Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation with or without Chemolipiodolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diagnosis
2.2. Patients Receiving PRFA
2.3. Patients Receiving CL
2.4. Treatment Outcome
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Survival Outcomes
3.3. Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
3.4. Patient Characteristics after Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
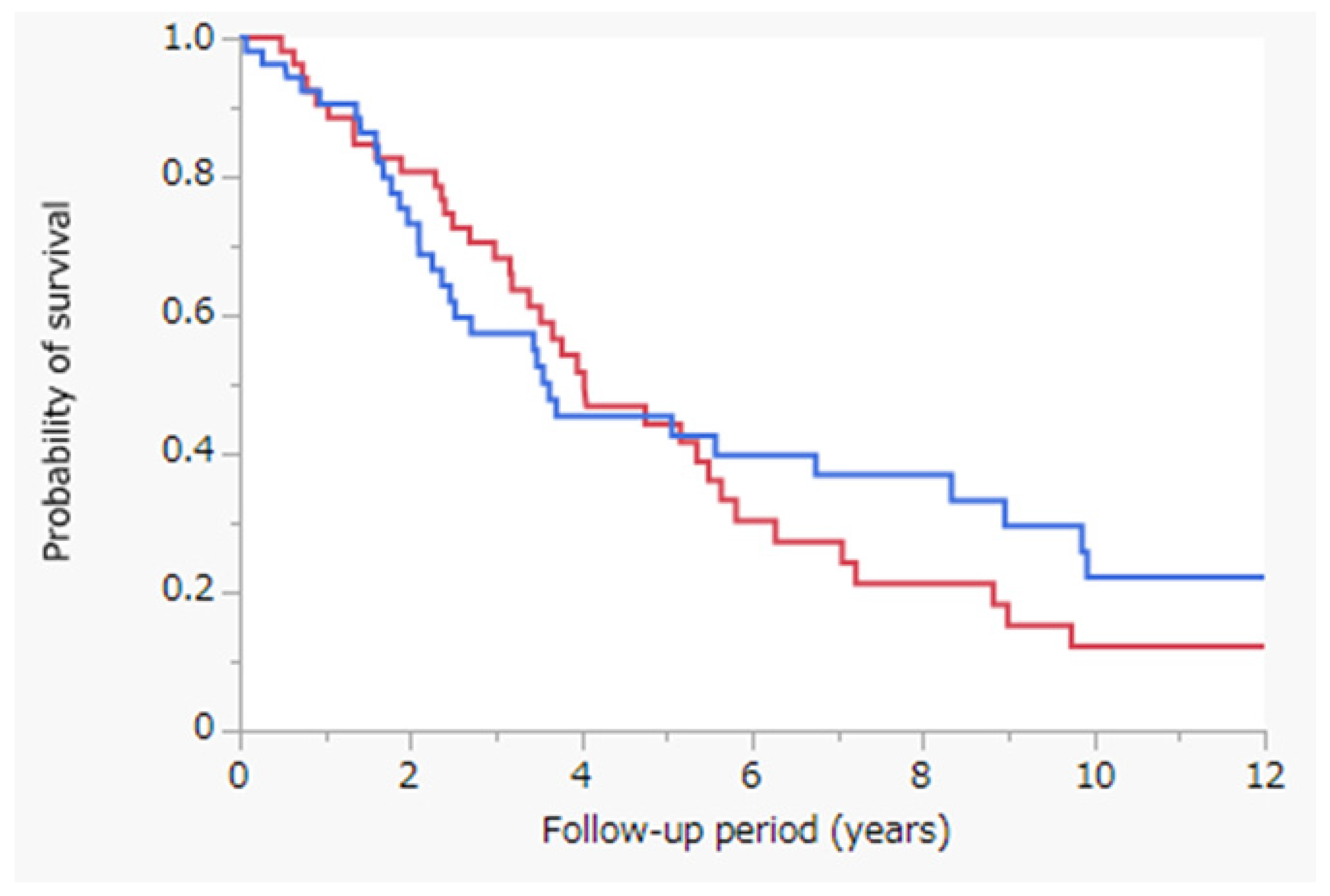
3.5. Survival Outcomes after Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
3.6. Survival Outcomes after Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis Post Stratification of Patients According to the Tumor Size
3.7. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of OS after Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singal, A.G.; Lampertico, P.; Nahon, P. Epidemiology and Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: New Trends. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration; Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Life Expectancy, All-Cause Mortality, and Cause-Specific Mortality for 249 Causes of Death, 1980–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grandhi, M.S.; Kim, A.K.; Ronnekleiv-Kelly, S.M.; Kamel, I.R.; Ghasebeh, M.A.; Pawlik, T.M. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 25, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartke, J.; Johnson, M.; Ghabril, M. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 34, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokudo, N.; Takemura, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Takayama, T.; Kubo, S.; Shimada, M.; Nagano, H.; Hatano, E.; Izumi, N.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2017 (4th JSH-HCC Guidelines) 2019 Update. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, M.S.; Xu, L.; Liang, H.H.; Lin, X.J.; Guo, R.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Lau, W.Y. Radiofrequency Ablation with or without Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prospective Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.J.; Bae, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.W.; Song, D.S.; You, C.R.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K. Combination Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation Therapy for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamai, T.; Oshige, A.; Tabu, K.; Tabu, E.; Ijyuin, S.; Sakae, H.; Onishi, H.; Muromachi, K.; Saisyoji, A.; Oda, K.; et al. Utility of Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation Alone or Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3199–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, H.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, H.K.; Ko, H.K.; Gwon, D.I.; Kim, P.N.; Sung, K.B.; Ko, G.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.H. Chemoembolization Combined with Radiofrequency Ablation for Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takuma, Y.; Takabatake, H.; Morimoto, Y.; Toshikuni, N.; Kayahara, T.; Makino, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Comparison of Combined Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation with Surgical Resection by Using Propensity Score Matching in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Milan Criteria. Radiology 2013, 269, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Won, H.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, H.K.; Sung, K.B.; Kim, P.N. Medium-Sized (3.1–5.0 Cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Transarterial Chemoembolization plus Radiofrequency Ablation versus Radiofrequency Ablation Alone. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, M.; Numata, K.; Kondou, M.; Nozaki, A.; Morita, S.; Tanaka, K. Midterm Outcomes in Patients with Intermediate-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized Controlled Trial for Determining the Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization. Cancer 2010, 116, 5452–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Lin, C.J.; Shen, L.J.; Li, C.F.; Jie, M.; Li, Z.W.; Wu, P.H. Chemolipiodolization with or without Embolization in Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Combined with Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31311–31321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lu, L.G.; Fang, W.Q.; Guo, R.P.; Chen, M.S.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, L.; Zou, R.H.; Lin, X.J.; et al. Roles Played by Chemolipiodolization and Embolization in Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Single-Blind, Randomized Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okusaka, T.; Kasugai, H.; Shioyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kudo, M.; Saisho, H.; Osaki, Y.; Sata, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Kumada, T.; et al. Transarterial Chemotherapy Alone versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized phase III Trial. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayasu, K.; Arii, S.; Ikai, I.; Kudo, M.; Matsuyama, Y.; Kojiro, M.; Makuuchi, M.; Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Overall Survival after Transarterial Lipiodol Infusion Chemotherapy with or without Embolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Propensity Score Analysis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaibori, M.; Tanigawa, N.; Kariya, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakahashi, Y.; Hirohara, J.; Koreeda, C.; Seki, T.; Sawada, S.; Okazaki, K.; et al. A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial of Preoperative Whole-Liver Chemolipiodolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M.; Llovet, J.M.; Beaugrand, M.; Lencioni, R.; Burroughs, A.K.; Christensen, E.; Pagliaro, L.; Colombo, M.; Rodés, J. EASL Panel of Experts on HCC. Clinical Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL Conference. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of Liver Function in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New Evidence-Based Approach-the ALBI Grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The BCLC Staging Classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.E.; de Lope, C.R.; Bruix, J. Current Strategy for Staging and Treatment: The BCLC Update and Future Prospects. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, M.; Uchiyama, K.; Ozawa, S.; Hayami, S.; Shigekawa, Y.; Tani, M.; Yamaue, H. Adjuvant Chemolipiodolization Reduces Early Recurrence Derived from Intrahepatic Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Hepatectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R.B., Jr. Propensity Score Methods for Bias Reduction in the Comparison of a Treatment to a Non-Randomized Control Group. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 2265–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; Tomlinson, G.A.; Hawker, G.A.; Granton, J.T.; Feldman, B.M. Propensity Score Methods for Bias Reduction in Observational Studies of Treatment Effect. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 44, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. The Performance of Different Propensity Score Methods for Estimating Marginal Hazard Ratios. Stat. Med. 2013, 32, 2837–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cammà, C.; Schepis, F.; Orlando, A.; Albanese, M.; Shahied, L.; Trevisani, F.; Andreone, P.; Craxì, A.; Cottone, M. Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Radiology 2002, 224, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Kim, J.H. Transarterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment: Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Staging System. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10327–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T. Percutaneous Microwave Coagulation Therapy (PMCT). Nihon Rinsho. 2001, 59 (Suppl. 6), 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.J.; Luo, K.L.; Liu, H.; Cai, B.; Tao, G.Q.; Su, X.F.; Hou, X.J.; Ye, F.; Li, X.Y.; Tian, Z.Q. Meta-Analysis of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization plus Radiofrequency Ablation versus Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Alone for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimose, S.; Tanaka, M.; Iwamoto, H.; Niizeki, T.; Shirono, T.; Aino, H.; Noda, Y.; Kamachi, N.; Okamura, S.; Nakano, M.; et al. Prognostic impact of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with radiofrequency ablation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with TACE alone using decision-tree analysis after propensity score matching. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2019, 49, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Garbagnati, F.; Lencioni, R.; Allgaier, H.P.; Marchianò, A.; Fornari, F.; Quaretti, P.; Tolla, G.D.; Ambrosi, C.; Mazzaferro, V.; et al. Percutaneous Radio-Frequency Thermal Ablation of Nonresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Occlusion of Tumor Blood Supply. Radiology 2000, 217, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | CL (+) (n = 76) | CL (−) (n = 145) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 73.1 ± 10.7 75.4 (32.8–88.6) | 73.7 ± 8.3 75.2 (46.0–88.6) | 0.6711 |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 52 (68%)/24 (32%) | 80 (55%)/65 (45%) | 0.0564 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/Both negative) | 4 (5%)/66 (87%)/6 (8%) | 8 (5%)/129 (90%)/8 (5%) | 0.7881 |
| Child–Pugh class (A/B) | 62 (82%)/14 (18%) | 120 (83%)/25 (17%) | 0.4766 |
| Tumor size (mm) | 25.3 ± 9.0 25 (9–48) | 18.1 ± 5.6 17 (8–35) | <0.0001 |
| BCLC stage (0/A/B) | 20 (26%)/30 (40%)/26 (34%) | 85 (59%)/50 (34%)/10 (7%) | <0.0001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.5 3.7 (2.7–4.7) | 3.7 ± 0.5 3.7 (2.5–4.8) | 0.4492 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.0 ± 0.4 0.8 (0.3–2.5) | 0.9 ± 0.5 0.8 (0.2–3.2) | 0.5275 |
| ALBI score | −2.30 ± 0.45 −2.32 (−3.38–1.29) | −2.36 ± 0.47 −2.40 (−3.52–1.21) | 0.3223 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 77.1 ± 12.2 75.2 (44.5–108.7) | 78.4 ± 12.7 78.7 (46.9–108.3) | 0.4631 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 296 ± 1009 32 (2–8400) | 118 ± 39 15 (1–5019) | 0.0758 |
| DCP (mAU/mL) | 905 ± 5042 47 (2–42,500) | 144 ± 443 25 (8–3930) | 0.0751 |
| Variable | CL (+) (n = 54) | CL (−) (n = 54) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 73.2 ± 11.4 75.7 (32.9–88.6) | 72.8 ± 7.8 74.5 (55.2–88.6) | 0.8496 |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 36 (67%)/18 (33%) | 37 (69%)/17 (31%) | 0.8371 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/Both negative) | 3 (6%)/48 (88%)/3 (6%) | 3 (6%)/46 (87%)/5 (7%) | 0.7624 |
| Child–Pugh class (A/B) | 45 (83%)/9 (17%) | 42 (78%)/12 (22%) | 0.4658 |
| Tumor size (mm) | 22.6 ± 7.6 22 (9–37) | 21.9 ± 6.2 21 (11–35) | 0.5990 |
| BCLC stage (0/A/B) | 18 (33%)/24 (45%)/12 (22%) | 17 (31%)/27 (50%)/10 (19%) | 0.8241 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.5 3.8 (2.5–4.5) | 3.59 ± 0.5 3.6 (2.5–4.8) | 0.7066 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.9 ± 0.4 0.8 (0.3–2.1) | 0.9 ± 0.4 0.9 (0.4–2.2) | 0.4172 |
| ALBI score | −2.32 ± 0.43 −2.33 (−3.20–1.37) | −2.27 ± 0.47 −2.24 (−3.52–1.21) | 0.5726 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 77.9 ± 12.8 78.3 (44.5–108.7) | 76.6 ± 14.4 74.8 (46.9–106.1) | 0.6370 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 154 ± 279 32 (2–1170) | 124 ± 312 22 (4–1628) | 0.5996 |
| DCP (mAU/mL) | 286 ± 700 46 (2–3310) | 282 ± 675 34 (8–3930) | 0.9781 |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (≥75.2 years) | 1.237 (0.771–1.993) | 0.3767 | 1.043 (0.614–1.785) | 0.8752 |
| Sex (Male) | 1.249 (0.758–2.057) | 0.3757 | 1.581 (0.906–2.759) | 0.0995 |
| Etiology (HCV) | 1.946 (0.980–4.447) | 0.0574 | 1.512 (0.697–3.655) | 0.3063 |
| Child–Pugh class (B) | 3.126 (1.616–5.720) | 0.0012 | 2.283 (1.117–4.507) | 0.0245 |
| Tumor size (≥22 mm) | 1.541 (0.963–2.494) | 0.0712 | 1.338 (0.690–2.804) | 0.4001 |
| BCLC stage (A or B) | 1.477 (0.888–2.566) | 0.1356 | 0.928 (0.411–1.994) | 0.8525 |
| ALBI score (≥−2.31) | 3.097 (1.750–5.488) | <0.0001 | 1.370 (0.749–2.496) | 0.3036 |
| AFP (≥27.6 ng/mL) | 2.059 (1.274–3.361) | 0.0032 | 1.669 (0.971–2.907) | 0.0638 |
| DCP (≥43 mAU/mL) | 1.862 (1.146–3.062) | 0.0119 | 1.705 (1.013–2.903) | 0.0442 |
| Treatment (PRFA with CL) | 1.155 (0.721–1.851) | 0.5477 | 1.012 (0.615–1.667) | 0.9600 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takaki, K.; Nakano, M.; Fukumori, K.; Yano, Y.; Zaizen, Y.; Niizeki, T.; Kuwaki, K.; Fukahori, M.; Sakaue, T.; Yoshimura, S.; et al. Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation with or without Chemolipiodolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061483
Takaki K, Nakano M, Fukumori K, Yano Y, Zaizen Y, Niizeki T, Kuwaki K, Fukahori M, Sakaue T, Yoshimura S, et al. Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation with or without Chemolipiodolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(6):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061483
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakaki, Kota, Masahito Nakano, Kazuta Fukumori, Yoichi Yano, Yuki Zaizen, Takashi Niizeki, Kotaro Kuwaki, Masaru Fukahori, Takahiko Sakaue, Sohei Yoshimura, and et al. 2022. "Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation with or without Chemolipiodolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 6: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061483
APA StyleTakaki, K., Nakano, M., Fukumori, K., Yano, Y., Zaizen, Y., Niizeki, T., Kuwaki, K., Fukahori, M., Sakaue, T., Yoshimura, S., Nakazaki, M., & Torimura, T. (2022). Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation with or without Chemolipiodolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(6), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061483






