The Partial Removal of Rectus Abdominis Muscle Inserting into Ribs in Ipsilateral Pedicled TRAM Flap for Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chart Review
2.2. Surgical Technique
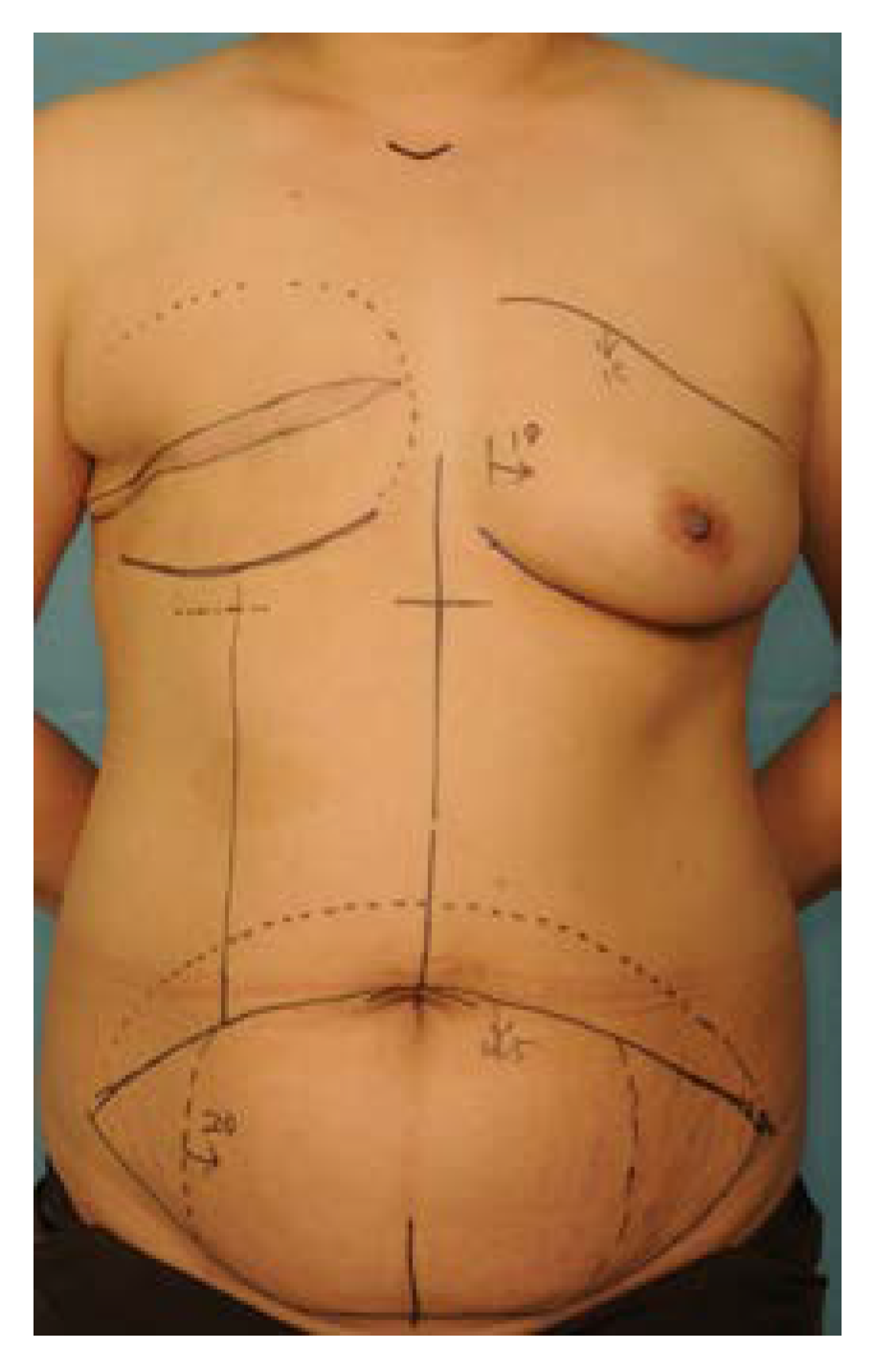
2.2.1. Preoperative Design and Incision
2.2.2. Flap Elevation
2.2.3. Partial Removal of Rectus Abdominis Muscle Inserting into Ribs and Flap Insetting
2.2.4. Dorsite Closure and Breast Shaping
2.3. Aesthetic Evaluation of the Inframammary Fold
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartrampf, C.R.; Scheflan, M.; Black, P.W. Breast reconstruction with a transverse abdominal island flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.B.; Bostwick, J., 3rd; Hartrampf, C.R., Jr.; Hester, T.R., Jr.; Nahai, F. The superiorly based rectus abdominis flap: Predicting and enhancing its blood supply based on an anatomic and clinical study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1988, 81, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codner, M.A.; Bostwick, J., 3rd; Nahai, F.; Bried, J.T.; Eaves, F.F. TRAM flap vascular delay for high-risk breast re construction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribuffo, D.; Muratori, L.; Antoniadou, K.; Fanini, F.; Martelli, E.; Marini, M.; Messineo, D.; Trinci, M.; Scuderi, N. A hemodynamic approach to clinical results in the TRAM flap after selective delay. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997, 99, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Beeraka, N.M.; Sinelnikov, M.Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, D.; Gu, Y.; Li, J.; Reshetov, I.V.; Startseva, O.I.; Liu, J.; et al. Patient Management Strategies in Perioperative, Intraoperative, and Postoperative Period in Breast Reconstruction With DIEP-Flap: Clinical Recommendations. Front Surg. 2022, 9, 729181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, J.; Beeraka, N.M.; Sinelnikov, M.Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Lu, P. Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Breast Surgery: Recent Evidence with Comparative Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, M.E. The pedicled TRAM as preference for immediate autogenous tissue breast reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 1994, 21, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestak, K.C. Breast reconstruction with a pedicled TRAM flap. Clin. Plast. Surg. 1998, 25, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartrampf, C.R., Jr. Abdominal wall competence in transverse abdominal island flap operations. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1984, 12, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D.C.; Larson, D.L.; Severinac, R.N.; Marcias, M. Rectus abdominis muscle innervation: Implications for TRAM flap elevation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harashina, T.; Sone, K.; Inoue, T.; Fukuzumi, S.; Enomoto, K. Augmentation of circulation of pedicled transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flaps by microvascular surgery. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1987, 40, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, B.J.; Schusterman, M.A.; Miller, M.J.; Kroll, S.S.; Wang, B.G. Bilateral breast reconstruction: Conventional versus free TRAM. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 93, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, D.L.; Yousif, N.J.; Sinha, R.K.; Latoni, J.; Korkos, T.G. A comparison of pedicled and free TRAM flaps for breast reconstruction in a single institution. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 104, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, S.L.; Serletti, J.M. Outcome comparison between free and pedicled TRAM flap breast reconstruction in the obese patient. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 108, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y.S.; Sinha, I.; Turko, A.; Lipsitz, S.; Pribaz, J.J. Outcomes and patient satisfaction following breast recon struction with bilateral pedicled TRAM flaps in 105 consecutive patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, J. Meta-analysis of flap perfusion and donor site complications for breast reconstruction using pedicled versus free TRAM and DIEP flaps. Breast 2018, 38, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.T.; Agarwal, J.P.; Ascherman, J.A.; Caterson, S.A.; Gray, D.D.; Hollenbeck, S.T.; Khan, S.A.; Loeding, L.D.; Mahabir, R.C.; Miller, A.S.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline: Autologous breast reconstruction with DIEP or pedicled TRAM abdominal flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 651e–664e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchateau, J.; Declety, A.; Lejour, M. Innervation of the rectus abdominis muscle: Implications for rectus flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1988, 82, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Oh, J.; Chung, M.S.; Ahn, H.C. The island-type pedicled TRAM flap: Improvement of the aesthetic out comes of breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2020, 73, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, L.F.; Hartrampf, C.R., Jr. Tailoring of the new breast using the transverse abdominal island flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1983, 72, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clugston, P.A.; Lennox, P.A.; Thompson, R.P. Intraoperative vascular monitoring of ipsilateral vs. contralateral TRAM flaps. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1998, 41, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olding, M.; Emory, R.E.; Barrett, W.L. Preferential use of the ipsilateral pedicle in TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1998, 40, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y.S.; Verma, K.; Sinha, I.; Rosen, H.; Hergrueter, C.; Wong, J.; Pribaz, J.J. Impact of prior ipsilateral chest wall radiation on pedicled TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 71, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G. The pedicled TRAM flap in breast reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2007, 34, 83–104, abstract vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.K.; Joethy, J.; Ong, Y.S.; Ho, G.H.; Pribaz, J.J. Preferred use of the ipsilateral pedicled TRAM flap for imme diate breast reconstruction: An illustrated approach. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2012, 36, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.I.; Samson, M.C.; Tamburrino, J.F.; Swartz, K.A.; Brunworth, L. An investigation of the application of laser-assisted indocyanine green fluorescent dye angiography in pedicle transverse rectus abdominus myocutaneous breast reconstruction. Can. J. Plast. Surg. 2011, 19, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejour, M.; Dome, M. Abdominal wall function after rectus abdominis transfer. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1991, 87, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Son, D.; Yeo, H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, J.; Han, K.; Lee, S. Anatomical and functional recovery of neurotized remnant rectus abdominis muscle in muscle-sparing pedicled transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flap. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2013, 40, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]









| Classical pTRAM Group (%) | PMR pTRAM Group (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients Median age (IQR), yr Mean body mass index (IQR), kg/m2 | 34 47.5 (7.75) 23.4 (3.73) | 28 44.0 (12.0) 22.4 (3.83) | 0.248 * 0.249 * |
| Breast reconstruction Immediate Delayed | 30 (88.2) 4 (11.8) | 17 (60.7) 11 (39.3) | 0.012 † 0.012 † |
| Vertical scar in the lower abdomen | 1 (2.9) | 4 (14.3) | 0.166 ‡ |
| Contralateral breast Augmentation Reduction Mastopexy | 0 6 (17.6) 1 (2.9) | 2 (7.1) 1 (3.6) 2 (7.1) | 0.200 ‡ 0.116 ‡ 0.585 ‡ |
| Radiation Preoperative Postoperative | 3 (8.8) 5 (14.7) | 0 (0.0) 2 (7.1) | 0.245 ‡ 0.442 ‡ |
| Complications | Classical pTRAM Group No. (%) | PMR pTRAM Group No. (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reconstructed Breast | |||
| pTRAM skin necrosis | 3 (8.8) | 1(3.6) | 0.620 ‡ |
| Mastectomy skin necrosis | 3 (8.8) | 1 (3.6) | 0.620 ‡ |
| Hematoma | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.6) | 0.452 ‡ |
| Wound dehiscence | 2 (5.9) | 2 (7.1) | 1.000 ‡ |
| Fat necrosis | 12 (35.3) | 9 (32.1) | 0.794 † |
| Donor site | |||
| Abdominal bulging | 1 (2.9) | 1 (3.6) | 1.000 ‡ |
| Skin necrosis | 1 (2.9) | 1 (3.6) | 1.000 ‡ |
| Classical pTRAM Group (%) | PMR pTRAM Group (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients with fat necrosis | 12/34 (36.1) | 9/28 (32.1) | 0.794 † |
| No. of patients with fat necrosis Immediate reconstruction Delayed reconstruction | 8/30 (26.7) 4/4 (100) | 5/17 (29.4) 4/11 (36.4) | 1.000 ‡ 0.077 ‡ |
| Classical pTRAM Group (%) (n = 31) | PMR pTRAM Group (%) (n = 27) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuity | 11.0 (3.5) | 11.0 (3.0) | 0.220 |
| Definition | 11.0 (5.0) | 12.0 (4.0) | 0.209 |
| Symmetry | 10.0 (3.0) | 11.0 (4.0) | 0.324 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, D.; Kim, J. The Partial Removal of Rectus Abdominis Muscle Inserting into Ribs in Ipsilateral Pedicled TRAM Flap for Breast Reconstruction. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226647
Son D, Kim J. The Partial Removal of Rectus Abdominis Muscle Inserting into Ribs in Ipsilateral Pedicled TRAM Flap for Breast Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226647
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Daegu, and Jaehoon Kim. 2022. "The Partial Removal of Rectus Abdominis Muscle Inserting into Ribs in Ipsilateral Pedicled TRAM Flap for Breast Reconstruction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226647
APA StyleSon, D., & Kim, J. (2022). The Partial Removal of Rectus Abdominis Muscle Inserting into Ribs in Ipsilateral Pedicled TRAM Flap for Breast Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226647






