Risk Factors, Clinical and Endoscopic Features, and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compliance with Ethical Standards
2.2. Patients
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Definitions
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with CMV Esophagitis
3.2. Clinical Manifestations of CMV Esophagitis
3.3. Results of Laboratory Examinations in Patients with CMV Esophagitis
3.4. Endoscopic Findings in Patients with CMV Esophagitis
3.5. Radiological Examination of Patients with CMV Esophagitis
3.6. Treatments and Outcomes in Patients with CMV Esophagitis
3.7. Differences between the CMV and Non-CMV Groups
3.8. Prognostic Factors for In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with CMV Esophagitis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.W.; Kuo, C.J.; Lin, W.R.; Hsu, C.M.; Ho, Y.P.; Lin, C.J.; Su, M.Y.; Chiu, C.T.; Wang, C.L.; Chen, K.H. The clinical characteristics and manifestations of cytomegalovirus esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoversten, P.; Kamboj, A.K.; Katzka, D.A. Infections of the esophagus: An update on risk factors, diagnosis, and management. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, doy094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoversten, P.; Kamboj, A.K.; Wu, T.T.; Katzka, D.A. Risk Factors, Endoscopic Features, and Clinical Outcomes of Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis Based on a 10-year Analysis at a Single Center. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chakinala, R.C. Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamuro, M.; Kondo, E.; Tanaka, T.; Hagiya, H.; Kawano, S.; Kawahara, Y.; Otsuka, F.; Okada, H. Endoscopic Manifestations and Clinical Characteristics of Cytomegalovirus Infection in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. Acta Med. Okayama 2017, 71, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.H.; Choi, J.; Gong, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.D.; Song, H.J.; Lee, G.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Chong, Y.P.; Lee, S.O.; et al. Can endoscopists differentiate cytomegalovirus esophagitis from herpes simplex virus esophagitis based on gross endoscopic findings? Medicine 2019, 98, e15845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esophagus. In AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Greene, F.L.; Page, D.L.; Fleming, I.D.; Fritz, A.G.; Balch, C.M.; Haller, D.G.; Morrow, M. (Eds.) Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Falk, G.W.; Iyer, P.G.; Gerson, L.B. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett’s Esophagus. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2016, 111, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, P.H.; Lin, W.R.; Kuo, C.J.; Wu, R.C.; Hsu, J.T.; Su, M.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Chiu, C.T. Clinical characteristics of cytomegalovirus colitis: A 15-year experience from a tertiary reference center. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaemsupaphan, T.; Limsrivilai, J.; Thongdee, C.; Sudcharoen, A.; Pongpaibul, A.; Pausawasdi, N.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P. Patient characteristics, clinical manifestations, prognosis, and factors associated with gastrointestinal cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompetent patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilcox, C.M.; Straub, R.F.; Schwartz, D.A. Prospective endoscopic characterization of cytomegalovirus esophagitis in AIDS. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1994, 40, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthazar, E.J.; Megibow, A.J.; Hulnick, D.; Cho, K.C.; Beranbaum, E. Cytomegalovirus esophagitis in AIDS: Radiographic features in 16 patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Huang, H.-C.; Chen, T.-C.; Cheng, H.-T. Cytomegalovirus esophagitis with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease in a kidney transplant recipient. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 859–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litle, V.R.; Rice, T.W. The esophagus: Do sex and gender matter? Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 23, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanuma, K.; Iijima, K.; Shimosegawa, T. Gender difference in gastro-esophageal reflux diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, J.C.; Vanoni, S.; Zeng, C.; Waggoner, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Uddin, J.; Karns, R.; Kottyan, L.; Mukkada, V.; et al. 17β-Estradiol protects the esophageal epithelium from IL-13-induced barrier dysfunction and remodeling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 2131–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, K. Does Estrogen Contribute to the Esophageal Barrier Function in Women? Gut Liver 2018, 12, 373–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, R.; Matsumoto, S.; Uneno, Y.; Nishikawa, Y.; Ozaki, Y.; Mori, Y.; Kanai, M.; Ishida, Y.; Sakanaka, K.; Hiraoka, M.; et al. Severe esophagitis associated with cytomegalovirus during concurrent chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 47, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, K.; Okada, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Funakoshi, Y.; Sanada, Y.; Chayahara, N.; Mayahara, H.; Fujii, M. Cytomegalovirus reactivation in esophageal cancer patients receiving chemoradiotherapy: A retrospective analysis. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 7525–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemoto, K.; Kojima, Y.; Nagata, N.; Yokoi, C.; Sakurai, T.; Kobayakawa, M.; Iizuka, T.; Igari, T.; Yanase, M.; Akiyama, J. Cytomegalovirus esophagitis developing during chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, P.J.; Chiu, C.T.; Lai, M.W.; Wu, R.C.; Chen, C.M.; Kuo, C.J.; Hsu, J.T.; Su, M.Y.; Lin, W.P.; Chen, T.H.; et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and prognostic factors of cytomegalovirus enteritis. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvari, J.; Habibi, A.; Moattari, A.; Eftehkar Sadat, A.T.; Ahangar Oskouee, M. Association of Epstein–Barr Virus and Cytomegalovirus Infections with Esophageal Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2021, 14, e114566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baba, R.; Herbein, G. Immune Landscape of CMV Infection in Cancer Patients: From “Canonical” Diseases Toward Virus-Elicited Oncomodulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.J.; Chiu, C.T.; Lai, M.W.; Wu, R.C.; Kuo, C.J.; Hsu, J.T.; Su, M.Y.; Le, P.H. Cytomegalovirus gastritis: Clinicopathological profile. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betjes, M.G.H. Immune cell dysfunction and inflammation in end-stage renal disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartzell, S.; Bin, S.; Cantarelli, C.; Haverly, M.; Manrique, J.; Angeletti, A.; Manna, G.L.; Murphy, B.; Zhang, W.; Levitsky, J.; et al. Kidney Failure Associates With T Cell Exhaustion and Imbalanced Follicular Helper T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetwittayakhlang, P.; Rujeerapaiboon, N.; Wetwittayakhlung, P.; Sripongpun, P.; Pruphetkaew, N.; Jandee, S.; Chamroonkul, N.; Piratvisuth, T. Clinical Features, Endoscopic Findings, and Predictive Factors for Mortality in Tissue-Invasive Gastrointestinal Cytomegalovirus Disease between Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Patients. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 8886525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

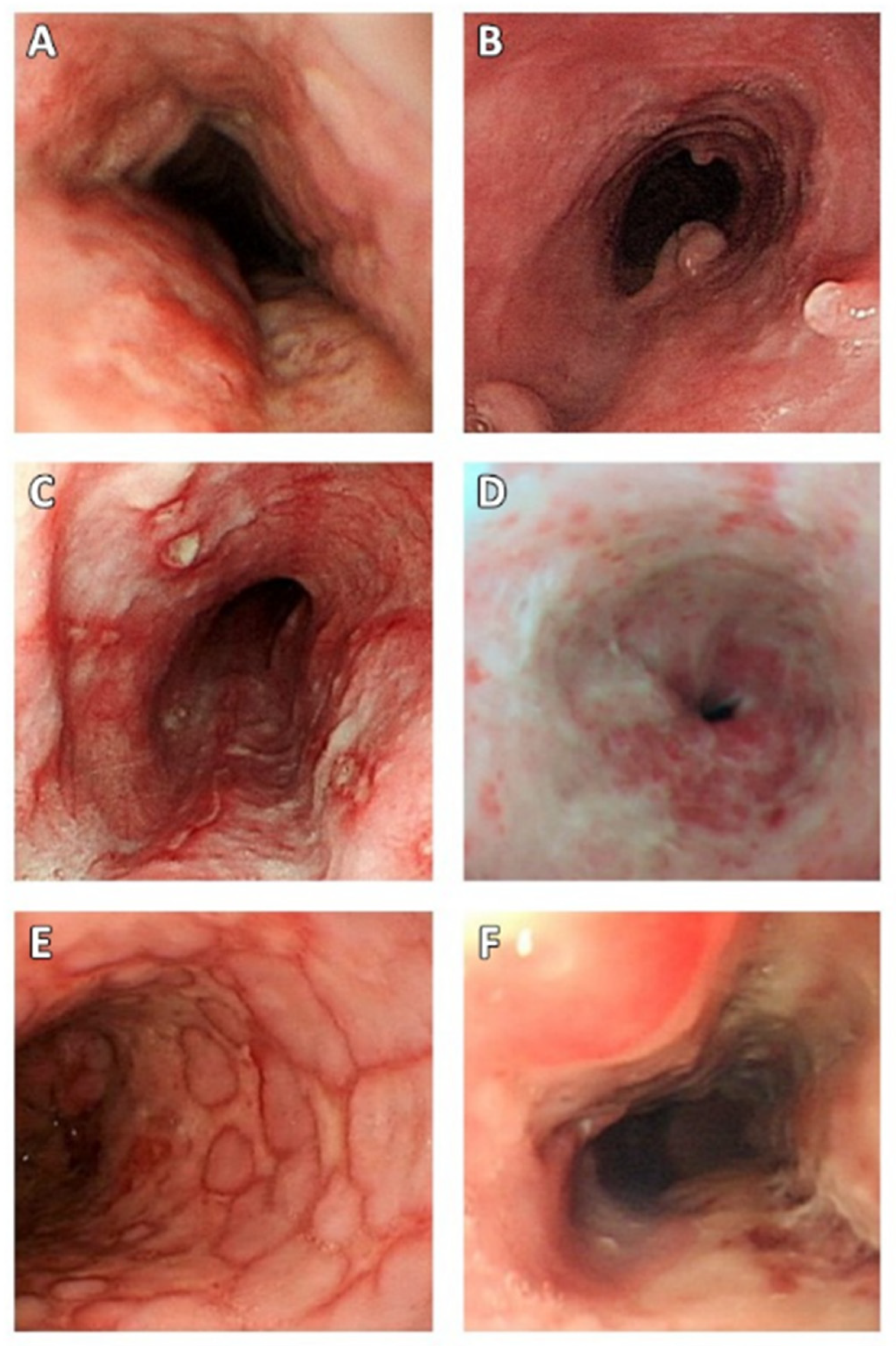
| Characteristics | Overall (n = 148) | CMV Esophagitis (n = 44) | Non-CMV Esophagitis (n = 104) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 56.7 ± 18.9 | 59.5 ± 18.5 | 56.9 ± 19.1 | 0.489 |
| Gender (M/F) | 96 (64.9%)/52 (35.1%) | 34 (77.3%)/10 (22.7%) | 62 (59.6%)/42 (40.4%) | 0.040 * |
| OPD patients | 71 (48%) | 11 (25%) | 60 (57.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Acquisition time (day) | 8 (5–14) | 11.5 (6.8–26) | 7 (4–12) | 0.005 * |
| General conditions | ||||
| Shock | 10 (6.8%) | 8 (18.2%) | 2 (1.9%) | 0.001 * |
| Pneumonia | 25 (16.9%) | 16 (36.4%) | 9 (8.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Intubation | 9 (6.1%) | 6 (13.6%) | 3 (2.9%) | 0.02 * |
| ICU required | 10 (6.8%) | 7 (15.9%) | 3 (3%) | 0.008 * |
| Immunocompromised | 68 (45.9%) | 34 (77.3%) | 34 (32.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Underlying diseases | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 29 (19.6%) | 8 (18.2%) | 21 (20.2%) | 0.78 |
| Hypertension | 54 (36.5%) | 19 (43.2%) | 35 (33.7%) | 0.27 |
| Autoimmune disease | 7 (4.7%) | 2 (4.5%) | 5 (4.8%) | 1 |
| Crohn’s disease | 1 (0.6%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1%) | 1 |
| Ulcerative colitis | 2 (1.4%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (1%) | 0.51 |
| Coronary artery disease | 8 (5.4%) | 5 (11.4%) | 3 (2.9%) | 0.05 |
| COPD | 8 (5.4%) | 4 (9.1%) | 4 (3.8%) | 0.24 |
| Renal disease | ||||
| AKI | 13 (8.8%) | 5 (11.4%) | 8 (7.7%) | 0.47 |
| CKD | 24 (16.2%) | 7 (15.9%) | 17 (16.3%) | 0.95 |
| ESRD | 11 (7.4%) | 4 (9.1%) | 7 (6.7%) | 0.73 |
| HIV infection | 11 (7.4%) | 8 (18.2%) | 3 (2.9%) | 0.003 * |
| Malignancies | 44 (29.7%) | 20 (45.5%) | 24 (23.1%) | 0.01 * |
| Transplantation | 3 (2%) | 3 (6.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0.03 * |
| GERD | 91 (61.5%) | 20 (45.5%) | 71 (68.3%) | 0.01 * |
| Immunosuppressive therapies | ||||
| Steroid | 35 (23.6%) | 23 (52.3%) | 12 (11.5%) | <0.001 * |
| Immunosuppressant | 11 (7.4%) | 6 (13.6%) | 5 (4.8%) | 0.06 |
| Chemotherapy | 27 (18.2%) | 15 (34.1%) | 12 (11.5%) | 0.001 * |
| Radiotherapy | 29 (19.6%) | 16 (36.4%) | 13 (12.5%) | 0.001 * |
| Other medications | ||||
| Antibiotics | 67 (45.3%) | 33 (75%) | 34 (32.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Proton pump inhibitor | 75 (50.7%) | 28 (63.6%) | 47 (45.2%) | 0.04 * |
| Other antacids | 24 (16.2%) | 14 (31.8%) | 10 (9.6%) | 0.001 * |
| Mucosal protectant | 31 (20.9%) | 14 (31.8%) | 17 (16.3%) | 0.03 * |
| Clinical presentation | ||||
| Fever | 23 (15.5%) | 16 (36.4%) | 7 (6.7%) | <0.001* |
| Epigastric pain | 48 (32.4%) | 18 (40.9%) | 30 (28.8%) | 0.15 |
| Vomiting | 34 (23%) | 11 (25%) | 23 (22.1%) | 0.70 |
| Hematemesis | 13 (8.8%) | 9 (20.5%) | 4 (3.8%) | 0.002 * |
| GI bleeding † | 29 (19.6%) | 13 (29.5%) | 16 (15.4%) | 0.05 * |
| Dysphagia | 37 (25%) | 13 (29.5%) | 24 (23.1%) | 0.41 |
| Odynophagia | 27 (18.2%) | 14 (31.8%) | 13 (12.5%) | 0.005 * |
| Abdominal fullness | 13 (8.8%) | 9 (20.5%) | 4 (3.8%) | 0.002 * |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| WBC count (/μL) | 6900 (4250–9750) | 4900 (2700–8575) | 7600 (5200–10,300) | 0.004 * |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.5 (9.2–12.1) | 10.4 (9–11.6) | 10.7 (9.4–13.2) | 0.026 * |
| Platelets (×1000/mm3) | 228 (136–284.5) | 173.5 (116.5–250) | 250 (183–295) | 0.005 * |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.9 (0.7–1.3) | 0.73 (0.6–1.11) | 0.9 (0.7–1.3) | 0.071 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 20 (14–33) | 24 (17.3–33) | 17 (12–29) | 0.022 * |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.9 (2.5–3.7) | 2.8 (2.3–2.9) | 3.3 (2.8–4) | 0.004 * |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 32.4 (6.9–63.9) | 43 (8.1–73.2) | 29.2 (3.4–58.5) | 0.415 |
| Endoscopic features | ||||
| Main findings | ||||
| Ulcer | 131 (88.5%) | 39 (88.6%) | 92 (88.5%) | 0.98 |
| Diffuse/multiple ulcers | 90 (60.8%) | 33 (75%) | 57 (54.8%) | 0.02 * |
| Inflammation | 5 (3.4%) | 1 (2.3%) | 4 (3.8%) | 1 |
| Polypoid lesion | 10 (6.8%) | 6 (13.6%) | 4 (3.8%) | 0.07 |
| Location of lesion | ||||
| Upper 3rd | 31 (20.9%) | 14 (31.8%) | 17 (16.3%) | 0.03 * |
| Middle 3rd | 85 (57.4%) | 27 (61.4%) | 58 (55.8%) | 0.53 |
| Lower 3rd | 110 (74.3%) | 38 (86.4%) | 72 (69.2%) | 0.03 * |
| Concurrent findings | ||||
| Reflux esophagitis | 75 (50.7%) | 17 (38.6%) | 58 (55.8%) | 0.06 |
| Esophageal candidiasis | 12 (8.1%) | 8 (18.2%) | 4 (3.8%) | 0.01 * |
| Barrett esophagus | 9 (6.1%) | 4 (9.1%) | 5 (4.8%) | 0.45 |
| Gastric ulcer | 25 (16.9%) | 13 (29.5%) | 12 (11.5%) | 0.01 * |
| CMV gastritis | 4 (2.7%) | 4 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0.01 * |
| CMV, others ‡ | 4 (2.7%) | 4 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0.01 * |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Follow-up duration (days) | 351 (112.5–1187.3) | 276 (64.8–738.8) | 451.1 (141.3–1345.5) | 0.198 |
| Hospital stay (days) | 17.5 (9–35.3) | 24 (11–47) | 14 (7–24) | 0.02 * |
| In-hospital mortality | 8 (5.4%) | 8 (18.2%) | 0 (0%) | <0.001 * |
| Overall mortality | 38 (25.7%) | 23 (52.3%) | 15 (14.4%) | <0.001 * |
| Characteristics | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.04 | 0.99–1.09 | 0.11 | |||
| Gender (Male) | 0.86 | 0.14–5.10 | 0.87 | |||
| Acquisition time | 1.06 | 1.00–1.13 | 0.04 * | |||
| General conditions | ||||||
| Shock | 18.33 | 2.87–117.33 | 0.002 * | |||
| Intubation | 17 | 2.33–124.19 | 0.01 * | |||
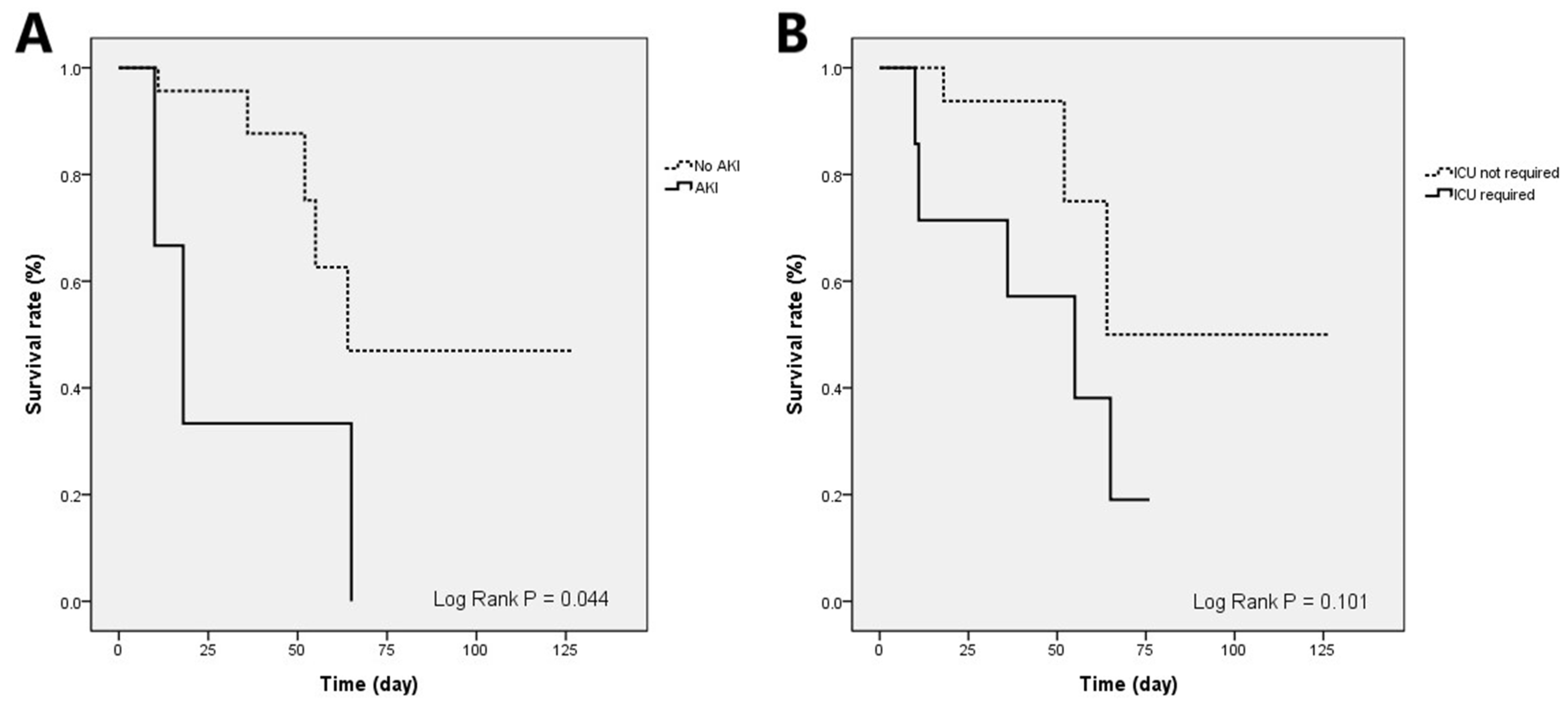
| ICU required | 28.33 | 3.76–213.70 | 0.001 * | 26.53 | 1.06–665.08 | 0.05 * |
| Immunocompromised | 0.86 | 0.14–5.10 | 0.87 | |||
| Underlying diseases | ||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.67 | 0.27–10.33 | 0.58 | |||
| Hypertension | 2.62 | 0.54–12.72 | 0.23 | |||
| Acute kidney injury | 10.2 | 1.35–76.93 | 0.02 * | 174.15 | 1.27–23,836.21 | 0.04 * |
| Chronic kidney disease | 2.07 | 0.32–13.25 | 0.44 | |||
| End-stage renal disease | 0 | 0–0 | 0.1 | |||
| Malignancy | 1.25 | 0.27–5.80 | 0.78 | |||
| Chemotherapy | 0.22 | 0.03–2.03 | 0.18 | |||
| Radiotherapy | 1.06 | 0.22–5.18 | 0.94 | |||
| Steroid usage | 1.67 | 0.35–8.04 | 0.53 | |||
| GERD | 0.13 | 0.01–1.15 | 0.07 | |||
| CMV gastritis | 5.67 | 0.66–48.33 | 0.11 | |||
| Clinical symptoms | ||||||
| Fever | 0.52 | 0.09–2.97 | 0.47 | |||
| Epigastric pain | 2.95 | 0.61–14.38 | 0.18 | |||
| Vomiting | 0.37 | 0.04–3.42 | 0.38 | |||
| Bloody vomiting | 6.2 | 1.16–33.17 | 0.03 * | |||
| GI bleeding | 12.43 | 2.05–75.24 | 0.01 * | |||
| Laboratory data | ||||||
| WBC count | 1 | 1–1 | 0.13 | |||
| Hemoglobin | 0.77 | 0.48–1.21 | 0.25 | |||
| Platelet | 0.10 | 0.99–1.01 | 0.76 | |||
| Creatinine | 0.85 | 0.42–1.73 | 0.66 | |||
| ALT | 1.04 | 0.99–1.09 | 0.09 | |||
| Albumin | 0.21 | 0.04–1.05 | 0.06 | |||
| C-reactive protein | 0.99 | 0.97–1.01 | 0.37 | |||
| Endoscopic features | ||||||
| Diffuse/multiple ulcers | 2.69 | 0.29–24.75 | 0.38 | |||
| Esophageal candidiasis | 0.59 | 0.06–5.63 | 0.65 | |||
| Barrett’s esophagus | 1.57 | 0.14–17.42 | 0.71 | |||
| Gastric ulcer | 12.43 | 2.05–75.24 | 0.01 * | |||
| Antiviral therapy | 1.19 | 0.246–5.764 | 0.828 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeh, P.-J.; Wu, R.-C.; Chen, C.-M.; Chiu, C.-T.; Lai, M.-W.; Chen, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-J.; Hsu, J.-T.; Su, M.-Y.; Le, P.-H. Risk Factors, Clinical and Endoscopic Features, and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061583
Yeh P-J, Wu R-C, Chen C-M, Chiu C-T, Lai M-W, Chen C-C, Kuo C-J, Hsu J-T, Su M-Y, Le P-H. Risk Factors, Clinical and Endoscopic Features, and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(6):1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061583
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeh, Pai-Jui, Ren-Chin Wu, Chien-Ming Chen, Cheng-Tang Chiu, Ming-Wei Lai, Chien-Chang Chen, Chia-Jung Kuo, Jun-Te Hsu, Ming-Yao Su, and Puo-Hsien Le. 2022. "Risk Factors, Clinical and Endoscopic Features, and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 6: 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061583
APA StyleYeh, P.-J., Wu, R.-C., Chen, C.-M., Chiu, C.-T., Lai, M.-W., Chen, C.-C., Kuo, C.-J., Hsu, J.-T., Su, M.-Y., & Le, P.-H. (2022). Risk Factors, Clinical and Endoscopic Features, and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(6), 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061583







