Liraglutide + PYY3-36 Combination Therapy Mimics Effects of Roux-en-Y Bypass on Early NAFLD Whilst Lacking-Behind in Metabolic Improvements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Drugs, Surgeries
2.2. Dissections and Sample Collection
2.3. Liver Histology
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.5. Liver Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. RNA Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Histological Assessment: All Treatments Significantly Improved Liver Steatosis Compared to Placebo
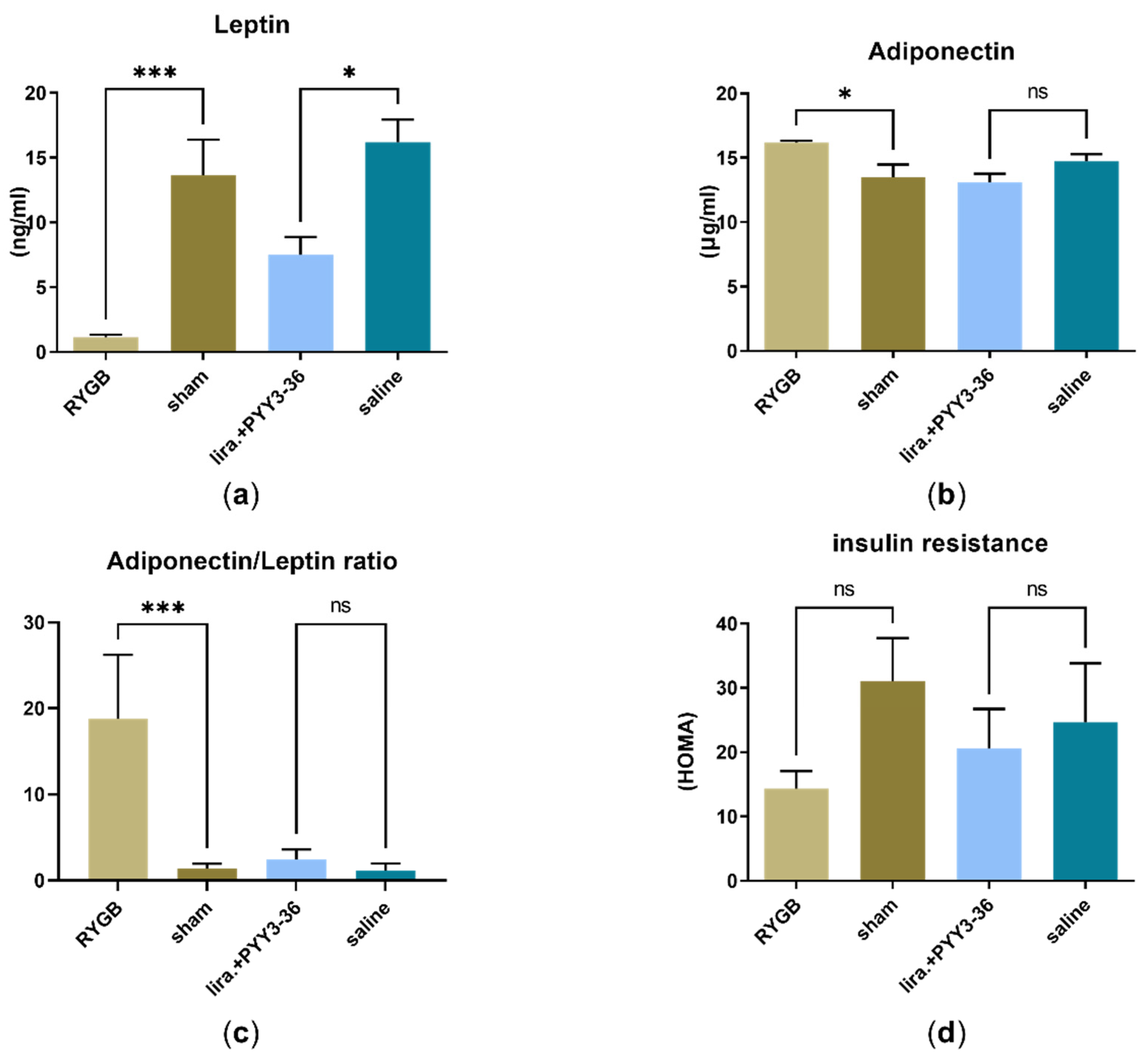
3.2. RYGB Improved HOMA-IR- (Insulin Resistance) and Adiponectin/Leptin-Ratio
3.3. No Significant Differences in Transaminase Levels (ALAT and ASAT)
3.4. No Inflammatory Activity Both in RT-qPCR- and Histological Assessment
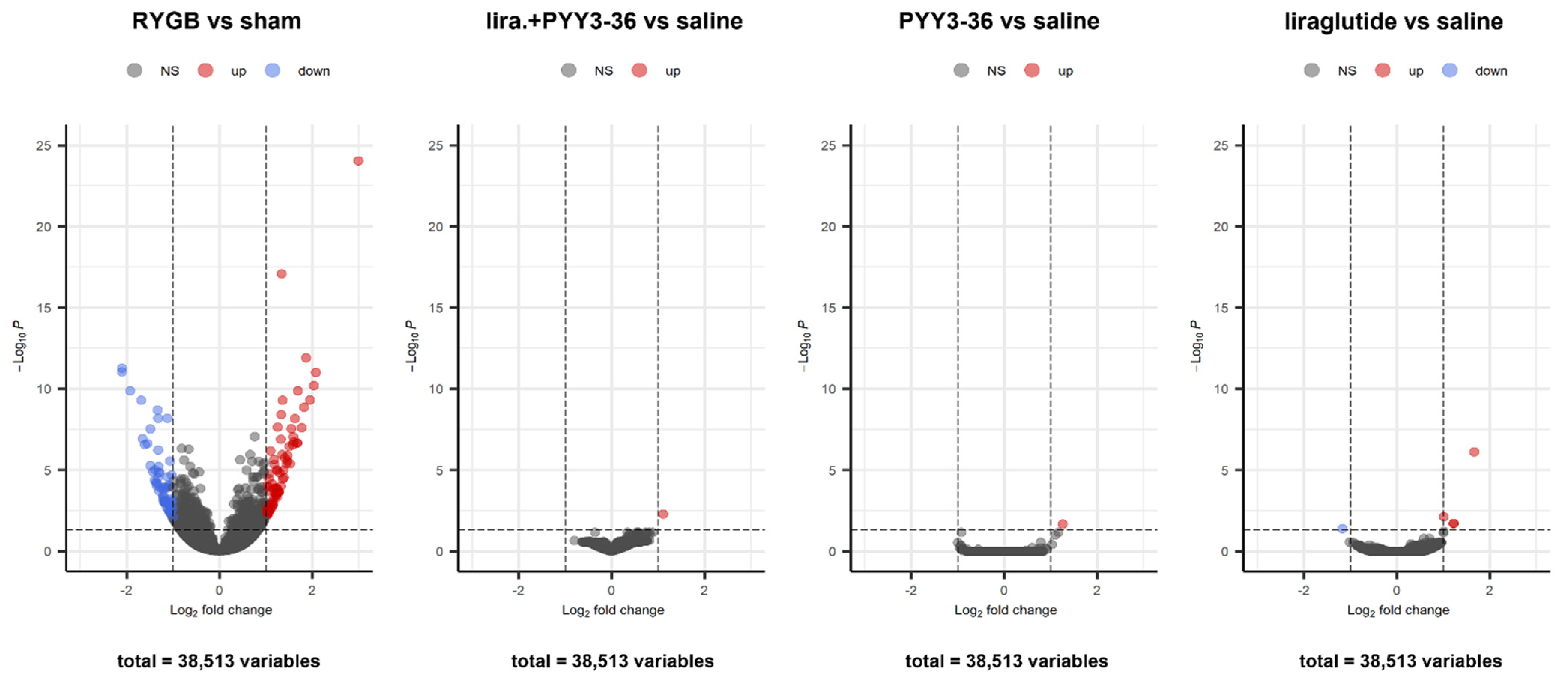
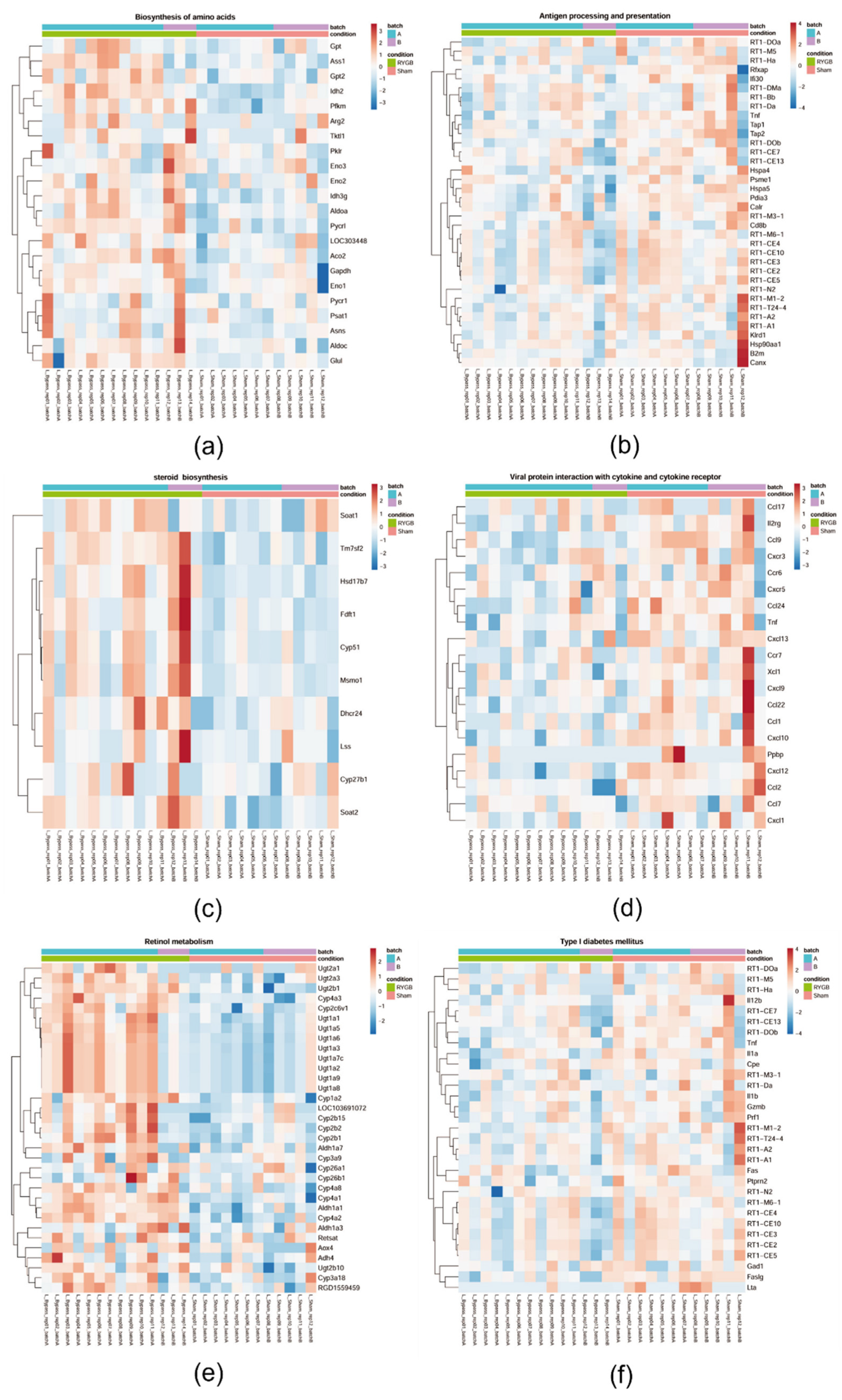
3.5. Only RYGB Impacts Global Liver mRNA Expression
4. Discussion
4.1. Treatment Effects Regarding Steatosis Are Comparable between Liraglutide+PYY3-36 and RYGB
4.2. RYGB Controls Metabolic Dysregulation
4.3. Limitations and Strengths of the Present Study
4.4. Synopsis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Jung, H.-S.; Cho, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yun, K.E.; Lazo, M.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Ahn, J.; Kim, C.-W.; Rampal, S.; et al. Metabolically Healthy Obesity and the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, D.-W.; Yan, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, S.-H.; Wang, B. Obesity is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, Y.; Hyogo, H.; Ono, M.; Mizuta, T.; Ono, N.; Fujimoto, K.; Chayama, K.; Saibara, T. Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the general population from 2009 to 2010 in Japan: A multicenter large retrospective study. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wree, A.; Kahraman, A.; Gerken, G.; Canbay, A. Obesity affects the liver-the link between adipocytes and hepatocytes. Digestion 2011, 83, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, P.; Hellerbrand, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander Sharma, B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Henry, L. Contribution of Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to the Burden of Liver-Related Morbidity and Mortality. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Sanderson, S.; Lindor, K.D.; Angulo, P. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.-U.; Cusi, K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.L.; Hagemann, C.A.; Wei, C.; Kazankov, K.; Thomsen, K.L.; Knop, F.K.; Grønbæk, H. Bariatric surgery in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-from pathophysiology to clinical effects. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, A.; Batterham, R.L. Mechanisms underlying the weight loss effects of RYGB and SG: Similar, yet different. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colquitt, J.L.; Pickett, K.; Loveman, E.; Frampton, G.K. Surgery for weight loss in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD003641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionut, V.; Bergman, R.N. Mechanisms responsible for excess weight loss after bariatric surgery. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1263–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muniesa, P.; Mártinez-González, M.-A.; Hu, F.B.; Després, J.-P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.A.; Martinez, J.A. Obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.S.; Yanagisawa, R.; Kini, S. Insulin resistance and bariatric surgery. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhry, T.K.; Mhaskar, R.; Schwitalla, T.; Muradova, E.; Gonzalvo, J.P.; Murr, M.M. Bariatric surgery improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A contemporary systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, R.E.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Asarian, L.; Horowitz, M.; Beglinger, C.; Geary, N. Ghrelin, CCK, GLP-1, and PYY(3-36): Secretory Controls and Physiological Roles in Eating and Glycemia in Health, Obesity, and After RYGB. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 411–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisello, S.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Urbano, F.; Piro, S.; Purrello, F.; Rabuazzo, A.M. Pathophysiological, Molecular and Therapeutic Issues of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheka, A.C.; Adeyi, O.; Thompson, J.; Hameed, B.; Crawford, P.A.; Ikramuddin, S. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeb, E.; Geier, A. Nichtalkoholische Steatohepatitis (NASH)—Aktuelle Behandlungsempfehlungen und zukünftige Entwicklungen. Z. Gastroenterol. 2019, 57, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, M.; Geier, A. An update on drug development for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-from ongoing clinical trials to future therapy. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Gaunt, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Barton, D.; Hull, D.; Parker, R.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Guo, K.; Abouda, G.; Aldersley, M.A.; et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.-S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlbauer, U.; Woods, S.C.; Langhans, W.; Meyer, U. PYY3-36: Beyond food intake. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.; Bain, S.C. The Role of Tirzepatide, Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS Clinical Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.; Salem, V.; Long, C.J.; Makwana, A.; Newbould, R.D.; Rabiner, E.A.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Matthews, P.M.; Beaver, J.D.; et al. The gut hormones PYY 3-36 and GLP-1 7-36 amide reduce food intake and modulate brain activity in appetite centers in humans. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.B.; Gregersen, N.T.; Pedersen, S.D.; Arentoft, J.L.; Ritz, C.; Schwartz, T.W.; Holst, J.J.; Astrup, A.; Sjödin, A. Effects of PYY3-36 and GLP-1 on energy intake, energy expenditure, and appetite in overweight men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E1248–E1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dischinger, U.; Hasinger, J.; Königsrainer, M.; Corteville, C.; Otto, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Hankir, M.; Seyfried, F.J.D. Toward a Medical Gastric Bypass: Chronic Feeding Studies With Liraglutide + PYY3-36 Combination Therapy in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 598843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin Ratio is a Functional Biomarker of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio: A promising index to estimate adipose tissue dysfunction. Relation with obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, B.; Li, H.; Long, X.; Rye, K.-A.; Ong, K.L. Fibroblast growth factor 21 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2019, 101, 153994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Petrasek, J. Inflammasome activation and function in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, V.L.; Skoien, R.; Powell, E.E.; Fagan, K.J.; Winterford, C.; Horsfall, L.; Irvine, K.; Clouston, A.D. The portal inflammatory infiltrate and ductular reaction in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dischinger, U.; Corteville, C.; Otto, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Seyfried, F.; Hankir, M.K. GLP-1 and PYY3-36 reduce high-fat food preference additively after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in diet-induced obese rats. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Menke, A.L.; Driessen, A.; Koek, G.H.; Lindeman, J.H.; Stoop, R.; Havekes, L.M.; Kleemann, R.; van den Hoek, A.M. Establishment of a General NAFLD Scoring System for Rodent Models and Comparison to Human Liver Pathology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Beamonte, R.; Navarro, M.A.; Larraga, A.; Strunk, M.; Barranquero, C.; Acín, S.; Guzman, M.A.; Iñigo, P.; Osada, J. Selection of reference genes for gene expression studies in rats. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 151, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, M.; Ståhlberg, A.; Rorsman, P.; Kubista, M. Gene expression profiling in single cells from the pancreatic islets of Langerhans reveals lognormal distribution of mRNA levels. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, A.; Bieniussa, L.; Gupta, R.; Samtleben, S.; Bischler, T.; Doering, K.; Sodmann, P.; Rittner, H.; Blum, R. Homeostatic calcium fluxes, ER calcium release, SOCE, and calcium oscillations in cultured astrocytes are interlinked by a small calcium toolkit. Cell Calcium 2021, 101, 102515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstedt, M.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Fredrikson, M.; Stål, P.; Kechagias, S.; Hultcrantz, R. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.R.; Kim, H.J.; Therneau, T.M. Association between noninvasive fibrosis markers and mortality among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, J.; Jaques, B.; Chattopadyhay, D.; Lochan, R.; Graham, J.; Das, D.; Aslam, T.; Patanwala, I.; Gaggar, S.; Cole, M.; et al. Hepatocellular cancer: The impact of obesity, type 2 diabetes and a multidisciplinary team. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, S.; Hardy, T.; Henderson, E.; Burt, A.D.; Day, C.P.; Anstee, Q.M. Evidence of NAFLD progression from steatosis to fibrosing-steatohepatitis using paired biopsies: Implications for prognosis and clinical management. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unamuno, X.; Izaguirre, M.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Silva, C.; Salvador, J.; et al. Increase of the Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio in Patients with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, S.; Tovoli, F.; Napoli, L.; Serio, I.; Ferri, S.; Bolondi, L. Current guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review with comparative analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3361–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazzolla, V.A.; Mangia, A. Noninvasive Diagnosis of NAFLD and NASH. Cells 2020, 9, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Vergniol, J.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Foucher, J.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Le Bail, B.; Choi, P.C.-L.; Kowo, M.; Chan, A.W.-H.; Merrouche, W.; et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, J.D.; Szczepaniak, L.S.; Dobbins, R.; Nuremberg, P.; Horton, J.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Grundy, S.M.; Hobbs, H.H. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: Impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Chiwanda Kaminga, A.; Liu, A.; Wen, S.W.; Chen, J.; Luo, J. Chemokines in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kitade, H.; Ni, Y.; Ota, T. Roles of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrar, A.; Hariharan, S.; Fazel, Y.; Moosvi, A.; Houry, M.; Younoszai, Z.; Jeffers, T.; Zheng, L.; Munkhzul, O.; Hunt, S.; et al. Analysis of human leukocyte antigen allele polymorphism in patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e16704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Herck, M.A.; Weyler, J.; Kwanten, W.J.; Dirinck, E.L.; De Winter, B.Y.; Francque, S.M.; Vonghia, L. The Differential Roles of T Cells in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Obesity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Dullaart, R.P.F.; Schreuder, T.C.M.A.; Blokzijl, H.; Faber, K.N. Disturbed Vitamin A Metabolism in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Nutrients 2017, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettinelli, P.; Arendt, B.M.; Teterina, A.; McGilvray, I.; Comelli, E.M.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; Allard, J.P. Altered hepatic genes related to retinol metabolism and plasma retinol in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, W. Glucagon Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Alter Pancreatic and Hepatic Histology and Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in High-fat Diet Mouse Model. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2021, 129, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, E.M.; Rawls, K.D.; Dougherty, B.V.; Li, Z.I.; Kolling, G.L.; Ye, P.; Wallqvist, A.; Papin, J.A. Reconciled rat and human metabolic networks for comparative toxicogenomics and biomarker predictions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreres, L.; Jílková, Z.M.; Vial, G.; Marche, P.N.; Decaens, T.; Lerat, H. Modeling Diet-Induced NAFLD and NASH in Rats: A Comprehensive Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B.; Sacks, G.; Ravussin, E. Increased food energy supply is more than sufficient to explain the US epidemic of obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, D.; Glaeser, E.; Shapiro, J. Why Have Americans Become More Obese? J. Econ. Perspect. 2003, 17, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, T.G.; Rinella, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease 2020: The State of the Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1851–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016-2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, H.; Stål, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Hemmingsson, T.; Andreasson, A. Overweight in late adolescence predicts development of severe liver disease later in life: A 39years follow-up study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Kraak, V.I.; Allender, S.; Atkins, V.J.; Baker, P.I.; Bogard, J.R.; Brinsden, H.; Calvillo, A.; De Schutter, O.; Devarajan, R.; et al. The Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition, and Climate Change: The Lancet Commission report. Lancet 2019, 393, 791–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M. Current and future pharmacological therapies for NAFLD/NASH. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Metzner, V.; Herzog, G.; Heckel, T.; Bischler, T.; Hasinger, J.; Otto, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Geier, A.; Seyfried, F.; Dischinger, U. Liraglutide + PYY3-36 Combination Therapy Mimics Effects of Roux-en-Y Bypass on Early NAFLD Whilst Lacking-Behind in Metabolic Improvements. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030753
Metzner V, Herzog G, Heckel T, Bischler T, Hasinger J, Otto C, Fassnacht M, Geier A, Seyfried F, Dischinger U. Liraglutide + PYY3-36 Combination Therapy Mimics Effects of Roux-en-Y Bypass on Early NAFLD Whilst Lacking-Behind in Metabolic Improvements. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(3):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030753
Chicago/Turabian StyleMetzner, Valentin, Gloria Herzog, Tobias Heckel, Thorsten Bischler, Julia Hasinger, Christoph Otto, Martin Fassnacht, Andreas Geier, Florian Seyfried, and Ulrich Dischinger. 2022. "Liraglutide + PYY3-36 Combination Therapy Mimics Effects of Roux-en-Y Bypass on Early NAFLD Whilst Lacking-Behind in Metabolic Improvements" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 3: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030753
APA StyleMetzner, V., Herzog, G., Heckel, T., Bischler, T., Hasinger, J., Otto, C., Fassnacht, M., Geier, A., Seyfried, F., & Dischinger, U. (2022). Liraglutide + PYY3-36 Combination Therapy Mimics Effects of Roux-en-Y Bypass on Early NAFLD Whilst Lacking-Behind in Metabolic Improvements. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030753





