Acute Kidney Injury Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Association with Contrast Media Dosage and Contrast Media Based Risk Predication Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
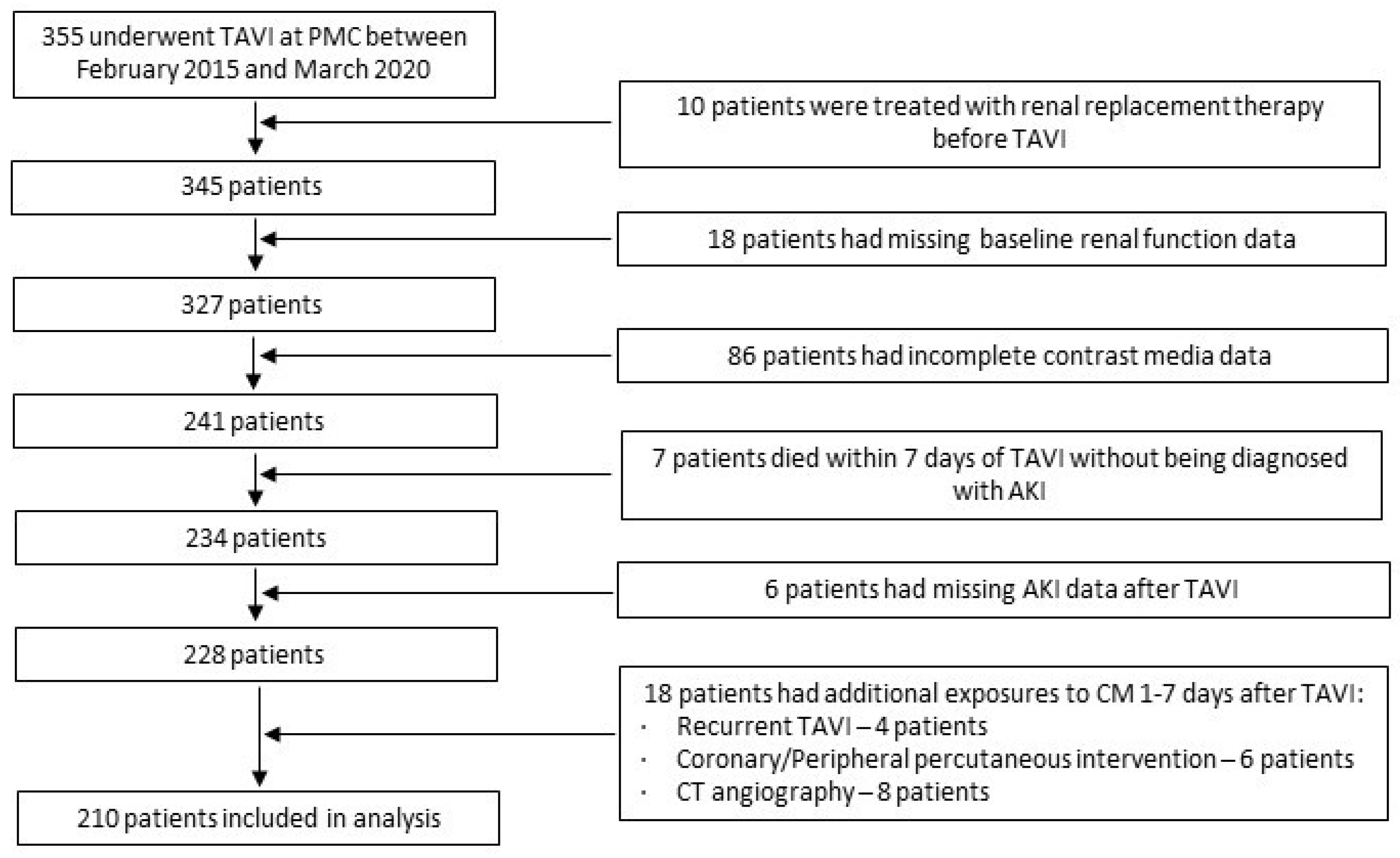
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gargiulo, G.; Sannino, A.; Capodanno, D.; Perrino, C.; Capranzano, P.; Barbanti, M.; Stabile, E.; Trimarco, B.; Tamburino, C.; Esposito, G. Impact of postoperative acute kidney injury on clinical outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A meta-analysis of 5,971 patients. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 86, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, G.; Capodanno, D.; Sannino, A.; Perrino, C.; Capranzano, P.; Stabile, E.; Trimarco, B.; Tamburino, C.; Esposito, G. Moderate and severe preoperative chronic kidney disease worsen clinical outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Me-ta-analysis of 4992 patients. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, e002220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes Filho, A.C.; Katz, M.; Campos, C.M.; Carvalho, L.A.; Siqueira, D.A.; Tumelero, R.T.; Portella, A.L.F.; Esteves, V.; Perin, M.A.; Sarmento-Leite, R.; et al. Impact of Acute Kidney Injury on Short- and Long-term Outcomes After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2019, 72, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbash, I.M.; Ben-Dor, I.; Dvir, D.; Maluenda, G.; Xue, Z.; Torguson, R.; Satler, L.F.; Pichard, A.D.; Waksman, R. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Am. Hear. J. 2012, 163, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhmidi, Y.; Bleiziffer, S.; Deutsch, M.-A.; Krane, M.; Mazzitelli, D.; Lange, R.; Piazza, N. Acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Incidence, predictors and impact on mortality. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 107, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zungur, M.; Gul, I.; Tastan, A.; Damar, E.; Tavli, T. Predictive Value of the Mehran Score for Contrast-Induced Nephropathy after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients with Aortic Stenosis. Cardiorenal Med. 2016, 6, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venturi, G.; Pighi, M.; Pesarini, G.; Ferrero, V.; Lunardi, M.; Castaldi, G.; Setti, M.; Benini, A.; Scarsini, R.; Ribichini, F.L. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing TAVI Compared with Coronary Interventions. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, N.; Hou, X.; Wang, L. Independent Risk Factors Contributing to Acute Kidney Injury According to Updated Valve Academic Research Consortium-2 Criteria After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: A Meta-analysis and Meta-regression of 13 Studies. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2017, 31, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madershahian, N.; Scherner, M.; Liakopoulos, O.; Rahmanian, P.; Kuhn, E.; Hellmich, M.; Mueller-Ehmsen, J.; Wahlers, T. Renal impairment and transapical aortic valve implantation: Impact of contrast medium dose on kidney function and survival. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2012, 41, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Hayashida, K.; Mouillet, G.; Chevalier, B.; Meguro, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Dubois-Rande, J.-L.; Morice, M.-C.; Lefèvre, T.; Teiger, E. Renal Function–Based Contrast Dosing Predicts Acute Kidney Injury Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 6, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskey, W.K.; Jenkins, C.; Selzer, F.; Marroquin, O.C.; Wilensky, R.L.; Glaser, R.; Holmes, D.R., Jr.; Cohen, H.A. Volume-to-Creatinine Clearance Ratio: A Pharmacokinetically Based Risk Factor for Prediction of Early Creatinine Increase After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freeman, R.V.; O’Donnell, M.; Share, D.; Meengs, W.L.; Kline-Rogers, E.; Clark, V.L.; DeFranco, A.C.; Eagle, K.A.; McGinnity, J.; Patel, K.; et al. Nephropathy requiring dialysis after percutaneous coronary intervention and the critical role of an adjusted contrast dose. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 90, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, R.; Aymong, E.D.; Nikolsky, E.; Lasic, Z.; Iakovou, I.; Fahy, M.; Mintz, G.S.; Lansky, A.J.; Moses, J.W.; Stone, G.W. A simple risk score for prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention: Development and initial validation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, N.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Jin, D.; Cong, H. Risk Score for the Prediction of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Elderly Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Angiology 2012, 64, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, V.E.; Campos, C.M.; Bacelar, A.; Abizaid, A.A.; Mangione, J.A.; Lemos, P.A.; Esteves, V.; Caramori, P.; Sampaio, R.O.; Tarasoutchi, F.; et al. Performance of Prediction Models for Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury after Transcutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement. Cardiorenal Med. 2021, 11, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, M.; Hasan, W.; Andreas, M.; Winkler, B.; Weiss, G.; Adlbrecht, C.; Delle-Karth, G.; Grabenwöger, M. Evaluating the Association between Contrast Medium Dosage and Acute Kidney Injury in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using Different Pre-dictive Models. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VARC-3 Writing Committee; Généreux, P.; Piazza, N.; Alu, M.C.; Nazif, T.; Hahn, R.T.; Pibarot, P.; Bax, J.J.; Leipsic, J.A.; Blanke, P.; et al. Valve Academic Research Consortium 3: Updated endpoint definitions for aortic valve clinical research. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1825–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.; Castro, A.F., III; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration). A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group Members. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamo, M.; Provini, M.; Fiorina, C.; Giannini, C.; Angelillis, M.; Testa, L.; Barbanti, M.; Merlanti, B.; Poli, A.; Ferrara, E.; et al. Interaction between severe chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury in predicting mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Insights from the Italian Clinical Service Project. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 96, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur, R.; Webb, J.G.; Nietlispach, F.; Dumont, E.; De Larochellière, R.; Doyle, D.; Masson, J.-B.; Gutiérrez, M.J.; Clavel, M.-A.; Bertrand, O.F.; et al. Acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Predictive factors, prognostic value, and comparison with surgical aortic valve replacement. Eur. Hear. J. 2010, 31, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nuis, R.-J.M.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Tzikas, A.; Piazza, N.; Otten, A.M.; Cheng, J.; van Domburg, R.T.; Betjes, M.; Serruys, P.W.; De Jaegere, P.P. Frequency, determinants, and prognostic effects of acute kidney injury and red blood cell transfusion in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2011, 77, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyxaras, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Wolf, A.; Schmitz, T.; Naber, C.K. Effect of Varying Definitions of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury and Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction on One-Year Mortality in Patients Having Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Morice, M.; O’Connor, S.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Leguerrier, A.; Leprince, P.; Laskar, M.; Iung, B.; Fajadet, J.; et al. Impact of pre- and post-procedural anemia on the incidence of acute kidney injury and 1-year mortality in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (from the French Aortic National CoreValve and Edwards 2 [FRANCE 2] Registry). Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 85, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, P.; Mezue, K.; Pressman, G.; Rangaswami, J. Acute kidney injury post-transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Clin. Cardiol. 2017, 40, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uygur, B.; Celik, O.; Demir, A.R.; Sahin, A.A.; Guner, A.; Avci, Y.; Bulut, U.; Tasbulak, O.; Demirci, G.; Uzun, F.; et al. A simplified acute kidney injury predictor following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: The ACEF score. Kardiol. Pol. 2021, 79, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivkovic, N.; Elbaz-Greener, G.; Qiu, F.; Arbel, Y.; Cheema, A.N.; Dvir, D.; Fefer, P.; Finkelstein, A.; Fremes, S.E.; Radhakrishnan, S.; et al. Bedside risk score for prediction of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.S.; Khalatbari, S.; Cohan, R.H.; Dillman, J.R.; Myles, J.D.; Ellis, J.H. Contrast material-induced nephrotoxicity and in-travenous low-osmolality iodinated contrast material: Risk stratification by using estimated glomerular filtration rate. Radiology 2013, 268, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Carter, R.E.; Katzberg, R.W.; Kallmes, D.F.; Williamson, E.E. Risk of intravenous contrast material-mediated acute kidney injury: A propensity score-matched study stratified by baseline-estimated glomerular filtration rate. Radiology 2014, 271, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aycock, R.D.; Westafer, L.M.; Boxen, J.L.; Majlesi, N.; Schoenfeld, E.M.; Bannuru, R.R. Acute Kidney Injury After Computed Tomography: A Meta-analysis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2018, 71, 44–53.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.S.; Perazella, M.A.; Yee, J.; Dillman, J.R.; Fine, D.; McDonald, R.J.; Rodby, R.A.; Wang, C.L.; Weinreb, J.C. Use of Intravenous Iodinated Contrast Media in Patients with Kidney Disease: Consensus Statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schönenberger, E.; Martus, P.; Bosserdt, M.; Zimmermann, E.; Tauber, R.; Laule, M.; Dewey, M. Kidney Injury after Intravenous versus Intra-arterial Contrast Agent in Patients Suspected of Having Coronary Artery Disease: A Randomized Trial. Radiology 2019, 292, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moideen, A.; Sajgure, A.; Dighe, T.; Bale, C. Sun-001 A Comparative Study on The Incidence of Contrast Induced Nephropathy and Its Risk Factors Following Intra-Arterial Versus Intravenous Contrast Administration. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, S205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, J.S.; Leake, C.B.; McDonald, R.J.; Gulati, R.; Katzberg, R.W.; Williamson, E.E.; Kallmes, D.F. Acute kidney injury after intra-venous versus intra-Arterial contrast material administration in a paired cohort. Investig. Radiol. 2016, 51, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhury, P.; Armanyous, S.; Harb, S.C.; Provenzano, L.F.; Ashour, T.; Jolly, S.E.; Arrigain, S.; Konig, V.; Schold, J.D.; Navaneethan, S.D.; et al. Intra-Arterial versus Intravenous Contrast and Renal Injury in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Propensity-Matched Analysis. Nephron Karger Publ. 2019, 141, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, U.; Almén, T.; Jacobsson, B.; Aspelin, P. Are intravenous injections of contrast media really less nephrotoxic than in-tra-arterial injections? Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, K. Evaluation of iodine contrast-induced acute kidney injury via different injection routes using BOLD-MRI. Ren Fail Taylor Fr. 2019, 41, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, S.W.; Barrett, B.J.; Parfrey, P.S. Contrast nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2000, 11, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangas, G.; Iakovou, I.; Nikolsky, E.; Aymong, E.D.; Mintz, G.S.; Kipshidze, N.N.; Lansky, A.J.; Moussa, I.; Stone, G.W.; Moses, J.W.; et al. Contrast-Induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary interventions in relation to chronic kidney disease and hemodynamic variables. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A.; Wolyn, R.; Rocher, L.L.; Levin, R.N.; O’Neill, W.W. Acute Renal Failure After Coronary Intervention: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Relationship to Mortality. Am. J. Med. 1997, 103, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihal, C.S.; Textor, S.C.; Grill, D.E.; Berger, P.B.; Ting, H.H.; Best, P.J.; Singh, M.; Bell, M.R.; Barsness, G.W.; Mathew, V.; et al. Incidence and Prognostic Importance of Acute Renal Failure After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Circulation 2002, 105, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Wahab, M.; Zahn, R.; Horack, M.; Gerckens, U.; Schuler, G.; Sievert, H.; Naber, C.; Voehringer, M.; Schäfer, U.; Senges, J.; et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with and without concomitant coronary artery disease: Comparison of characteristics and early outcome in the German multicenter TAVI registry. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2012, 101, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.T.; Pibarot, P.; Stewart, W.J.; Weissman, N.J.; Gopalakrishnan, D.; Keane, M.G.; Anwaruddin, S.; Wang, Z.; Bilsker, M.; Lindman, B.R.; et al. Comparison of transcatheter and surgical aortic valve replacement in severe aortic stenosis: A longitudinal study of echocardiog-raphy parameters in cohort A of the PARTNER trial (placement of aortic transcatheter valves). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 2514–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michail, M.; Hughes, A.; Comella, A.; Cameron, J.; Gooley, R.P.; McCormick, L.M.; Mathur, A.; Parker, K.H.; Brown, A.J. Acute Effects of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement on Central Aortic Hemodynamics in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjan, V.Y.; Herrmann, H.C.; Pibarot, P.; Stewart, W.J.; Kapadia, S.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Babaliaros, V.; Thourani, V.H.; Szeto, W.Y.; Bavaria, J.E.; et al. Evaluation of Flow After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Re-placement in Patients with Low-Flow Aortic Stenosis: A Secondary Analysis of the PARTNER Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kliuk-Ben Bassat, O.; Sadon, S.; Sirota, S.; Steinvil, A.; Konigstein, M.; Halkin, A.; Bazan, S.; Grupper, A.; Banai, S.; Finkelstein, A.; et al. Assessment of Kidney Function After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsky, D.; Naami, R.; Shehadeh, F.; Elias, A.; Kerner, A.; Aronson, D. Risk of Worsening Renal Function Following Repeated Exposures to Contrast Media During Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2021, 10, e021473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, M.; Castelvecchio, S.; Menicanti, L.; Frigiola, A.; Pelissero, G. Reply to Letters Regarding Article, “Risk of Assessing Mortality Risk in Elective Cardiac Operations: Age, Creatinine, Ejection Fraction, and the Law of Parsimony”. Circulation 2010, 121, e227–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cigarroa, R.G.; Lange, R.A.; Williams, R.H.; Hillis, D. Dosing of contrast material to prevent contrast nephropathy in patients with renal disease. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denegri, A.; Mehran, R.; Holy, E.; Taramasso, M.; Pasotti, E.; Pedrazzini, G.; Moccetti, T.; Maisano, F.; Nietlispach, F.; Obeid, S. Post procedural risk assessment in patients undergoing trans aortic valve implantation according to the age, creatinine, and ejection fraction-7 score: Advantages of age, creatinine, and ejection fraction-7 in stratification of post-procedural outcome. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AKI (−) (n = 172) | AKI (+) (n = 38) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical data | Age; Years | 79 ± 7.9 | 81.8 ± 8.2 | 0.1 | |
| Female; n (%) | 97 (56.4) | 21 (55.3) | 0.9 | ||
| Body mass index; (kg/m2) | 28.92 ± 5.17 | 28.2 ± 5.97 | 0.46 | ||
| Hypertension; n (%) | 151 (87.8) | 34 (89.5) | 0.77 | ||
| Dyslipidemia; n (%) | 133 (77.3) | 23 (60.5) | 0.032 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus; n (%) | 76 (44.2) | 20 (52.6) | 0.34 | ||
| Smoking history; n (%) | 26 (15.1) | 6 (15.8) | 0.92 | ||
| Cardio-vascular disease; n (%) | 96 (55.8) | 23 (60.5) | 0.596 | ||
| Coronary artery disease; n (%) | 91 (52.9) | 23 (60.5) | 0.728 | ||
| Peripheral arterial disease; n (%) | 19 (11) | 7 (18.4) | 0.211 | ||
| Past PCI; n (%) | 70 (40.4) | 15 (41.7) | 0.98 | ||
| Past CABG; n (%) | 20 (11.6) | 3 (7.9) | 0.51 | ||
| Past CVA/TIA; n (%) | 12 (7) | 7 (18.4) | 0.026 | ||
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; n (%) | 22 (12.8) | 8 (21.1) | 0.19 | ||
| Atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter; n (%) | 43 (25) | 15 (39.5) | 0.071 | ||
| Pacemaker/CRT/ICD; n (%) | 23 (13.4) | 4 (10.5) | 0.64 | ||
| NYHA functional class; n (%) | 1 | 5 (2.9) | 1 (2.6) | 0.727 | |
| 2 | 133 (77.3) | 29 (76.3) | |||
| ≥3 | 8 (4.7) | 3 (7.9) | |||
| Urgent TAVI; n (%) | 40 (23.4) | 10 (26.3) | 0.7 | ||
| Surgical risk | STS, mortality; % | 3.79 ± 2.37 | 4.91 ± 2.27 | 0.009 | |
| EuroScore II; % | 3.83 ± 3.71 | 4.7 ± 3.48 | 0.22 | ||
| Laboratory data | Hemoglobin; g/dL | 11.55 ± 1.71 | 10.77 ± 1.4 | 0.01 | |
| Creatinine; mg/dL | 1.07 ± 0.48 | 1.35 ± 0.58 | 0.002 | ||
| eGFR; mL/min/1.73 m2 | 64.5 ± 19 | 51 ± 19.3 | <0.001 | ||
| CKD category; n (%) | 1–2 | 109 (63.4) | 15 (39.5) | <0.001 | |
| 3a–3b | 54 (31.4) | 17 (44.7) | |||
| ≥4 | 9 (5.2) | 6 (15.8) | |||
| Echo- cardiography data | Left ventricle ejection fraction; % | 58 ± 10.5 | 58 ± 11.1 | 0.917 | |
| Aortic valve area; cm2, | 0.77 ± 0.16 | 0.82 ± 0.19 | 0.166 | ||
| Aortic valve area index; cm2/m2 | 0.43 ± 0.07 | 0.46 ± 0.06 | 0.081 | ||
| Aortic valve mean pressure gradient; mmHg | 43 ± 12 | 41 ± 14.8 | 0.58 | ||
| Severe mitral regurgitation; n (%) | 11 (6.9) | 3 (8.1) | 0.737 | ||
| Severe tricuspid regurgitation; n (%) | 6 (4) | 1 (2.7) | 0.79 | ||
| Severe pulmonary hypertension; n (%) | 14 (9.5) | 4 (11.4) | 0.634 | ||
| Procedural data | Trans-femoral access; n (%) | 170 (98.8) | 38 (100) | 0.99 | |
| THV type; n (%) | Evolut-R™ (Medtronic) | 124 (72.5) | 27 (71.1) | 0.676 | |
| SAPIEN-3™ (Edwards Lifesciences) | 28 (16.4) | 5 (13.2) | |||
| ACURATE-Neo™ (Boston Scientific) | 19 (11.1) | 6 (15.8) | |||
| Anesthesia Type; n (%) | General anesthesia | 72 (51.4) | 16 (48.5) | 0.12 | |
| Local anesthesia with sedation | 68 (48.6) | 17 (51.5) | |||
| AKI (−) (n = 172) | AKI (+) (n = 38) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine; mg/dL | Highest (In-hospital) | 1.08 ± 0.31 | 2 ± 1 | <0.001 |
| 30-day | 1.12 ± 0.42 | 1.45 ± 0.55 | 0.011 | |
| 12-month | 1.21 ± 0.5 | 2 ± 1 | 0.014 | |
| eGFR; mL/min/1.73 m2 | Lowest (In-hospital) | 62 ± 20 | 27 ± 12 | <0.001 |
| 30-day | 60.9 ± 20.6 | 44.9 ± 19.2 | 0.005 | |
| 12-month | 58.4 ± 21.3 | 44 ± 20.9 | 0.035 | |
| Within 30 Days | Within 7 Days | During TAVI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKI (−) (n = 38) | AKI (+) (n = 172) | p Value | AKI (−) (n = 38) | AKI (+) (n = 172) | p Value | AKI (−) (n = 38) | AKI (+) (n = 172) | p Value | |
| CM volume; mL | 319 ± 92 | 320 ± 105 | 0.97 | 246 ± 89 | 259 ± 111 | 0.54 | 187 ± 53 | 201 ± 83 | 0.316 |
| CM volume prior to TAVI; mL | 133 ± 74 | 119 ± 65 | 0.41 | 59 ± 73 | 58 ± 71 | 0.93 | NR | NR | NR |
| Mehran score | 13.52 ± 4.15 | 16.07 ± 3.63 | 0.004 | 12.76 ± 4.06 | 15.46 ± 3.73 | 0.025 | 12.2 ± 4.05 | 14.72 ± 3.75 | 0.004 |
| Modified Mehran score ^ | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 10.33 ± 3.97 | 12.87 ± 3.87 | 0.004 |
| CR4EATME3AD3 | 10.09 ± 3.88 | 12.03 ± 3.75 | 0.007 | 9.56 ± 3.87 | 11.55 ± 3.63 | 0.004 | 9.09 ± 3.87 | 11.13 ± 3.78 | 0.004 |
| Modified CR4EATME3AD ^ | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 8.45 ± 3.81 | 10.45 ± 3.85 | 0.006 |
| (CM × SCr)/BMI | 11.83 ± 6.27 | 15.52 ± 9.8 | 0.004 | 9.1 ± 5.25 | 12.36 ± 9.78 | 0.005 | 7.02 ± 4.29 | 9.33 ± 5.6 | 0.005 |
| (CM × SCr)/BW | 4.5 ± 2.41 | 5.85 ± 3.44 | 0.005 | 3.48 ± 2.04 | 4.69 ± 3.48 | 0.005 | 2.66 ± 1.61 | 3.58 ± 2.13 | 0.004 |
| CM/CrCl | 5.45 ± 2.66 | 7.04 ± 3.6 | 0.002 | 4.18 ± 2.25 | 5.71 ± 3.56 | <0.001 | 3.24 ± 1.95 | 4.41 ± 2.56 | 0.002 |
| n = 210 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | ||
| eGFR reduction by 1 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 1.036 | 1.017–1.056 | <0.001 | |
| eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 4.14 | 1.93–8.9 | 0.003 | |
| Hemoglobin reduction by 1 g/dL | 1.33 | 1.06–1.66 | 0.013 | |
| STS score for mortality | 1.0387 | 1.009–1.069 | 0.009 | |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1.4 | 0.694–2.835 | 0.345 | |
| Hypertension | 1.18 | 0.381–3.66 | 0.772 | |
| Body mass index | 0.974 | 0.91–1.04 | 0.458 | |
| Gender | 0.955 | 0.471–1.936 | 0.9 | |
| Age | 1.041 | 0.992–1.094 | 0.1 | |
| Left ventricle ejection fraction | 0.998 | 0.965–1.032 | 0.917 | |
| NYHA functional class | 1.252 | 0.474–3.303 | 0.65 | |
| Coronary artery disease | 1.836 | 0.881–3.824 | 0.105 | |
| Peripheral arterial disease | 1.818 | 0.704–4.695 | 0.217 | |
| Within 30 Days | CM volume | 1.001 | 0.997–1.003 | 0.971 |
| CM/CrCl | 1.182 | 1.058–1.321 | 0.004 | |
| (CM × Scr)/BMI | 1.062 | 1.014–1.113 | 0.011 | |
| (CM × Scr)/BW | 1.169 | 1.036–1.139 | 0.012 | |
| Mehran Score | 1.109 | 1.03–1.195 | 0.006 | |
| CR4EATME3AD3 score | 1.137 | 1.035–1.249 | 0.007 | |
| Within 7 Days | Volume of CM | 1.009 | 0.998–1.004 | 0.538 |
| CM/CrCl | 1.216 | 1.073–1.379 | 0.002 | |
| (CM × Scr)/BMI | 1.069 | 1.012–1.128 | 0.017 | |
| (CM × Scr)/BW | 1.19 | 1.036–1.367 | 0.014 | |
| Mehran Score | 1.118 | 1.037–1.205 | 0.004 | |
| CR4EATME3AD3 score | 1.146 | 1.041–1.262 | 0.005 | |
| TAVI | Volume of CM | 1.002 | 0.998–1.007 | 0.295 |
| CM/CrCl | 1.237 | 1.069–1.43 | 0.004 | |
| (CM × SCr)/BMI | 1.092 | 1.021–1.167 | <0.001 | |
| (CM × SCr)/BW | 1.275 | 1.069–1.521 | 0.007 | |
| Mehran Score | 1.102 | 1.013–1.2 | 0.025 | |
| CR4EATME3AD3 score | 1.147 | 1.043–1.261 | 0.005 | |
| Modified Mehran score ^ | 1.11 | 1.028–1.199 | 0.008 | |
| Modified CR4EATME3AD3 score ^ | 1.146 | 1.041–1.261 | 0.005 | |
| STS Score | Hemoglobin | eGFR ≤ 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | ||
| Within 30 Days | Mehran risk score | 1.02 (0.93–1.12) | 0.63 | 1.1 (0.94–1.29) | 0.24 | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | 0.165 | 2.67 (1.1–6.5) | 0.03 |
| CR4EATME3AD3 | 1.04 (0.92–1.17) | 0.514 | 1.08 (0.92–1.27) | 0.355 | 0.84 (0.65–1.08) | 0.168 | 2.5 (1.01–6.28) | 0.049 | |
| CM/CrCl | 1.05 (0.9–1.26) | 0.539 | 1.08 (0.91–1.27) | 0.345 | 0.83 (0.64–1.06) | 0.137 | 2.35 (0.85–6.49) | 0.099 | |
| (CM× SCr)/BMI | 1.02 (0.97–1.08) | 0.397 | 1.09 (0.92–1.29) | 0.302 | 0.84 (0.65–1.08) | 0.163 | 2.48 (0.99–6.19) | 0.053 | |
| (CM × SCr)/BW | 1.04 (0.91–1.2) | 0.548 | 1.09 (0.92–1.28) | 0.328 | 0.84 (0.65–1.08) | 0.163 | 2.61 (1.04–6.56) | 0.041 | |
| Within 7 Days | Mehran risk score | 1.03 (0.94–1.13) | 0.518 | 1.07 (0.91–1.26) | 0.41 | 0.84 (0.65–1.09) | 0.194 | 2.62 (1.07–6.39) | 0.034 |
| CR4EATME3AD3 | 1.05 (0.93–1.18) | 0.417 | 1.08 (0.92–1.27) | 0.364 | 0.84 (0.65–1.08) | 0.17 | 2.46 (0.98–6.15) | 0.054 | |
| CM/CrCl | 1.01 (0.94–1.28) | 0.216 | 1.08 (0.91–1.27) | 0.364 | 0.83 (0.64–1.06) | 0.123 | 2.15 (0.8–5.7) | 0.125 | |
| (CM × SCr)/BMI | 1.02 (0.97–1.09) | 0.313 | 1.09 (0.92–1.28) | 0.323 | 0.83 (0.64–1.07) | 0.151 | 2.44 (1.0–6.1) | 0.049 | |
| (CM × SCr)/BW | 1.07 (0.92–1.24) | 0.377 | 1.08 (0.92–1.28) | 0.361 | 0.83 (0.64–1.07) | 0.15 | 2.54 (1.03–6.28) | 0.044 | |
| TAVI | Mehran risk score | 1.02 (0.92–1.12) | 0.761 | 1.1 (0.94–1.29) | 0.228 | 0.83 (0.64–1.08) | 0.173 | 2.76 (1.11–6.82) | 0.028 |
| CR4EATME3AD3 | 1.05 (0.93–1.18) | 0.429 | 1.08 (0.92–1.26) | 0.357 | 0.84 (0.65–1.08) | 0.175 | 2.46 (0.98–6.19) | 0.054 | |
| CM/CrCl | 1.08 (0.89–1.31) | 0.43 | 1.09 (0.92–1.28) | 0.309 | 0.83 (0.64–1.06) | 0.134 | 2.39 (0.85–6.7) | 0.1 | |
| (CM × SCr)/BMI | 1.03 (0.97–1.12) | 0.406 | 1.1 (0.93–1.29) | 0.262 | 0.83 (0.65–1.07) | 0.156 | 2.48 (0.93–6.45) | 0.07 | |
| (CM × SCr)/BW | 1.09 (0.88–1.35) | 0.414 | 1.09 (0.93–1.29) | 0.287 | 0.83 (0.64–1.07) | 0.159 | 2.47 (0.94–6.55) | 0.067 | |
| Modif-ied ^ | Mehran risk score | 1.00 (0.91–1.11) | 0.888 | 1.08 (0.92–1.27) | 0.373 | 0.83 (0.64–1.08) | 0.161 | 2.8 (1.13–6.93) | 0.026 |
| CR4EATME3AD3 | 1.03 (0.91–1.17) | 0.62 | 1.08 (0.92–1.26) | 0.362 | 0.83 (0.65–1.08) | 0.163 | 2.55 (1.0–6.11) | 0.051 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sudarsky, D.; Drutin, Y.; Kusniec, F.; Grosman-Rimon, L.; Lubovich, A.; Kinany, W.; Hazanov, E.; Gelbstein, M.; Birati, E.Y.; Marai, I. Acute Kidney Injury Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Association with Contrast Media Dosage and Contrast Media Based Risk Predication Models. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051181
Sudarsky D, Drutin Y, Kusniec F, Grosman-Rimon L, Lubovich A, Kinany W, Hazanov E, Gelbstein M, Birati EY, Marai I. Acute Kidney Injury Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Association with Contrast Media Dosage and Contrast Media Based Risk Predication Models. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(5):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051181
Chicago/Turabian StyleSudarsky, Doron, Yarden Drutin, Fabio Kusniec, Liza Grosman-Rimon, Ala Lubovich, Wadia Kinany, Evgeni Hazanov, Michael Gelbstein, Edo Y. Birati, and Ibrahim Marai. 2022. "Acute Kidney Injury Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Association with Contrast Media Dosage and Contrast Media Based Risk Predication Models" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 5: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051181
APA StyleSudarsky, D., Drutin, Y., Kusniec, F., Grosman-Rimon, L., Lubovich, A., Kinany, W., Hazanov, E., Gelbstein, M., Birati, E. Y., & Marai, I. (2022). Acute Kidney Injury Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Association with Contrast Media Dosage and Contrast Media Based Risk Predication Models. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(5), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051181






