Helicobacter pylori-Associated Iron Deficiency Anemia in Childhood and Adolescence-Pathogenesis and Clinical Management Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Aspects of H. pylori-Associated IDA
2.1. Iron Absorption in Humans
2.2. Clinical Evidence
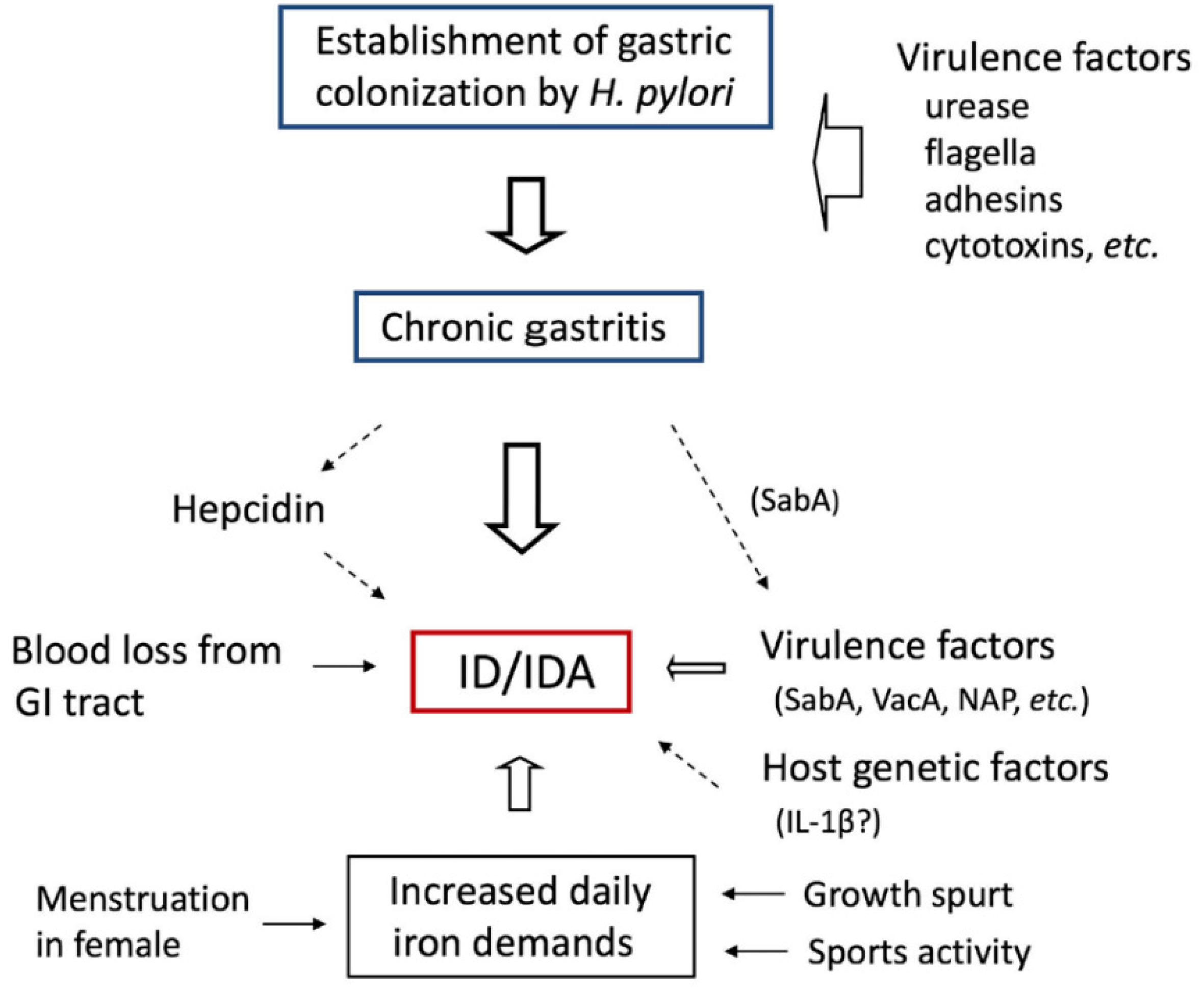
3. Pathogenesis
3.1. Gastrointestinal Mucosal Lesions and IDA
3.2. Impaired Gastric Acid Secretion
3.3. Hepcidin
3.4. Recent Pathogenetic Hypothesis
3.4.1. Iron-Uptake Mechanisms in H. pylori
3.4.2. Bacterial Virulence Factors
H. pylori Colonization and Adhesins
Major Cytotoxins
IDA-Specific Bacterial Factors
3.4.3. Host Factors
Increased Iron Demands as Acquired Factors
Host Genetic Factors
4. Clinical Management Strategies
5. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McColl, K.E. Clinical practice. Helicobacter pylori infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shatila, M.; Thomas, A.S. Current and future perspectives in the diagnosis and management of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, N.; Okamoto, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsumura, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamakido, M.; Taniyama, K.; Sasaki, N.; Schlemper, R.J. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Sherman, P.M. What is new related to Helicobacter pylori infection in children and teenagers? Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. 2005, 159, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Schistosomes, Liver Flukes and Helicobacter pylori; IARC: Lyon, France, 1994; pp. 1–241. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N.L.; Koletzko, S.; Goodman, K.; Bontems, P.; Cadranel, S.; Casswall, T.; Czinn, S.; Gold, B.D.; Guarner, J.; Elitsur, Y.; et al. Joint ESPGHAN/NASPGHAN guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori in children and adolescents (Update 2016). J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Shimizu, T.; Toyoda, S.; Gold, B.D.; Ida, S.; Ishige, T.; Fujimura, S.; Kamiya, S.; Konno, M.; Kuwabara, K.; et al. The updated JSPGHAN guideline for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in childhood. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 1315–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, A.; Bagheri, N.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Shirzad, M.; Rahimian, G.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Shirzad, H. Comparative immune response in children and adults with H. pylori infection. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 315957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barabino, A. Helicobacter pylori-related iron deficiency anemia: A review. Helicobacter 2002, 7, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockey, D.C.; Altayar, O.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Kalmaz, D. AGA technical review on gastrointestinal evaluation of iron deficiency anemia. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1097–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, M.; Chua, E.; O’Toole, P. Regulation of intestinal non-haem iron absorption. Gut 1997, 40, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendt, N.; Kool, P.; Teesalu, K.; Lillemäek, K.; Maaroos, H.I.; Oona, M. Iron deficiency and Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Acta Paediatr. 2011, 100, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggett, H.C.; Parkinson, A.J.; Muth, P.T.; Gold, B.D.; Gessener, B.D. Endemic iron deficiency associated with Helicobacter pylori infection among school-aged children in Alaska. Pediatrics 2006, 117, e396–e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janjetic, M.A.; Goldman, C.G.; Balcarce, N.E.; Rua, E.C.; González, A.B.; Fuda, J.A.; Meseri, E.I.; Torti, H.E.; Barrado, J.; Zubillaga, M.B.; et al. Iron, zinc, and copper nutritional status in children infected with Helicobacter Pylori. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thankachan, P.; Muthayya, S.; Sierksma, A.; Eilander, A.; Thomas, T.; Duchateau, G.S.; Frenken, L.G.J.; Kurpad, A.V. Helicobacter pylori infection does not influence the efficacy of iron and vitamin B(12) fortification in marginally nourished Indian children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, E.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Perez-Perez, G.; Mera, R.; Vilchis, J.; Moran, S.; Rivera, O.; Coria, R.; Torres, J.; Correa, P.; et al. Present and past Helicobacter pylori infection in Mexican school children. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.A.; Mahmud, H.; Davidsson, L.; Alam, N.H.; Ahmed, T.; Alam, N.; Salam, M.A.; Beglinger, C.; Gyr, N.; Fuchs, G.J. Causal relationship of Helicobacter pylori with iron-deficiency anemia or failure of iron supplementation in children. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashorn, M.; Ruuska, T.; Mäkipernaa, A. Helicobacter pylori and iron deficiency anemia in children. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 36, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, R.P.; Dunaway, C.E.; Bruden, D.L.; Parkinson, A.J.; Gessner, B.D. Controlled, household-randomized, open-label trial of the effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on iron deficiency anemia among children in rural Alaska: Results at 40 months. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.H.; Huang, X.L.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Lu, L.G.; Sun, X.; Rong, L.; Zhong, L.; Sun, D.Y.; et al. Does Helicobacter pylori infection play a role in iron deficiency anemia? A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 886–896. [Google Scholar]
- Hudak, L.; Jaraisy, A.; Haj, S.; Muhsen, K. An updated systematic review and meta-analysis on the association between Helicobacter pylori infection and iron deficiency anemia. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, D.M.M.; Harris, P.R.; Sanderson, I.R.; Windle, H.J.; Walker, M.M.; Rocha, A.M.C.; Rocha, G.A.; Carvalho, S.D.; Bittencourt, P.F.S.; Castro, L.P.F.; et al. Iron status and Helicobacter pylori infection in symptomatic children: An international multi-centered study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Selgrad, M. Helicobacter pylori infection and current clinical areas of contention. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 26, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Yumin, L.; Kehu, Y.; Bin, M.; Quanlin, G.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Iron deficiency anemia in Helicobacter pylori infection: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DuBois, S.; Kearney, D.J. Iron-deficiency anemia and Helicobacter pylori infection: A review of the evidence. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheibi, S.; Farrokh-Eslamlou, H.R.; Noroozi, M.; Pakniyat, A. Refractory iron deficiency anemia and Helicobacter pylori infection in pediatrics: A review. Iran. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 15, 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, S.; Gold, B.D.; Kato, A. The resolution of severe iron-deficiency anemia after successful eradication of Helicobacter pylori in teenagers. JPGN Rep. 2022, 3, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibale, B.; Marignani, M.; Monarca, B.; Antonelli, G.; Marcheggiano, A.; Martino, G.; Mandelli, F.; Caprilli, R.; Delle Fave, G. Reversal of iron deficiency anemia after Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with asymptomatic gastritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 131, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marignani, M.; Angeletti, S.; Bordi, C.; Malagnino, F.; Mancino, C.; Delle Fave, G.; Annibale, B. Reversal of long-standing iron deficiency anemia after eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGirolamo, A.M.; Perry, G.S.; Gold, B.D.; Parkinson, A.; Provost, E.M.; Parvanta, I.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. Helicobacter pylori, anemia, and iron deficiency: Relationship explored among Alaska native children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2007, 26, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Ozawa, A.; Ebina, K.; Nakagawa, H. Endoscopic ethanol injection for treatment of bleeding peptic ulcer. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1994, 153, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Takeyama, J.; Ebina, K.; Naganuma, H. Omeprazole-based dual and triple regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication in children. Pediatrics 1997, 100, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Nishino, Y.; Ozawa, K.; Konno, M.; Maisawa, S.; Toyoda, S.; Tajiri, H.; Ida, S.; Fujisawa, T.; Iinuma, K. The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Japanese children with gastritis or peptic ulcer disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Osaki, T.; Kamiya, S.; Zhang, X.S.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori sabA gene is associated with iron deficiency anemia in childhood and adolescence. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virkkula, A.; Kivela, L.; Hiltunen, P.; Sotka, A.; Huhtala, H.; Kurppa, K.; Repo, M. Prevalence and clinical significance of Helicobacter pylori-negative chronic gastritis in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 74, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annibale, B.; Capurso, G.; Lahner, E.; Passi, S.; Ricci, R.; Maggio, F.; Fave, G.D. Concomitant alterations in intragastric pH and ascorbic acid concentration in patients with Helicobacter pylori gastritis and associated iron deficiency anaemia. Gut 2003, 52, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, P.R.; Serrano, C.A.; Villagran, A.; Walker, M.M.; Thomson, M.; Duarte, I.; Windle, H.J.; Crabtree, J.E. Helicobacter pylori-associated hypochlorhydria in children, and development of iron deficiency. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 66, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windle, H.J.; Kelleher, D.; Crabtree, J.E. Childhood Helicobacter pylori infection and growth impairment in developing countries: A vicious cycle? Pediatrics 2007, 119, e754–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Nakajima, S.; Nishino, Y.; Ozawa, K.; Minoura, T.; Konno, M.; Maisawa, S.; Toyoda, S.; Yoshimura, N.; Vaid, A.; et al. Association between gastric atrophy and Helicobacter pylori infection in Japanese children: A retrospective multicenter study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2006, 51, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Su, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, C. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and pathological changes in the gastric mucosa in Chinese children. Intern. Med. 2014, 53, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Queiroz, D.M.M.; Rocha, A.M.C.; Melo, F.F.; Rocha, G.A.; Teixeira, K.N.; Carvalho, S.D.; Bittencourt, P.F.S.; Castro, L.P.F.; Crabtree, J.E. Increased gastric IL-1β concentration and iron deficiency parameters in H. pylori infected children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.T.; Ni, Y.H.; Liu, S.H. Potential association of IL1B polymorphism with iron deficiency risk in childhood Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, e36–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Omar, E.M.; Oien, K.; El-Nujumi, A.; Gillen, D.; Wirz, A.; Dahill, S.; Williams, C.; Ardill, J.E.; McColl, K.E. Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastric acid hyposecretion. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Ozawa, K.; Koike, T.; Sekine, H.; Ohara, S.; Minoura, T.; Iinuma, K. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric acid secretion and meal-stimulated serum gastrin in children. Helicobacter 2004, 9, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, N.C. Anemia of inflammation: The cytokine-hepcidin link. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nemeth, E.; Valore, E.V.; Territo, M.; Schiller, G.; Lichtenstein, A.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin, a putative mediator of anemia of inflammation, is a type II acute-phase protein. Blood 2003, 101, 2461–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azab, S.F.; Esh, A.M. Serum hepcidin levels in Helicobacter pylori-infected children with iron-deficiency anemia: A case-control study. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, E. Hepcidin mimetics from microorganisms? A possible explanation for the effect of Helicobacter pylori on iron homeostasis. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2007, 38, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.K.; Williams, S.M. Helicobacter pylori infection causes both protective and deleterious effects in human health and disease. Genes Immun. 2021, 22, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, S.; Konno, M.; Mino, E.; Sato, K.; Takahashi, M.; Fujii, N. Enhanced Fe ion-uptake activity in Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from patients with iron-deficiency anemia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, e31–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S.C.; Robinson, A.K.; Rodríguez-Quiñones, F. Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Vliet, A.H.; Stoof, J.; Vlasblom, R.; Wainwright, S.A.; Hughes, N.J.; Kelly, D.J.; Bereswill, S.; Bijlsma, J.J.; Hoogenboezem, T.; Vandenbrouck-Grauls, C.M.; et al. The role of the Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) in regulation of Helicobacter pylori iron uptake. Helicobacter 2002, 7, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Worst, D.J.; Otto, B.R.; de Graaff, J. Iron-repressible outer membrane proteins of Helicobacter pylori involved in heme uptake. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4161–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaenens, L.; Szczebara, F.; Husson, M.O. Identification, characterization, and immunogenicity of the lactoferrin-binding protein from Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ernst, F.D.; Bereswill, S.; Waidner, B.; Stoof, J.; Mäder, U.; Kusters, J.G.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kist, M.; van Vliet, A.H.; Homuth, G. Transcriptional profiling of Helicobacter pylori Fur- and iron-regulated gene expression. Microbiology 2005, 151, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterbenc, A.; Jarc, E.; Poljak, M.; Homan, M. Helicobacter pylori virulence genes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4870–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J.; Berg, D.E. Helicobacter pylori genetic diversity and risk of human disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.L.; Mo, X.Q.; Huang, G.R.; Huang, Y.Q.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, L.J.; Wei, H.Y.; Liang, Q. Gene polymorphism of pathogenic Helicobacter pylori in patients with different types of gastrointestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 28, 9718–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta De, D.; Roychoudhury, S. To be or not to be: The host genetic factor and beyond in Helicobacter pylori mediated gastro-duodenal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2883–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyaullah, M.; AlShahrani, A.M.; Ahmad, I. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection and host cytokine gene polymorphism with gastric cancer. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 8810620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, M.; Ocroinin, T.; Suerbaum, S.; Josenhans, C.; Drumm, B. Adherence isogenic flagellum-negative mutants of Helicobacter pylori and Helicobacter mustelae to human and ferret gastric epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4335–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doohan, D.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Waskito, L.A.; Yamaoka, Y.; Miftahussurur, M. Helicobacter pylori BabA-SabA key roles in the adherence phase: The synergic mechanism for successful colonization and diseases development. Toxins 2021, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Klerk, N.; Maudsdotter, L.; Gebreegziabher, H.; Saroj, S.D.; Eriksson, B.; Eriksson, O.S.; Roos, S.; Lindén, S.; Sjölinder, H.; Jonsson, A.B. Lactobacilli reduce Helicobacter pylori attachment to host gastric epithelial cells by inhibiting adhesion gene expression. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahdavi, J.; Sondén, B.; Hurtig, M.; Olfat, F.O.; Forsberg, L.; Roche, N.; Angström, J.; Larsson, T.; Teneberg, S.; Karlsson, K.A.; et al. Helicobacter pylori SabA adhesin in persistent infection and chronic inflammation. Science 2002, 297, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheu, B.S.; Odenbreit, S.; Hung, K.H.; Liu, C.P.; Sheu, S.M.; Yang, H.B.; Wu, J.J. Interaction between host gastric sialyl-Lewis x and H. pylori SabA enhances H. pylori density in patients lacking gastric Lewis b antigen. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj, J.; Forma, A.; Sitarz, M.; Portincasa, P.; Garruti, G.; Krasowska, D.; Maciejewski, R. Helicobacter pylori virulence factors-Mechanisms of bacterial pathogenicity in the gastric microenvironment. Cells 2021, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unemo, M.; Aspholm-Hurtig, M.; Ilver, D.; Bergström, J.; Borén, T.; Danielsson, D.; Teneberg, S. The sialic acid binding SabA adhesin of Helicobacter pylori is essential for nonopsonic activation of human neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15390–15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, Y. Mechanisms of disease: Helicobacter pylori virulence factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueiredo, C.A.; Marques, C.R.; Costa, R.S.; Silva, H.B.F.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M. Cytokines, cytokine gene polymorphisms and Helicobacter pylori infection: Friend or foe? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5235–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, M.; Luzar, B.; Kocjan, B.J.; Orel, R.; Mocilnik, T.; Shrestha, M.; Kveder, M.; Poljak, M. Prevalence and clinical relevance of cagA, vacA, and iceA genotypes of Helicobacter pylori isolated from Slovenian children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Kato, S.; Zhou, W.; Yamazaki, S.; Yamakawa, A.; Ohtani, M.; Fujiwara, S.; Minoura, T.; Iinuma, K.; Kato, T. Diversity of vacA and cagA genes of Helicobacter pylori in Japanese children. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20 (Suppl. S1), 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghwan; Chowdhury, R. Host cell contact induces Fur-dependent expression of virulence factors CagA and VacA in Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, D.; Hussey, S.; Ang, M.; Terebiznik, M.R.; Sibony, M.; Galindo-Mata, E.; Gupta, V.; Blanke, S.R.; Delgado, A.; Romero-Gallo, J.; et al. Vacuolating cytotoxin and variants in Atg16L1 that disrupt autophagy promote Helicobacter pylori infection in humans. Gastroeterology 2012, 142, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, D.; Zambon, C.F.; Letley, D.P.; Stranges, A.; Marchet, A.; Rhead, J.L.; Schiavon, S.; Guariso, G.; Ceroti, M.; Nitti, D.; et al. Clinical relevance of Helicobacter pylori cagA and vacA gene polymorphisms. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djekic, A.; Müller, A. The immunomodulator VacA promotes immune tolerance and persistent Helicobacter pylori infection through its activities on T-cells and antigen-presenting cells. Toxin 2016, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.P.; Li, T.; Li, Z.H.; Yang, G.Z.; Hu, B.Y.; Shi, X.D.; Shi, T.L.; Tong, S.Q.; Guo, X.K. mRNA expression profiling reveals a role of Helicobacter pylori vacuolating toxin in escaping host defense. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 1528–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambon, C.F.; Navaglia, F.; Basso, D.; Rugge, M.; Plebani, M. Helicobacter pylori babA2, cagA, and s1 vacA genes work synergistically in causing intestinal metaplasia. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 56, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.A.; Lee, H.W.; Hong, M.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Choe, Y.H.; Ahn, B.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, N.G. Comparative proteomic analysis of Helicobacter pylori strains associated with iron deficiency anemia. Proteomics 2006, 6, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, Y.H.; Hwang, T.S.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.H.; Song, S.U.; Choi, M.S. A possible relation of the Helicobacter pylori pfr gene to iron deficiency anemia? Helicobacter 2001, 6, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amedei, A.; Cappon, A.; Codolo, G.; Cabrelle, A.; Polenghi, A.; Benagiano, M.; Tasca, E.; Azzurri, A.; D’Elios, M.M.; Del Prete, G.; et al. The neutrophil-activating protein of Helicobacter pylori promotes Th1 immune responses. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Elios, M.M.; Amedei, A.; Cappon, A.; Del Prete, G.; de Bernard, M. The neutrophil-activating protein of Helicobacter pylori (HP-NAP) as an immune modulating agent. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 50, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokota, S.; Toita, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Fujii, N.; Konno, M. Positive relationship between a polymorphism in Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein A gene and iron-deficiency anemia. Helicobacter 2013, 18, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, W.; Kung, H.F.; Ge, R. Comparison of iron-binding ability between Thr70-NapA and Ser70-NapA of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, J.T.; Beckett, A.C.; Scholz, M.B.; Cover, T.L. High-salt conditions alter transcription of Helicobacter pylori genes encoding outer membrane proteins. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00626-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.; Biggs, B.A.; Pasricha, S.R. Effects of daily iron supplementation in 2- to 5-years-old children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2013, 131, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choe, Y.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Jung, M.K.; Kang, S.K.; Hwang, T.S.; Hong, Y.C. Helicobacter pylori-associated iron deficiency anemia in adolescent female athletes. J. Pediatr. 2001, 139, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, G.; Rödjer, S.; Kaijser, B.; Börjesson, M. Helicobacter pylori antibodies and iron deficiency in female adolescents. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malaty, H.M.; Engstrand, L.; Pedersen, N.L.; Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori infection: Genetic and environmental influences. A study of twins. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melit, L.E.; Marginean, C.O.; Marginean, C.D.; Marginean, M.O. The relationship between Tool-like receptors and Helicobacter pylori-related gastropathies: Still a controversial topic. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 8197048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Golenbock, D.; Bowie, A.G. The history of toll-like receptors—Redefining innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano-Rodríguez, N.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Pardo, A.L.; Goh, K.L.; Fock, K.M.; Mitchell, H.M. Genetic polymorphisms in the toll-like receptor signaling pathway in Helicobacter pylori infection and related gastric cancer. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Omar, E.M.; Ng, M.T.; Hold, G.L. Polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor genes and risk of cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Omar, E.M.; Rabkin, C.S.; Gammon, M.D.; Vaughan, T.L.; Risch, H.A.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Stanford, J.L.; Mayne, S.T.; Goedert, J.; Blot, W.J.; et al. Increased risk of noncardia gastric cancer associated with proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, T.; Shirai, N.; Takashima, M.; Xiao, F.; Sugimura, H. Effect of genotypic differences in interleukin-1 beta on gastric acid secretion in Japanese patients infected with Helicobacter pylori. Am. J. Med. 2002, 112, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.A.; Villagrán, A.; Toledo, H.; Crabtree, J.E.; Harris, P.R. Iron deficiency and IL1β polymorphisms in Helicobacter pylori-infected children. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emiralioglu, N.; Yenicesu, I.; Sari, S.; Egritas, O.; Poyraz, A.; Pasaoglu, O.T.; Celik, B.; Dalgic, B. An insight into the relationship between prohepcidin, iron deficiency anemia, and interleukin-6 values in pediatric Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amieva, M.; Peek, R.M., Jr. Pathobiology of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaser, M.J.; Chen, Y.; Reibman, J. Does Helicobacter pylori protect against asthma and allergy? Gut 2008, 57, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lionetti, E.; Leonardi, S.; Lanzafame, A.; Garozzo, M.T.; Filippeli, M.; Tomarchio, S.; Ferrara, V.; Salpietro, C.; Pulvirenti, A.; Francavilla, R.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and atopic diseases: Is there a relationship? A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17635–17647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gishert, J.P.; Liou, J.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.H.; Leja, M.; O'Morain, C.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut 2022, 71, 1724–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, C.W.; Siddique, S.M.; Patel, A.; Harris, A.; Sultan, S.; Altayar, O.; Falck-Ytter, Y. AGA clinical practice guidelines on the gastrointestinal evaluation of iron deficiency anemia. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Kao, J.Y.; Kanwal, F.; Gilger, M.; LoVecchio, F.; Moss, S.F.; Crowe, S.E.; Elfant, A.; Haas, T.; Hapke, R.J.; et al. Houston consensus conference on testing for Helicobacter pylori infection in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.E.; Dale, A.; Bunn, J.E.G.; Harding, M.; Coward, W.A.; Cole, T.J.; Weaver, L.T. Early Helicobacter pylori colonization: The association with growth faltering in the Gambia. Arch. Dis. Child. 2004, 89, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mera, R.M.; Correa, P.; Fontham, E.E.; Reina, J.C.; Pradilla, A.; Alzate, A.; Bravo, L.E. Effects of a new Helicobacter pylori infection on height and weight in Colombian children. Ann. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Function (Hypothetical) | Iron-Deplete Condition | Fur-Regulated |
|---|---|---|---|
| fur | Ferric uptake regulator | up-regulation | - |
| fecA | Ferric dicitrate transportor | up-regulation | Yes |
| feoB | Ferrous iron transportor | up-regulation | Yes |
| frpB | Iron-regulated OMP * | up-regulation | Yes |
| pfr | Iron-containing ferritin | down-regulation | Yes |
| ceuE | Iron-transport protein | no regulation? | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kato, S.; Gold, B.D.; Kato, A. Helicobacter pylori-Associated Iron Deficiency Anemia in Childhood and Adolescence-Pathogenesis and Clinical Management Strategy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247351
Kato S, Gold BD, Kato A. Helicobacter pylori-Associated Iron Deficiency Anemia in Childhood and Adolescence-Pathogenesis and Clinical Management Strategy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247351
Chicago/Turabian StyleKato, Seiichi, Benjamin D. Gold, and Ayumu Kato. 2022. "Helicobacter pylori-Associated Iron Deficiency Anemia in Childhood and Adolescence-Pathogenesis and Clinical Management Strategy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247351
APA StyleKato, S., Gold, B. D., & Kato, A. (2022). Helicobacter pylori-Associated Iron Deficiency Anemia in Childhood and Adolescence-Pathogenesis and Clinical Management Strategy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247351






