, D.H.; Li, H.Q.; Tan, L.; Xu, W.; Dong, Q.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of Cerebral Microbleeds with Cognitive Decline: A Longitudinal Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 75, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Ding, C.; Xiao, J.; Jiang, X.; Shan, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, D. Total magnetic resonance imaging burden of cerebral small-vessel disease is associated with post-stroke depression in patients with acute lacunar stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| All PD Patients (n = 122) | PD-NCI Group (n = 53) | PD-CI Group (n = 69) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical variables | ||||
| Male 2 | 88 (72.1%) | 36 (67.9%) | 52 (75.4%) | 0.364 |
| Age, years 1 | 64.96 ± 8.94 | 61.40 ± 9.85 | 67.70 ± 7.10 | 0.000 * |
| MMSE score 1 | 24.45 ± 4.20 | 28.02 ± 0.91 | 21.71 ± 3.62 | 0.000 * |
| Duration, years 1 | 4.17 ± 3.64 | 3.53 ± 2.82 | 4.67 ± 4.11 | 0.088 |
| Education level 3 | 1.98 ± 1.27 | 2.68 ± 0.976 | 1.45 ± 1.21 | 0.000 * |
| Hoehn-Yahr staging 3 | 2.35 ± 0.68 | 2.24 ± 0.66 | 2.45 ± 0.69 | 0.043 * |
| Hypertension 2 | 38 (31.1%) | 10 (18.9%) | 28 (40.6%) | 0.010 * |
| Diabetes 2 | 13 (10.7%) | 6 (11.3%) | 7 (10.1%) | 0.835 |
| Smoking 2 | 22 (18.0%) | 6 (11.3%) | 16 (23.2%) | 0.091 |
| Imaging findings | ||||
| SLI 1 | 23 (18.9%) | 1 (1.9%) | 22 (31.9%) | 0.000 * |
| CMB 1 | 24 (19.7%) | 5 (9.4%) | 19 (27.5%) | 0.013 * |
| DWMH 2 | 0.69 ± 0.88 | 0.38 ± 0.53 | 0.93 ± 1.01 | 0.002 * |
| PVH 2 | 0.69 ± 0.98 | 0.30 ± 0.50 | 0.99 ± 1.14 | 0.001 * |
| CS-EPVS 2 | 2.45 ± 0.74 | 2.40 ± 0.77 | 2.49 ± 0.72 | 0.468 |
| BG-EPVS 2 | 1.64 ± 0.68 | 1.47 ± 0.61 | 1.77 ± 0.71 | 0.019 * |
| Midbrain-EPVS 1 | 58 (47.5%) | 26 (49.1%) | 32 (46.4%) | 0.769 |
| Total CSVD score 2 | 1.30 ± 1.07 | 0.77 ± 0.64 | 1.70 ± 1.17 | 0.000 * |
| The Total Burden of CSVD | PVH | MMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | −0.269 * | −0.197 * | ns |
| Age | 0.559 * | 0.546 * | −0.350 * |
| MMSE | −0.483 * | −0.342 * | / |
| Disease Duration | ns | ns | ns |
| Education level | ns | ns | 0.538 * |
| Hoehn-Yahr staging | 0.192 * | 0.252 * | −0.277 * |
| Hypertension | 0.325 * | 0.241 * | −0.244 * |
| Diabetes | ns | 0.274 * | ns |
| Smoking | ns | ns | ns |
| Midbrain-EPVS | / | / | ns |
| SLI | / | / | −0.335 * |
| CMB | / | / | ns |
| DWMH | / | / | −0.303 * |
| PVH | / | / | −0.324 * |
| CS-EPVS | / | / | ns |
| BG-EPVS | / | / | −0.247 * |
| CSVD | / | / | −0.483 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Cai, G.; Chen, X.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Y. Total Burden of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease on MRI May Predict Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185381
Zhu R, Li Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Cai G, Chen X, Ye Q, Chen Y. Total Burden of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease on MRI May Predict Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185381
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ruihan, Yunjing Li, Lina Chen, Yingqing Wang, Guoen Cai, Xiaochun Chen, Qinyong Ye, and Ying Chen. 2022. "Total Burden of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease on MRI May Predict Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185381
APA StyleZhu, R., Li, Y., Chen, L., Wang, Y., Cai, G., Chen, X., Ye, Q., & Chen, Y. (2022). Total Burden of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease on MRI May Predict Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185381







