Detection of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis from X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- This is the first study to address the problem of identifying lumbar slippage in true lateral, flexion and extension lateral views of X-ray images.
- LumbarNet presents a novel design for the detection of spondylolisthesis by using piecewise slope detection (PSD), dynamic shifting (DS), and the hybrid judgement of P-grade and PSD value to enhance slippage identification in the lumbar spine.
- Our method is robust against the presence of lumbar sacralization and reaches a high accuracy accordingly.
2. Materials and Methods
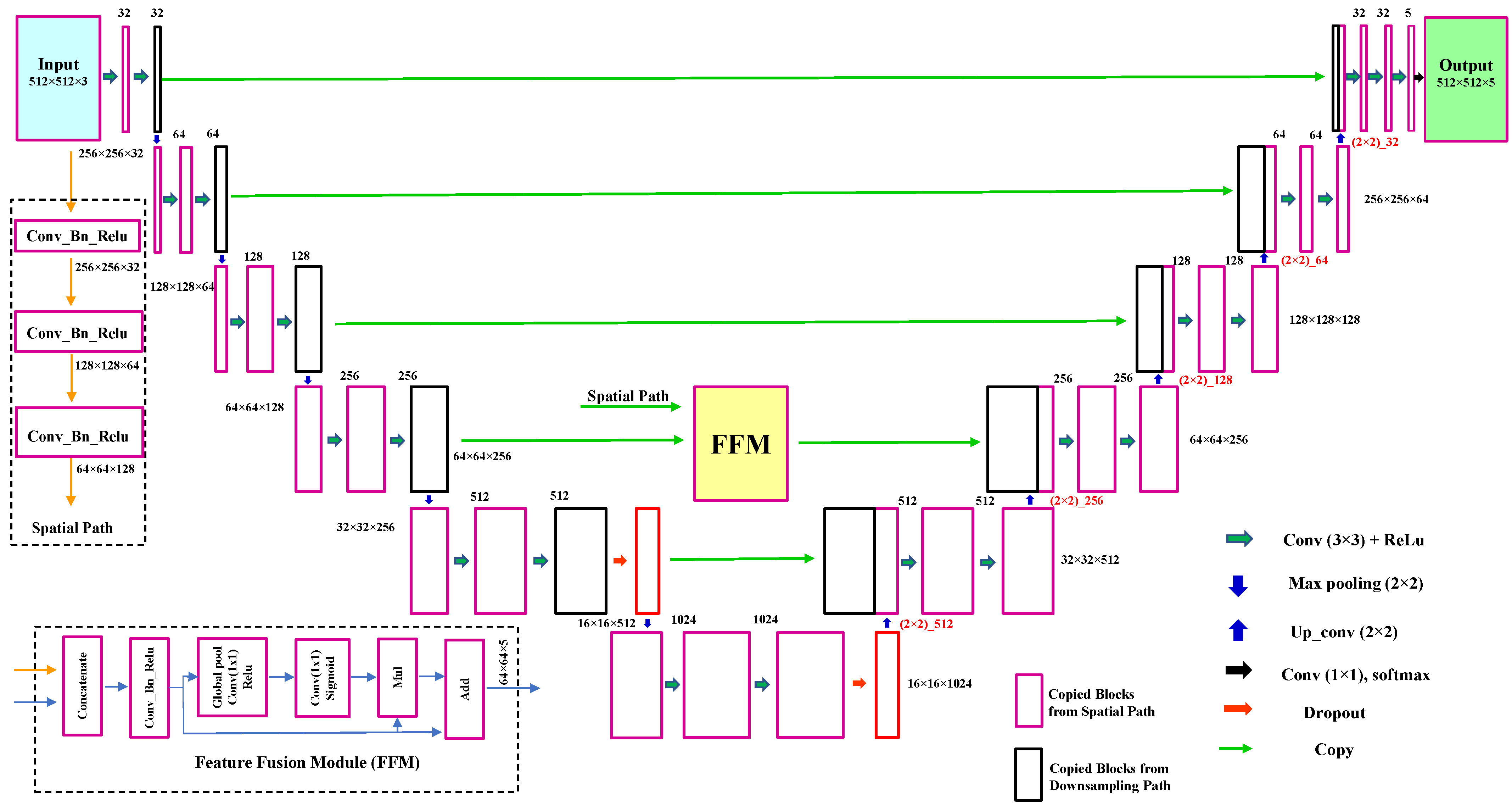
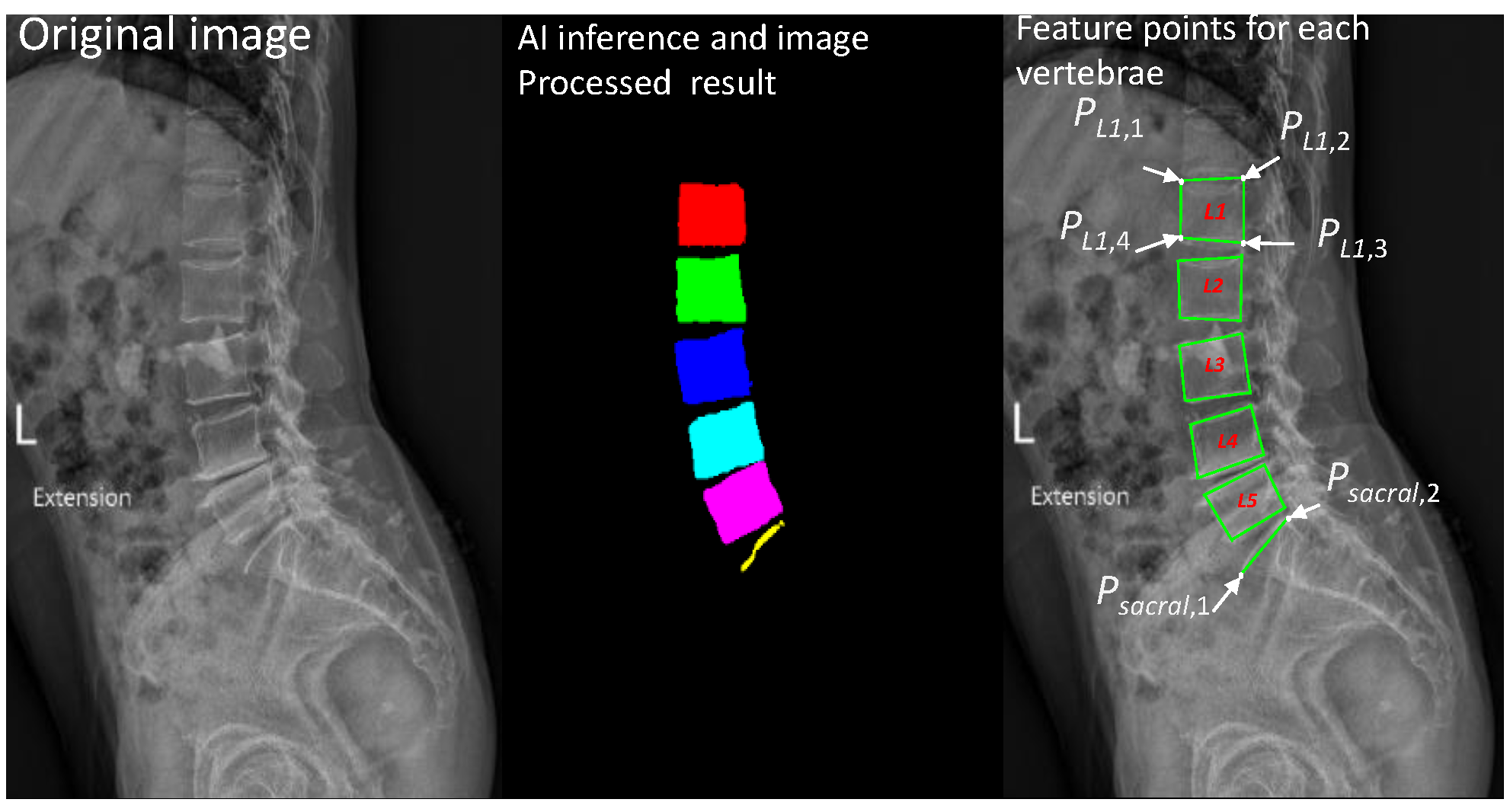
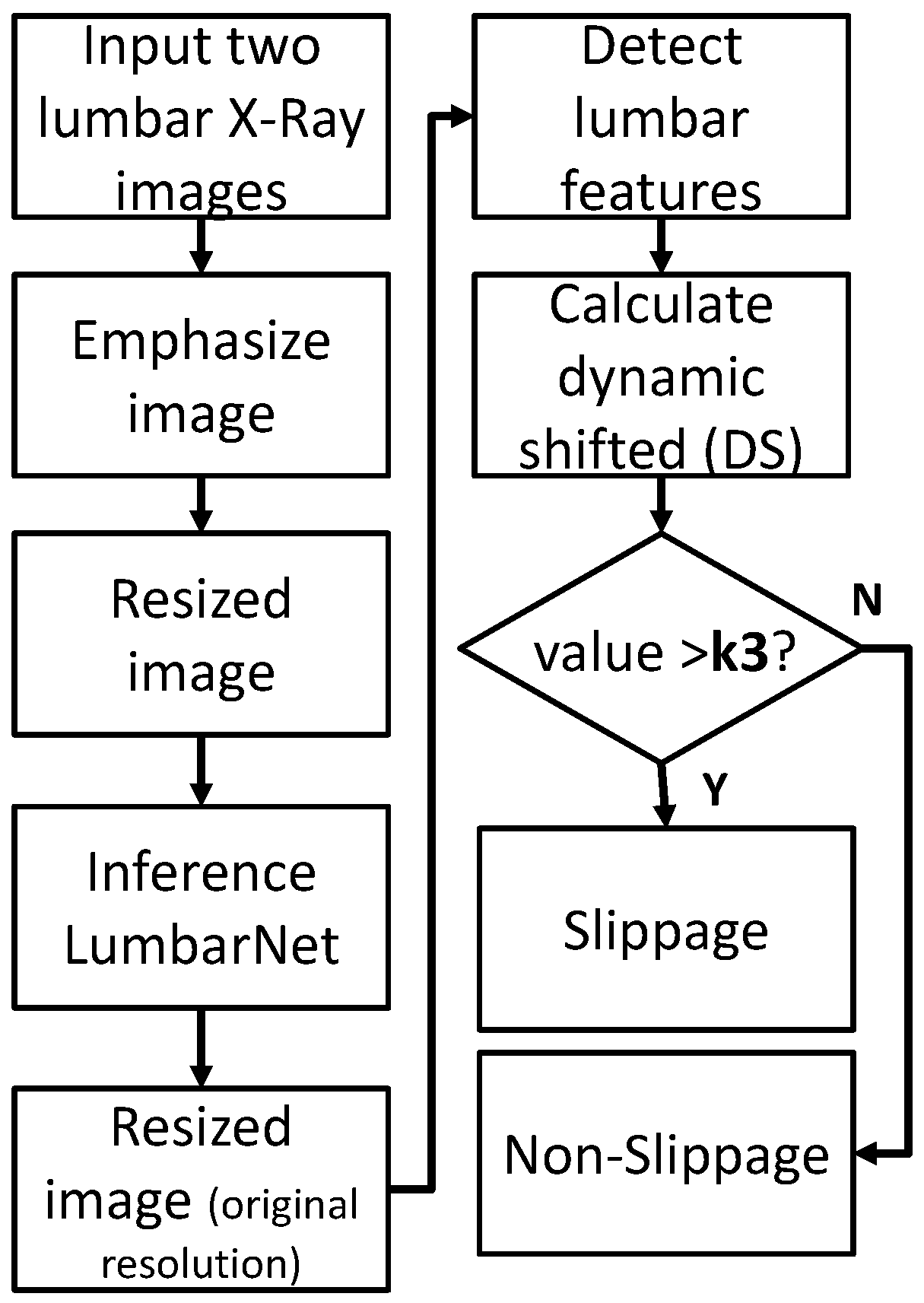
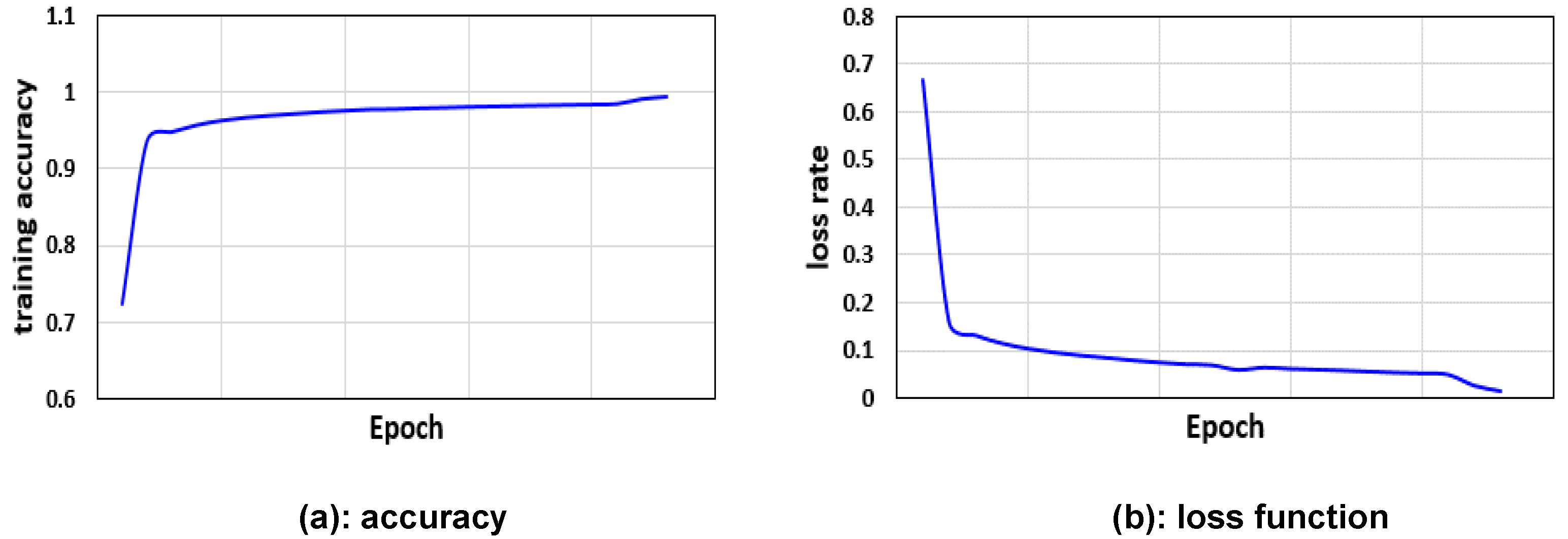
2.1. LumbarNet for Segmenting Vertebral Regions from X-ray Images
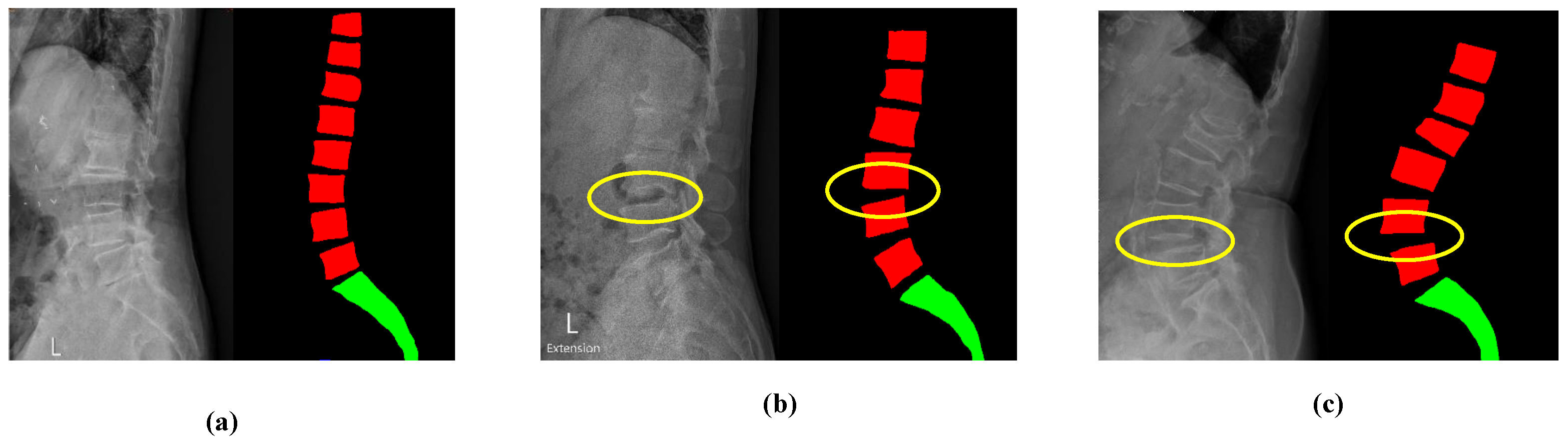
2.2. Detection of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
2.2.1. P-Grade
2.2.2. Piecewise Slope Detection (PSD)
2.2.3. Dynamic Shift (DS) Detection
3. Results
3.1. Data Set
3.2. Analytical Experiments
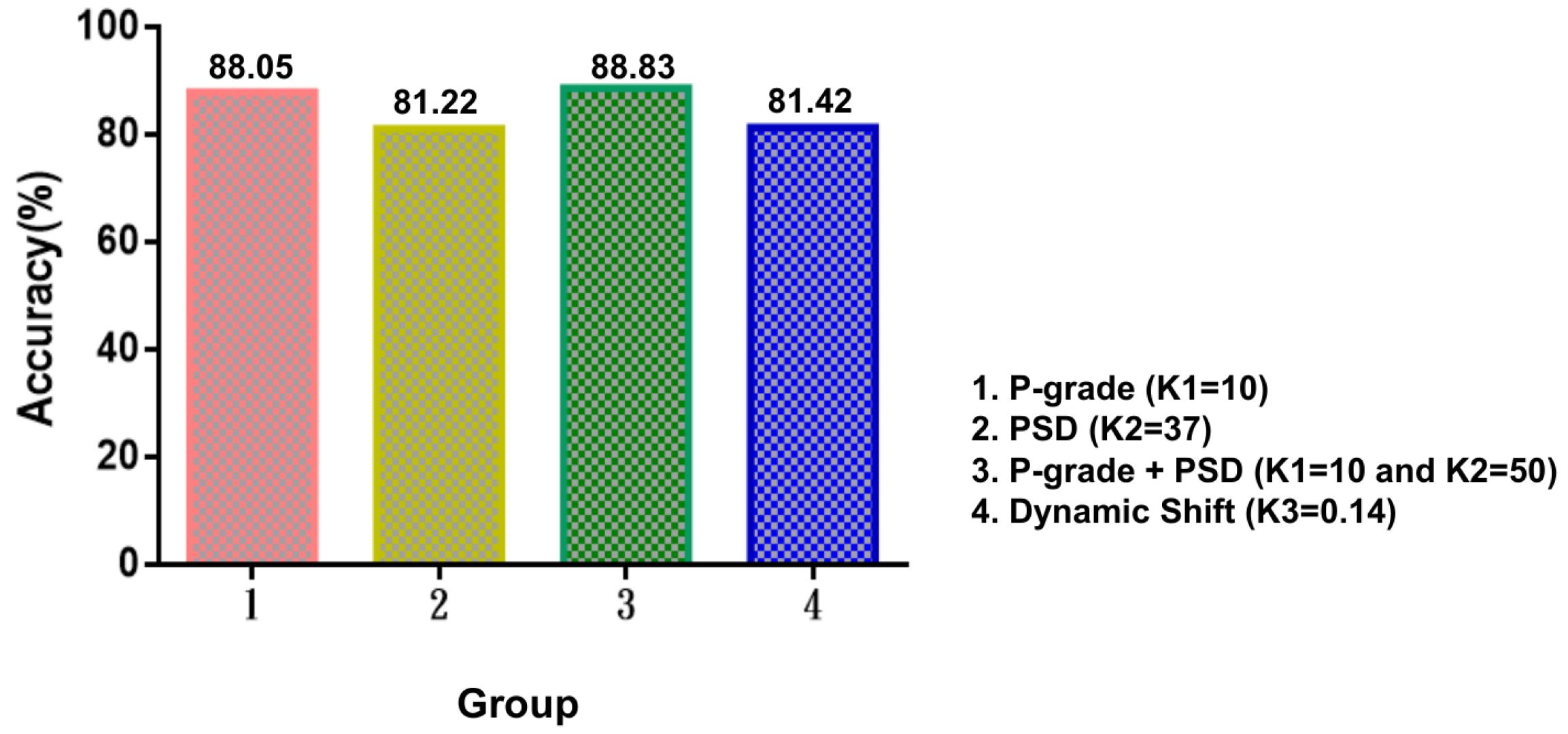
3.2.1. Experiments for P-Grade
3.2.2. Experiments for PSD
3.2.3. Experiments for DS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cramer, G.D.; Darby, S.A. Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and ANS; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sąsiadek, M.J.; Bladowska, J. Imaging of degenerative spine disease the state of the art. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2012, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gallucci, M.; Limbucci, N.; Paonessa, A.; Splendiani, A. Degenerative disease of the spine. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2007, 17, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeely, M.L.; Torrance, G.; Magee, D. A systematic review of physiotherapy for spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Man. Ther. 2003, 8, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier, R.; Herman, M.J.; Cheung, E.V.; Pizzutillo, P.D. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents: I. Diagnosis, natural history, and nonsurgical management. JAAOS-J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2006, 14, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, C.; Park, J.; Chung, N.; Son, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J. Degenerative retrolisthesis: Is it a compensatory mechanism for sagittal imbalance? Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, C.J.; Shah, D.; Saha, S.; Houghton, R. Spondylolisthesis: A pictorial review. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2012, 73, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Razi, A.; Lurie, J.D.; Hanscom, B.; Weinstein, J. Retrolisthesis and lumbar disc herniation: A preoperative assessment of patient function. Spine J. 2007, 7, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, T.; Wakami, T.; Kurihara, A.; Kasahara, K.; Yoshiya, S.; Nishida, K. Lumbar multilevel degenerative spondylolisthesis: Radiological evaluation and factors related to anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis. Clin. Spine Surg. 2002, 15, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaer, J.W.; McKeough, D.M.; Boissonnault, W.G. Lumbar isthmic spondylolisthesis detection with palpation: Interrater reliability and concurrent criterion-related validity. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2006, 14, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslosky, E.; Gendelberg, D. Classification in Brief: The Meyerding classification system of spondylolisthesis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrzycki, J.; Smidova, N.; Litak, J.; Ausiyevich, A. Numerical Analysis of Spinal Loads in Spondylolisthesis Treatment using Pedicle Screws–Preliminary Research. Appl. Comput. Sci. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, V.M.; Senglaub, S.S.; Rattani, A.; Dewan, M.C.; Härtl, R.; Bisson, E.; Park, K.B.; Shrime, M.G. Degenerative lumbar spine disease: Estimating global incidence and worldwide volume. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, N.; Hamed, H.N.A.; Ibrahim, Z.; Ibrahim, K. 2D Photogrammetry Image of Scoliosis Lenke Type Classification Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 9th International Conference on System Engineering and Technology (ICSET), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 7 October 2019; pp. 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Bailey, C.; Rasoulinejad, P.; Li, S. Automated comprehensive adolescent idiopathic scoliosis assessment using MVC-Net. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassman, S.D.; Bridwell, K.; Dimar, J.R.; Horton, W.; Berven, S.; Schwab, F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine 2005, 30, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.; Kim, S.W. Retrolisthesis as a compensatory mechanism in degenerative lumbar spine. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2015, 57, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawchuk, G.; Guan, R.; Keen, C.; Hauer, B.; Kondrak, G. Using artificial intelligence algorithms to identify existing knowledge within the back pain literature. Eur. Spine J. Off. Publ. Eur. Spine Soc. Eur. Spinal Deform. Soc. Eur. Sect. Cerv. Spine Res. Soc. 2020, 29, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Cloud, G.; Kerry, S.; Markus, H.S. Imaging of vertebral artery stenosis: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Radev, D.; Malhotra, A. Identification of patients with carotid stenosis using natural language processing. Imaging Inform. Artif. Intell. 2020, 30, 4125–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, A.B.; Akgul, Y.S. Diagnosis of degenerative intervertebral disc disease with deep networks and SVM. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Computer and Information Sciences, Krakow, Poland, 27–28 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, E.; Khanbare, S.; Yousefi, H.; Sharpasand, H.; Sojoodi Sheyjani, O. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Automated Diagnosis of Disc Herniation on Axial MRI. In Proceedings of the 2019 Scientific Meeting on Electrical-Electronics Biomedical Engineering and Computer Science (EBBT), Istanbul, Turkey, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Burns, J.; Liu, J.; Summers, R.M. Detection of Degenerative Osteophytes of the Spine on PET/CT Using Region-Based Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop and Challenge, CSI 2016: International Workshop on Computational Methods and Clinical Applications for Spine Imaging, Athens, Greece, 17 October 2016; pp. 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lubelski, D.; Alentado, V.J.; Williams, S.K.; O’Rourke, C.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Wang, J.C.; Steinmetz, M.P.; Melillo, A.J.; Benzel, E.C.; Modic, M.T.; et al. Variability in surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis among spine surgeons. World Neurosurg. 2018, 111, e564–e572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Han, B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 1520–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Du, S.; Emery, W.J. Object-Based Convolutional Neural Network for High-Resolution Imagery Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3386–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglovikov, V.; Seferbekov, S.; Buslaev, A.; Shvets, A. Ternausnetv2: Fully convolutional network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Stoian, A.; Poulain, V.; Inglada, J.; Poughon, V.; Derksen, D. Land cover maps production with high resolution satellite image time series and convolutional neural networks: Adaptations and limits for operational systems. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.05566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budd, S.; Robinson, E.; Kainz, B. A Survey on Active Learning and Human-in-the-Loop Deep Learning for Medical Image Analysis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.02923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecron, F.; Mahmoudi, S.A.; Benjelloun, M.; Mahmoudi, S.; Manneback, P. Heterogeneous Computing for Vertebra Detection and Segmentation in X-Ray Images. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2011, 2011, 640208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Konya, S.; Sai Natarajan, T.R.; Allouch, H.; Nahleh, K.A.; Dogheim, O.Y.; Boehm, H. Convolutional Neural Networks based automated segmentation and labelling of the lumbar spine X-ray. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03364. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. Yolact: Real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9157–9166. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, B.; Kaji, D.; Cheung, Z.; Ye, I.B.; Tang, R.; Ahn, A.; Carrillo, O.; Schwartz, J.T.; Valliani, A.A.; Oermann, E.K.; et al. Automated Measurement of Lumbar Lordosis on Radiographs Using Machine Learning and Computer Vision. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, F. FSSD: Feature fusion single shot multibox detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.00960. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets and Fully Connected CRFs. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Chen, B.; Li, S. Automatic spondylolisthesis grading from MRIs across modalities using faster adversarial recognition network. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Sajjad, F.; Naveed, N.; Shafi, I.; ul-Qayyum, Z. Diagnosis of vertebral column disorders using machine learning classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Information Science and Applications (ICISA), Suwon, Korea, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Karabulut, E.M.; Ibrikci, T. Effective automated prediction of vertebral column pathologies based on logistic model tree with SMOTE preprocessing. J. Med. Syst. 2014, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akben, S.B. Importance of the shape and orientation of the spine and pelvis for the vertebral column pathologies diagnosis with using machine learning methods. Biomed. Res.-India 2016, 27, S337–S342. [Google Scholar]
- Unal, Y.; Polat, K.; Kocer, H.E. Pairwise FCM based feature weighting for improved classification of vertebral column disorders. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 46, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha Neto, A.R.; de Alencar Barreto, G. On the application of ensembles of classifiers to the diagnosis of pathologies of the vertebral column: A comparative analysis. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2009, 7, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
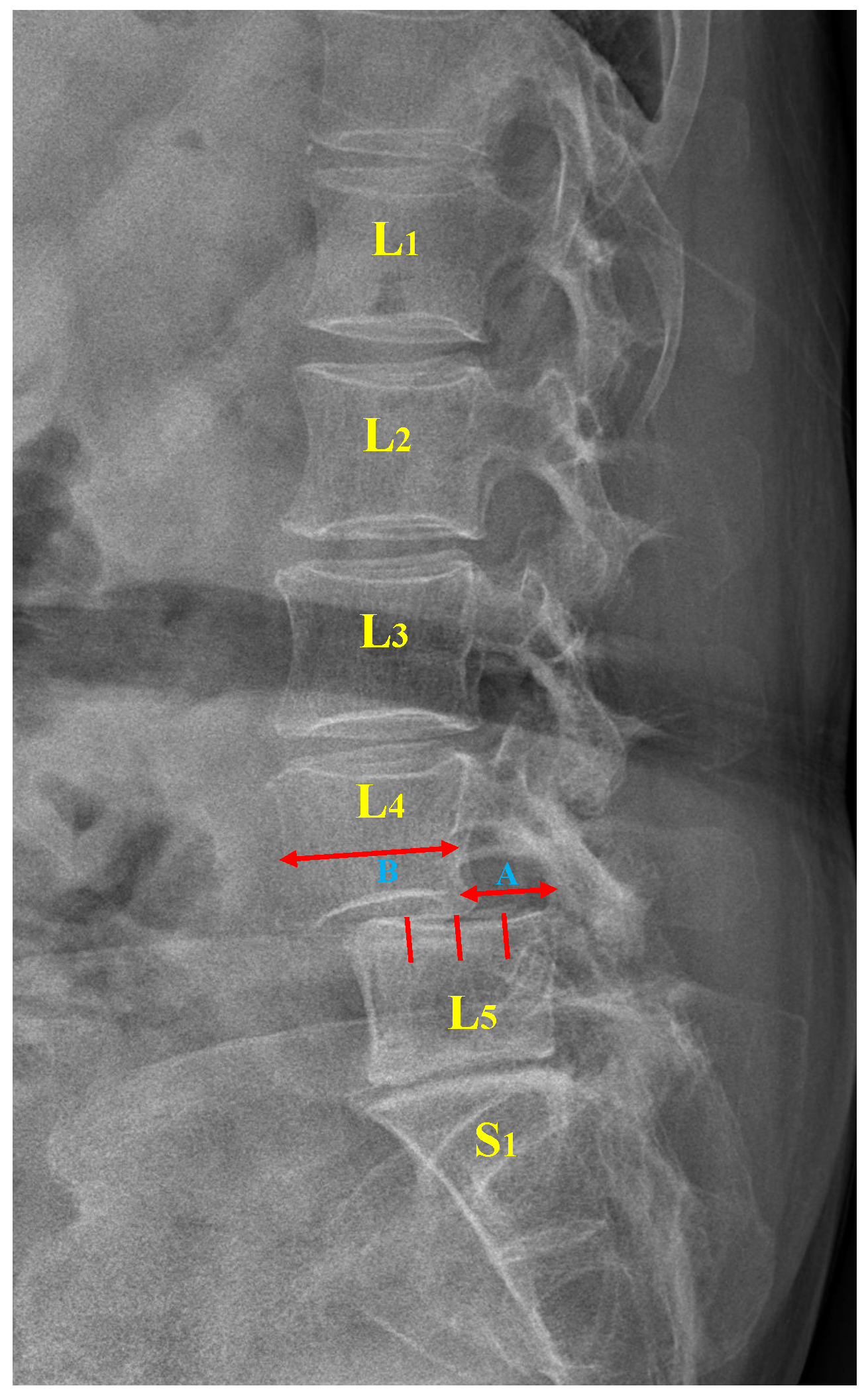


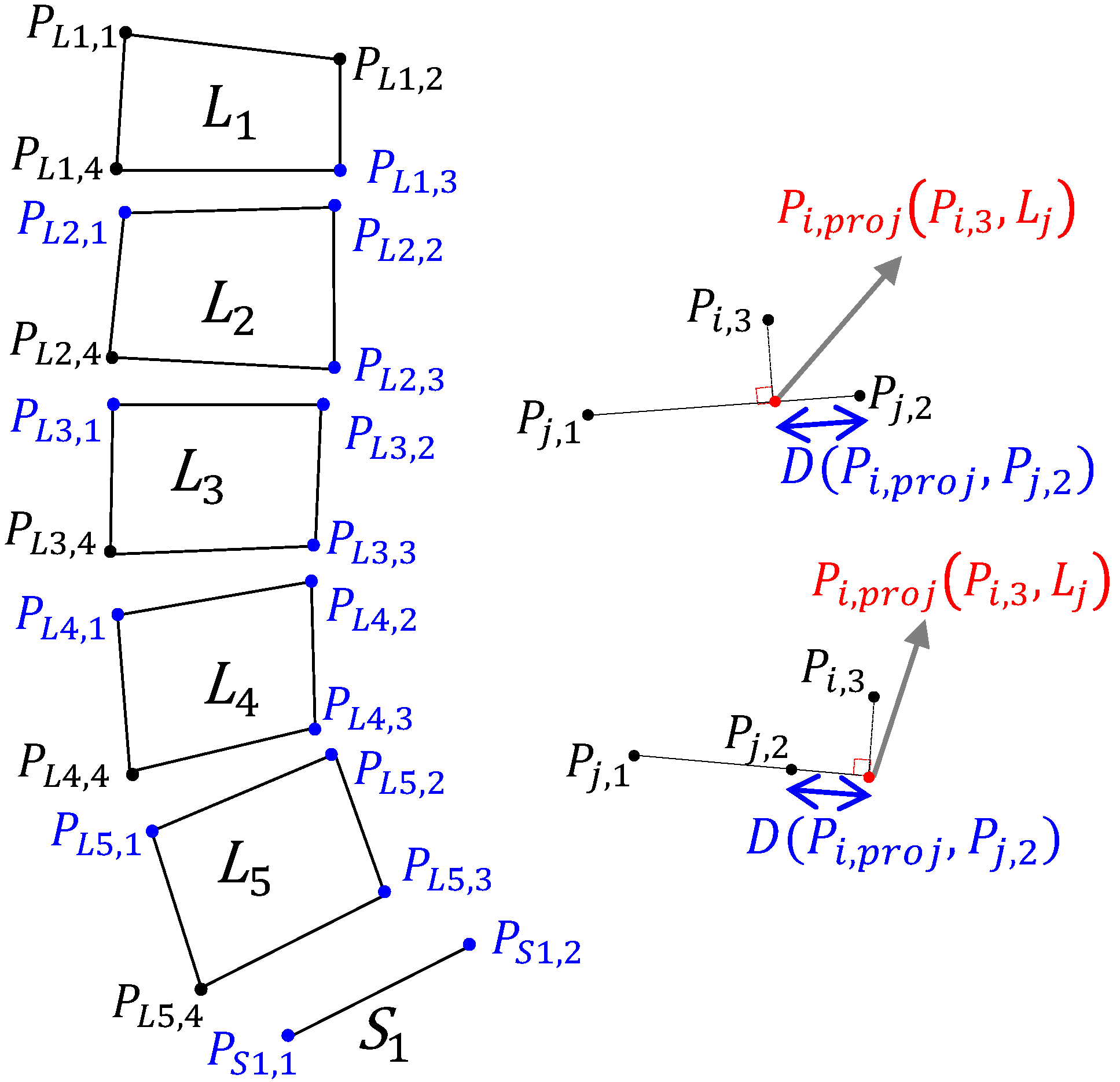



| P-Grade (A/B) | % | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | 0–25% | Low grade |
| Grade 2 | 26–50% | |
| Grade 3 | 51–75% | High grade |
| Grade 4 | 76–100% | |
| Grade 5 | Complete dislocation of vertebral body (>100%) | Spondyloptosis |
| Average | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | |||||||
| LumbarNet |
| P-Grade | PSD | P-Grade + PSD | DS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ( = 10) | ( = 37) | ( = 10 + = 50) | ( = 0.14) | |
| Accuracy | ||||
| (95% CI, 80%–91%) | (95% CI, 75%–90%) | (95% CI, 84%–91%) | (95% CI, 80%–82%) | |
| Sensitivity | ||||
| (95% CI, 79%–94%) | (95% CI, 81%–92%) | (95% CI, 85%–93%) | (95% CI, 79%–83%) | |
| Specificity | ||||
| (95% CI, 81%–86%) | (95% CI, 61%–90%) | (95% CI, 81%–84%) | (95% CI, 79%–81%) | |
| False positive | ||||
| (95% CI, 4%–6%) | (95% CI, 4%–12%) | (95% CI, 4%–6%) | (95% CI, 9%–10%) | |
| False negative | ||||
| (95% CI, 4%–15%) | (95% CI, 5%–13%) | (95% CI, 5%–11%) | (95% CI, 8%–10%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trinh, G.M.; Shao, H.-C.; Hsieh, K.L.-C.; Lee, C.-Y.; Liu, H.-W.; Lai, C.-W.; Chou, S.-Y.; Tsai, P.-I.; Chen, K.-J.; Chang, F.-C.; et al. Detection of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis from X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Network. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5450. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185450
Trinh GM, Shao H-C, Hsieh KL-C, Lee C-Y, Liu H-W, Lai C-W, Chou S-Y, Tsai P-I, Chen K-J, Chang F-C, et al. Detection of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis from X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Network. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5450. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185450
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrinh, Giam Minh, Hao-Chiang Shao, Kevin Li-Chun Hsieh, Ching-Yu Lee, Hsiao-Wei Liu, Chen-Wei Lai, Sen-Yi Chou, Pei-I Tsai, Kuan-Jen Chen, Fang-Chieh Chang, and et al. 2022. "Detection of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis from X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Network" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5450. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185450
APA StyleTrinh, G. M., Shao, H.-C., Hsieh, K. L.-C., Lee, C.-Y., Liu, H.-W., Lai, C.-W., Chou, S.-Y., Tsai, P.-I., Chen, K.-J., Chang, F.-C., Wu, M.-H., & Huang, T.-J. (2022). Detection of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis from X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Network. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5450. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185450







