Electrocautery, Harmonic, and Thunderbeat Instruments in Parotid Surgery: A Retrospective Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
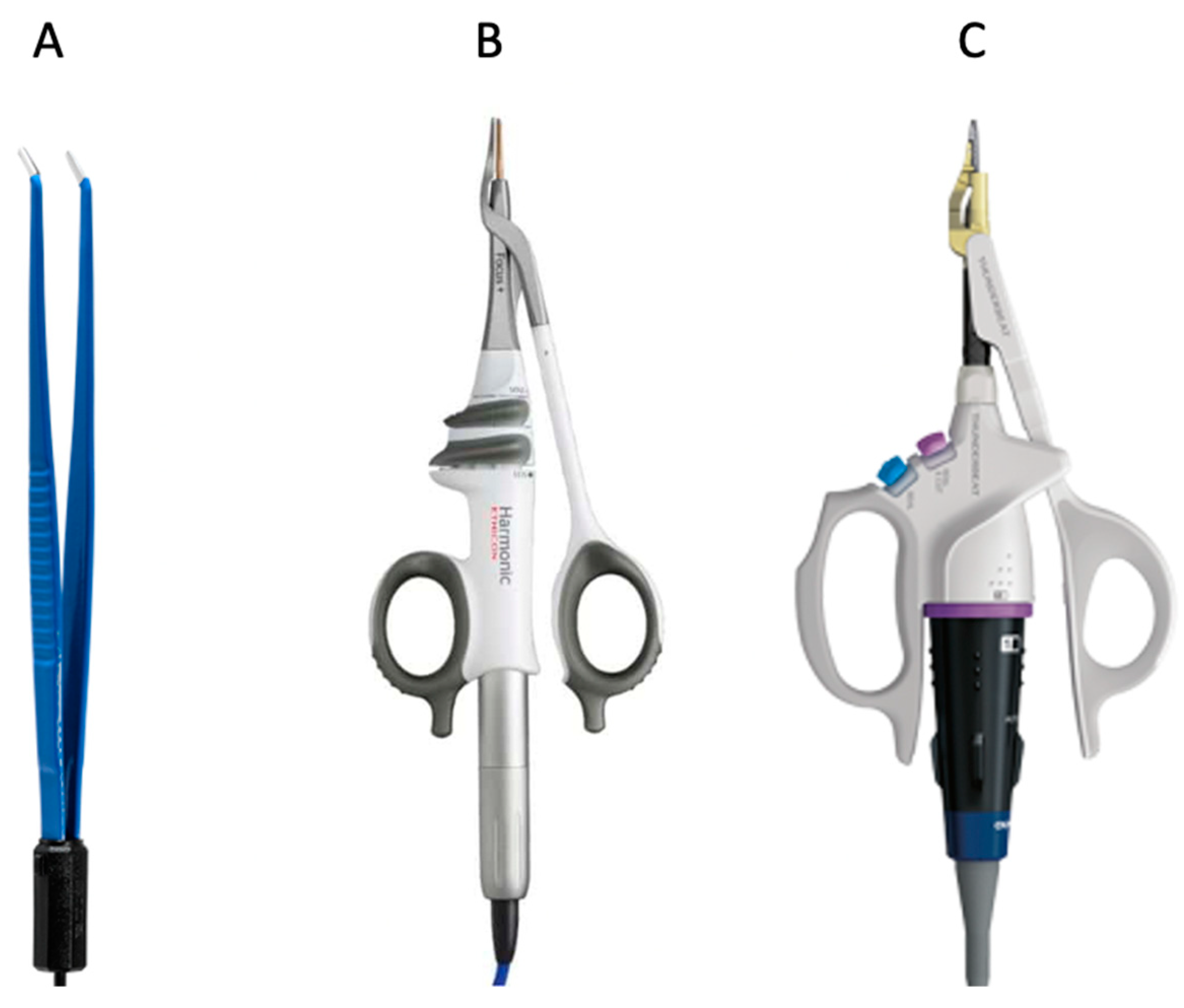
- Classic electrocautery hemostasis group: patients operated on with bipolar forceps (Aesculap Inc., Center Valley, PA, USA) between January 2016 and October 2018 (the CH group).
- Ultrasonic instrument group: patients operated on with Harmonic Focus Shears® (Ethicon Inc., Raritam, NJ, USA) between November 2018 and April 2020 (the HA group).
- Combined energy instrument group: patients operated on with Thunderbeat open fine jaw® (Olympus Medical Systems Corp., Tokyo, Japan) between May 2020 and April 2022 (the TB group).
2.1. Surgical Procedure
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mashrah, M.A.; Al-Sharani, H.M.; Al-Aroomi, M.A.; Abdelrehem, A.; Aldhohrah, T.; Wang, L. Surgical interventions for management of benign parotid tumors: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Head Neck 2021, 43, 3631–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovenzi, C.D.; Ciolek, P.; Crippen, M.; Curry, J.M.; Krein, H.; Heffelfinger, R. Reconstructive trends and complications following parotidectomy: Incidence and predictors in 11,057 cases. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 48, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambiel, S.; Dulguerov, N.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Dulguerov, P. Minor parotidectomy complications: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.; MacKay, C.; Rigby, M.H.; Trites, J.; Taylor, S.M. Haemostatic devices in parotid surgery: A systematic review. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2021, 135, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kallakuri, S.; Cavanaugh, J.M.; Broughton, D.; Clymer, J.W. Acute and subacute effects of the ultrasonic blade and electrosurgery on nerve physiology. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 29, 569–573. [Google Scholar]
- Hnatuk, L.A.; Li, K.T.; Carvalho, A.J.; Freeman, J.L.; Bilbao, J.M.; McKee, N.H. The effect of bipolar electrocautery on peripheral nerves. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 101, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispi, C.P.; Crispi, C.P., Jr.; da Silva Reis, P.S., Jr.; Mendes, F.L.F.; Filgueiras, M.M.; de Freitas Fonseca, M. Hemostasis with the ultrasonic scalpel. JSLS 2018, 22, e2018.00042. [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro, M.A.; Borzì, L.; Lo Bianco, S.; Okatyeva, V.; Cavallaro, A.; Buffone, A. Comparison between focus harmonic scalpel and hemostatic techniques in open thyroidectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2016, 38, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Vaira, L.A.; De Riu, G.; Ligas, E.; Deiana, G.; Vacca, G.; Massarelli, O.; Piombino, P.; Brevi, B.C. Neck dissection with harmonic instruments and electrocautery: A prospective comparative study. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 25, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, G.; Del Piero, G.C.; Perrino, F. Ultracision harmonic scalpel in oral and oropharyngeal cancer resection. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, A.; Bavazzano, M.; Mora, R.; Dellepiane, M. Harmonic scalpel in pharyngolaryngectomy with radical neck dissection. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 37, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muhanna, N.; Peleg, U.; Schwartz, Y.; Shaul, H.; Perez, R.; Sichel, J.Y. Harmonic scalpel assisted superficial parotidectomy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2014, 123, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polacco, M.A.; Pintea, A.M.; Gosselin, B.J.; Paydarfar, J.A. Parotidectomy using the harmonic scalpel: Ten years of experience at a rural academic health center. Head Face Med. 2017, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jackson, L.L.; Gourin, C.G.; Thomas, D.S.; Porubsky, E.S.; Klippert, F.N.; Terris, D.J. Use of the harmonic scalpel in superficial and total parotidectomy for benign and malignant disease. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Larruscain-Sarasola, E.; Gonzàlez-Garcìa, J.A.; Sistiaga-Suarez, J.A.; Altuna-Mariezcurrena, X. Cold knife dissection and bipolar diathermy vs harmonic scalpel in parotid gland surgery for benign tumours. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Engl. Ed. 2020, 71, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, D.R.; Gourin, C.G.; Porubsky, E.A.; Porubsky, E.S.; Klippert, F.N.; Whitaker, E.G.; Terris, D.J. Harmonic scalpel versus cold knife dissection in superficial parotidectomy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 131, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, A.; Dellepiane, M.; Bavazzano, M.; Crippa, B.; Mora, F.; Mora, R. New trends in head and neck surgery: A prospective evaluation of the harmonic scalpel. Med. Sci. Monit. 2008, 14, PI1–PI5. [Google Scholar]
- Deganello, A.; Meccariello, G.; Busoni, M.; Parrinello, G.; Bertolai, R.; Gallo, O. Dissection with harmonic scalpel versus cold instruments in parotid surgery. B-ENT 2014, 10, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Prgomet, D.; Janjanin, S.; Bilic, M.; Prstacic, R.; Kovac, L.; Rudes, M.; Katic, V. A prospective observational study of 363 cases operated with three different harmonic scalpels. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 266, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Kou, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ning, C.; Zhao, T. The harmonic scalpel versus electrocautery for parotidectomy: A meta-analysis. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, J.; Trencheva, K.; Monette, S.; Pavoor, R.; Shukla, P.; Ma, J.; Sonoda, T. Evaluation of the safety, efficacy, and versatility of a new surgical energu device (THUNDERBEAT) in comparison with Harmonic ACE, LigaSure V, and EnSeal devices in a porcine model. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2012, 22, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaix, M.E.; Furnée, E.J.; Arezzo, A.; Mistrangelo, M.; Morino, M. Energy sources for laparoscopic colorectal surgery: Is one better than the others? J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2016, 26, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Slycke, S.; Gillardin, J.P.; Van Den Heede, K.; Minguet, J.; Vermeersch, H.; Brusselaers, N. Comparison of the harmonic focus and the thunderbeat for open thyroidectomy. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2016, 401, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canu, G.L.; Medas, F.; Cappellacci, F.; Casti, F.; Bura, R.; Erdas, E.; Calò, P.G. The use of harmonic focus and thunderbeat open fine jaw in thyroid surgery: Experience of a high-volume center. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canu, G.L.; Medas, F.; Podda, F.; Tatti, A.; Pisano, G.; Erdas, E.; Calò, P.G. Thyroidectomy with energy-based devices: Surgical outcomes and complications-comparison between harmonic focus, LigaSure small jaw and Thunderbeat open fine jaw. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Gitelis, M.; Meiselman, D.; Abar, B.; Zapf, M.; Carbray, J.; Vigneswaran, Y.; Zhao, J.C.; Ujiki, M. Evaluation of vessel sealing performance among ultrasonic devices in a porcine model. Surg. Innov. 2015, 22, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.W.; Brackmann, D.E. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi (Version 2.3). 2022. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Kochhar, A.; Larian, B.; Azizzadeh, B. Facial nerve and parotid gland anatomy. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 49, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, A.; Gasco, L.; Zhang, D.; Carcoforo, P.; Micieli, P.; Delia, G.; Frattini, F.; Dionigi, G.; d’Alcontres, F.S. Energy-based devices affect aesthetic outcome of cervical thyroidectomy and parathyroidectomy. A retrospective study. Surg. Technol. Int. 2021, 39, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, C.J.; Stein, A.P.; Gessert, T.; Pflum, Z.; Saha, S.; Hartig, G.K. Factors influencing sialocele or salivary fistula formation postparotidectomy. Head Neck 2017, 39, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, K.; Kaya, I.; Turhal, G.; Ozturk, A.; Gursan, G.; Akyildiz, S. A comparison of electrothermal bipolar vessel sealing system and electrocautery in selective neck dissection. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3835–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.W.; Hsin, L.J.; Lin, W.N.; Tsai, Y.T.; Tsai, M.S.; Lee, Y.C. LigaSure versus conventional parotidectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, P.A.; Awad, S.; Perkins, A.C.; Lobo, D.N. Comparison of lateral thermal spread using monopolar and bipolar diathermy, the harmonic scalpel and the ligasure. Br. J. Surg. 2010, 97, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefermehl, L.J.; Largo, R.A.; Hermanns, T.; Poyet, C.; Sulser, T.; Eberli, D. Lateral temperature spread of monopolar, bipolar and ultrasonic instruments for robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery. BJU Int. 2014, 114, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, T.A.; Cuschieri, A. How safe is high-power ultrasonic dissection? Ann. Surg. 2003, 237, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehofer, D.; Mogl, M.; Boas-Knoop, S.; Unger, J.; Schirmeier, A.; Chopra, S.; Eurich, D. Safety and efficacy of new integrated bipolar and ultrasonic scissors compared to conventional laparoscopic 5-mm sealing and cutting instruments. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, D.; Dong, L. Comparison of complications in parotid surgery with harmonic scalpel versus cold instruments. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, e343–e344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashrah, M.A.; Aldhohrah, T.; Abdelrehem, A.; Koraitim, M.; Wang, L. What is the best method for prevention of postparotidectomy Frey syndrome? Network meta-analysis. Head Neck 2021, 43, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulguerov, P.; Marchal, F.; Lehmann, W. Postparotidectomy facial nerve paralysis: Possible etiologic factors and results with routine facial nerve monitoring. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, K.; Hur, N.; Kim, M.J.; Choe, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S. A prospective, randomized, controlled, comparative study of three energy devices in open thyroid surgery: Thunderbeat, harmonic and ligasure. J. Endocr. Surg. 2019, 19, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| CH Group (n = 37) | HA Group (n = 32) | TB Group (n = 33) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender n (%) | ||||
| Male | 16 (43.2%) | 16 (50%) | 18 (54.5%) | 0.635 * |
| Female | 21 (56.8%) | 16 (50%) | 15 (45.5%) | |
| Age (years) Mean ± SD | 54.8 ± 15.6 | 57.1 ± 14.9 | 55.9 ± 12.5 | 0.815 ** |
| Tumor size (cm) Mean ± SD | 2.27 ± 1.14 | 2.31 ± 1.13 | 2.44 ± 0.95 | 0.769 ** |
| Tumor type n (%) | ||||
| Pleomorphic adenoma | 28 (75.7%) | 21 (65.6%) | 23 (69.7%) | 0.792 * |
| Warthin tumor | 9 (24.3%) | 10 (31.3%) | 9 (27.3%) | |
| Oncocytoma | 0 (0%) | 1 (3.1%) | 1 (3%) |
| Complication n (%) | CH Group (n = 37) | HA Group (n = 32) | TB Group (n = 33) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salivary fistula | 3 (8.1%) | 1 (3.1%) | 3 (9.1%) | 0.593 * |
| Hemorrhage | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 * |
| Hematoma | 1 (2.7%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 0.624 * |
| Seroma | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 * |
| Frey syndrome | 2 (5.4%) | 1 (3.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0.408 * |
| Facial nerve weakness | 17 (45.9%) | 4 (12.5%) | 7 (21.2%) | 0.005 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaira, L.A.; Rizzo, D.; Murrocu, C.; Zullo, C.F.; Dessy, M.; Mureddu, L.; Ligas, E.; Salzano, G.; Biglio, A.; Mayo-Yáñez, M.; et al. Electrocautery, Harmonic, and Thunderbeat Instruments in Parotid Surgery: A Retrospective Comparative Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247414
Vaira LA, Rizzo D, Murrocu C, Zullo CF, Dessy M, Mureddu L, Ligas E, Salzano G, Biglio A, Mayo-Yáñez M, et al. Electrocautery, Harmonic, and Thunderbeat Instruments in Parotid Surgery: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247414
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaira, Luigi Angelo, Davide Rizzo, Claudia Murrocu, Caterina Francesca Zullo, Margherita Dessy, Luca Mureddu, Enrica Ligas, Giovanni Salzano, Andrea Biglio, Miguel Mayo-Yáñez, and et al. 2022. "Electrocautery, Harmonic, and Thunderbeat Instruments in Parotid Surgery: A Retrospective Comparative Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247414
APA StyleVaira, L. A., Rizzo, D., Murrocu, C., Zullo, C. F., Dessy, M., Mureddu, L., Ligas, E., Salzano, G., Biglio, A., Mayo-Yáñez, M., Lechien, J. R., Piombino, P., Bussu, F., & De Riu, G. (2022). Electrocautery, Harmonic, and Thunderbeat Instruments in Parotid Surgery: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247414








