Formulations of Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—Current Treatment and Emerging Possibilities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
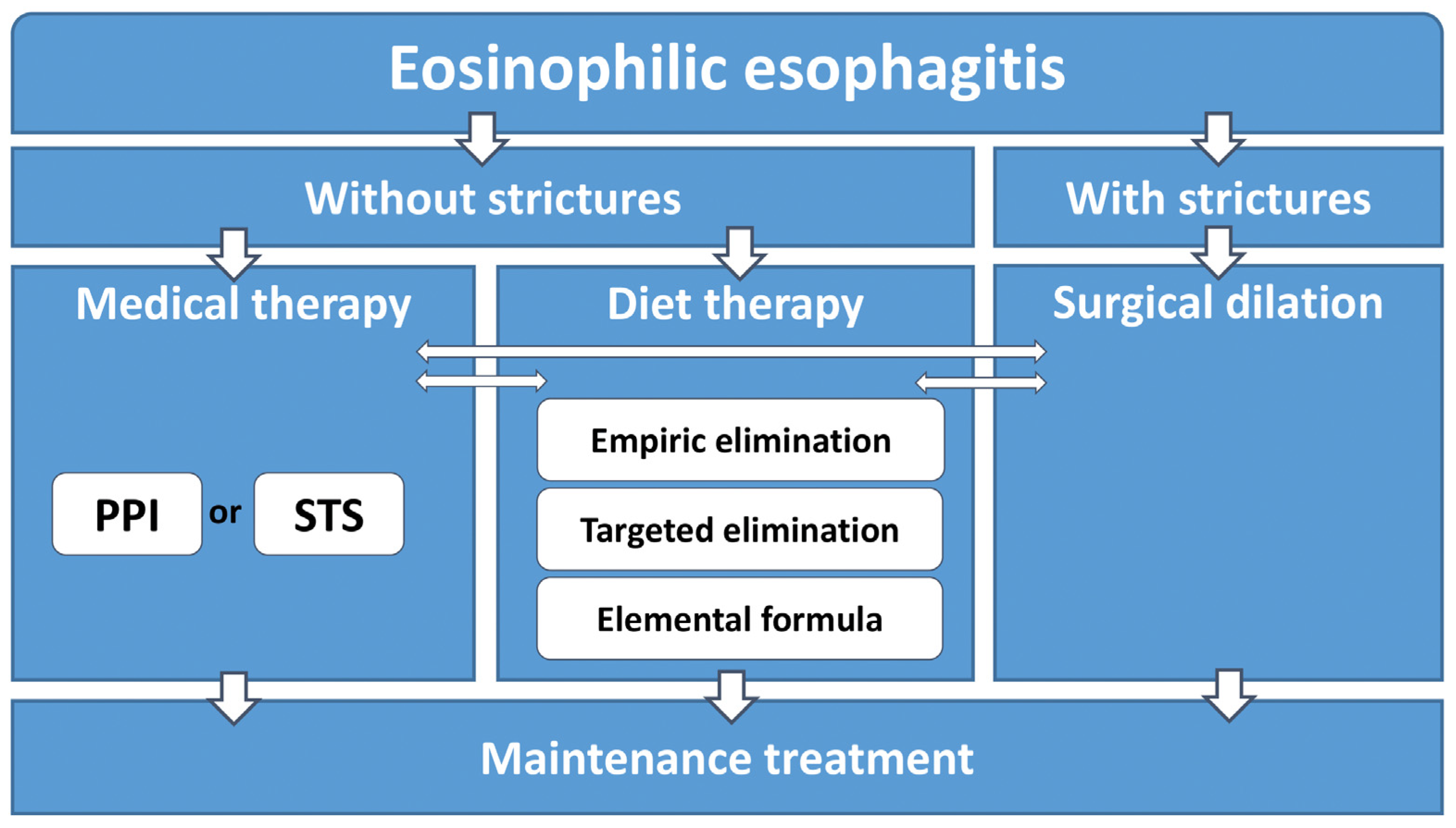
2. General Treatment Recommendations for EoE
3. Mechanism of Activity and Effectiveness of Swallowed Topical Steroids
4. STS Formulations
4.1. Budesonide
- Oral viscous budesonide (OVB)
- 2.
- Nebulised budesonide
- 3.
- Orodispersible tablets
4.2. Fluticasone
- 4.
- Fluticasone metered-dose inhaler (MDI)
- 5.
- Fluticasone powder
- 6.
- Oral viscous fluticasone
- 7.
- Orally disintegrating tablets
4.3. Mometasone
4.4. Ciclesonide
4.5. Beclomethasone
5. Emerging Delivery Methods
5.1. EsoCap System
5.2. Fluticasone-Eluting String and Fluticasone-Eluting 3D Printed Ring
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Amil Dias, J.; Bove, M.; González-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarro, P.; Arias, Á.; Arias-González, L.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Ruiz-Ponce, M.; Lucendo, A.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The growing incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Mukkada, V.; Eichinger, C.S.; Schofield, H.; Todorova, L.; Falk, G.W. Natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review of epidemiology and disease course. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, doy015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Liacouras, C.A.; Molina-Infante, J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Zevit, N.; Spechler, S.J.; Attwood, S.E.; Straumann, A.; Aceves, S.S.; et al. Updated international consensus diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1022–1033.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dellon, E.S.; Hirano, I. Epidemiology and natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 319–332.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, Á.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Tenías, J.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Safroneeva, E.; Bussmann, C.; Kuchen, T.; Portmann, S.; Simon, H.; Straumann, A. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1230–1236.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirano, I.; Chan, E.S.; Rank, M.A.; Sharaf, R.N.; Stollman, N.H.; Stukus, D.R.; Wang, K.; Greenhawt, M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Chachu, K.A.; et al. AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Casabona, S.; Savarino, E.; Perelló, A.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Guagnozzi, D.; Barrio, J.; Guardiola, A.; Asensio, T.; de la Riva, S.; et al. Efficacy of therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in real-world practice. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2903–2911.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, E.T.; Fitzgerald, J.F.; Molleston, J.P.; Croffie, J.M.; Pfefferkorn, M.D.; Corkins, M.R.; Lim, J.D.; Steiner, S.J.; Gupta, S.K. Comparison of oral prednisone and topical fluticasone in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: A randomized trial in children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofien, A.; Rea, F.; do Céu Espinheira, M.; Amil Dias, J.; Romano, C.; Oliva, S.; Auth, M.K.-H.; Zangen, T.; Kalach, N.; Domínguez-Ortega, G.; et al. Systemic steroids have a role in treating esophageal strictures in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Casabona, S.; Guagnozzi, D.; Savarino, E.; Perelló, A.; Guardiola-Arévalo, A.; Barrio, J.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Lund Krarup, A.; Alcedo, J.; et al. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor therapy for eosinophilic oesophagitis in 630 patients: Results from the EoE Connect Registry. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safroneeva, E.; Hafner, D.; Kuehni, C.E.; Zwahlen, M.; Trelle, S.; Biedermann, L.; Greuter, T.; Vavricka, S.R.; Straumann, A.; Schoepfer, A.M. Systematic assessment of adult patients’ satisfaction with various eosinophilic esophagitis therapies. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, Á.; González-Cervera, J.; Tenias, J.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Efficacy of dietary interventions for inducing histologic remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J. Meta-analysis-based guidance for dietary management in eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashaw, H.; Schwartz, S.; Kagalwalla, A.F.; Wechsler, J.B. Tutorial: Nutrition therapy in eosinophilic esophagitis—Outcomes and deficiencies. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; Alcedo, J.; Garcia-Romero, R.; Casabona-Frances, S.; Prieto-Garcia, A.; Modolell, I.; Gonzalez-Cordero, P.L.; Perez-Martinez, I.; Martin-Lorente, J.L.; et al. Step-up empiric elimination diet for pediatric and adult eosinophilic esophagitis: The 2–4–6 study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Lucendo, A.J. Eosinophilic esophagitis: A practical approach to diagnosis and management. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 8, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eluri, S.; Tappata, M.; Huang, K.Z.; Koutlas, N.T.; Robey, B.S.; Fan, C.; Reed, C.C.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. Distal esophagus is the most commonly involved site for strictures in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2020, 33, doz088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Runge, T.M.; Eluri, S.; Cotton, C.C.; Burk, C.M.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. Outcomes of esophageal dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: Safety, efficacy, and persistence of the fibrostenotic phenotype. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saligram, S.; McGrath, K. The safety of a strict wire-guided dilation protocol for eosinophilic esophagitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Gonsalves, N.; Bussmann, C.; Conus, S.; Simon, H.-U.; Straumann, A.; Hirano, I. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: Effectiveness, safety, and impact on the underlying inflammation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommel, K.A.; Franciosi, J.P.; Hente, E.A.; Ahrens, A.; Rothenberg, M.E. Treatment adherence in pediatric eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2012, 37, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hommel, K.A.; Franciosi, J.P.; Gray, W.N.; Hente, E.A.; Ahrens, A.; Rothenberg, M.E. behavioral functioning and treatment adherence in pediatric eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 23, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.; Beukema, K.R.; Shen, A.H. Allergic mechanisms of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 29, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straumann, A.; Spichtin, H.; Grize, L.; Bucher, K.A.; Beglinger, C.; Simon, H. Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: A follow-up of 30 adult patients for up to 11.5 years. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves, S.S.; Newbury, R.O.; Chen, D.; Mueller, J.; Dohil, R.; Hoffman, H.; Bastian, J.F.; Broide, D.H. Resolution of remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis correlates with epithelial response to topical corticosteroids: Resolution of esophageal remodeling in children. Allergy 2010, 65, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajan, J.; Newbury, R.O.; Anilkumar, A.; Dohil, R.; Broide, D.H.; Aceves, S.S. Long-term assessment of esophageal remodeling in patients with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis treated with topical corticosteroids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 147–156.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, C.; Mingler, M.K.; Vicario, M.; Abonia, J.P.; Wu, Y.Y.; Lu, T.X.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Wells, S.I.; Rothenberg, M.E. IL-13 involvement in eosinophilic esophagitis: Transcriptome analysis and reversibility with glucocorticoids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Degen, L.; Felder, S.; Kummer, M.; Engel, H.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.; Simon, U. Budesonide is effective in adolescent and adult patients with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1526–1537.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzka, D.A.; Tadi, R.; Smyrk, T.C.; Katarya, E.; Sharma, A.; Geno, D.M.; Camilleri, M.; Iyer, P.G.; Alexander, J.A.; Buttar, N.S. Effects of topical steroids on tight junction proteins and spongiosis in esophageal epithelia of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1824–1829.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatman, K.S.H.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I.; Bryce, P.J. Expression of mast cell–associated genes is upregulated in adult eosinophilic esophagitis and responds to steroid or dietary therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1307–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faubion, W.A.; Perrault, J.; Burgart, L.J.; Zein, N.N.; Clawson, M.; Freese, D.K. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with inhaled corticosteroids. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 27, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawas, T.; Dhalla, S.; Sayyar, M.; Pasricha, P.J.; Hernaez, R. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Pharmacological interventions for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.D.; Xiao, Y.L.; Chen, M.H. Steroids therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Thandra, K.C.; Gaduputi, V. Efficacy and safety of budesonide in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: Updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized studies. Drugs RD 2018, 18, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomizawa, Y.; Melek, J.; Komaki, Y.; Kavitt, R.T.; Sakuraba, A. Efficacy of pharmacologic therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, D.; Heifert, T.A.; Min, S.B.; Maydonovitch, C.L.; Baker, T.P.; Chen, Y.-J.; Moawad, F.J. Comparisons of fluticasone to budesonide in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fable, J.M.; Fernandez, M.; Goodine, S.; Lerer, T.; Sayej, W.N. Retrospective comparison of fluticasone propionate and oral viscous budesonide in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchen, T.; Straumann, A.; Safroneeva, E.; Romero, Y.; Bussmann, C.; Vavricka, S.; Netzer, P.; Reinhard, A.; Portmann, S.; Schoepfer, A.M. Swallowed topical corticosteroids reduce the risk for long-lasting bolus impactions in eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy 2014, 69, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.A.; Halland, M. Oesophageal lichen planus: The efficacy of topical steroid-based therapies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golekoh, M.C.; Hornung, L.N.; Mukkada, V.A.; Khoury, J.C.; Putnam, P.E.; Backeljauw, P.F. Adrenal insufficiency after chronic swallowed glucocorticoid therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. 2016, 170, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harel, S.; Hursh, B.E.; Chan, E.S.; Avinashi, V.; Panagiotopoulos, C. Adrenal suppression in children treated with oral viscous budesonide for eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Woosley, J.T.; Arrington, A.; McGee, S.J.; Covington, J.; Moist, S.E.; Gebhart, J.H.; Tylicki, A.E.; Shoyoye, S.O.; Martin, C.F.; et al. Efficacy of budesonide vs. fluticasone for initial treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 65–73.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzaki, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Okura, Y.; Nozaka, T.; Yauchi, M.; Watabe, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Furumoto, Y.; Horiuchi, T.; et al. A case of cytomegalovirus esophagitis during topical steroid therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Sheikh, A.; Speck, O.; Woodward, K.; Whitlow, A.B.; Hores, J.M.; Ivanovic, M.; Chau, A.; Woosley, J.T.; Madanick, R.D.; et al. Viscous topical is more effective than nebulized steroid therapy for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 321–324.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comer, G.M.; Bush, M.A.; Dellon, E.S.; Marino, M.T. Effect of food intake and body position on the pharmacokinetics of swallowed APT-1011, a fluticasone orally disintegrating tablet, in healthy adult volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 60, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, E.; Hait, E.E.; Mitchell, P.D.; Lee, J.J. Every-other-day dosing of oral viscous budesonide is not effective in the management of eosinophlic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohil, R.; Newbury, R.; Fox, L.; Bastian, J.; Aceves, S. oral viscous budesonide is effective in children with eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 418–429.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, B.A.; Roberts, A.; Nestmann, E.R. critical review of the current literature on the safety of sucralose. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 324–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, G.A.; Borghoff, S.J.; Pham, L.L.; Doepker, C.L.; Wikoff, D.S. Lack of potential carcinogenicity for sucralose—Systematic evaluation and integration of mechanistic data into the totality of the evidence. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, E.; Lee, J.J.; Fried, A.; Logvinenko, T.; Ngo, P.; McDonald, D.; Hait, E.J. Comparison of 2 delivery vehicles for viscous budesonide to treat eosinophilic esophagitis in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, C.C.; Fan, C.; Koutlas, N.; Stefanadis, Z.; Eluri, S.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. Compounded Oral Viscous Budesonide Is Effective And Provides a Durable Response in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 7, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, S.; Rossetti, D.; Papoff, P.; Tiberti, A.; Rossi, P.; Isoldi, S.; Amil Dias, J.; Lucarelli, S.; Cucchiara, S. A new formulation of oral viscous budesonide in treating paediatric eosinophilic oesophagitis: A pilot study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shuker, M.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.; Cianferoni, A.; Gober, L.; Muir, A.; Verma, R.; Liacouras, C.; Spergel, J.M. Oral viscous budesonide can be successfully delivered through a variety of vehicles to treat eosinophilic esophagitis in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehlke, S.; Hruz, P.; Vieth, M.; Bussmann, C.; von Arnim, U.; Bajbouj, M.; Schlag, C.; Madisch, A.; Fibbe, C.; Wittenburg, H.; et al. A randomised, double-blind trial comparing budesonide formulations and dosages for short-term treatment of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut 2016, 65, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehlke, S.; Lucendo, A.J.; Straumann, A.; Jan Bredenoord, A.; Attwood, S. Orodispersible budesonide tablets for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: A review of the latest evidence. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 175628482092728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Miehlke, S.; Schlag, C.; Vieth, M.; von Arnim, U.; Molina-Infante, J.; Hartmann, D.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Ciriza de los Rios, C.; Schubert, S.; et al. Efficacy of budesonide orodispersible tablets as induction therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 74–86.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straumann, A.; Lucendo, A.J.; Miehlke, S.; Vieth, M.; Schlag, C.; Biedermann, L.; Vaquero, C.S.; Ciriza de los Rios, C.; Schmoecker, C.; Madisch, A.; et al. Budesonide orodispersible tablets maintain remission in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1672–1685.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.A.; Jung, K.W.; Arora, A.S.; Enders, F.; Katzka, D.A.; Kephardt, G.M.; Kita, H.; Kryzer, L.A.; Romero, Y.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. Swallowed fluticasone improves histologic but not symptomatic response of adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 742–749.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, F.J.; Veerappan, G.R.; Dias, J.A.; Baker, T.P.; Maydonovitch, C.L.; Wong, R.K.H. Randomized controlled trial comparing aerosolized swallowed fluticasone to esomeprazole for esophageal eosinophilia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konikoff, M.R.; Noel, R.J.; Blanchard, C.; Kirby, C.; Jameson, S.C.; Buckmeier, B.K.; Akers, R.; Cohen, M.B.; Collins, M.H.; Assa’ad, A.H.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fluticasone propionate for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreae, D.A.; Hanna, M.G.; Magid, M.S.; Malerba, S.; Andreae, M.H.; Bagiella, E.; Chehade, M. Swallowed fluticasone propionate is an effective long-term maintenance therapy for children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sastre, J.; Mosges, R. Local and systemic safety of intranasal corticosteroids. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 22, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Kia, L.; Nelson, M.; Zalewski, A.; Gregory, D.; Gonsalves, N.; Straumann, A.; Hirano, I. Oral delivery of fluticasone powder improves esophageal eosinophilic inflammation and symptoms in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, doy098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketchem, C.J.; Reed, C.C.; Stefanadis, Z.; Dellon, E.S. Treatment with compounded fluticasone suspension improves the clinical, endoscopic, and histologic features of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2020, 30, doaa120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, I.; Safroneeva, E.; Roumet, M.C.; Comer, G.M.; Eagle, G.; Schoepfer, A.; Falk, G.W. Randomised clinical trial: The safety and tolerability of fluticasone propionate orally disintegrating tablets versus placebo for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syverson, E.P.; Hait, E.; McDonald, D.R.; Rubinstein, E.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Ngo, P.D.; Mitchell, P.D.; Lee, J.J. Oral viscous mometasone is an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1107–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, H.; Larsson, H.; Johansson, L.; Bove, M. Dysphagia and quality of life may improve with mometasone treatment in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: A pilot study. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytor, J.; Larsson, H.; Bove, M.; Johansson, L.; Bergquist, H. Topically Applied mometasone furoate improves dysphagia in adult eosinophilic esophagitis—Results from a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, S.; Fleischer, D.M.; Masterson, J.C.; Gelfand, E.; Furuta, G.T.; Atkins, D. Successful treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with ciclesonide. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.J.; Fried, A.J.; Hait, E.; Yen, E.H.; Perkins, J.M.; Rubinstein, E. Topical inhaled ciclesonide for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Ishmael, F.; Lehman, E.; Bethards, D.; Ruggiero, F.; Ghaffari, G. Effect of topical beclomethasone on inflammatory markers in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis: A pilot study. Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 8, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.K.; Vitanza, J.M.; Collins, M.H. Efficacy and safety of oral budesonide suspension in pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 66–76.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Degen, L.; Frei, C.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.; Simon, U. Long-term budesonide maintenance treatment is partially effective for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 400–409.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butz, B.K.; Wen, T.; Gleich, G.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.; King, E.; Kramer, R.E.; Collins, M.H.; Stucke, E.; Mangeot, C.; et al. Efficacy, dose reduction, and resistance to high-dose fluticasone in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 324–333.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, K.A.; Thomas, K.L.; Hilden, K.; Emerson, L.L.; Wills, J.C.; Fang, J.C. Comparison of esomeprazole to aerosolized, swallowed fluticasone for eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, A.; Gennari, C.G.; Musazzi, U.M.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Bordignon, S.; Minghetti, P. Mucoadhesive budesonide formulation for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnet, M.; Dermu, M.; Roessle, C.; Bellaiche, M.; Abarou, T.; Vasseur, V.; Benakouche, S.; Storme, T. Formulation of a 3-months stability oral viscous budesonide gel and development of an indicating stability HPLC method. Pharm. Technol. Hosp. Pharm. 2018, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hefner, J.N.; Howard, R.S.; Massey, R.; Valencia, M.; Stocker, D.J.; Philla, K.Q.; Goldman, M.D.; Nylund, C.M.; Min, S.B. A randomized controlled comparison of esophageal clearance times of oral budesonide preparations. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.; Rosenbaum, C.; Grimm, M.; Rump, A.; Keßler, R.; Hosten, N.; Weitschies, W. The EsoCap-system—An innovative platform to drug targeting in the esophagus. J. Controlled Release 2020, 327, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasher, A.; Shrivastava, R.; Dahl, D.; Sharma-Huynh, P.; Maturavongsadit, P.; Pridgen, T.; Schorzman, A.; Zamboni, W.; Ban, J.; Blikslager, A.; et al. Steroid eluting esophageal-targeted drug delivery devices for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Polymers 2021, 13, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, M. (Anthony); Chinnaratha, M.A.; Hancock, D.G.; Woodman, R.; Wong, G.R.; Cock, C.; Fraser, R.J. Topical steroid therapy for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipka, S.; Kumar, A.; Miladinovic, B.; Richter, J.E. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: Comparative effectiveness of topical steroids vs. PPIs for the treatment of the spectrum of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, A.R.; Gupta, A.; Attar, B.M.; Ravi, V.; Koduru, P. Topical steroids in eosinophilic esophagitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials: Efficacy of topical steroids in EoE. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkas, T.; Niv, Y.; Malfertheiner, P. A Network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults and children. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 55, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heer, J.; Miehlke, S.; Rösch, T.; Morgner, A.; Werner, Y.; Ehlken, H.; Becher, H.; Aigner, A. Histologic and clinical effects of different topical corticosteroids for eosinophilic esophagitis: Lessons from an updated meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized trials. Digestion 2021, 102, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug | Phase of Treatment | Children | Adults |
|---|---|---|---|
| Budesonide | Induction | 1–2 mg/day | 2–4 mg/day |
| Maintenance | 1 mg/day | 2 mg/day | |
| Fluticasone propionate | Induction | 880–1760 mcg/day | 1760 mcg/day |
| Maintenance | 440–880 mcg/day | 880–1760 mcg/day |
| Preparation Vehicle |
|---|
| sucralose (Splenda®®) |
| amino acid formula (Neocate®® Nutra) |
| Duocal®® |
| Truvia®® |
| Methocel E4M Premium (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) |
| xylitol |
| stevia |
| honey |
| Steroid | Vehicles Used | Preparation | Dose | Dosing | Period † | Response ‡ | Study Group | Study Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| budesonide | sucralose | budesonide resuples (Pulmicort) mixed with sucralose | 1–2 mg (approx. 8 mL solution) | QD | 3 months | histologic, clinical | children | randomised, placebo-controlled | [49] |
| budesonide | proprietary medication in RCT | oral viscous suspension—proprietary medication in clinical trial | 0.35–2.0 mg (7–10 mL solution) | QD or BID | 12 weeks | histologic, clinical | children | randomised, placebo-controlled | [74] |
| budesonide | proprietary medication in RCT | oral viscous suspension | 1–2 mg | BID | 2 weeks | histologic, clinical | adults | randomised, placebo-controlled | [56] |
| budesonide | sucralose | budesonide respules (Pulmicort) mixed with 5 mg of sucralose | 1 mg | BID | 8 weeks | histologic, clinical | adults | randomised, comparative | [46] |
| budesonide | xylitol | budesonide suspended in xylitol | 1–2 mg (5–10 mL solution) | BID | 12 weeks | histologic, clinical | children | prospective, open-label, not blinded | [54] |
| budesonide | sucralose, applesauce, honey, cocoa mix, pear sauce, rice cereal, xanthan gum | budesonide respules mixed with sucralose or applesauce, or honey, or other (such as hot cocoa mix, pear sauce, rice cereal, xanthan gum) | 0.5–1 mg | BID | 6 weeks | Histologic § | children | retrospective, cohort | [55] |
| budesonide | sucralose (Splenda®), Neocate® Duocal, Truvia, Stevia, pasteurised maple syrup, honey | budesonide respules mixed with 5 g of sucralose (Splenda®) or one tablespoon of Neocate® Duocal, or 2 packets of Truvia, or 2 packets of Stevia, or one tablespoon of pasteurised maple syrup or honey | 0.5–1 mg | BID | 8–12 weeks | histologic, clinical | children | retrospective, cohort | [39] |
| fluticasone | Methocel gel | viscous suspension of fluticasone with Methocel gel | 1.5–4 mg daily | no data | 8 weeks | histologic, clinical | adults | retrospective, cohort | [66] |
| budesonide | Splenda®, honey | budesonide respules mixed with Splenda or honey | 0.5–1 mg | BID | 8 weeks | histologic, clinical | children and adults | retrospective, comparative | [38] |
| Steroid | Form | Method of Delivery | Dose | Dosing | Period † | Response ‡ | Study Group | Study Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| budesonide | suspension (Pulmicort) | via inhalation system (light compressor and TIA nebulizer)—swallowing continuously the aerolized liquid | 0.5 mg | BID | 50 weeks | histologic, clinical § | adults and adolescents | randomised, placebo-controlled | [75] |
| budesonide | suspension (Pulmicort) | via inhalation system—swallowing the mist continuously for 5 min | 1 mg | BID | 8 weeks | clinical | adults | randomised, comparative | [46] |
| budesonide | suspension (Pulmicort) | via inhalation system (light compressor and TIA nebulizer)—swallowing continuously the aerolized liquid | 2 mg | BID | 15 days | histologic, clinical | adolescents, adults | prospective, open-labelled, not blinded | [30] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 880 µg | BID | 6 weeks | histologic | adults | randomised, placebo-controlled | [60] |
| fluticasone | no data | no data | 880 μg | BID | 3 months | histologic | children and adults | randomised, placebo-controlled | [76] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 440 μg | BID | 3 months | histologic, clinical | children and adults | randomised, comparative | [62] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 220–440 μg | 4 times dayily | 4 weeks | histologic, clinical | children | randomised, comparative | [10] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 440 μg | BID | 8 weeks | histologic, clinical | adults | randomised, comparative | [77] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 440 μg | BID | 8 weeks | histologic | adults | randomised, comparative | [61] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 176–440 μg | BID | <4 months | histologic, clinical | children | open-label, prospective | [63] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 220–440 μg | BID | 8 weeks | histologic, clinical | children and adults | retrospective, comparative | [38] |
| fluticasone | fluticasone inhaler | swallowing the mist | 220–440 μg | BID | 8–12 weeks | histologic, clinical | children | retrospective, comparative | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Główczewski, A.; Krogulska, A. Formulations of Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—Current Treatment and Emerging Possibilities. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051454
Główczewski A, Krogulska A. Formulations of Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—Current Treatment and Emerging Possibilities. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(5):1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051454
Chicago/Turabian StyleGłówczewski, Adam, and Aneta Krogulska. 2022. "Formulations of Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—Current Treatment and Emerging Possibilities" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 5: 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051454
APA StyleGłówczewski, A., & Krogulska, A. (2022). Formulations of Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—Current Treatment and Emerging Possibilities. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(5), 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051454






