Visual Tract Degradation in Bilateral Normal-Tension Glaucoma—Cortical Thickness Maps and Volumetric Study of Visual Pathway Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jonas, J.B.; Aung, T.; Bourne, R.R.; Bron, A.M.; Ritch, R.; Panda-Jonas, S. Glaucoma. Lancet 2017, 390, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, H.A.; Dunkelberger, G.R.; Green, W.R. Retinal ganglion cell atrophy correlated with automated perimetry in human eyes with glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1989, 107, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, H.; Broman, A.T. The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuster, A.K.; Erb, C.; Hoffmann, E.M.; Dietlein, T.; Pfeiffer, N. The diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killer, H.E.; Pircher, A. Normal tension glaucoma: Review of current understanding and mechanisms of the pathogenesis. Eye 2018, 32, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flammer, J.; Orgül, S.; Costa, V.P.; Orzalesi, N.; Krieglstein, G.K.; Serra, L.M.; Renard, J.P.; Stefánsson, E. The impact of ocular blood flow in glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2002, 21, 359–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, R.; Martucci, A.; Cesareo, M.; Giannini, C.; Corasaniti, M.T.; Bagetta, G.; Nucci, C. Glaucoma and Alzheimer Disease: One Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disease of the Brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 16, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucci, C.; Martucci, A.; Cesareo, M.; Garaci, F.; Morrone, L.A.; Russo, R.; Corasaniti, M.T.; Bagetta, G.; Mancino, R. Links among glaucoma, neurodegenerative, and vascular diseases of the central nervous systemb. Prog. Brain Res. 2015, 221, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dervisevic, E.; Pavljasevic, S.; Dervisevic, A.; Kasumovic, S.S. Challenges In Early Glaucoma Detection. Med. Arch. 2016, 70, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frezzotti, P.; Giorgio, A.; Toto, F.; De Leucio, A.; De Stefano, N. Early changes of brain connectivity in primary open angle glaucoma. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 4581–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, K.H.; Kim, D.M.; Jeoung, J.W. Glaucoma diagnostic ability of layer-by-layer segmented ganglion cell complex by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 4799–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.J.; Mi, X.S.; So, K.F. Normal tension glaucoma: From the brain to the eye or the inverse? Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, T.J.; Wang, I.J.; Shen, Y.D.; Chi, N.F.; Chien, L.N. Erratum: Glaucoma, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease: An 8-Year population-based follow-up study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eraslan, M.; Çerman, E.; Çekıç, O.; Balci, S.; Derıcıoğlu, V.; Şahin, Ö.; Süer, D.; Chabou, B.; Tuncer Elmaci, E.N. Neurodegeneration in ocular and central nervous systems: Optical coherence tomography study in normal-tension glaucoma and Alzheimer disease. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 45, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurano, S.T.P.; da Silva, D.J.; Ávila, M.P.; Magacho, L. Cognitive evaluation of patients with glaucoma and its comparison with individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Int. Ophthalmol. 2018, 38, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.C.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.X.; Wu, X.S.; Jonas, J.B. Anterior visual pathway assessment by magnetic resonance imaging in normal-pressure glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 90, e295–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidek, S.; Ramli, N.; Rahmat, K.; Ramli, N.M.; Abdulrahman, F.; Tan, L.K. Glaucoma severity affects diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters of the optic nerve and optic radiation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, Z.; Sun, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Xiao, Z. White matter abnormalities and correlation with severity in normal tension glaucoma: A whole brain atlas-based diffusion tensor study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.E.; Insausti, R.; Lerma-Usabiaga, G.; Bocchetta, M.; Van Leemput, K.; Greve, D.N.; van der Kouwe, A.; Fischl, B.; Caballero-Gaudes, C.; Paz-Alonso, P.M. A probabilistic atlas of the human thalamic nuclei combining ex vivo MRI and histology. Neuroimage 2018, 183, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; Rajendran, N.; Busa, E.; Augustinack, J.; Hinds, O.; Yeo, B.T.T.; Mohlberg, H.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. Cortical folding patterns and predicting cytoarchitecture. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B.; Van Der Kouwe, A.; Destrieux, C.; Halgren, E.; Ségonne, F.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Seidman, L.J.; Goldstein, J.; Kennedy, D.; et al. Automatically Parcellating the Human Cerebral Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Destrieux, C.; Fischl, B.; Dale, A.; Halgren, E. Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, N.; Hedley-Whyte, E.T.; Dreyer, E.B. Lateral geniculate nucleus in glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1993, 116, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior-Jarecka, E.; Pankowska, A.; Polit, P.; Stępniewski, A.; Symms, M.R.; Kozioł, P.; Żarnowski, T.; Pietura, R. Volume of Lateral Geniculate Nucleus in Patients with Glaucoma in 7Tesla MRI. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucci, C.; Martucci, A.; Cesareo, M.; Mancino, R.; Russo, R.; Bagetta, G.; Cerulli, L.; Garaci, F.G. Brain involvement in glaucoma: Advanced neuroimaging for understanding and monitoring a new target for therapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezzotti, P.; Giorgio, A.; Motolese, I.; De Leucio, A.; Iester, M.; Motolese, E.; Federico, A.; De Stefano, N. Structural and functional brain changes beyond visual system in patients with advanced glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawlor, M.; Danesh-Meyer, H.; Levin, L.A.; Davagnanam, I.; De Vita, E.; Plant, G.T. Glaucoma and the brain: Trans-synaptic degeneration, structural change, and implications for neuroprotection. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2018, 63, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.B.; Schmidt, A.M.; Muller-Bergh, J.A.; Schlotzer-Schrehardt, U.M.; Naumann, G.O.H. Human optic nerve fiber count and optic disc size. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kastner, S.; Schneider, K.A.; Wunderlich, K. Beyond a relay nucleus: Neuroimaging views on the human LGN. Prog. Brain Res. 2006, 155, 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.A.; Knott, M.; Heidemann, R.; Michelson, G.; Kober, T.; Dörfler, A.; Engelhorn, T. Investigation of lateral geniculate nucleus volume and diffusion tensor imaging in patients with normal tension glaucoma using 7 tesla magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.; Weinreb, R.N.; Kaufman, P.L.; Gupta, N. Atrophy of relay neurons in magno- and parvocellular layers in the lateral geniculate nucleus in experimental glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 3216–3222. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Greenberg, G.; De Tilly, L.N.; Gray, B.; Polemidiotis, M.; Yücel, Y.H. Atrophy of the lateral geniculate nucleus in human glaucoma detected by magnetic resonance imaging. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, Y.Y.; Ryu, T.; Cho, Z.H.; Kim, Y.B. An investigation of lateral geniculate nucleus volume in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma using 7 tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 3468–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Shimazawa, M.; Chen, Y.N.; Tsuruma, K.; Yamashima, T.; Araie, M.; Hara, H. Morphological changes in the visual pathway induced by experimental glaucoma in Japanese monkeys. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somogyi, J.; Eysel, U.; Hamori, J. A quantitative study of morphological reorganization following chronic optic deafferentation in the adult cat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1987, 255, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlanetto, R.L.; Teixeira, S.H.; Gracitelli, C.P.B.; Lottenberg, C.L.; Emori, F.; Michelan, M.; Amaro, E.; Paranhos, A. Structural and functional analyses of the optic nerve and lateral geniculate nucleus in glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.K.; Paxinos, G. The Human Nervous System; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780123742360. [Google Scholar]
- Fischl, B.; Dale, A.M. Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeAngelis, G.C.; Ohzawa, I.; Freeman, R.D. Receptive-field dynamics in the central visual pathways. Trends Neurosci. 1995, 18, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.L.; Lackey, J.; Wizov, S.S.; Chia, T.M.T.; Gatla, S.; Moster, M.L.; Sergott, R.; Spaeth, G.L.; Lai, S. Evidence for widespread structural brain changes in glaucoma: A preliminary voxel-based MRI study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5880–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Xie, L.; Dai, C.; Xie, B.; Liang, M.; Zhao, L.; Yin, X.; Wang, J. Progressive thinning of visual cortex in primary open-angle glaucoma of varying severity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzpatrick, D.; Lund, J.S.; Blasdel, G.G. Intrinsic connections of macaque striate cortex: Afferent and efferent connections of lamina 4C. J. Neurosci. 1985, 5, 3329–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandel, E.R. Intermediate-Level Visual Processing and Visula Primitives, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill, Ed.: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boucard, C.C.; Hanekamp, S.; Ćurčić-Blake, B.; Ida, M.; Yoshida, M.; Cornelissen, F.W. Neurodegeneration beyond the primary visual pathways in a population with a high incidence of normal-pressure glaucoma. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2016, 36, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgio, A.; Zhang, J.; Costantino, F.; De Stefano, N.; Frezzotti, P. Diffuse brain damage in normal tension glaucoma. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, J.J.; Verkhratsky, A. Neuroglial roots of neurodegenerative diseases? Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 43, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, M.; Forrester, J.V. Para-inflammation in the aging retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2009, 28, 348–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, J.S.; Stryker, M.P. Development and Plasticity of the Primary Visual Cortex. Neuron 2012, 75, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baroncelli, L.; Lunghi, C. Neuroplasticity of the visual cortex: In sickness and in health. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 335, 113515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabet, L.B.; Pascual-Leone, A. Neural reorganization following sensory loss: The opportunity of change. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voss, P.; Zatorre, R.J. Organization and reorganization of sensory-deprived cortex. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R168–R173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parise, M.; Kubo, T.T.A.; Doring, T.M.; Tukamoto, G.; Vincent, M.; Gasparetto, E.L. Cuneus and fusiform cortices thickness is reduced in trigeminal neuralgia. J. Headache Pain 2014, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, J.; Yan, T.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, W. Brain morphological alterations of cerebral cortex and subcortical nuclei in high-tension glaucoma brain and its associations with intraocular pressure. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Komatsu, H. Representation of Angles Embedded within Contour Stimuli in Area V2 of Macaque Monkeys. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3313–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, O.M.; Cumming, B.G.; Parker, A.J. A specialization for relative disparity in V2. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shamayleh, Y.; Kumbhani, R.D.; Dhruv, N.T.; Movshon, J.A. Visual response properties of V1 neurons projecting to V2 in macaque. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 16594–16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.D.; Chen, G.; Tanigawa, H.; Roe, A.W. A Motion Direction Map in Macaque V2. Neuron 2010, 68, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Xie, B.; Yin, X.; Liang, M.; Evans, A.C.; Wang, J.; Dai, C. Reduced Cortical Thickness in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Its Relationship to the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.W.; Wang, N.; Cai, S.; Fang, Z.; Yu, M.; Wu, Q.; Tang, L.; Guo, B.; Feng, Y.; Jonas, J.B.; et al. Structural brain abnormalities in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma: A study with 3T MR imaging. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yin, X.; Dai, C.; Liang, M.; Wei, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Xie, B.; Wang, J. Morphologic changes in the anterior and posterior subregions of V1 and V2 and the V5/MT+ in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Brain Res. 2014, 1588, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikou, A.K.; Kitsos, G.; Tzarouchi, L.C.; Astrakas, L.; Alexiou, G.A.; Argyropoulou, M.I. Voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging of the optic pathway in primary open-angle glaucoma: A preliminary study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, M.T.; Strother, L. Does right hemisphere superiority sufficiently explain the left visual field advantage in face recognition? Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2020, 82, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux-Sibilon, A.; Rutgé, F.; Aptel, F.; Attye, A.; Guyader, N.; Boucart, M.; Chiquet, C.; Peyrin, C. Scene and human face recognition in the central vision of patients with glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sotimehin, A.E.; Ramulu, P.Y. Measuring Disability in Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2018, 27, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirji, S.H.; Liebmann, J.M.; Hood, D.C.; Cioffi, G.A.; Blumberg, D.M. Macular Damage in Glaucoma is Associated with Deficits in Facial Recognition. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 217, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, T.; Sabel, B.A.; Chen, Z.; Wen, H.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Yang, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, N.; et al. Structural brain alterations in primary open angle glaucoma: A 3T MRI study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzi, R.; Dallorto, L.; Rolle, T. Changes of visual pathway and brain connectivity in glaucoma: A systematic review. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qu, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Xian, J. Altered information flow and microstructure abnormalities of visual cortex in normal-tension glaucoma: Evidences from rest-state fMRI and DKI. Brain Res. 2020, 1741, 146874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ciò, F.; Garaci, F.; Minosse, S.; Passamonti, L.; Martucci, A.; Lanzafame, S.; Di Giuliano, F.; Picchi, E.; Cesareo, M.; Guerrisi, M.G.; et al. Reorganization of the structural connectome in primary open angle Glaucoma. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 28, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, N. Functional MRI signal changes in primary visual cortex corresponding to the central normal visual field of patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4627–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

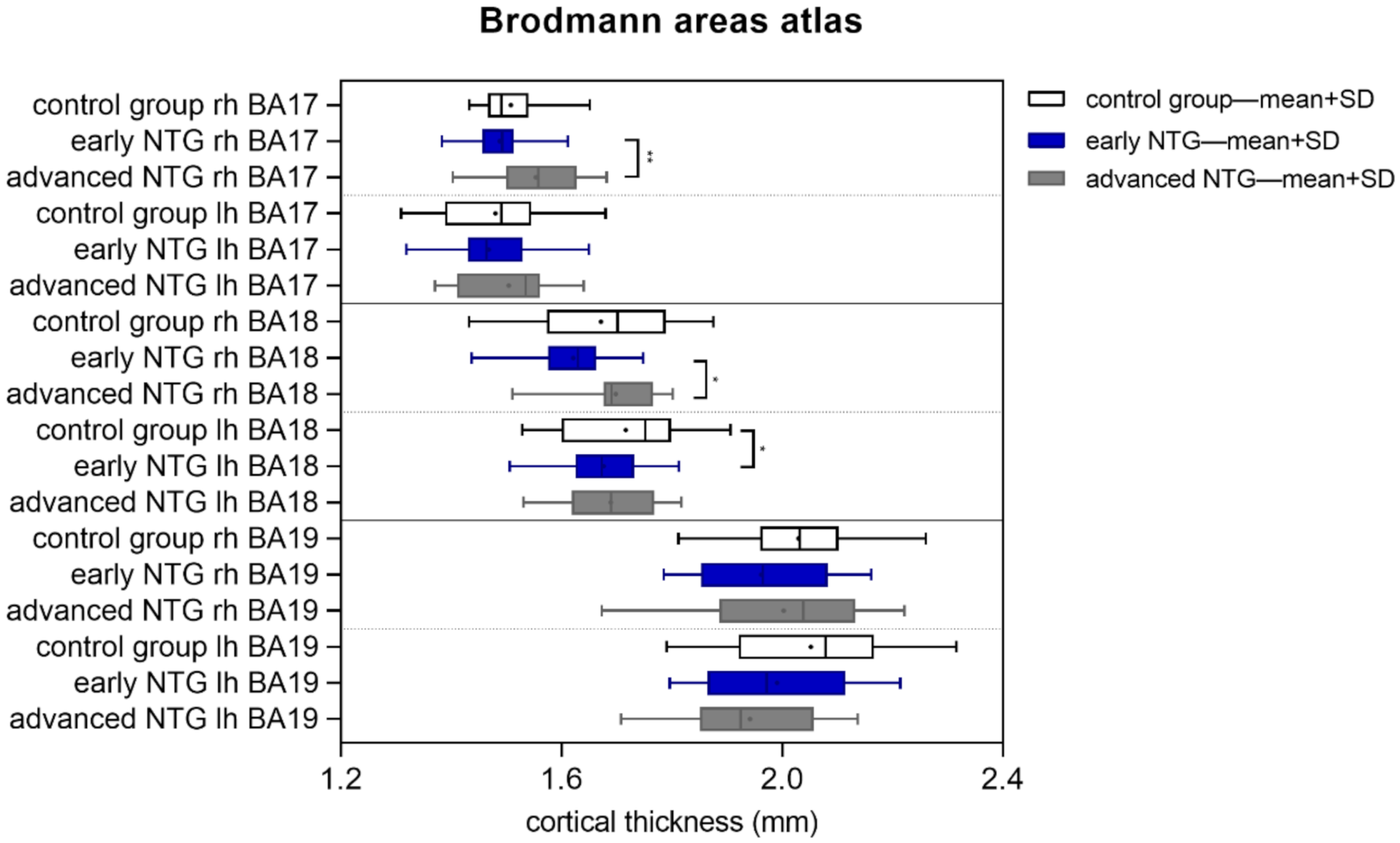

| Control Group n = 17 | Early Glaucoma n = 28 | Advanced Glaucoma n = 17 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 68.5 ± 11.8 | 63.2 ± 11.4 | 65 ± 14.7 |
| Male/female | 4/13 | 8/20 | 5/11 |
| Mean visual field MD (dB)—right eye | - | −2.97 (from −5.88 to −0.11) | −19.45 (form −29.53 to −16.18) |
| Mean visual field MD (dB)—left eye | - | −3.96 (from −5.93 to −0.43) | −18.33 (form −25.48 to −14.1) |
| Destrieux Anatomical Atlas | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Structure Name | Side | Control Group | Early-Stage NTG | Advanced-Stage NTG | ANOVA | ANOVA Post-Hoc (p-Value) | ||
| Con vs. Erl | Con vs. Adv | Erl vs. Adv | ||||||
| Lingual gyrus | right | 1.51 | 1.49 | 1.54 | 0.131 | 0.795 | 0.427 | 0.110 |
| left | 1.65 | 1.61 | 1.63 | 0.478 | 0.446 | 0.794 | 0.873 | |
| bilateral | 1.58 | 1.55 | 1.58 | 0.301 | 0.520 | 0.949 | 0.325 | |
| Calcarine sulcus | right | 2.10 | 2.09 | 2.02 | 0.147 | 0.941 | 0.181 | 0.219 |
| left | 1.71 | 1.71 | 1.76 | 0.334 | 1.000 | 0.424 | 0.356 | |
| bilateral | 1.89 | 1.90 | 1.89 | 0.988 | 0.987 | 0.995 | 0.999 | |
| Cuneus | right | 1.61 | 1.56 | 1.65 | 0.016 | 0.206 | 0.541 | 0.013 |
| left | 1.65 | 1.61 | 1.63 | 0.478 | 0.446 | 0.794 | 0.873 | |
| bilateral | 1.63 | 1.58 | 1.64 | 0.024 | 0.105 | 0.909 | 0.034 | |
| Collateral sulcus and lingual sulcus | right | 2.01 | 2.04 | 2.01 | 0.758 | 0.863 | 0.988 | 0.767 |
| left | 1.69 | 1.63 | 1.71 | 0.032 | 0.188 | 0.757 | 0.034 | |
| bilateral | 1.87 | 1.86 | 1.84 | 0.823 | 0.934 | 0.971 | 0.814 | |
| Occipital pole | right | 1.51 | 1.50 | 1.49 | 0.905 | 0.918 | 0.918 | 0.999 |
| left | 1.67 | 1.68 | 1.78 | 0.007 | 0.966 | 0.014 | 0.013 | |
| bilateral | 1.59 | 1.59 | 1.64 | 0.247 | 0.989 | 0.382 | 0.248 | |
| Contrast | Anatomical Region—Desikan and Killiany Atlas | Value | Findings | Size | Talairach Coordinates | Vertex | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm2 | X | Y | Z | |||||
| Control–early | Right lateral occipital gyrus | 2.98 | Con > Erl | 101.3 | 39.1 | −81.8 | 2.5 | 144 |
| Left lingual gyrus | 2.06 | Con > Erl | 5.2 | −3.9 | −87.8 | −6.2 | 6 | |
| Control–advanced | Right lateral occipital gyrus | 3.10 | Con > Adv | 103.8 | 45.6 | −79.9 | 0.9 | 150 |
| Right pericalcarine | −2.99 | Con < Adv | 97.4 | 13.6 | −91.7 | 7.1 | 131 | |
| Left lingual gyrus | 2.62 | Con > Adv | 25.4 | −22.1 | −54.5 | −1.7 | 75 | |
| Left lingual gyrus | 2.06 | Con > Adv | 5.5 | −15.8 | −59.1 | −5.3 | 9 | |
| Early–advanced | Right lateral occipital gyrus | 3.08 | Erl > Adv | 98.6 | 44.7 | −78.2 | 0.2 | 137 |
| Right cuneus | −2.97 | Erl < Adv | 431.1 | 6.5 | −86.2 | 14.6 | 516 | |
| Right lingual gyrus | −2.84 | Erl < Adv | 237.6 | 4.5 | −85.7 | −5 | 257 | |
| Right lateral occipital gyrus | −2.13 | Erl < Adv | 12.6 | 21.4 | −92.8 | −8.5 | 13 | |
| Left lateral occipital gyrus | 2.46 | Erl > Adv | 41.8 | −40 | −85 | −6.5 | 59 | |
| Pearson Correlation | Spearman Correlation | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Early NTG | Advanced NTG | Control | Early NTG | Advanced NTG | |||||||
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | |
| MD and RNFL vs. mean LGN volume—corresponding eyes | ||||||||||||
| MD | - | - | −0.13 | 0.424 | −0.05 | 0.797 | - | - | −0.12 | 0.465 | −0.04 | 0.864 |
| Average RNFL | −0.05 | 0.859 | 0.16 | 0.317 | −0.02 | 0.926 | −0.14 | 0.625 | 0.16 | 0.315 | 0.02 | 0.945 |
| Superior RNFL | −0.33 | 0.251 | 0.16 | 0.321 | 0.33 | 0.186 | −0.15 | 0.599 | 0.14 | 0.381 | 0.20 | 0.433 |
| Temporal RNFL | 0.09 | 0.756 | 0.34 | 0.027 | 0.03 | 0.915 | 0.16 | 0.594 | 0.29 | 0.059 | 0.18 | 0.486 |
| Inferior RNFL | 0.11 | 0.703 | 0.07 | 0.659 | −0.13 | 0.593 | 0.35 | 0.226 | 0.02 | 0.908 | −0.07 | 0.798 |
| Nasal RNFL | 0.20 | 0.498 | −0.14 | 0.368 | −0.37 | 0.130 | 0.04 | 0.887 | −0.14 | 0.373 | −0.50 | 0.035 |
| MD and RNFL vs. mean LGN volume—opposite eyes | ||||||||||||
| MD | - | - | 0.12 | 0.450 | 0.18 | 0.393 | - | - | 0.15 | 0.359 | 0.13 | 0.521 |
| Average RNFL | 0.15 | 0.597 | 0.38 | 0.012 | 0.08 | 0.758 | 0.07 | 0.805 | 0.47 | 0.002 | 0.31 | 0.206 |
| Superior RNFL | −0.06 | 0.844 | 0.26 | 0.103 | 0.41 | 0.088 | 0.12 | 0.675 | 0.43 | 0.005 | 0.38 | 0.122 |
| Temporal RNFL | 0.48 | 0.082 | 0.39 | 0.011 | 0.30 | 0.227 | 0.46 | 0.094 | 0.50 | 0.001 | 0.44 | 0.067 |
| Inferior RNFL | 0.18 | 0.548 | 0.37 | 0.016 | −0.15 | 0.553 | 0.18 | 0.532 | 0.36 | 0.019 | −0.07 | 0.773 |
| Nasal RNFL | 0.09 | 0.762 | 0.04 | 0.805 | −0.48 | 0.043 | 0.17 | 0.557 | 0.07 | 0.670 | −0.51 | 0.029 |
| Pearson Correlations | Spearman Correlations | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Early NTG | Advanced NTG | Control | Early NTG | Advanced NTG | |||||||
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-value | R | p-Value | |
| MD vs. mean cortical thickness—corresponding eyes | ||||||||||||
| V1–BA17 | −0.08 | 0.608 | −0.50 | 0.009 | −0.12 | 0.480 | −0.52 | 0.006 | ||||
| V2–BA18 | −0.25 | 0.119 | −0.32 | 0.121 | −0.25 | 0.123 | −0.34 | 0.105 | ||||
| V5/MT–BA19 | 0.02 | 0.871 | −0.38 | 0.064 | 0.08 | 0.576 | −0.50 | 0.011 | ||||
| Lingual gyrus | −0.04 | 0.781 | −0.06 | 0.777 | −0.02 | 0.906 | −0.20 | 0.316 | ||||
| Calcarine sulcus | 0.30 | 0.058 | −0.13 | 0.551 | 0.33 | 0.034 | −0.05 | 0.807 | ||||
| Cuneus | −0.27 | 0.079 | −0.16 | 0.443 | −0.23 | 0.148 | −0.18 | 0.366 | ||||
| Collateral sulcus and lingual sulcus | 0.17 | 0.281 | −0.17 | 0.413 | 0.20 | 0.202 | −0.08 | 0.693 | ||||
| Occipital pole | −0.30 | 0.048 | 0.08 | 0.717 | −0.35 | 0.019 | −0.06 | 0.773 | ||||
| MD vs. mean cortical thickness—opposite eyes | ||||||||||||
| V1–BA17 | −0.24 | 0.143 | −0.40 | 0.046 | −0.29 | 0.072 | −0.48 | 0.014 | ||||
| V2–BA18 | 0.03 | 0.857 | −0.16 | 0.466 | 0.01 | 0.942 | −0.19 | 0.375 | ||||
| V5/MT–BA19 | 0.04 | 0.799 | −0.10 | 0.619 | 0.03 | 0.834 | −0.17 | 0.410 | ||||
| Lingual gyrus | 0.07 | 0.634 | −0.28 | 0.170 | 0.11 | 0.475 | −0.28 | 0.180 | ||||
| Calcarine sulcus | −0.24 | 0.128 | 0.11 | 0.605 | −0.24 | 0.126 | −0.04 | 0.855 | ||||
| Cuneus | 0.07 | 0.640 | −0.13 | 0.521 | 0.10 | 0.512 | −0.19 | 0.365 | ||||
| Collateral sulcus and lingual sulcus | −0.13 | 0.399 | 0.26 | 0.218 | −0.12 | 0.459 | 0.09 | 0.689 | ||||
| Occipital pole | 0.04 | 0.796 | −0.15 | 0.485 | 0.05 | 0.763 | −0.09 | 0.658 | ||||
| Average RNFL vs. mean cortical thickness—corresponding eyes | ||||||||||||
| V1–BA17 | −0.15 | 0.591 | 0.00 | 0.980 | −0.08 | 0.750 | −0.13 | 0.634 | 0.13 | 0.382 | −0.10 | 0.685 |
| V2–BA18 | −0.40 | 0.135 | −0.14 | 0.345 | −0.31 | 0.230 | −0.32 | 0.240 | −0.08 | 0.617 | −0.14 | 0.582 |
| V5/MT–BA19 | −0.45 | 0.127 | 0.05 | 0.756 | −0.41 | 0.087 | −0.19 | 0.540 | 0.12 | 0.389 | −0.37 | 0.130 |
| Lingual gyrus | −0.27 | 0.314 | 0.11 | 0.458 | 0.12 | 0.668 | −0.24 | 0.374 | 0.21 | 0.171 | 0.13 | 0.642 |
| Calcarine sulcus | 0.18 | 0.520 | 0.10 | 0.524 | −0.22 | 0.406 | 0.09 | 0.746 | 0.10 | 0.494 | −0.23 | 0.367 |
| Cuneus | −0.31 | 0.240 | 0.00 | 0.977 | 0.20 | 0.432 | −0.28 | 0.299 | 0.05 | 0.757 | 0.15 | 0.574 |
| Collateral sulcus and lingual sulcus | 0.13 | 0.630 | 0.08 | 0.603 | −0.21 | 0.412 | 0.00 | 0.987 | 0.06 | 0.661 | −0.30 | 0.229 |
| Occipital pole | −0.19 | 0.476 | −0.09 | 0.532 | 0.06 | 0.828 | −0.36 | 0.175 | −0.05 | 0.756 | 0.08 | 0.761 |
| Average RNFL vs. mean cortical thickness—opposite eyes | ||||||||||||
| V1–BA17 | −0.16 | 0.578 | −0.17 | 0.273 | 0.08 | 0.755 | −0.16 | 0.580 | −0.07 | 0.664 | 0.04 | 0.880 |
| V2–BA18 | −0.36 | 0.188 | 0.02 | 0.885 | −0.14 | 0.599 | −0.22 | 0.440 | 0.04 | 0.767 | −0.01 | 0.957 |
| V5/MT–BA19 | −0.25 | 0.401 | 0.13 | 0.361 | −0.12 | 0.629 | −0.12 | 0.703 | 0.20 | 0.155 | −0.06 | 0.812 |
| Lingual gyrus | −0.14 | 0.605 | 0.21 | 0.167 | −0.36 | 0.166 | −0.25 | 0.356 | 0.19 | 0.206 | −0.41 | 0.114 |
| Calcarine sulcus | 0.07 | 0.808 | 0.01 | 0.960 | −0.04 | 0.892 | −0.01 | 0.965 | 0.00 | 0.982 | 0.15 | 0.568 |
| Cuneus | −0.27 | 0.307 | −0.01 | 0.940 | 0.00 | 0.987 | −0.25 | 0.356 | 0.06 | 0.682 | 0.07 | 0.796 |
| Collateral sulcus and lingual sulcus | −0.08 | 0.779 | −0.03 | 0.859 | 0.05 | 0.839 | −0.06 | 0.833 | −0.03 | 0.857 | 0.33 | 0.182 |
| Occipital pole | 0.12 | 0.654 | 0.09 | 0.554 | −0.28 | 0.294 | 0.10 | 0.724 | 0.14 | 0.339 | −0.33 | 0.218 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pankowska, A.; Matwiejczuk, S.; Kozioł, P.; Żarnowski, T.; Pietura, R.; Kosior-Jarecka, E. Visual Tract Degradation in Bilateral Normal-Tension Glaucoma—Cortical Thickness Maps and Volumetric Study of Visual Pathway Areas. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071907
Pankowska A, Matwiejczuk S, Kozioł P, Żarnowski T, Pietura R, Kosior-Jarecka E. Visual Tract Degradation in Bilateral Normal-Tension Glaucoma—Cortical Thickness Maps and Volumetric Study of Visual Pathway Areas. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(7):1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071907
Chicago/Turabian StylePankowska, Anna, Sylwester Matwiejczuk, Paulina Kozioł, Tomasz Żarnowski, Radosław Pietura, and Ewa Kosior-Jarecka. 2022. "Visual Tract Degradation in Bilateral Normal-Tension Glaucoma—Cortical Thickness Maps and Volumetric Study of Visual Pathway Areas" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 7: 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071907
APA StylePankowska, A., Matwiejczuk, S., Kozioł, P., Żarnowski, T., Pietura, R., & Kosior-Jarecka, E. (2022). Visual Tract Degradation in Bilateral Normal-Tension Glaucoma—Cortical Thickness Maps and Volumetric Study of Visual Pathway Areas. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(7), 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071907







