Association between Pulmonary Function and Body Composition in Children and Adolescents with and without Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of the Study Participants
2.2. Evaluated Markers—Demographic, Clinical, and Laboratory
2.2.1. Anthropometric Markers and Vital Signs
2.2.2. Pulmonary Function—Spirometry and Dysanapsis Index
2.2.3. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
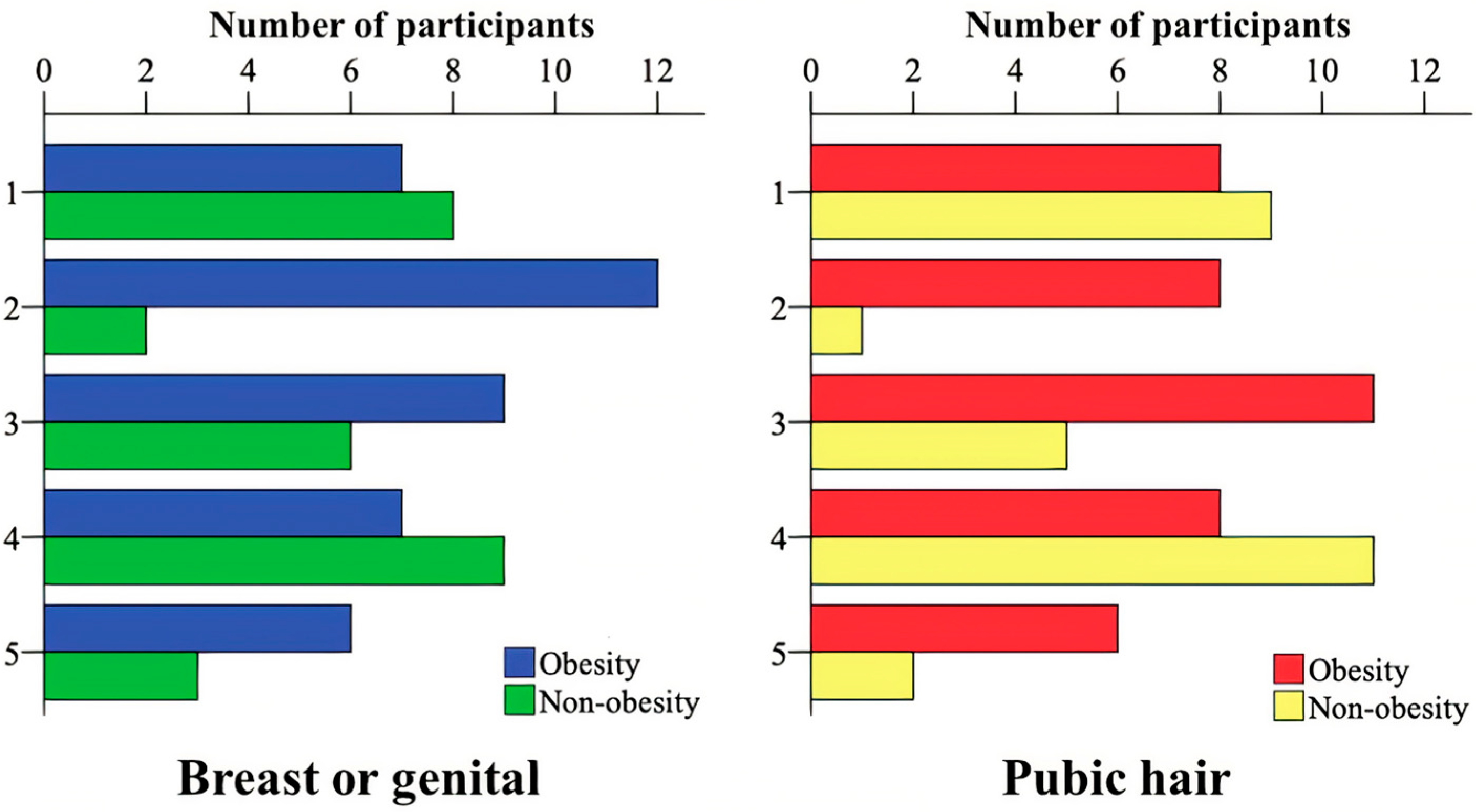
2.2.4. Physical Activity and Pubertal Development
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Güngör, N.K. Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2014, 6, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbeling, C.B.; Pawlak, D.B.; Ludwig, D.S. Childhood obesity: Public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet 2002, 360, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadoria, A.; Sahoo, K.; Sahoo, B.; Choudhury, A.; Sufi, N.; Kumar, R. Childhood obesity: Causes and consequences. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2015, 4, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleton, S.W. Impact of obesity on respiratory function. Respirology 2012, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.C.; Silva, M.A.M.; Calles, A.C.N. Obesity and lung function: A systematic review. Einstein 2014, 12, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salome, C.M.; King, G.G.; Berend, N. Physiology of obesity and effects on lung function. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 64, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancuso, P. Obesity and Lung Inflammation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 108, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.C.; Tsai, H.J.; Chang, S.W.; Chung, R.H.; Hsu, J.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Liao, S.L.; Hua, M.C.; Lai, S.H.; Chen, L.C.; et al. Obesity disproportionately impacts lung volumes, airflow and exhaled nitric oxide in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, R.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, H.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.; Yi, X.; Xu, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z. Weight Status Is Associated with Blood Pressure, Vital Capacity, Dental Decay, and Visual Acuity among School-Age Children in Chengdu, China. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Little, J.; Chen, Y. Relationship Between Adiposity and Pulmonary Function in School-Aged Canadian Children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2014, 27, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.G.; Ribeiro, M.A.G.O.; Marson, F.A.L.; Schivinski, C.I.S.; Severino, S.D.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Barros Filho, A.A. Effect of exercise test on pulmonary function of obese adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2014, 90, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LoMauro, A.; Cesareo, A.; Agosti, F.; Tringali, G.; Salvadego, D.; Grassi, B.; Sartorio, A.; Aliverti, A. Effects of a multidisciplinary body weight reduction program on static and dynamic thoraco-abdominal volumes in obese adolescents. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Rennie, D.; Cormier, Y.; Dosman, J.A. Waist circumference associated with pulmonary function in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.S.; Mendes, R.T.; Marson, F.A.L.; Zambon, M.P.; Antonio, M.A.R.G.M.; Paschoal, I.A.; Toro, A.A.; Severino, S.D.; Ribeiro, M.A.; Ribeiro, J.D. Espirometria e capnografia volumétrica na avaliação da função pulmonar de indivíduos obesos e eutróficos sem asma. J. Pediatr. 2017, 93, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.J.; Msc, K.A.M.-R.; Witmans, M.B.; Montgomery, M.D.; Ball, G.D.; Egbogah, S.; Eves, N.D. Negatively impacts lung function in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2014, 49, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spathopoulos, D.; Paraskakis, E.; Trypsianis, G.; Tsalkidis, A.; Arvanitidou, V.; Emporiadou, M.; Bouros, D.; Chatzimichael, A. The effect of obesity on pulmonary lung function of school aged children in Greece. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunger, D.B.; Ahmed, M.L.; Ong, K.K. Effects of obesity on growth and puberty. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 19, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forno, E.; Weiner, D.J.; Mullen, J.; Sawicki, G.; Kurland, G.; Han, Y.Y.; Cloutier, M.M.; Canino, G.; Weiss, S.T.; Litonjua, A.A.; et al. Obesity and Airway Dysanapsis in Children with and without Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixon, A.E.; Peters, U. The effect of obesity on lung function. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, C.S.; Salome, C.M. Asthma and obesity: A known association but unknown mechanism. Respirology 2012, 17, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilo, D.F.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Toro, A.D.C.; Baracat, E.C.E.; Filho, A.A.B. Obesity and asthma: Association or coincidence? J. Pediatr. 2010, 86, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forno, E.; Han, Y.Y.; Mullen, J.; Celedón, J.C. Overweight, obesity, and lung function in children and adults-A meta-analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafort, T.T.; Rufino, R.; Costa, C.H.; Lopes, A.J. Obesity: Systemic and pulmonary complications, biochemical abnormalities, and impairment of lung function. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2016, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sole, D.; Vanna, A.T.; Yamada, E.; Rizzo, M.C.; Naspitz, C.K. International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) written questionnaire: Validation of the asthma component among Brazilian children. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1998, 8, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onis, M.A.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malachias, M.V.B.; Souza, W.K.S.B.; Plavinik, F.L.; Rodrigues, C.I.S.; Brandão, A.A.; Neves, M.F.T. 7a diretriz brasileira de hipertensão arterial. Arq. Bras. Cardilogia 2016, 107, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mead, J. Dysanapsis in normal lungs assessed by the relationship between maximal flow, static recoil, and vital capacity. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1980, 121, 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Tager, I.B.; Weiss, S.T.; Munoz, A.; Welty, C.; Speizer, F.E. Determinants of response to eucapneic hyperventilation with cold air in a population-based study. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 134, 502–508. [Google Scholar]
- Matsudo, S.; Araujo, T.; Matsudo, V.; Andrade, D.; Andrade, E.; Oliveira, L.C.; Braggion, G. Questionário Internacional de atividade física (IPAQ): Estudo de validade e reprodutibilidade no Brasil. Rev. Bras. Ativ. Fís. Saúde 2001, 6, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in the pattern of pubertal changes in Boys. Arch. Dis. Child. 1970, 45, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in Pattern of Pubertal Changes in Girls. Arch. Dis. Child. 1969, 44, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuttall, F.Q. Body mass index: Obesity, BMI, and health: A critical review. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention. Body Mass Index: Considerations for Practitioners. 2011; pp. 1–4. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/25368 (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Nelson, M.C.; Neumark-Stzainer, D.; Hannan, P.J.; Sirard, J.R.; Story, M. Longitudinal and Secular Trends in Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior During Adolescence. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e1627–e1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidding, L.M.; Altenburg, T.M.; van Ekris, E.; Chinapaw, M.J.M. Why do children engage in sedentary behavior? Child- and parent-perceived determinants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coombs, N.; Shelton, N.; Rowlands, A.; Stamatakis, E. Children’s and adolescents’ sedentary behaviour in relation to socioeconomic position. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2013, 67, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerra, P.H.; Farias Júnior, J.C.d.; Florindo, A.A. Sedentary behavior in Brazilian children and adolescents: A systematic review. Rev. Saude Publica 2016, 50, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeBlanc, A.G.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Barreira, T.V.; Broyles, S.T.; Chaput, J.P.; Church, T.S.; Fogelholm, M.; Harrington, D.M.; Hu, G.; Kuriyan, R.; et al. Correlates of total sedentary time and screen time in 9–11 year-old children around the world: The international study of childhood obesity, lifestyle and the environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tandon, P.S.; Zhou, C.; Sallis, J.F.; Cain, K.L.; Frank, L.D.; Saelens, B.E. Home environment relationships with children’s physical activity, sedentary time, and screen time by socioeconomic status. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farley, T.A.; Meriwether, R.A.; Baker, E.T.; Watkins, L.T.; Johnson, C.C.; Webber, L.S. Safe play spaces to promote physical activity in inner-city children: Results from a pilot study of an environmental intervention. Am. J. Public Health 2007, 97, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.K.; Yu, S.M.; Siahpush, M.; Kogan, M.D. High levels of physical inactivity and sedentary behaviors among US immigrant children and adolescents. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2008, 162, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cote, A.T.; Harris, K.C.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Sandor, G.G.S.; Devlin, A.M. Childhood obesity and cardiovascular dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franks, P.W.; Hanson, R.L.; Knowler, W.C.; Sievers, M.L.; Bennett, P.H.; Looker, H.C. Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death paul. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, K.; Todd, D.C.; Soth, M. Altered respiratory physiology in obesity. Can. Respir. J. 2006, 13, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.-Q.; Wong, T.-W.; Du, L.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Qiu, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.-W.; Wu, J.-G.; Yu, I.T.-S. Respiratory health in overweight and obese Chinese children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomauro, A.; Aliverti, A. Sex differences in respiratory function. Breathe 2018, 14, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.H.; Roncada, C.; Fernandes, M.T.C.; Filho, J.P.H.; Icaza, E.E.S.; Mattiello, R.; Pitrez, P.M.C.; Pinto, L.A.; Stein, R. Asthma and Obesity in Children Are Independently Associated with Airway Dysanapsis. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 18, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.A.; Patel, D.R.; Darmawan, D. Participation in sports in relation to adolescent growth and development. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, T.; Murara, P.; Vancini, R.L.; de Lira, C.A.B.; Andrade, M.S. Influence of Biological Maturity on the Muscular Strength of Young Male and Female Swimmers. J. Hum. Kinet. 2021, 78, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Q.; Deng, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Story, M. Association between Obesity and Puberty Timing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S. Growth and Puberty in Obese Children and Implications of Body Composition. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 26, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Marker | Group | Obesity (n = 41) | Control (n = 28) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex 1 | Male | 14 (34.1%) | 14 (50%) | 0.188 |
| Female | 27 (65.9%) | 14 (50%) | ||
| Ethnicity (race) 2 | White | 25 (61%) | 25 (85.7%) | 0.038 |
| Black | 8 (19.5%) | 1 (3.6%) | ||
| Mixed race * | 8 (19.5%) | 2 (7.1%) | ||
| Asian | − | 1 (3.6%) | ||
| Height 3 (cm) | 153.27 ± 13.86; 155.50 (142.70 to 163.25) | 152.65 ± 22.75; 161.90 (134.50 to 171.90) | 0.460 | |
| Weight 4 (kg) | 74.04 ± 23.67; 69.10 (58.35 to 89.45) | 44.98 ± 17.22; 49.30 (29.27 to 61.53) | <0.001 | |
| BMI 3 (kg/m2) | 30.85 ± 6.63; 29.92 (27.24 to 33.44) | 18.30 ± 2.54; 18.84 (15.57 to 20.3) | <0.001 | |
| BMI Z-score 3 | 3.25 ± 1.09; 3 (2.57 to 3.73) | −0.16 ± 0.68; −0.20 (−0.63 to 0.22) | <0.001 | |
| Age 3 (years) | 11.98 ± 3.62; 11.74 (8.99 to 14.94) | 12.97 ± 4.91; 14.18 (8.72 to 18.05) | 0.213 | |
| DI1 4 | 0.20 ± 0.40; 0.19 (0.16 to 0.23) | 0.22 ± 0.50; 0.19 to 0.26) | 0.031 | |
| DI2 4 | 0.98 ± 0.24; 0.95 (0.81 to 1.14) | 1.09 ± 0.27; 1.13 (0.87 to 1.25) | 0.065 |
| A 1 | Obesity | Control | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sedentary | 1 (2.4%) | − | 0.777 |
| Irregularly active A | 8 (19.5%) | 3 (10.7%) | |
| Irregularly active B | 14 (34.1%) | 9 (32.1%) | |
| Active | 6 (14.6%) | 6 (21.4%) | |
| Very active | 12 (29.3%) | 10 (35.7%) | |
| B 2 | Obesity | Control | p |
| Sedentary or irregularly active | 23 (56.1%) | 12 (42.90%) | 0.280 |
| Active or very active | 18 (43.9%) | 16 (57.1%) |
| Variable | Obesity | Control | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate 1 | 85.83 ± 15.65; 87 (73 to 97.50) | 81.11 ± 13.70; 82 (70.25 to 90.50) | 0.200 |
| Respiratory rate 1 | 21.44 ± 3.97; 22 (18 to 23.50) | 18.43 ± 4.51; 18 (15.25 to 22.75) | 0.005 |
| SpO2 2 | 97.44 ± 1.21; 98 (97 to 98) | 97.50 ± 0.92; 97 (97 to 98) | 0.798 |
| Blood pressure | Obesity | Control | p |
| Systolic 1 | 118.39 ± 14.03; 120 (87 to 147) | 102.50 ± 12.23; 103 (86 to 124) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic 2 | 78.12 ± 10.54; 78 (71 to 80) | 67.89 ± 7.36; 70 (60 to 70) | <0.001 |
| Mean 2 | 91.54 ± 10.96; 92.33 (85 to 96.50) | 79.43 ± 8.28; 80.17 (70.17 to 86) | <0.001 |
| Markers | Fat Mass | Lean Body Mass | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Trunk | Android | Gynoid | Total | Fat Percentage | Trunk | Android | Gynoid | Total | Fat-Free Mass | |
| FVC z-score | CC | 0.329 | 0.338 | 0.301 | 0.315 | 0.359 | −0.033 | 0.011 | −0.074 | −0.042 | −0.073 |
| p | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.791 | 0.926 | 0.548 | 0.731 | 0.551 | |
| FVC—percentile | CC | 0.330 | 0.339 | 0.302 | 0.317 | 0.358 | −0.031 | 0.014 | −0.072 | −0.040 | −0.071 |
| p | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.802 | 0.911 | 0.556 | 0.744 | 0.561 | |
| FEV1/FVC z-score | CC | −0.256 | −0.260 | −0.236 | −0.244 | −0.263 | 0.029 | −0.010 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.030 |
| p | 0.034 | 0.031 | 0.051 | 0.043 | 0.029 | 0.811 | 0.937 | 0.855 | 0.840 | 0.805 | |
| Inspiratory capacity | CC | 0.162 | 0.133 | 0.152 | 0.144 | −0.063 | 0.341 | 0.338 | 0.334 | 0.322 | 0.340 |
| p | 0.206 | 0.298 | 0.235 | 0.259 | 0.624 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.006 | |
| ERV | CC | −0.090 | −0.063 | −0.066 | −0.064 | 0.091 | −0.262 | −0.253 | −0.271 | −0.241 | −0.266 |
| p | 0.481 | 0.621 | 0.605 | 0.616 | 0.477 | 0.036 | 0.044 | 0.030 | 0.055 | 0.034 | |
| PEF | CC | 0.065 | 0.067 | 0.081 | 0.072 | −0.092 | 0.287 | 0.258 | 0.268 | 0.291 | 0.276 |
| p | 0.599 | 0.587 | 0.509 | 0.559 | 0.457 | 0.018 | 0.033 | 0.027 | 0.016 | 0.023 | |
| Obesity | |||||||||||
| FVC z-score | CC | 0.210 | 0.209 | 0.233 | 0.184 | −0.019 | 0.183 | 0.194 | 0.166 | 0.160 | 0.142 |
| p | 0.188 | 0.189 | 0.143 | 0.249 | 0.907 | 0.253 | 0.225 | 0.300 | 0.300 | 0.377 | |
| FVC—percentile | CC | 0.216 | 0.215 | 0.239 | 0.190 | −0.019 | 0.187 | 0.198 | 0.170 | 0.164 | 0.145 |
| p | 0.176 | 0.177 | 0.133 | 0.234 | 0.906 | 0.242 | 0.214 | 0.289 | 0.306 | 0.365 | |
| FEV1/FVC z-score | CC | 0.023 | 0.002 | 0.049 | 0.061 | 0.065 | 0.008 | −0.032 | 0.013 | 0.005 | 0.022 |
| p | 0.888 | 0.988 | 0.760 | 0.703 | 0.686 | 0.961 | 0.842 | 0.937 | 0.977 | 0.890 | |
| Inspiratory capacity | CC | 0.352 | 0.295 | 0.265 | 0.290 | −0.213 | 0.401 | 0.390 | 0.369 | 0.383 | 0.411 |
| p | 0.033 | 0.076 | 0.114 | 0.081 | 0.205 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 0.011 | |
| ERV | CC | −0.175 | −0.126 | −0.077 | −0.115 | 0.175 | −0.171 | −0.165 | −0.133 | −0.149 | −0.184 |
| p | 0.294 | 0.450 | 0.645 | 0.491 | 0.292 | 0.303 | 0.323 | 0.427 | 0.372 | 0.270 | |
| PEF | CC | 0.472 | 0.457 | 0.458 | 0.467 | 0.017 | 0.519 | 0.497 | 0.529 | 0.510 | 0.478 |
| p | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.914 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | |
| Without obesity | |||||||||||
| FVC z-score | CC | −0.184 | −0.167 | −0.208 | −0.208 | 0.285 | −0.355 | −0.287 | −0.406 | −0.381 | −0.424 |
| p | 0.349 | 0.396 | 0.288 | 0.289 | 0.141 | 0.064 | 0.138 | 0.032 | 0.046 | 0.024 | |
| Continue | |||||||||||
| FVC—percentile | CC | −0.187 | −0.169 | −0.209 | −0.208 | 0.286 | −0.361 | −0.292 | −0.414 | −0.386 | −0.431 |
| p | 0.342 | 0.391 | 0.286 | 0.287 | −0.140 | 0.059 | 0.131 | 0.029 | 0.042 | 0.022 | |
| FEV1/FVC z-score | CC | −0.113 | −0.111 | −0.061 | −0.079 | −0.251 | 0.171 | 0.136 | 0.130 | 0.174 | 0.168 |
| p | 0.568 | 0.573 | 0.757 | 0.690 | 0.198 | 0.385 | 0.489 | 0.509 | 0.375 | 0.394 | |
| Inspiratory capacity | CC | 0.095 | 0.050 | 0.191 | 0.127 | −0.092 | 0.272 | 0.294 | 0.364 | 0.316 | 0.309 |
| p | 0.645 | 0.810 | 0.350 | 0.536 | 0.655 | 0.179 | 0.144 | 0.067 | 0.116 | 0.124 | |
| ERV | CC | −0.257 | −0.218 | −0.274 | −0.247 | 0.028 | −0.355 | −0.359 | −0.458 | −0.379 | −0.377 |
| p | 0.205 | 0.284 | 0.176 | 0.223 | 0.893 | 0.075 | 0.072 | 0.018 | 0.056 | 0.058 | |
| PEF | CC | −0.389 | −0.351 | −0.279 | −0.320 | −0.367 | 0.003 | −0.049 | −0.003 | 0.032 | 0.054 |
| p | 0.045 | 0.073 | 0.158 | 0.103 | 0.060 | 0.988 | 0.806 | 0.988 | 0.873 | 0.789 | |
| Markers | Obesity | Control | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| FVC z-score | 0.43 ± 0.62; 0.41 (0.025 to 0.82) | −0.20 ± 0.92; −0.23 (−0.98 to 0.49) | 0.002 1 |
| FVC—percentile | 64.32 ± 19.77; 66 (51 to 79) | 43.46 ± 28.89; 41 (16.50 to 68.50) | 0.003 2 |
| FEV1 z-score | 0.39 ± 0.69; 0.36 (0.01 to 0.79) | 0.06 ± 0.96; 0.05 (−0.66 to 0.77) | 0.125 1 |
| FEV1—percentile | 63.24 ± 21.54; 64 (50.50 to 78.50) | 51.86 ± 29.16; 51.50 (25.75 to 77.75) | 0.124 2 |
| FEV1/FVC z-score | −0.10 ± 1.01; −0.33 (−0.76 to 0.49) | 0.54 ± 1.14; 0.75 (−0.50 to 1.45) | 0.020 1 |
| FEV1/FVC percentile | 45.90 ± 29.79; 37 (22.50 to 69) | 61.37 ± 33.48; 71 (27.25 to 92.75) | 0.049 2 |
| FEF25–75% z-score | −0.13 ± 0.97; −0.15 (−0.73 to 0.63) | −0.09 ± 1.08; −0.02 (−0.97 to 0.64) | 0.885 1 |
| FEF25–75% percentile | 45.95 ± 28.43; 44 (23.50 to 73.50) | 47.64 ± 31.14; 49.50 (16.75 to 73.75) | 0.869 2 |
| Inspiratory capacity | 103.34 ± 38.77; 97.70 (71.75 to 140.45) | 101.65 ± 31.79; 100.25 (80.73 to 124.10) | 0.791 2 |
| Expiratory reserve volume | 117.44 ± 84.25; 103.65 (49.13 to 167.73) | 123.87 ± 113.40; 111.45 (53.48 to 149.03) | 0.796 1 |
| Peak expiratory flow | 87.64 ± 15.72; 88 (76.05 to 96.85) | 89.28 ± 14.36; 90.40 (79.80 to 100.90) | 0.665 1 |
| Trunk Fat Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 16.96 ± 5.80; 18.30 (11.20 to 21.56) | 3.79 ± 2.22; 3.00 (2.17 to 5.19) | <0.001 |
| Female | 15.47 ± 7.56; 13.80 (11.26 to 17.77) | 4.17 ± 2.19; 4.32 (1.77 to 5.85) | <0.001 |
| p | 0.204 | 0.635 | |
| Android Fat Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 2.84 ± 1.06; 3.07 (1.73 to 3.75) | 0.47 ± 0.34; 0.34 (0.23 to 0.70) | <0.001 |
| Female | 2.48 ± 1.32; 2.15 (1.75 to 2.78) | 0.49 ± 0.29; 0.47 (0.20 to 0.74) | <0.001 |
| p | 0.176 | 0.874 | |
| Gynoid Fat Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 5.76 ± 1.63; 5.66 (4.22 to 7.34) | 1.68 ± 0.80; 1.28 (1.02 to 2.42) | <0.001 |
| Female | 5.55 ± 2.38; 5.36 (4.34 to 6.51) | 2.26 ± 1.11; 2.47 (0.86 to 3.09) | <0.001 |
| p | 0.488 | 0.246 | |
| Total Fat Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 34.50 ± 9.19; 37.23 (25.82 to 42.26) | 10.09 ± 4.26; 8.56 (6.57 to 13.75) | <0.001 |
| Female | 32.63 ± 13.95; 29.60 (27.24 to 38.02) | 11.56 ± 5.06; 12.60 (5.65 to 15.28) | <0.001 |
| p | 0.320 | 0.667 | |
| Fat Percentage | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 43.64 ± 5.74; 43.07 (39.51 to 46.61) | 20.87 ± 4.45; 21.20 (17.61 to 23.86) | <0.001 |
| Female | 46.03 ± 4.21; 46.12 (44.62 to 48.17) | 28.00 ± 5.33; 27.10 (24.86 to 32.39) | <0.001 |
| p | 0.108 | 0.001 |
| Trunk Lean Body Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 19.47 ± 5.34; 20.10 (15.90 to 23.49) | 17.01 ± 6.53; 20.48 (11.15 to 22.78) | 0.286 |
| Female | 16.15 ± 5.16; 14.99 (11.59 to 19.04) | 12.89 ± 4.27; 15.02 (8.50 to 15.87) | 0.050 |
| p | 0.060 | 0.061 | |
| Android Lean Body Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 2.87 ± 0.73; 2.90 (2.37 to 3.40) | 2.41 ± 0.93; 2.83 (1.51 to 3.26) | 0.165 |
| Continue | |||
| Female | 2.37 ± 0.78; 2.18 (1.76 to 2.87) | 1.84 ± 0.61; 2.13 (1.21 to 2.32) | 0.033 |
| p | 0.054 | 0.069 | |
| Gynoid Lean Body Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 6.83 ± 2.12; 6.99 (5.27 to 8.34) | 5.90 ± 2.76; 7.42 (3.22 to 8.31) | 0.323 |
| Female | 5.52 ± 2.05; 5.20 (3.75 to 6.67) | 4.21 ± 1.64; 5.05 (2.52 to 5.41) | 0.044 |
| p | 0.061 | 0.062 | |
| Total Lean Body Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 43.51 ± 11.95; 44.20 (35.18 to 53.85) | 37.98 ± 14.81; 46.32 (24.50 to 50.61) | 0.287 |
| Female | 35.89 ± 11.35; 34.18 (26.33 to 40.92) | 27.89 ± 9.04; 31.57 (18.24 to 34.66) | 0.028 |
| p | 0.052 | 0.041 | |
| Fat-Free Mass | Obesity | Control | p |
| Male | 44.86 ± 12.59; 45.19 (35.61 to 55.29) | 39.52 ± 15.54; 48.87 (25.67 to 51.34) | 0.327 |
| Female | 37.19 ± 11.70;35.95 (27.56 to 41.48) | 28.59 ± 9.58; 32.15 (18.24 to 36.67) | 0.023 |
| p | 0.060 | 0.036 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, M.S.; Marson, F.A.L.; Wolf, V.L.W.; Zambon, M.P.; Antonio, M.Â.R.d.G.M.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Mendes, R.T. Association between Pulmonary Function and Body Composition in Children and Adolescents with and without Obesity. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247410
Ferreira MS, Marson FAL, Wolf VLW, Zambon MP, Antonio MÂRdGM, Ribeiro JD, Mendes RT. Association between Pulmonary Function and Body Composition in Children and Adolescents with and without Obesity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247410
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Mariana Simões, Fernando Augusto Lima Marson, Vaneza Lira Waldow Wolf, Mariana Porto Zambon, Maria Ângela Reis de Góes Monteiro Antonio, José Dirceu Ribeiro, and Roberto Teixeira Mendes. 2022. "Association between Pulmonary Function and Body Composition in Children and Adolescents with and without Obesity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247410
APA StyleFerreira, M. S., Marson, F. A. L., Wolf, V. L. W., Zambon, M. P., Antonio, M. Â. R. d. G. M., Ribeiro, J. D., & Mendes, R. T. (2022). Association between Pulmonary Function and Body Composition in Children and Adolescents with and without Obesity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247410







