Injury Patterns after Falling down Stairs—High Ratio of Traumatic Brain Injury under Alcohol Influence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
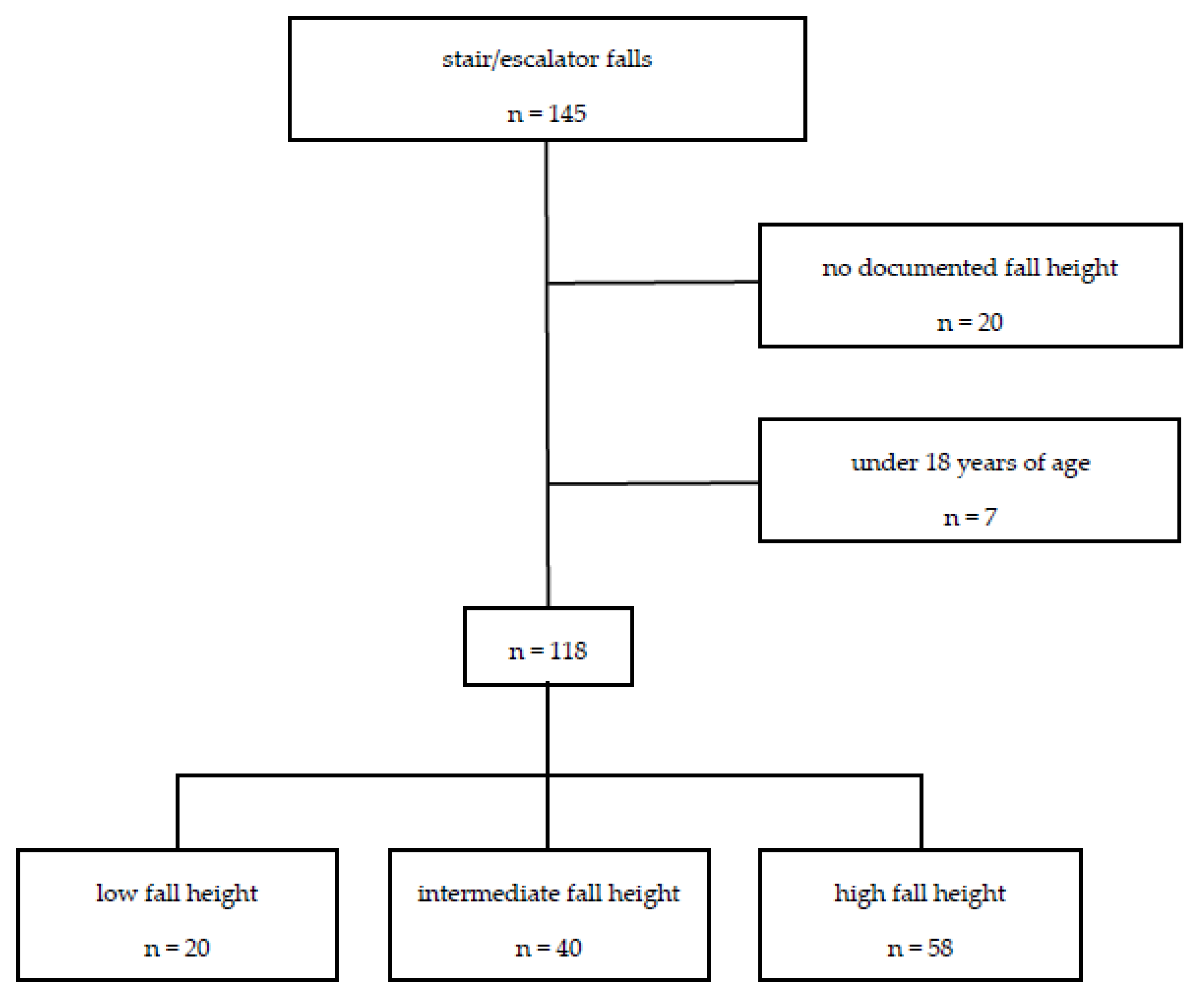
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/falls (accessed on 27 December 2021).
- Lesko, K.; Deasy, C. Low Falls Causing Major Injury: A Retrospective Study. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 189, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriades, D.; Murray, J.; Brown, C.; Velmahos, G.; Salim, A.; Alo, K.; Rhee, P. High-Level Falls: Type and Severity of Injuries and Survival Outcome According to Age. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2005, 58, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nau, C.; Leiblein, M.; Verboket, R.D.; Hörauf, J.A.; Sturm, R.; Marzi, I.; Störmann, P. Falls from Great Heights: Risk to Sustain Severe Thoracic and Pelvic Injuries Increases with Height of the Fall. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazewick, D.H.; Chounthirath, T.; Hodges, N.L.; Collins, C.L.; Smith, G.A. Stair-Related Injuries Treated in United States Emergency Departments. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragg, M.; Hwang, S.; Steinhart, B. Analysis of Serious Injuries Caused by Stairway Falls. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2000, 12, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatha, H.; Sammy, I.; Hickey, M.; Sattout, A.; Hollingsworth, J. Falling down a Flight of Stairs: The Impact of Age and Intoxication on Injury Pattern and Severity. Trauma 2018, 20, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kool, B.; Ameratunga, S.; Hazell, W.; Ng, A. Unintentional Falls at Home among Young and Middle-Aged New Zealanders Resulting in Hospital Admission or Death: Context and Characteristics. N. Z. Med. J. 2010, 123, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Friedland, D.; Brunton, I.; Potts, J. Falls and Traumatic Brain Injury in Adults Under the Age of Sixty. J. Community Health 2014, 39, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, S.; Rapp, K.; Rissmann, U.; Becker, C.; König, H.H. Cost of Falls in Old Age: A Systematic Review. Osteoporos. Int. 2010, 21, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaniolas, K.; Cheng, J.D.; Gestring, M.L.; Sangosanya, A.; Stassen, N.A.; Bankey, P.E. Ground Level Falls Are Associated with Significant Mortality in Elderly Patients. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2010, 69, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Ryoo, H.W.; Park, J.B.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, D.E.; Seo, K.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Moon, S. Comparison of Traffic Collision Victims between Older and Younger Drivers in South Korea: Epidemiologic Characteristics, Risk Factors and Types of Collisions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kistler, B.M.; Khubchandani, J.; Jakubowicz, G.; Wilund, K.; Sosnoff, J. Falls and Fall-Related Injuries among US Adults Aged 65 or Older with Chronic Kidney Disease. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2018, 15, E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, L.A.; Musiol, R.J.; Witham, E.K.; Metter, E.J. Falls in Young, Middle-Aged and Older Community Dwelling Adults: Perceived Cause, Environmental Factors and Injury. BMC Public Health 2005, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillespie, L.D.; Robertson, M.C.; Gillespie, W.J.; Sherrington, C.; Gates, S.; Clemson, L.; Lamb, S.E. Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older People Living in the Community. Edited by Cochrane Bone, Joint and Muscle Trauma Group. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.P.; Hsu, N.W.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, H.C.; Tsao, H.M.; Lo, S.S.; Chou, P. Relationship between Muscle Strength and Fall Episodes among the Elderly: The Yilan Study, Taiwan. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keall, M.D.; Pierse, N.; Howden-Chapman, P.; Cunningham, C.; Cunningham, M.; Guria, J.; Baker, M.G. Home Modifications to Reduce Injuries from Falls in the Home Injury Prevention Intervention (HIPI) Study: A Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Sun, W.; Sugiura, Y.; Hayashida, I.; Kusabiraki, T.; Tamaki, J. Sarcopenia and Falls in Community-Dwelling Elderly Subjects in Japan: Defining Sarcopenia According to Criteria of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 59, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, S.; Winzenberg, T.; Wills, K.; Scott, D.; Jones, G.; Aitken, D.; Callisaya, M.L. Prospective Associations of Low Muscle Mass and Function with 10-Year Falls Risk, Incident Fracture and Mortality in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheetz, L.J. Injury Patterns, Severity and Outcomes among Older Adults Who Sustained Brain Injury Following a Same Level Fall: A Retrospective Analysis. Int. Emerg. Nurs. 2015, 23, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyé, N.D.; Mattace-Raso, F.U.; Van der Velde, N.; Van Lieshout, E.M.; De Vries, O.J.; Hartholt, K.A.; Kerver, A.J.; Bruijninckx, M.M.; Van der Cammen, T.J.; Patka, P.; et al. Circumstances Leading to Injurious Falls in Older Men and Women in the Netherlands. Injury 2014, 45, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, H.F.; Cheng, C.H.; Chien, D.K.; Yu, W.Y.; Lin, M.R. Risk Factors for Traumatic Brain Injuries During Falls in Older Persons. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2015, 30, E9–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boele van Hensbroek, P.; Mulder, S.; Luitse, J.S.; Van Ooijen, M.R.; Goslings, J.C. Staircase Falls: High-Risk Groups and Injury Characteristics in 464 Patients. Injury 2009, 40, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidler, R.D.; Bernard, J.A.; Burutolu, T.B.; Fling, B.W.; Gordon, M.T.; Gwin, J.T.; Kwak, Y.; Lipps, D.B. Motor Control and Aging: Links to Age-Related Brain Structural, Functional, and Biochemical Effects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polytrauma Guideline Update Group. Level 3 Guideline on the Treatment of Patients with Severe/Multiple Injuries: AWMF Register-Nr. 012/019. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2018, 44, S3–S271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alizo, G.; Sciarretta, J.D.; Gibson, S.; Muertos, K.; Romano, A.; Davis, J.; Pepe, A. Fall from Heights: Does Height Really Matter? Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2018, 44, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petaros, A.; Slaus, M.; Coklo, M.; Sosa, I.; Cengija, M.; Bosnar, A. Retrospective Analysis of Free-Fall Fractures with Regard to Height and Cause of Fall. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 226, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.G.; Demling, R.H. The Pathophysiology of Free-Fall Injury. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1986, 15, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry-Jones, B.L.; Vaughan, F.L.; Cox, W.M. Traumatic Brain Injury and Substance Misuse: A Systematic Review of Prevalence and Outcomes Research (1994–2004). Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2006, 16, 537–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustenberger, T.; Inaba, K.; Barmparas, G.; Talving, P.; Plurad, D.; Lam, L.; Konstantinidis, A.; Demetriades, D. Ethanol Intoxication Is Associated with a Lower Incidence of Admission Coagulopathy in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Skrifvars, M.B.; Kivisaari, R.; Hernesniemi, J.; Lappalainen, J.; Siironen, J. Acute Alcohol Intoxication and Long-Term Outcome in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mörs, K.; Hörauf, J.A.; Kany, S.; Wagner, N.; Sturm, R.; Woschek, M.; Perl, M.; Marzi, I.; Relja, B. Ethanol Decreases Inflammatory Response in Human Lung Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting the Canonical NF-kB-Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franz, N.; Dieteren, S.; Köhler, K.; Mörs, K.; Sturm, R.; Marzi, I.; Perl, M.; Relja, B.; Wagner, N. Alcohol Binge Reduces Systemic Leukocyte Activation and Pulmonary PMN Infiltration after Blunt Chest Trauma and Hemorrhagic Shock. Inflammation 2018, 42, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörauf, J.A.; Kany, S.; Janicova, A.; Xu, B.; Vrdoljak, T.; Sturm, R.; Dunay, I.R.; Martin, L.B.; Relja, B. Short Exposure to Ethanol Diminishes Caspase-1 and ASC Activation in Human HepG2 Cells In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, A.; Heuvel, F.O.; Palmer, A.; Linkus, B.; Ludolph, A.C.; Boeckers, T.M.; Relja, B.; Huber-Lang, M.; Roselli, F. Acute Ethanol Administration Results in a Protective Cytokine and Neuroinflammatory Profile in Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 51, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 118) | Low Fall Height (n = 20) | Intermediate Fall Height (n = 40) | High Fall Height (n = 58) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fall height (number of steps), mean ± SD | 11.3 ± 5.6 | 3.9 ± 1.1 | 8.3 ± 1.6 | 16 ± 3.7 | 0.000 |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 59.5 ± 22.8 | 62.9 ± 26.7 | 60.2 ± 22.7 | 57.8 ± 21.7 | 0.672 |
| sex (male) | 66.9% (n = 79) | 55% (n = 11) | 75% (n = 30) | 65.5% (n = 38) | 0.284 |
| ISS (points), median (IQR) | 5.5 (14) | 5.5 (8) | 5 (11) | 9 (20) | 0.468 |
| NISS (points), median (IQR) | 6 (19) | 5.5 (9) | 6 (14) | 9 (21) | 0.537 |
| AIShead (points), mean ± SD | 2.01 ± 1.6 | 1.65 ± 1.4 | 1.88 ± 1.5 | 2.22 ± 1.6 | 0.290 |
| AISface (points), mean ± SD | 0.33 ± 0.7 | 0.25 ± 0.6 | 0.20 ± 0.6 | 0.45 ± 0.9 | 0.231 |
| AISthorax (points), mean ± SD | 0.52 ± 1.1 | 0.5 ± 1.1 | 0.45 ± 1.2 | 0.57 ± 1.1 | 0.873 |
| AISabdomen (points), mean ± SD | 0.25 ± 0.7 | 0.25 ± 0.8 | 0.18 ± 0.6 | 0.29 ± 0.7 | 0.719 |
| AISextremities (points), mean ± SD | 0.31 ± 0.8 | 0.25 ± 0.6 | 0.35 ± 0.8 | 0.31 ± 0.8 | 0.888 |
| domestic fall | 50% (n = 59) | 45% (n = 9) | 57.5% (n = 23) | 46.5% (n = 27) | 0.503 |
| stair fall | 81.4% (n = 96) | 85% (n = 17) | 80% (n = 32) | 81% (n = 47) | 0.892 |
| anticoagulatory long-term medication | 22.9% (n = 27) | 20% (n = 4) | 22.5% (n = 9) | 24.1% (n = 14) | 0.928 |
| Total (n = 118) | Low Fall Height (n = 20) | Intermediate Fall Height (n = 40) | High Fall Height (n = 58) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCSat scene (points), mean ± SD | 11.7 ± 4.3 | 11.6 ± 4.7 | 11.9 ± 4.4 | 11.7 ± 4.2 | 0.972 |
| GCSin-hospital (points), mean ± SD | 12.1 ± 4.7 | 11.9 ± 5.1 | 12.6 ± 4.3 | 11.7 ± 4.8 | 0.693 |
| preclinical intubation | 15.3% (n = 18) | 20% (n = 4) | 10% (n = 4) | 17.2% (n = 10) | 0.454 |
| SBPin-hospital (mmHg), mean ± SD | 151.6 ± 35.8 | 150 ± 27.4 | 160.5 ± 36.2 | 146.1 ± 37.5 | 0.160 |
| HRin-hospital (bpm), mean ± SD | 85.1 ± 18.9 | 80.4 ± 17.4 | 85.9 ± 22.1 | 86.2 ± 16.9 | 0.495 |
| hemoglobin in-hospital (g/dL), mean ± SD | 13.1 ± 1.9 | 12.9 ± 1.5 | 13.3 ± 1.8 | 13.1 ± 2.1 | 0.691 |
| platelet count in-hospital (cells/µL), mean ± SD | 208,263.9 ± 70,446.1 | 192,944.4 ± 53,932.9 | 200,062.2 ± 76,988.9 | 218,607.1 ± 70,110.9 | 0.280 |
| positive BAC | 44.9% (n = 53) | 25% (n = 5) | 47.5% (n = 19) | 50% (n = 29) | 0.141 |
| Total (n = 118) | Low Fall Height (n = 20) | Intermediate Fall Height (n = 40) | High Fall Height (n = 58) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBI | 83.1% (n = 98) | 75% (n = 15) | 80% (n = 32) | 87.9% (n = 51) | 0.338 |
| EDH | 4.2% (n = 5) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 9.4% (n = 5) | 0.067 |
| SDH | 19.5% (n = 23) | 5% (n = 1) | 12.5% (n = 5) | 29.3% (n = 17) | 0.024 |
| SAH | 24.6% (n = 29) | 5% (n = 1) | 25% (n = 10) | 31% (n = 18) | 0.066 |
| ICH | 19.5% (n = 23) | 5% (n = 1) | 15% (n = 6) | 27.6% (n = 16) | 0.06 |
| fractures | 47.6% (n = 56) | 10% (n = 2) | 35% (n = 14) | 68.9% (n = 40) | 0.015 |
| Total (n = 118) | Low Fall Height (n = 20) | Intermediate Fall Height (n = 40) | High Fall Height (n = 58) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| emergency operation head | 10.2% (n = 12) | 5% (n = 1) | 10% (n = 4) | 12.1% (n = 7) | 0.652 |
| operation (head excluded) | 24.6% (n = 29) | 10% (n = 2) | 30% (n = 12) | 25.9% (n = 15) | 0.947 |
| LOS ICU (days), mean ± SD | 2.9 ± 6.4 | 1.3 ± 2.8 | 2.2 ± 3.8 | 4.1 ± 8.4 | 0.156 |
| LOS hospital (days), mean ± SD | 7.4 ± 9.1 | 4.8 ± 4.4 | 7.5 ± 9.2 | 8.3 ± 9.9 | 0.334 |
| mortality | 11% (n = 13) | 10% (n = 2) | 10% (n = 4) | 12.1% (n = 7) | 0.938 |
| BAC Negative | BAC Positive | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BACadmission (g/dL), mean ± SD | 0 | 2.45 ± 0.98 | 0.000 |
| BACadmission (per mille), mean ± SD | 0 | 1.99 ± 0.79 | 0.000 |
| fall height (number of steps), mean ± SD | 10.8 ± 5.6 | 11.9 ± 5.5 | 0.219 |
| GCSat scene (points), mean ± SD | 11.5 ± 4.7 | 11.9 ± 3.9 | 0.499 |
| GCSin-hospital (points), mean ± SD | 11.4 ± 5.2 | 12.8 ± 3.9 | 0.624 |
| ISS (points), median (IQR) | 8 (16) | 5 (9) | 0.195 |
| NISS (points), median (IQR) | 9 (20) | 6 (12) | 0.335 |
| AIShead (points), mean ± SD | 2.17 ± 1.58 | 1.81 ± 1.51 | 0.205 |
| AISface (points), mean ± SD | 0.32 ± 0.72 | 0.43 ± 0.81 | 0.406 |
| AISthorax (points), mean ± SD | 0.77 ± 1.29 | 0.21 ± 0.74 | 0.004 |
| AISabdomen (points), mean ± SD | 0.32 ± 0.74 | 0.36 ± 0.71 | 0.896 |
| AISextremities (points), mean ± SD | 0.38 ± 0.82 | 0.23 ± 0.64 | 0.215 |
| LOS ICU (days), mean ± SD | 3.5 ± 7.7 | 2.3 ± 4.3 | 0.479 |
| LOS hospital (days), mean ± SD | 8.3 ± 10.4 | 6.3 ± 6.8 | 0.372 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hörauf, J.-A.; Nau, C.; Mühlenfeld, N.; Verboket, R.D.; Marzi, I.; Störmann, P. Injury Patterns after Falling down Stairs—High Ratio of Traumatic Brain Injury under Alcohol Influence. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030697
Hörauf J-A, Nau C, Mühlenfeld N, Verboket RD, Marzi I, Störmann P. Injury Patterns after Falling down Stairs—High Ratio of Traumatic Brain Injury under Alcohol Influence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(3):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030697
Chicago/Turabian StyleHörauf, Jason-Alexander, Christoph Nau, Nils Mühlenfeld, René D. Verboket, Ingo Marzi, and Philipp Störmann. 2022. "Injury Patterns after Falling down Stairs—High Ratio of Traumatic Brain Injury under Alcohol Influence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 3: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030697
APA StyleHörauf, J.-A., Nau, C., Mühlenfeld, N., Verboket, R. D., Marzi, I., & Störmann, P. (2022). Injury Patterns after Falling down Stairs—High Ratio of Traumatic Brain Injury under Alcohol Influence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030697






