Embolization in Pediatric Patients: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Procedures, and Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
3. General Considerations Regarding Periprocedural Care
4. Congenital and Acquired Diseases of the Cardiovascular System
4.1. Indications
4.2. Techniques
4.3. Clinical Outcomes
5. Pulmonary Vascular Malformations
5.1. Indications
5.2. Techniques
5.3. Clinical Outcomes
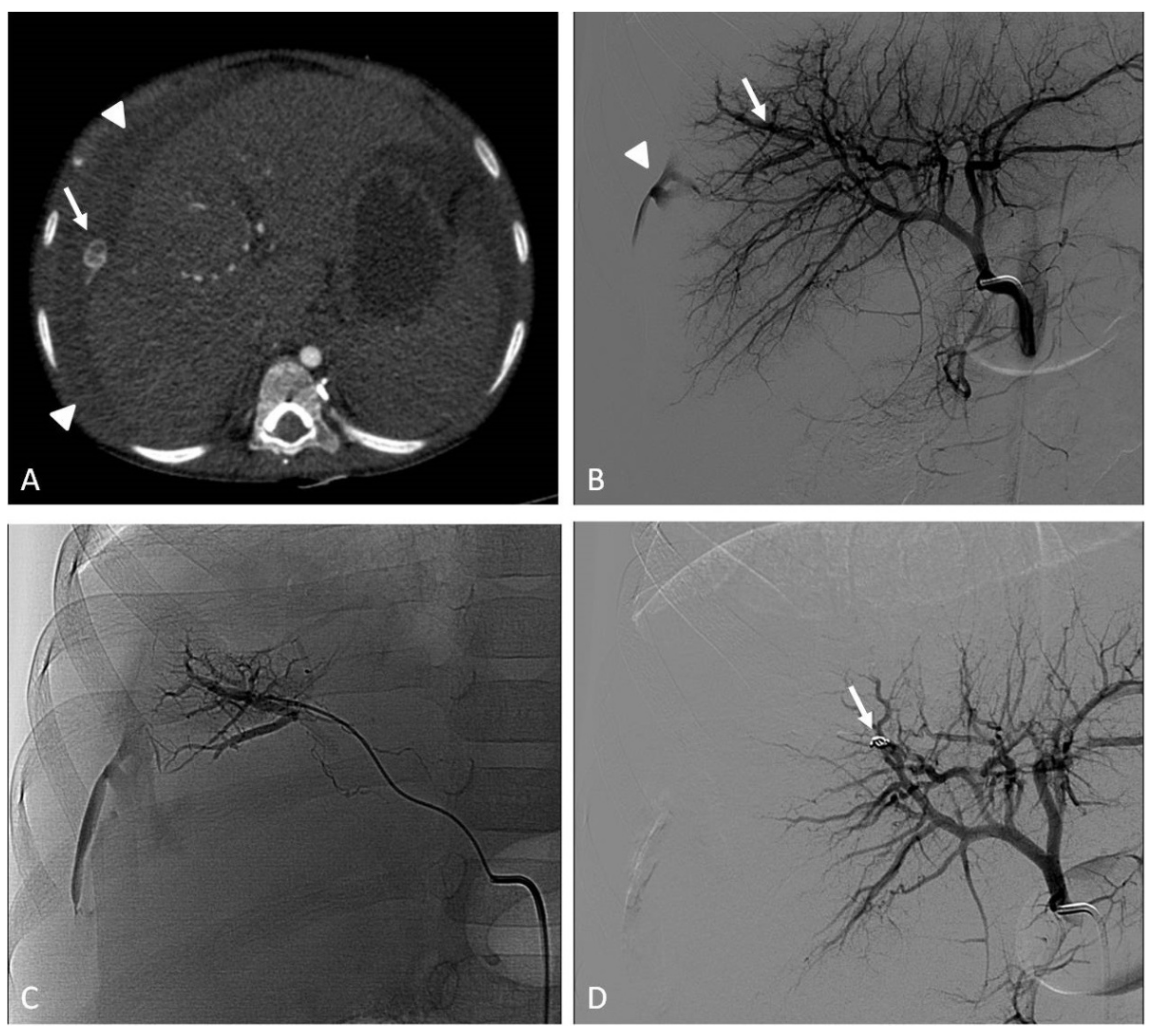
6. Traumatic, Spontaneous, and Iatrogenic Arterial Bleeding
6.1. Indications
6.2. Techniques
6.3. Clinical Outcomes
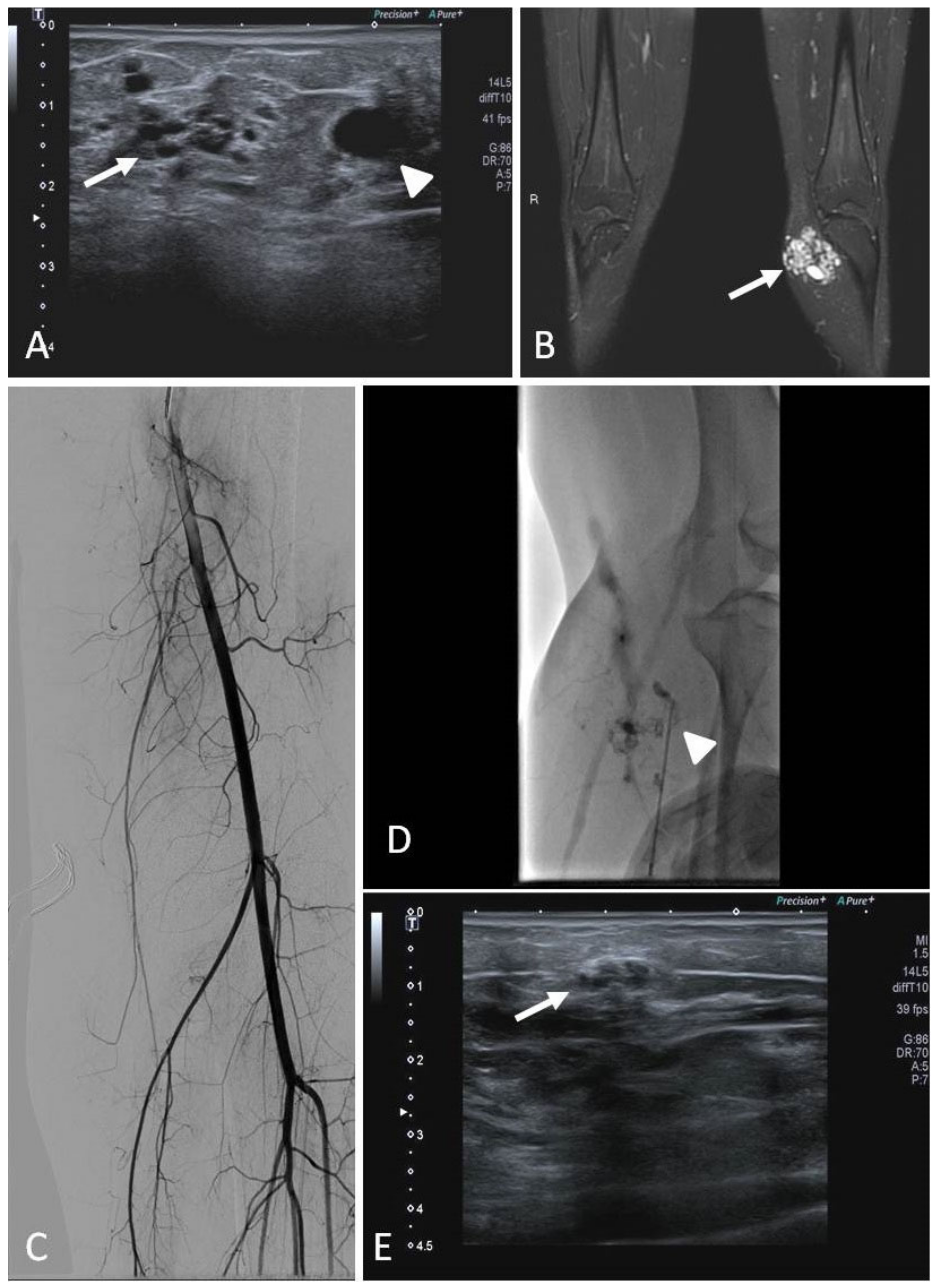
7. Congenital and Acquired Vascular Malformations (VMs)
7.1. Indications
7.2. Techniques
7.3. Clinical Outcomes
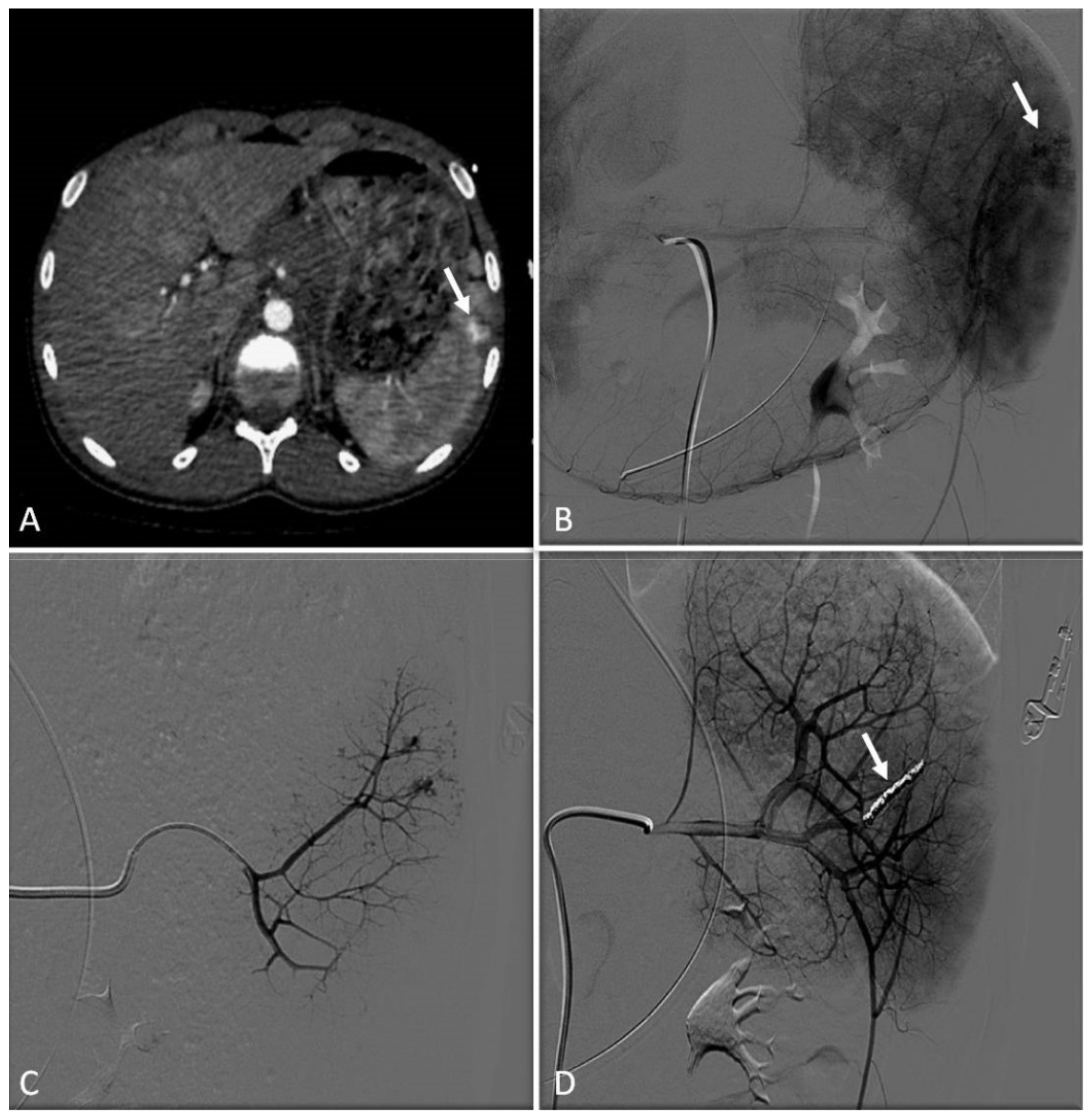
8. Hypervascular Tumors
8.1. Indications
8.2. Techniques
8.3. Benign Tumors
8.3.1. Hemangioma
8.3.2. Paraganglioma
8.3.3. Renal Angiomyolipoma
8.4. Tumors with Malignant Behavior
8.4.1. Hepatic Neoplasms
8.4.2. Wilms Tumor (WT) and Neuroblastoma
8.4.3. Bone Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas
8.4.4. Hypervascular Brain Tumors
9. Arterial Aneurysms and Pseudoaneurysms
9.1. Indications
9.2. Techniques
9.3. Clinical Outcomes
10. Bronchial Arteries
10.1. Indications
10.2. Techniques
10.3. Clinical Outcomes
11. Lymphatic Embolization
11.1. Lymphatic Malformations and Cysts
11.1.1. Indications
11.1.2. Techniques
11.1.3. Clinical Outcomes
11.2. Lymphatic Leakages, Chylothorax and Chylous Ascites
11.2.1. Techniques
11.2.2. Clinical Outcomes
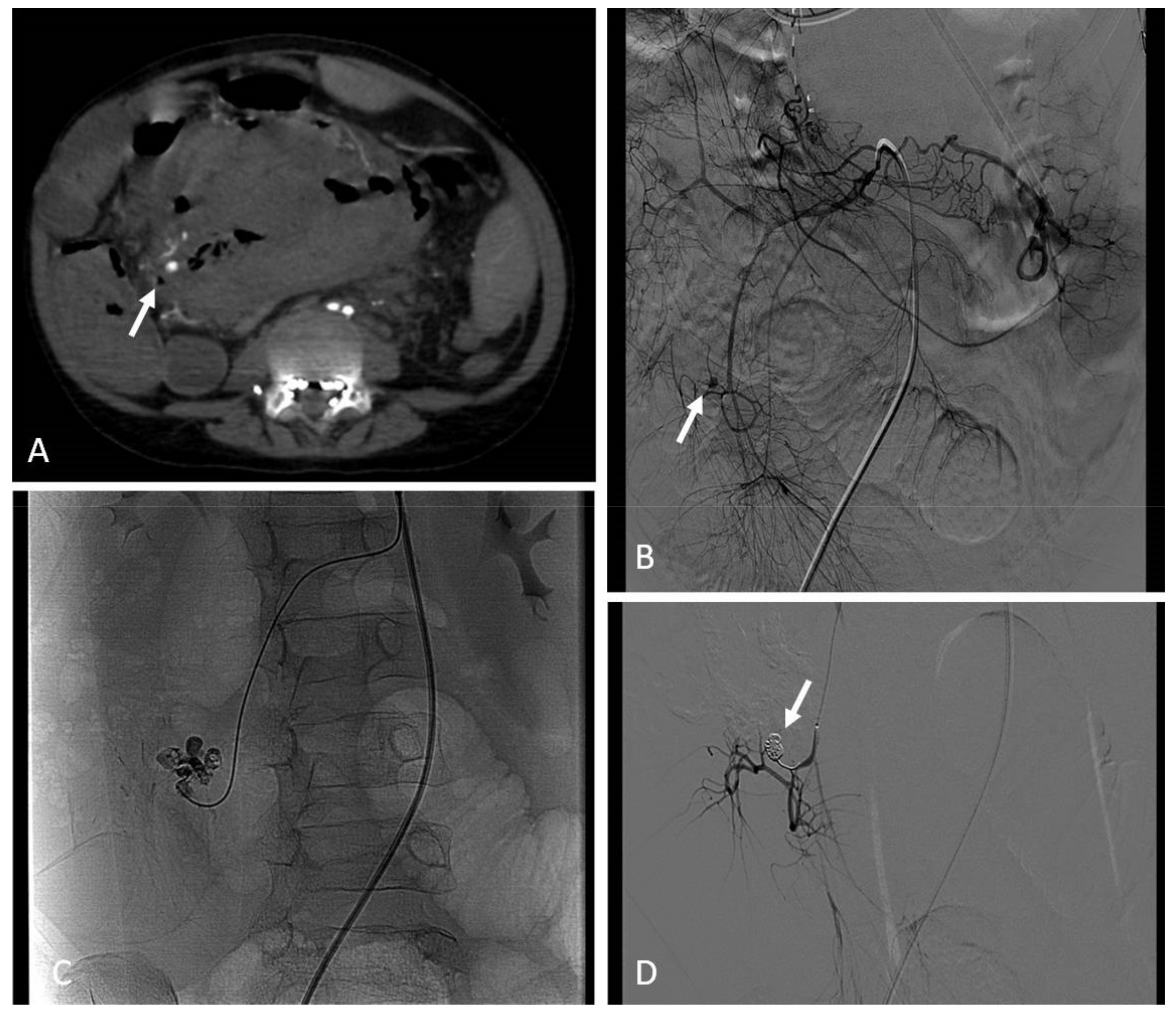
12. Porto-Systemic Shunts
12.1. Indications
12.2. Techniques
12.3. Clinical Outcomes
13. Sclero-Embolization of Male Varicocele
13.1. Indications
13.2. Techniques
13.3. Clinical Outcomes
14. Technical and Procedural Aspects
14.1. Vascular Access, Sheaths, Catheter, and Microcatheters
14.2. Embolic Materials
14.2.1. Sclerosants
14.2.2. Glues and Non-Adhesive Liquid Embolics
14.2.3. Particles
14.2.4. Resorbable Agents
14.2.5. Mechanical Devices
14.2.6. Stents
14.2.7. Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion (REBOA)
14.3. Radiation Protection
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Venturini, M.; Piacentino, F.; Coppola, A.; Bettoni, V.; Macchi, E.; De Marchi, G.; Curti, M.; Ossola, C.; Marra, P.; Palmisano, A.; et al. Visceral Artery Aneurysms Embolization and Other Interventional Options: State of the Art and New Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heran, M.K.S.; Burrill, J. Vascular Pediatric Interventional Radiology. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2012, 63, S59–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roebuck, D.J.; Barnacle, A.M. Haemoptysis and bronchial artery embolization in children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2008, 9, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, F.; Abella, S.F.; McLin, V.; Ackermann, O.; Girard, M.; Cervoni, J.P.; Savale, L.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Valla, D.; Hillaire, S.; et al. Congenital portosystemic shunts. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, D.J.E.; Chennapragada, S.M. Embolization in Neonates and Infants. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 14, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Cui, C.; Zhang, D.; Hou, C.; Zhang, P.; Chen, H.; Meng, L. Simultaneous Transcatheter In-tervention for Atrial Septal Defect Complicated with Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A 13-Year Single Institutional Retrospective Study. J. Interv. Med. 2018, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, R.N.; Pereira, F.L.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Pedra, S.R.F.; Succi, F.; Marques, P.; Jatene, M.B.; Fontes, V.F.; Pedra, C.A.C. Percutaneous vs. Surgical Treatment of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Children and Adolescents. Rev. Bras. Cardiol. Invasiva 2012, 20, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; McWilliams, J.P. Approach to Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations: A Comprehensive Update. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathanandam, S.; Gutfinger, D.; Morray, B.; Berman, D.; Gillespie, M.; Forbes, T.; Johnson, J.N.; Garg, R.; Malekzadeh-Milani, S.; Fraisse, A.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Periprocedural Complications of Transcatheter Patent Ductus Arteriosus Closure with the Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2021, 42, 1258–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, M.; Bhatt, A.B.; Zaragoza-Macias, E.; Dendukuri, N.; Marelli, A. Interventional Therapy Versus Medical Therapy for Secundum Atrial Septal Defect: A Systematic Review (Part 2) for the 2018 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, e814–e830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J.; Fu, L.; Shi, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, F. Clinical Study of Transcatheter Occlusion in Treating Ventricular Septal Defect Combined with Right Coronary Cusp Bulge. J. Interv. Med. 2018, 1, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathanandam, S.; Justino, H.; Waller, B.R.; Gowda, S.T.; Radtke, W.; Qureshi, A.M. The Medtronic Micro Vascular Plug™ for Vascular Embolization in Children with Congenital Heart Diseases. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2017, 30, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churton, T. Multiple Aneurysms of Pulmonary Artery. Br. Med. J. 1897, 1, 1223. [Google Scholar]
- Contegiacomo, A.; Del Ciello, A.; Rella, R.; Attempati, N.; Coppolino, D.; Larici, A.R.; Di Stasi, C.; Marano, G.; Manfredi, R. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: What the interventional radiologist needs to know. Radiol. Med. 2019, 124, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.I.; Pollak, J.S.; Wirth, J.A. Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations: Diagnosis and Transcatheter Embolotherapy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1996, 7, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faughnan, M.E.; Mager, J.J.; Hetts, S.W.; Palda, V.A.; Lang-Robertson, K.; Buscarini, E.; Deslandres, E.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Lausman, A.; Poetker, D.; et al. Second International Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, K.; Moriwaki, H.; Higashi, M.; Kimura, K.; Naritomi, H. A Small Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation as a Cause of Recurrent Brain Embolism. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 428–430. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saleh, S.; Dragulescu, A.; Manson, D.; Golding, F.; Traubici, J.; Mei-Zahav, M.; MacLusky, I.B.; Faughnan, M.E.; Carpenter, S.; Ratjen, F. Utility of Contrast Echocardiography for Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation Screening in Pediatric Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 1039.e1–1043.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthuis, S.; Buscarini, E.; Mager, J.J.; Vorselaars, V.M.M.; Van Gent, M.W.F.; Gazzaniga, P.; Manfredi, G.; Danesino, C.; Diederik, A.L.; Vos, J.A.; et al. Predicting the size of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations on chest computed tomography: A role for transthoracic contrast echocardiography. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukotynski, K.; Chan, R.P.; Chow, C.-M.; Cohen, J.H.; Faughnan, M.E. Contrast Echocardiography Grading Predicts Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations on CT. Chest 2007, 132, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, J.A.; Bueno, J.; Zarauza, J.; Farinas-Alvarez, C.; Cuesta, J.M.; Ortiz, P.; Zarrabeitia, R.; del Molino, A.P.; Bustamante, M.; Botella, L.M.; et al. Graded contrast echocardiography in pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowers, K.L.; Sekarski, L.; White, A.J.; Grady, R.M. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in children with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: A longitudinal study. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 8, 2045894018786696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosman, A.E.; de Gussem, E.M.; Balemans, W.A.F.; Gauthier, A.; Westermann, C.J.J.; Snijder, R.J.; Post, M.C.; Mager, J.J. Screening children for pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: Evaluation of 18 years of experience. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratjen, A.; Au, J.; Carpenter, S.; John, P.; Ratjen, F. Growth of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations in Pediatric Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. J. Pediatr. 2019, 208, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faughnan, M.E.; Thabet, A.; Mei-Zahav, M.; Colombo, M.; MacLusky, I.; Hyland, R.H.; Pugash, R.A.; Chait, P.; Henderson, K.J.; White, R.I. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in children: Outcomes of transcatheter embolotherapy. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.N.; Hyun, D. Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation and Its Vascular Mimickers. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Hülsbeck, S.; Marques, L.; Maleux, G.; Osuga, K.; Pelage, J.-P.; Wohlgemuth, W.A.; Andersen, P.E. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.E.; Duvnjak, S.; Gerke, O.; Kjeldsen, A.D. Long-Term Single-Center Retrospective Follow-Up After Embolization of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations Treated Over a 20-year Period: Frequency of Re-canalization with Various Embolization Materials and Clinical Outcome. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, U.R.; Cha, J.G.; Lee, J.; Cha, S.-I.; Kim, C.-H. Efficacy and Safety of AMPLATZER Vascular Plug Type IV for Embolization of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukay, F.; Özdemir, M.; Şenol, E.; Okten, S.; Ereren, M.; Karan, A. Large Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations: Long-Term Results of Embolization with AMPLATZER Vascular Plugs. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, J.J.; Overtoom, T.T.C.; Blauw, H.; Lammers, J.W.J.; Westermann, C.J.J. Embolotherapy of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations: Long-term Results in 112 Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004, 15, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Jackson, J.E.; Bamford, K.B.; Jenkins, I.H.; Benjamin, A.R.; Ramadan, H.; Kulinskaya, E. Primary determinants of ischaemic stroke/brain abscess risks are independent of severity of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Thorax 2008, 63, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kochar, P.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, N.; Li, S.; Hooda, K.; Kumar, Y. A case of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation: Role of interventional radiology in diagnosis and treatment. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 345–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notrica, D.M. Pediatric blunt abdominal trauma. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2015, 21, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, P.; Dulcetta, L.; Carbone, F.; Agazzi, R.; Muglia, R.; Bonaffini, P.; Bonanomi, E.; Colledan, M.; D’Antiga, L.; Venturini, M.; et al. Arterioportal Fistulas (APFs) in Pediatric Patients: Single Center Experience with Interventional Radiological versus Conservative Management and Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.C.; Toh, L.; Lo, R.H.; Yap, T.-L.; Narasimhan, K. Primary hepatic artery embolization in pediatric blunt hepatic trauma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2012, 47, 2316–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.; Van Houwelingen, L.; Bütter, A. The significance of pseudoaneurysms in the nonoperative management of pediatric blunt splenic trauma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltiel, H.J.; Barth, R.A.; Bruno, C.; Chen, A.E.; Deganello, A.; Harkanyi, Z.; Henry, M.K.; Ključevšek, D.; Back, S.J. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of blunt abdominal trauma in children. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021, 51, 2253–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweed, Y.; Singer-Jordan, J.; Papura, S.; Loberant, N.; Yulevich, A. Angiographic Embolization in Pediatric Abdominal Trauma. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2016, 18, 665–668. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, N.-J.; Althoen, M.; Hippe, D.S.; Prabhu, S.J.; Valji, K.; Padia, S.A. Pediatric Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma: Safety and Efficacy of Arterial Embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantasdemir, M.; Gulsen, F.; Solak, S.; Gulsen, G.Y.; Kantarci, F.; Numan, F. The use of Onyx for embolization of peripheral vascular malformations in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2012, 28, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, R.; Aziz-Sultan, M.A.; Soltanolkotabi, M.; Schoeneman, S.E.; Alden, T.D.; Hurley, M.C.; Dipatri, A.J.; Tomita, T.; Elhammady, M.S.; Shaibani, A. Safety and Efficacy of Onyx Embolization for Pediatric Cranial and Spinal Vascular Lesions and Tumors. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, A.M.; Nijs, E.L.F. Pediatric Vascular Malformations: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and the Role of Interventional Radiology. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 34, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, C.R.; Barnacle, A.M. Vascular anomalies: Special considerations in children. CVIR Endovasc. 2020, 3, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies. ISSVA Classification of Vascular Anomalies ©2018. Available online: issva.org/classification (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Dubois, J.M.; Sebag, G.H.; De Prost, Y.; Teillac, D.; Chretien, B.; Brunelle, O.F. Soft-tissue venous malformations in children: Percutaneous sclerotherapy with Ethibloc. Radiology 1991, 180, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.; Alison, M. Vascular anomalies: What a radiologist needs to know. Pediatr. Radiol. 2010, 40, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, S.; Casati, B.; Staudenherz, A.; Paya, K. Vascular low-flow malformations in children: Current concepts for classification, diagnosis and therapy. Eur. J. Radiol. 2005, 53, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, S.; Aref, H.; Chigot, V.; Bonin, B.; Brunelle, F. Classification of venous malformations in children and implications for sclerotherapy. Pediatr. Radiol. 2003, 33, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, R.; Munoz, F.G. Endovascular approaches in pediatric interventional oncology. CVIR Endovasc. 2021, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, J.B.; Glowacki, J. Hemangiomas and Vascular Malformations in Infants and Children. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, L.; Betalli, P.; Bravi, M.; Stroppa, P.; Cheli, M.; Sonzogni, A.; Licini, L.; Agazzi, R.; Colledan, M.; Parolini, F.; et al. Hepatic hemangioendothelioma of infancy: Clinical features of a large cohort of patients and proposed management. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2021, 37, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krowchuk, D.P.; Frieden, I.J.; Mancini, A.J.; Darrow, D.H.; Blei, F.; Greene, A.K.; Annam, A.; Baker, C.N.; Frommelt, P.C.; Hodak, A.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Infantile Hemangiomas. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20183475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchakulla, M.; Shah, A.H.; Armstrong, V.; Jernigan, S.; Bhatia, S.; Niazi, T.N. Multimodal management of pediatric carotid body tumors: A systematic review and case illustrations. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2018, 23, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamblin, W.R.; ReMine, W.H.; Sheps, S.G.; Harrison, E.G. Carotid body tumor (chemodectoma): Clinicopathologic analysis of ninety cases. Am. J. Surg. 1971, 122, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.J.; Walker, P.J.; Foster, W.J.; Jenkins, J.S.; Boyne, N.S.; Jenkins, J. Important observations made managing carotid body tumors during a 25-year experience. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 52, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nora, J.D.; Hallett, J.W.; O’Brien, P.C.; Naessens, J.M.; Cherry, K.J.; Pairolero, P.C. Surgical Resection of Carotid Body Tumors: Long-Term Survival, Recurrence, and Metastasis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1988, 63, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gözen, E.D.; Tevetoğlu, F.; Kara, S.; Kızılkılıç, O.; Yener, H.M. Is Preoperative Embolization Necessary for Carotid Paraganglioma Resection: Experience of a Tertiary Center. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 101, NP180–NP185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, M.M.; Elezz, T.A.E.A.; Mikahail, P.M.; Bassam, M.K.S. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Preoperative Embolization on the Outcomes of Carotid Body Tumor Surgery. QJM Int. J. Med. 2021, 114 (Suppl. S1), hcab094.015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texakalidis, P.; Charisis, N.; Giannopoulos, S.; Xenos, D.; Rangel-Castilla, L.; Tassiopoulos, A.K.; Jabbour, P.; Grossberg, J.A.; Machinis, T. Role of Preoperative Embolization in Carotid Body Tumor Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, 503.e2–513.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ghanem, S.; Yehuda, M.; Carmel, N.N.; Abergel, A.; Fliss, D.M. Impact of preoperative embolization on the outcomes of carotid body tumor surgery: A meta-analysis and review of the literature. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. S1), E2386–E2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.S.; Myhill, J.A.; Padhya, T.A.; McCaffrey, J.C.; McCaffrey, T.V.; Mhaskar, R.S. The Effects of Preoperative Embolization on Carotid Body Paraganglioma Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 153, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohnert, T.; Muhlsteiner, J.; Siegl, G.; Deutschmann, H. Preoperative Embolization in Carotid Body Tumor Surgery—Benefit or Risk? IPC Int. Poster Compet. 2020, 72, E65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeoluwa, A.; Lázár, I.; Szövördi, E.; Karosi, T. Management of carotid body tumor in pediatric patients: A case report and review of the literature. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 93, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.J.M.; Nazari, M.A.; Jha, A.; Pacak, K. Pediatric Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis, Genetics, and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 936178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelousi, A.; Kassi, E.; Zografos, G.; Kaltsas, G. Metastatic pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flum, A.S.; Hamoui, N.; Said, M.A.; Yang, X.J.; Casalino, D.D.; McGuire, B.B.; Perry, K.T.; Nadler, R.B. Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Renal Angiomyolipoma. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.S.; Goldman, S.M.; Fishman, E.K.; Marshall, F.F. The Natural History of Renal Angiomyolipoma. J. Urol. 1993, 150, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baal, J.; Smits, N.; Keeman, J.; Lindhout, D.; Verhoef, S. The Evolution of Renal Angiomyolipomas in Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis. J. Urol. 1994, 152, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennelly, M.J.; Grossman, H.B.; Cho, K.J. Outcome Analysis of 42 Cases of Renal Angiomyolipoma. J. Urol. 1994, 152, 1988–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakado, K.; Tanaka, N.; Nakagawa, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Yanagawa, M.; Takeda, K. Renal Angiomyolipoma: Relationships between Tumor Size, Aneurysm Formation, and Rupture. Radiology 2002, 225, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongyo, H.; Higashihara, H.; Osuga, K.; Kashiwagi, E.; Kosai, S.; Nagai, K.; Tanaka, K.; Ono, Y.; Ujike, T.; Uemura, M.; et al. Efficacy of prophylactic selective arterial embolization for renal angiomyolipomas: Identifying predictors of 50% volume reduction. CVIR Endovasc. 2020, 3, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, D.A.; Northrup, H.; Northrup, H.; Krueger, D.A.; Roberds, S.; Smith, K.; Sampson, J.; Korf, B.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Mowat, D.; et al. Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Surveillance and Management: Recommendations of the 2012 International Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Consensus Conference. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 49, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, J.A. Treatment of Renal Angiomyolipoma and Other Hamartomas in Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDQ® Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Childhood Liver Cancer Treatment; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/liver/hp/child-liver-treatment-pdq (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Weiss, K.E.; Sze, D.Y.; Rangaswami, A.A.; Esquivel, C.O.; Concepcion, W.; Lebowitz, E.A.; Kothary, N.; Lungren, M.P. Transarterial chemoembolization in children to treat unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Pediatr. Transplant. 2018, 22, e13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungren, M.P.; Towbin, A.J.; Roebuck, D.J.; Monroe, E.J.; Gill, A.E.; Thakor, A.; Towbin, R.B.; Cahill, A.M.; Hawkins, C.M. Role of interventional radiology in managing pediatric liver tumors. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) Assessment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.; Murtha-Lemekhova, A.; Rabaux-Eygasier, L.; Kessler, M.; Ruping, F.; Günther, P.; Hoffmann, K. Evidence on Indications and Techniques to Increase the Future Liver Remnant in Children Undergoing Extended Hepatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 915642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dome, J.S.; Fernandez, C.V.; Mullen, E.A.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Geller, J.I.; Huff, V.; Gratias, E.J.; Dix, D.B.; Ehrlich, P.F.; Khanna, G.; et al. Children’s Oncology Group’s 2013 blueprint for research: Renal tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujanić, G.M.; Gessler, M.; Ooms, A.H.; Collini, P.; Coulomb-L’Hermine, A.; D’Hooghe, E.; De Krijger, R.R.; Perotti, D.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Vokuhl, C.; et al. The UMBRELLA SIOP–RTSG 2016 Wilms tumour pathology and molecular biology protocol. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Tang, D.; Gu, W.; Mao, J.; Shu, Q. Current treatment for Wilms tumor: COG and SIOP standards. World J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 2, e000038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. Wilms Tumor and Other Childhood Kidney Tumors Treatment (PDQ®): Health Professional Version; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002.
- Krauel, L.; Albert, A.; Mora, J.; Sola, T.; Cruz, O.; Mortera, C.; Ribó, J.M. Use of angioembolization as an effective technique for the management of pediatric solid tumors. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Yang, S.; Cai, S.; Ren, Q.; Han, W.; Yang, W.; Cheng, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, H. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of 47 cases with ruptured neuroblastoma in children. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, K.J.; Yang, E.J.; Park, K.M.; Kim, J.H.; Jeon, U.B.; Jang, J.Y.; Lim, Y.T. Two Pediatric Cases of Spontaneous Ruptured Solid Tumors Successfully Treated with Transcutaneous Arterial Embolization. Clin. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 25, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, L.; Avanzini, S.; Gandolfo, C.; Martucciello, G.; Granata, C.; Boscarelli, A.; Garaventa, A.; Mattioli, G. Successful treatment of Neuroblastoma in an adolescent with intra-arterial embolization before surgery. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 20, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-H.; Luo, C.-B.; Guo, W.-Y.; Wu, H.-M.; Lirng, J.-F.; Wong, T.-T.; Lu, Y.-H.; Chang, F.-C. Preoperative embolization of hypervascular pediatric brain tumors: Evaluation of technical safety and outcome. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2013, 29, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, A.N.; Jennings, J.W.; Tutton, S.; Tam, A.L.; Kelekis, A.; Wood, B.J.; Dupuy, D.E.; Napoli, A.; Park, S.S.; Robinson, S.I.; et al. Musculoskeletal Oncologic Interventions: Proceedings from the Society of Interventional Radiology and Society of Interventional Oncology Research Consensus Panel. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 32, 1089.e1–1089.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.J. Embolization of Musculoskeletal Bone Tumors. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 27, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avritscher, R.; Javadi, S. Transcatheter Intra-arterial Limb Infusion for Extremity Osteosarcoma: Technical Considerations and Outcomes. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 14, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Coran, A.G.; Cilley, R.E.; Lindenauer, S.M.; Stanley, J.C. Arterial Aneurysms in Children: Clinicopathologic Classification. J. Vasc. Surg. 1991, 13, 47–56, discussion 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.M.; Eliason, J.L.; Ganesh, S.K.; Blatt, N.B.; Stanley, J.C.; Coleman, D.M. Pediatric nonaortic arterial aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 466.e1–476.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffroy, R. Endovascular management of visceral artery aneurysms: When to watch, when to intervene? World J. Radiol. 2015, 7, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, P.; Sebastian, L.J.D.; Jain, N.; Prabhakar, A.; Garg, A.; Gaikwad, S. Management of Arterial Pseudoaneurysms of the Neck in a Pediatric Population: An Endovascular Case Series and Review of Literature. World Neurosurg. 2019, 125, e273–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.-Y.; Li, Q.; Xiang, P.; Feng, C.; Yi, Q.-J.; Lu, T.-W. Potential Factors Affected Safety and Efficacy of Transcatheter Plug Closure for Pediatric Hemoptysis with Anomalous Bronchial Arteries. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenbach, J.; Ittrich, H.; Gaubert, J.Y.; Gebauer, B.; Vos, J.A. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Bronchial Artery Embolisation. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.-M.; Zhao, L.; He, L.; Wu, L.; Lu, Y.; Chu, C.; Wang, L.-B.; Niu, C.; Liu, F. Bronchial Artery Embolization in Pediatric Pulmonary Hemorrhage: A Single-Center Experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanlialp, I.; Karnak, I.; Tanyel, F.; Senocak, M.; Büyükpamukçu, N. Sclerotherapy for lymphangioma in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2003, 67, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poldervaart, M.T.; Breugem, C.C.; Speleman, L.; Pasmans, S. Treatment of Lymphatic Malformations with OK-432 (Picibanil). J. Craniofacial Surg. 2009, 20, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogita, S.; Tsuto, T.; Deguchi, E.; Tokiwa, K.; Nagashima, M.; Iwai, N. OK-432 therapy for unresectable lymphangiomas in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1991, 26, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdalany, B.S.; Saad, W.A.; Chick, J.F.B.; Khaja, M.S.; Cooper, K.; Srinivasa, R. Pediatric lymphangiography, thoracic duct embolization and thoracic duct disruption: A single-institution experience in 11 children with chylothorax. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Song, M.K.; Hur, S. Successful thoracic duct embolisation in a child with recurrent massive pericardial effusion diagnosed as a lymphatic anomaly. Cardiol. Young 2020, 30, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.C.; Foley, P.T.; Lyon, S.M. Percutaneous Management of High-Output Chylothorax: Case Reviews. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 32, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itkin, M.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Naim, M.Y.; Bird, G.L.; Keller, M.S. Percutaneous Thoracic Duct Embolization as a Treatment for Intrathoracic Chyle Leaks in Infants. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e237–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itkin, M.; Kucharczuk, J.C.; Kwak, A.; Trerotola, S.O.; Kaiser, L.R. Nonoperative thoracic duct embolization for traumatic thoracic duct leak: Experience in 109 patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, D.; Itkin, M. Pediatric Lymphatics Review: Current State and Future Directions. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 37, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Itkin, M. Thoracic Duct Embolization for Chylous Leaks. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 28, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleux, G.; Storme, E.; Cools, B.; Heying, R.; Boshoff, D.; Louw, J.J.; Frerich, S.; Malekzadeh-Milanii, S.; Hubrechts, J.; Brown, S.C.; et al. Percutaneous embolization of lymphatic fistulae as treatment for protein-losing enteropathy and plastic bronchitis in patients with failing Fontan circulation. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 94, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Kim, M.J. The Update of Treatment for Primary Intestinal Lymphangiectasia. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2021, 24, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolski, G.J.; Itkin, M. Feasibility of Ultrasound-guided Intranodal Lymphangiogram for Thoracic Duct Embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajebi, M.R.; Chaudry, G.; Padua, H.M.; Dillon, B.; Yilmaz, S.; Arnold, R.W.; Landrigan-Ossar, M.F.; Alomari, A.I. Intranodal Lymphangiography: Feasibility and Preliminary Experience in Children. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi-Abella, S.; Branchereau, S.; Lambert, V.; Fabre, M.; Steimberg, C.; Losay, J.; Riou, J.-Y.; Pariente, D.; Gauthier, F.; Jacquemin, E.; et al. Complications of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children: Therapeutic Options and Outcomes. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiges, A.; Turon, F.; Simón-Talero, M.; Tasayco, S.; Bueno, J.; Zekrini, K.; Plessier, A.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Guerin, F.; Mukund, A.; et al. Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts (Abernethy Malformation): An International Observational Study. Hepatology 2020, 71, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishna, R.; Hurkadli, P.S.; Puthukudy, N.K.; Nair, H.R. Embolization of Portosystemic Shunt for Treatment of Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bruckheimer, E.; Dagan, T.; Atar, E.; Schwartz, M.; Kachko, L.; Superina, R.; Amir, G.; Shapiro, R.; Birk, E. Staged Transcatheter Treatment of Portal Hypoplasia and Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggen, M.; Cools, B.; Maleux, G.; Gewillig, M. A custom-made percutaneous flow-restrictor to manage a symptomatic congenital porto-systemic shunt in an infant. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 92, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Karuppasamy, K.; Radhakrishnan, K.; Fagan, T.E. Restriction of congenital portosystemic shunt using the modified microvascular plug. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 98, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, H.; Nosaka, S.; Miyazaki, O.; Sakamoto, S.; Fukuda, A.; Shigeta, T.; Nakazawa, A.; Kasahara, M. The classification based on intrahepatic portal system for congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, A.; Naljayan, M.; Vachharajani, T.J. Vascular Access Guidelines: Summary, Rationale, and Controversies. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 20, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, E.J.; Reitelman, C. Adolescent Varicocele. Urol. Clin. North Am. 1995, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Reyes, T.; Locke, J.; Afshar, K. Varicoceles in the pediatric population: Diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2017, 11, S34–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarski, P. Endovascular embolization of varicoceles using n-butyl cyanoacrylate (NBCA) glue. Pol. J. Radiol. 2013, 78, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, D.J.E.; Burrows, P.E. Pediatric varicocele embolization. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 6, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunnen, M. Neue Technik Zur Embolisation Der Vena Spermatica Interna: Intravenöser Gewebekleber. RöFo—Fortschr. Auf Dem Geb. Der Röntgenstrahlen Und Der Bildgeb. Verfahr. 1980, 133, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silay, M.S.; Hoen, L.; Quadackaers, J.; Undre, S.; Bogaert, G.; Dogan, H.S.; Kocvara, R.; Nijman, R.J.; Radmayr, C.; Tekgul, S.; et al. Treatment of Varicocele in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis from the European Association of Urology/European Society for Paediatric Urology Guidelines Panel. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarella, R.; Calogero, A.E.; Condorelli, R.A.; Giacone, F.; Aversa, A.; La Vignera, S. Management and Treatment of Varicocele in Children and Adolescents: An Endocrinologic Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, B.L.; Trerotola, S.O.; Venbrux, A.C.; Savader, S.J.; Lund, G.B.; Peppas, D.S.; Mitchell, S.E.; Gearhart, J.P.; White, R.I.; Osterman, F.A. Percutaneous Embolotherapy of Adolescent Varicocele: Results and Long-term Follow-up. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1994, 5, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, G.; Kondo, K.L. Pharmacology of Sclerotherapy. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 27, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.M. Sclerosants: A comparative review. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Morishita, H.; Sato, Y.; Hamaguchi, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Tokue, H.; Yonemitsu, T.; Murakami, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Sofue, K.; et al. Guidelines for the use of NBCA in vascular embolization devised by the Committee of Practice Guidelines of the Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology (CGJSIR), 2012 edition. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2014, 32, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenstein, A. Study of PHIL® Embolic System in the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in the Pediatric Population. Prospective, Single-Center, Single-Arm Clinical Study. 2018; ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier (NCT Number): NCT03731000. GCO 18-1298. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03731000 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Vaidya, S.; Tozer, K.R.; Chen, J. An Overview of Embolic Agents. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 25, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, T.; Medina, S.; Montes, G.; Nunez-Atahualpa, L.; Valdez, M.; Maynar, M. Endoluminal Occlusion Devices: Technology Update. Med. Devices 2014, 7, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.W. Use of an Intra-Aortic Balloon Catheter Tamponade for Controlling Intra-Abdominal Hemorrhage in Man. Surgery 1954, 36, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kinney, T.B. Radiologic history exhibit. Charles T. Dotter: A pioneering interventional radiologist. RadioGraphics 1996, 16, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, L.; Skibber, M.; Kumar, A.; George, M.; Aziz, S.; Harting, M.T.; Moore, L.J.; Cox, C.S. Morphometric and Physiologic Modeling Study for Endovascular Occlusion in Pediatric Trauma Patients. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leef, J. Interventional Radiologists Should Take the Lead in Revising REBOA. Applied Radiology Digital Portals. 2021. Available online: https://appliedradiology.com/Communities/Vascular-IR-Imaging/interventional-radiologists-should-take-the-lead-in-revising-reboa (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Sidhu, M.K.; Goske, M.J.; Coley, B.J.; Connolly, B.; Racadio, J.; Yoshizumi, T.T.; Utley, T.; Strauss, K.J. Image Gently, Step Lightly: Increasing Radiation Dose Awareness in Pediatric Interventions through an International Social Marketing Campaign. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.D.; Frush, D.P. Image Gently Have-a-Heart Campaign. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploussi, A.; Brountzos, E.; Rammos, S.; Apostolopoulou, S.; Efstathopoulos, E.P. Radiation Exposure in Pediatric Interventional Procedures. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beels, L.; Bacher, K.; De Wolf, D.; Werbrouck, J.; Thierens, H. Gamma-H2AX foci as a biomarker for patient X-ray exposure in pediatric cardiac catheterization: Are we underestimating radiation risks? Circulation 2009, 10, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marra, P.; Di Fazio, B.; Dulcetta, L.; Carbone, F.S.; Muglia, R.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Valle, C.; Corvino, F.; Giurazza, F.; Muscogiuri, G.; et al. Embolization in Pediatric Patients: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Procedures, and Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226626
Marra P, Di Fazio B, Dulcetta L, Carbone FS, Muglia R, Bonaffini PA, Valle C, Corvino F, Giurazza F, Muscogiuri G, et al. Embolization in Pediatric Patients: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Procedures, and Clinical Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226626
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarra, Paolo, Barbaro Di Fazio, Ludovico Dulcetta, Francesco Saverio Carbone, Riccardo Muglia, Pietro Andrea Bonaffini, Clarissa Valle, Fabio Corvino, Francesco Giurazza, Giuseppe Muscogiuri, and et al. 2022. "Embolization in Pediatric Patients: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Procedures, and Clinical Outcomes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226626
APA StyleMarra, P., Di Fazio, B., Dulcetta, L., Carbone, F. S., Muglia, R., Bonaffini, P. A., Valle, C., Corvino, F., Giurazza, F., Muscogiuri, G., Venturini, M., & Sironi, S. (2022). Embolization in Pediatric Patients: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Procedures, and Clinical Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226626






