Reduction of Thoracic Hyper-Kyphosis Improves Short and Long Term Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Nonspecific Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Multimodal Program
2.2. TENS and Heat Therapy
2.3. Soft Tissue Mobilization
2.4. Thoracic Spine Manipulation
2.5. Functional Exercises
- (1)
- TheraBand™;
- (2)
- 3 lbs;
- (3)
- 3 lbs and TheraBand™;
- (4)
- 5 lbs;
- (5)
- 5 lbs and TheraBand™;
- (6)
- 8 lbs;
- (7)
- Using 8 lbs and TheraBand™.
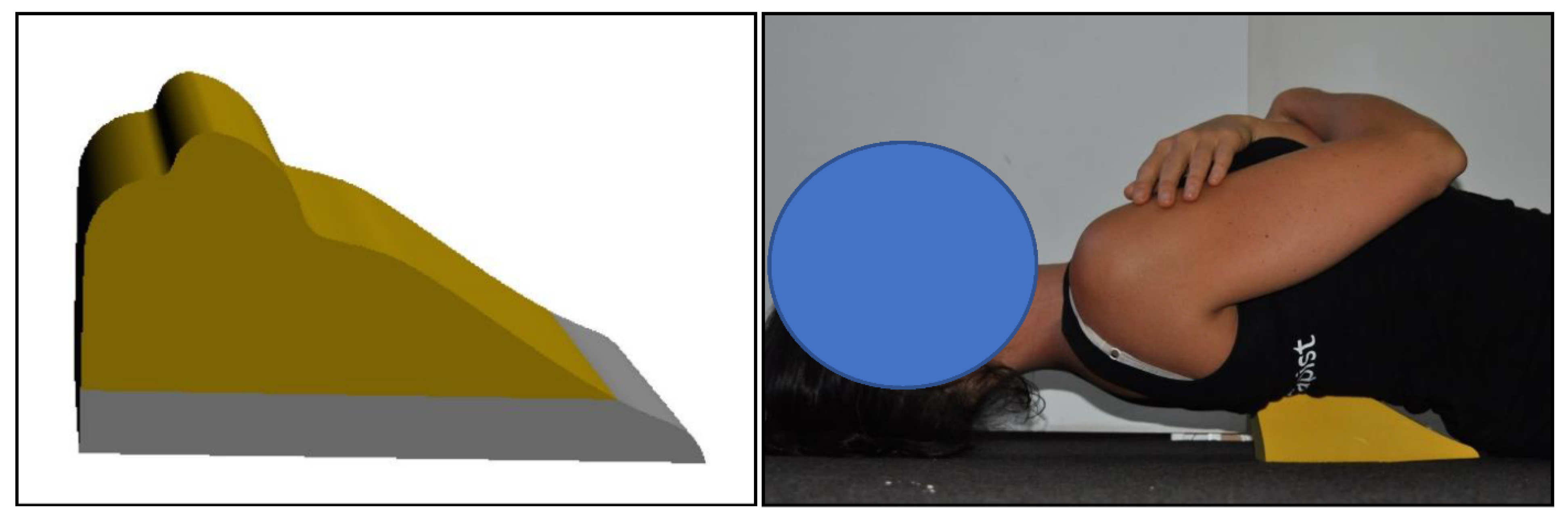
2.6. Denneroll™ Thoracic Traction Orthotic (DTTO)
2.7. Outcome Measures
2.8. ICT-ITL (Max)
2.9. Neck Disability Index
2.10. Numerical Rating Score (NRS)
2.11. Sensorimotor Control Measures
2.12. Cervical Joint Position Sense Testing
2.13. Head and Eye Movement Control: Smooth Pursuit Neck Torsion Test (SPNT)
2.14. Postural Stability
3. Statistical Analysis
3.1. Sample Size
3.2. Data Analysis
3.3. Imputation of Missing Values
4. Results
4.1. Baseline Demographics and Characteristics
4.2. Between Group Analysis
4.3. The 10-Week Evaluation
- -
- Thoracic kyphotic angle
- -
- NDI and Pain Intensity
- -
- Sensori-motor control
4.4. One-Year Follow-up
5. Discussion
5.1. Thoracic Kyphosis Improvement
5.2. Pain, Disability, and Sensorimotor Control
5.3. Limitations and Summary
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, S.P. Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Neck Pain. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oxland, T.R. Fundamental biomechanics of the spine—What we have learned in the past 25 years and future directions. J. Biomech. 2015, 49, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.T.; Cheung, K.Y.; Chan, K.B.; Chan, M.H.; Lo, K.Y.; Chiu, T.T.W. Relationships between sagittal postures of thoracic and cervical spine, presence of neck pain, neck pain severity and disability. Man. Ther. 2010, 15, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, T.F.; Peterson, D.H. Chiropractic Technique Principles and Procedures; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Norlander, S.; Gustavsson, B.A.; Lindell, J.; Nordgren, B. Reduced mobility in the cervico-thoracic motion segment: A risk factor for musculoskeletal neck-shoulder pain: A two-year prospective follow-up study. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1997, 29, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Norlander, S.; Aste-Norlander, U.; Nordgren, B.; Sahlstedt, B. Mobility in the cervico-thoracic motion segment: An indicative factor of musculo-skeletal neck-shoulder pain. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1996, 28, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Fernández-Carnero, J.; Fernández, A.P.; Lomas-Vega, R.; Miangolarra-Page, J.C. Dorsal Manipulation in Whiplash Injury Treatment. J. Whiplash Relat. Disord. 2004, 3, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, J.; Selleck, B.; Stowell, T.; Browne, L.; Alberini, S.; Cyr, H.S.; Caron, T. Short-Term Effects of Thoracic Manipulation on Lower Trapezius Muscle Strength. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2004, 12, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jull, G.A.; O’Leary, S.P.; Falla, D.L. Clinical Assessment of the Deep Cervical Flexor Muscles: The Craniocervical Flexion Test. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2008, 31, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, J.; Pua, Y.-H.; Clark, R.A.; Bryant, A.L. Effects of thoracic kyphosis and forward head posture on cervical range of motion in older adults. Man. Ther. 2013, 18, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Çelenay, T. An investigation of sagittal thoracic spinal curvature and mobility in subjects with and without chronic neck pain: Cut-off points and pain relationship. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 47, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falla, D.; Gizzi, L.; Parsa, H.; Dieterich, A.; Petzke, F. People with Chronic Neck Pain Walk with a Stiffer Spine. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Balthillaya, G.; Neelapala, Y.V.R. Thoracic Posture and Mobility in Mechanical Neck Pain Population: A Review of the Literature. Asian Spine J. 2019, 13, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, M. Treatment of a Patient with Cervical Radiculopathy Using Thoracic Spine Thrust Manipulation, Soft Tissue Mobilization, and Exercise. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2008, 16, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oakly, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Reducing thoracic hyperkyphosis subluxation deformity: A systematic review of chiropractic biophysics® methods employed in its structural improvement. J. Contemp. Chiropr. 2018, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Oakley, P.A.; Ehsani, N.N.; Moustafa, I.M.; Harrison, D.E. Restoring lumbar lordosis: A systematic review of controlled trials utilizing Chiropractic Bio Physics® (CBP®) non-surgical approach to increasing lumbar lordosis in the treatment of low back disorders. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2020, 32, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, P.A.; Ehsani, N.N.; Moustafa, I.M.; Harrison, D.E. Restoring cervical lordosis by cervical extension traction methods in the treatment of cervical spine disorders: A systematic review of controlled trials. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2021, 33, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, C.; Ward, A.R.; Robertson, V.J. Comparison of the analgesic efficacy of interferential therapy and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Physiotherapy 2006, 92, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, J.M.; Plastaras, C.; Becker, S. Cervical radiculopathy. In Therapeutic Programs for Musculoskeletal Disorders, 1st ed.; Wyss, J.F., Patel, A.D., Eds.; Demos Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Harman, K.; Hubley-Kozey, C.; Butler, H. Effectiveness of an Exercise Program to Improve Forward Head Posture in Normal Adults: A Randomized, Controlled 10-Week Trial. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2005, 13, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.W. The Thoracic Spine and Rib Cage: Musculoskeletal Evaluation and Treatment; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 171–201. [Google Scholar]
- Betsch, M.; Wild, M.; Jungbluth, P.; Hakimi, M.; Windolf, J.; Haex, B.; Horstmann, T.; Rapp, W. Reliability and validity of 4D rasterstereography under dynamic conditions. Comput. Biol. Med. 2011, 41, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerich, J.M.; Hertzler, K.; Knott, P.; Mardjetko, S. Comparison of Radiographic and Surface Topography Measurements in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Open Orthop. J. 2012, 6, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, D.E.; Janik, T.J.; Harrison, D.D.; Cailliet, R.; Harmon, S.F. Can the Thoracic Kyphosis Be Modeled With a Simple Geometric Shape? J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2002, 15, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDermid, J.C.; Walton, D.M.; Avery, S.; Blanchard, A.; Etruw, E.; McAlpine, C.; Goldsmith, C.H. Measurement Properties of the Neck Disability Index: A Systematic Review. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2009, 39, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundeberg, T.; Lund, I.; Dahlin, L.; Borg, E.; Gustafsson, C.; Sandin, L.; Rosén, A.; Kowalski, J.; Eriksson, S.V. Reliability and responsiveness of three different pain assessments. J. Rehabil. Med. 2001, 33, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bijur, P.E.; Latimer, C.T.; Gallagher, E.J. Validation of a verbally administered numerical rating scale of acute pain for use in the emergency department. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2003, 10, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibault, J.; Vaillant, J.; Vuillerme, N.; Dedering, A.; Peolsson, A. Using the cervical range of motion (CROM) device to assess head repositioning accuracy in individuals with cervical radiculopathy in comparison to neck- healthy individuals. Man. Ther. 2013, 18, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loudon, J.K.; Ruhl, M.; Field-Fote, E. Ability to Reproduce Head Position after Whiplash Injury. Spine 1997, 22, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treleaven, J.; Jull, G.; Sterling, M. Dizziness and unsteadiness following whiplash injury: Characteristic features and relationship with cervical joint position error. J. Rehabil. Med. 2003, 35, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tyler, C.W. Measurement of saccadic eye movements by electrooculography for simultaneous EEG recording. Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 51, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tjell, C.; Rosenhall, U. Smooth pursuit neck torsion test: A specific test for cervical dizziness. Am. J. Otol. 1998, 19, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, R.; Arnold, B. Intertester and Intratester Reliability of a Dynamic Balance Protocol Using the Biodex Stability System. J. Sport Rehabil. 1998, 7, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parraca, J.; Olivares, P.; Carbonell-baeza, A.; Aparicio, V.; Adsuar, J.; Gusi, N. Test-Retest Reliability of Biodex Balance SD on Physically Active Old People. J Hum. Sport Exerc. 2011, 8, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, N.; Dzurino, D.; Karleskint, M.; Tucker, J. Examining the reliability, correlation, and validity of commonly used as-sessment tools to measure balance. Health Sci. Rep. 2018, 1, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinman, M.R. Factors Affecting Reliability of the Biodex Balance System: A Summary of Four Studies. J. Sport Rehabil. 2000, 9, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, D.B. Multiple Imputation for Nonresponse in Surveys; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Pellise, F.; Vila-Casademunt, A.; Ferrer, M.; Domingo-Sabat, M.; Bago, J.; Perez-Grueso, F.J.; Alanay, A.; Mannion, A.F.; Acaroglu, E.; European Spine Study Group, ESSG. Impact on health related quality of life of adult spine deformity (ASD) compared with other chronic conditions. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bess, S.; Line, B.; Fu, K.M.; McCarthy, I.; Lafage, V.; Schwab, F.; Shaffrey, C.; Ames, C.; Akbarnia, B.; Jo, H.; et al. The Health Impact of Symptomatic Adult Spi-nal Deformity: Comparison of Deformity Types to United States Population Norms and Chronic Diseases. Spine 2016, 41, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bess, S.; Protopsaltis, T.S.; Lafage, V.; Lafage, R.; Ames, C.P.; Errico, T.; Smith, J.S.; International Spine Study Group. Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Adult Spinal Deformity. Clin. Spine Surg. 2016, 29, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharaporn, M.; Pawelek, J.; Bastrom, T.; Lonner, B.; Newton, P.O. The Relationship between Thoracic Hyperkyphosis and the Scoliosis Research Society Outcomes Instrument. Spine 2007, 32, 2226–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissinen, M.; Heliövaara, M.; Seitsamo, J.; Poussa, M. Left Handedness and Risk of Thoracic Hyperkyphosis in Prepubertal Schoolchildren. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 24, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gálvez, N.; Gea-García, G.M.; Marcos-Pardo, P.J. Effects of exercise programs on kyphosis and lordosis angle: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pizzutillo, P.D. Nonsurgical treatment of kyphosis. Instr. Course Lect. 2004, 53, 485–491. [Google Scholar]
- Bezalel, T.; Carmeli, E.; Levi, D.; Kalichman, L. The Effect of Schroth Therapy on Thoracic Kyphotic Curve and Quality of Life in Scheuermann’s Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Asian Spine J. 2019, 13, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hunter, D.J.; Rivett, D.A.; McKiernan, S.; Weerasekara, I.; Snodgrass, S.J. Is the inclinometer a valid measure of thoracic kyphosis? A cross-sectional study. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2018, 22, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Youssef, A.; Ahbouch, A.; Tamim, M.; Harrison, D.E. Is forward head posture relevant to autonomic nervous system function and cervical sensorimotor control? Cross sectional study. Gait Posture 2020, 77, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Diab, A.A.; Harrison, D.E. The effect of normalizing the sagittal cervical configuration on dizziness, neck pain, and cervicocephalic kinesthetic sensibility: A 1-year randomized controlled study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Int. Group (n = 40) | Con. Group (n = 40) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 25.05 ± 3 | 24 ± 4.2 |
| Weight (kg) | 66 ± 10 | 60 ± 9 |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 28 (70%) | 30 (75%) |
| Female | 12 (30%) | 10 (25%) |
| Single | 31 (77.5%) | 29 (72.5%) |
| Married | 9 (22.5%) | 11 (27.5%) |
| Separated, divorced, or widowed | 0 | 0 |
| Pain duration (%) [Mean ± SD] | ||
| 1–3 y | 11 (27.5%) [5.3 ± 2] | 9 (22.5%) [5.8 ± 1] |
| 3–5 y | 16 (40%) [4.9 ± 1.5] | 18 (45%) [5.4 ± 1.3] |
| >5 y | 13 (32.5%) [4.8 ± 2] | 15 (37.5%) [5.7 ± 0.9] |
| Smoking | ||
| Light smoker | 15 (37.5%) | 18 (45%) |
| Heavy smoker | 4 (10%) | 2 (5%) |
| No Smoker | 21 (52.5%) | 20 (50%) |
| Baseline | 10-Weeks | 1-Year Follow-up | Cohen’s d 10-Weeks vs. Baseline | Cohen’s d 1-Year vs. Baseline | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | T | G vs. T | |||||||
| ICT-ITL max | I | 82.15 ± 5.3 | 63.40 ± 6.2 | 64.6 ± 5.7 | d = 3.2 | d = 3.18 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 83.15 ± 4.9 | 82.2 ± 4.5 | 83.8 ± 3.8 | d = 0.2 | d = −0.14 | ||||
| p-value C.I. | 0.5 [−4.3, 2.3] | <0.001 * [−22.9, −15.8] | <0.001 * [−22.3, −16.1] | ||||||
| Baseline | 10-Weeks | 1-Year Follow up | Cohen’s d 10-Weeks vs. Baseline | Cohen’s d 1-Year vs. Baseline | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | T | G vs. T | |||||||
| NDI | I | 31.1 ± 3.2 | 20.6 ± 4.5 | 10.9 ± 2.4 | d = 2.6 | d = 7.14 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 32.2 ± 2 | 29 ± 3.9 | 28.1 ± 5.1 | d = 1.03 | d = 1.05 | ||||
| p-Value 95% C.I. | 0.6 [−2.28, 0.08] | <0.001 * [−10.27, −6.52] | <0.001 * [−18.9, −15.4] | ||||||
| Pain intensity | I | 5 ± 1.5 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 0.5 ± 1 | d = 2.65 | d = 3.53 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 5.6 ± 1 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 3.2 ± 1.6 | d = 2.8 | d = 1.7 | ||||
| p-Value 95% C.I. | 0.04 [−1.16, −0.03] | <0.001 * [−1.07, −0.12] | <0.001 * [−3.29, −2.1] | ||||||
| Baseline | 10-Weeks | 1-Year Follow-up | Cohen’s d 10-Weeks vs. Baseline | Cohen’s d 1-Year vs. Baseline | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | T | G vs. T | |||||||
| HRA Right | I | 3.4 ± 1.4 | 2.1 ± 1.3 | 2 ± 1.5 | d = 1.4 | d = 1.3 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 4 ± 1.5 | 2.7 ± 1.1 | 3.2 ± 1.6 | d = 0.9 | d = 0.51 | ||||
| p-value C.I. | 0.06 [−1.24, 0.04] | 0.02 * [−1.13, −0.06] | <0.001 * [−1.89, −0.5] | ||||||
| HRA Left | I | 4.3 ± 1.4 | 2.6 ± 1.4 | 1.8 ± 1.1 | d = 1.21 | d = 1.98 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 3.7 ± 1.6 | 2.9 ± 1.6 | 2.8 ± 1.2 | d = 0.5 | d = 0.63 | ||||
| p-value C.I. | 0.07 [−0.06, 1.26] | 0.3 [−0.96, 0.36] | <0.001 * [−1.51, −0.48] | ||||||
| SPENT | I | 0.41 ± 0.17 | 0.28 ± 0.1 | 0.18 ± 0.09 | d = 0.93 | d = 1.6 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 0.34 ± 0.16 | 0.3 ± 0.06 | 0.29 ± 0.12 | d = 0.09 | d = 0.35 | ||||
| p-value C.I. | 0.06 [−0.003, 0.14] | 0.48 [−0.06, 0.02] | <0.001 * [−0.15, −0.06] | ||||||
| OSI | I | 0.62 ± 0.13 | 0.46 ± 0.1 | 0.41 ± 0.2 | d = 1.37 | d = 1.24 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 0.57 ± 0.11 | 0.52 ± 0.16 | 0.58 ± 0.19 | d = 0.364 | d = −0.06 | ||||
| p-value C.I. | 0.06 [−0.003, 0.103] | 0.047 * [−0.11, −0.0007] | <0.001 * [−0.25, −0.08] | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moustafa, I.M.; Shousha, T.M.; Walton, L.M.; Raigangar, V.; Harrison, D.E. Reduction of Thoracic Hyper-Kyphosis Improves Short and Long Term Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Nonspecific Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206028
Moustafa IM, Shousha TM, Walton LM, Raigangar V, Harrison DE. Reduction of Thoracic Hyper-Kyphosis Improves Short and Long Term Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Nonspecific Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206028
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoustafa, Ibrahim Moustafa, Tamer Mohamed Shousha, Lori M. Walton, Veena Raigangar, and Deed E. Harrison. 2022. "Reduction of Thoracic Hyper-Kyphosis Improves Short and Long Term Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Nonspecific Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206028
APA StyleMoustafa, I. M., Shousha, T. M., Walton, L. M., Raigangar, V., & Harrison, D. E. (2022). Reduction of Thoracic Hyper-Kyphosis Improves Short and Long Term Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Nonspecific Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 6028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206028







