Best Fit 3D Basilar Membrane Reconstruction to Routinely Assess the Scalar Position of the Electrode Array after Cochlear Implantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cochlear Images Used in This Study
- A set of 100 CT images from pre-implanted patients;
- Images of 30 cadaveric temporal bones, including pre- and post-implantation CBCT;
- A collection of 22 CT images of non-implanted cochleae—20 from the SMIR database of cochlea data descriptors (SICAS Medical Repository, Corroux, Switzerland) [28] and 2 from our own database.
2.2. Registration Procedure
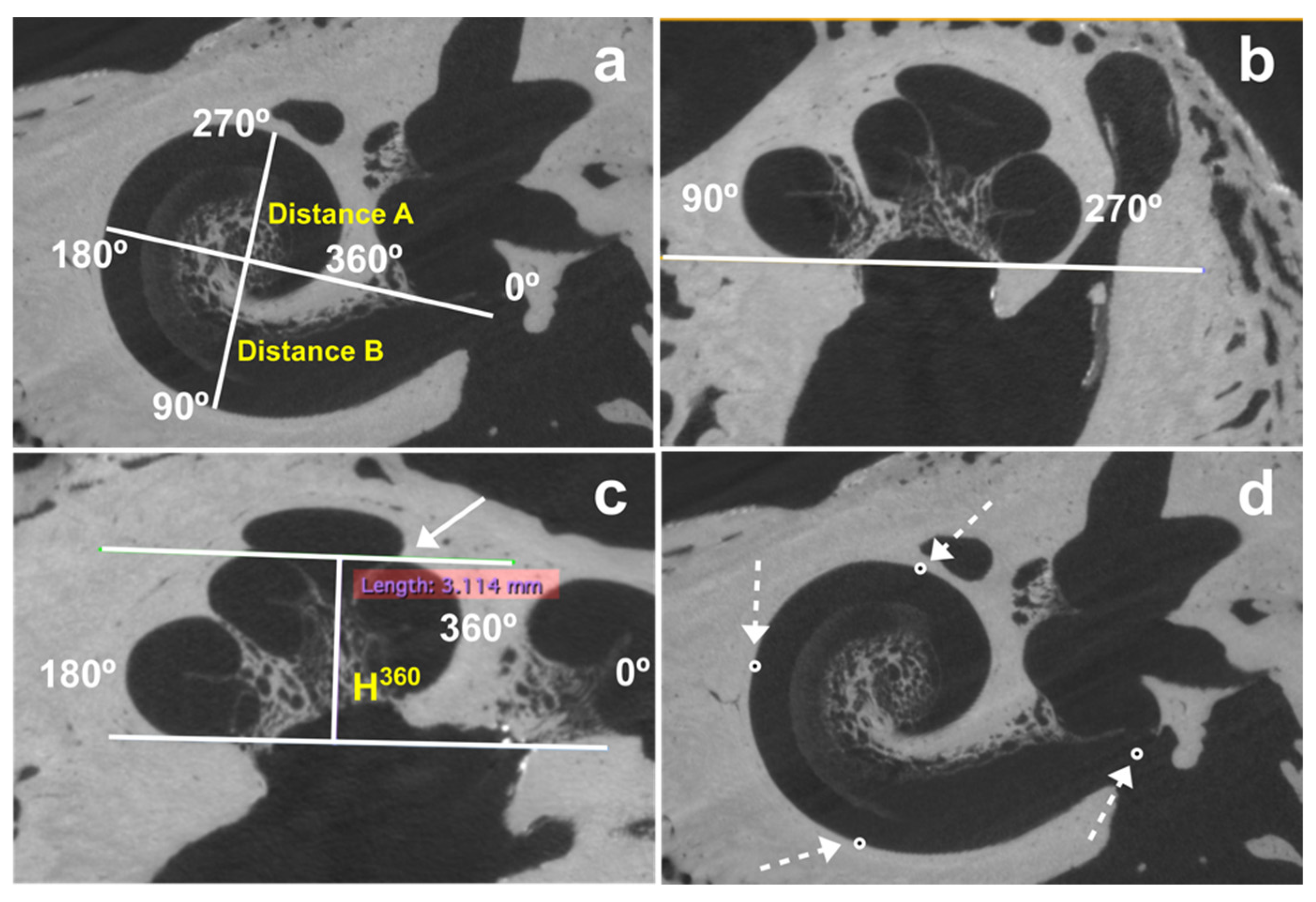
2.2.1. Determination of Cochlea Dimensions
- Distance A (A) between the center of the round window and lateral wall at 180°;
- Distance B (B) between the lateral wall at 90° and 270°;
- The height at 360° (H360), measured from the base of the cochlea to the highest point of the cochlear turn at 360°.
2.2.2. Determination of the Position of Four Electrode Array Landmarks
2.2.3. “Basilar Membrane” Segmentation
2.2.4. Electrode Array Segmentation
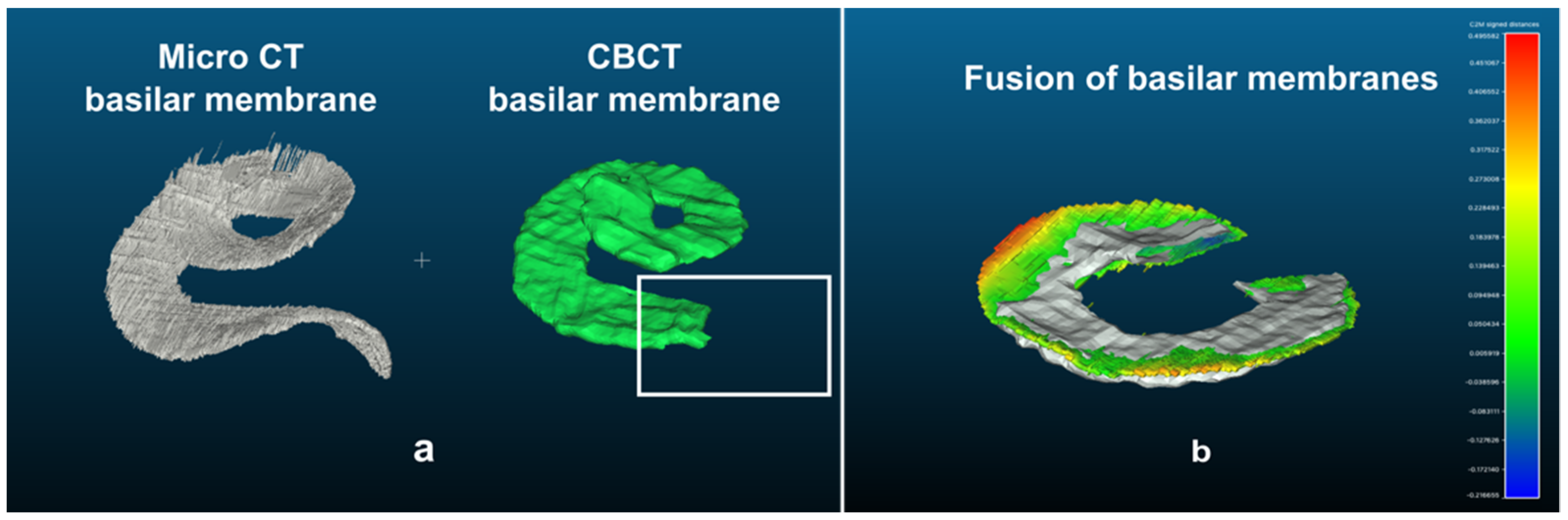
2.2.5. Procedure for Merging 3D Reconstruction Models
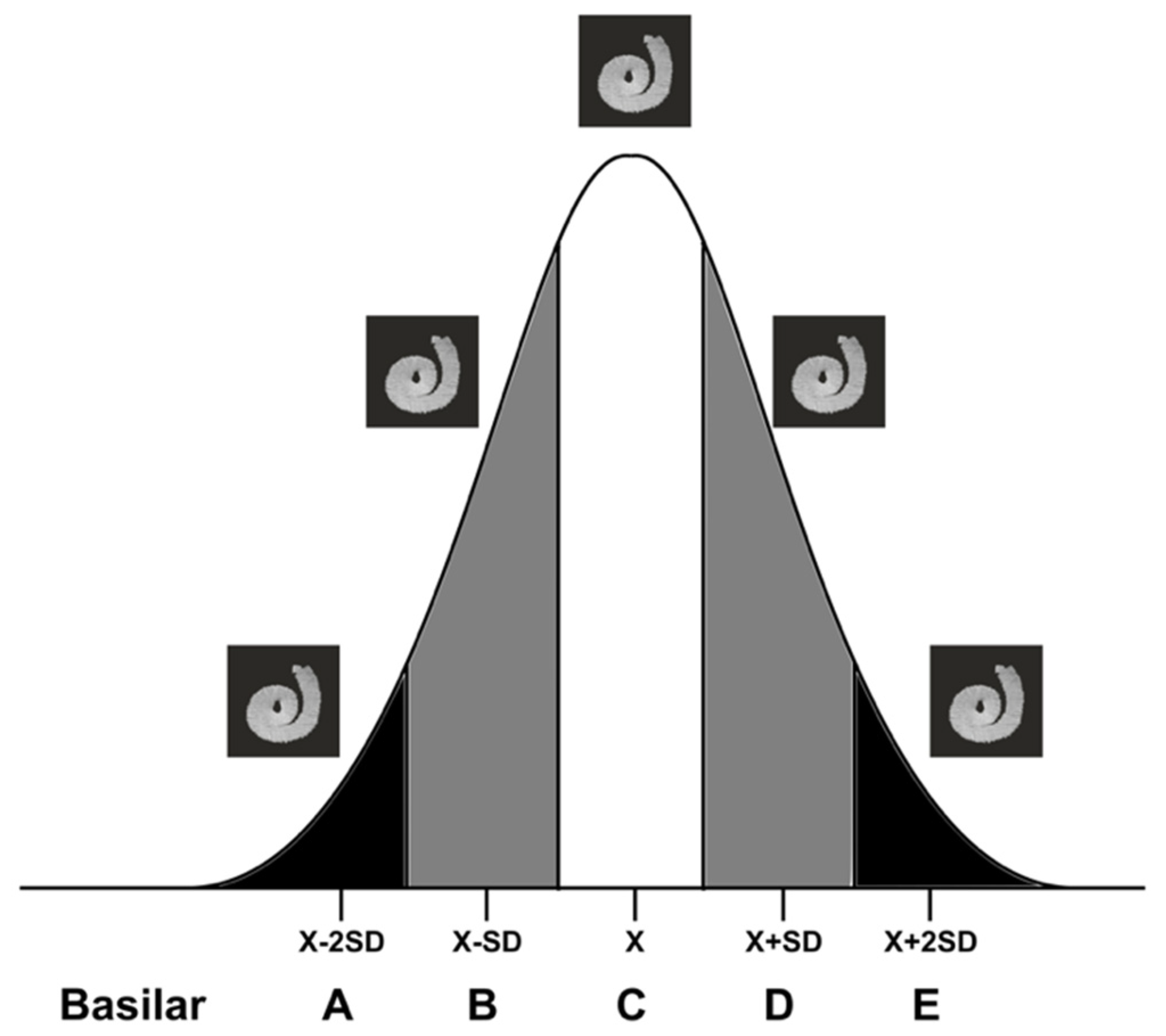
2.3. The “Basilar Membrane” Templates
2.4. Determination of the Intrascalar Position of Each Electrode
- Scala tympani electrode: ≥50% of the electrode under the “basilar membrane”.
- Intermediate electrode: ≥10% to <50% of the electrode under the “basilar membrane”.
- Scala vestibuli electrode: <10% under the “basilar membrane”.
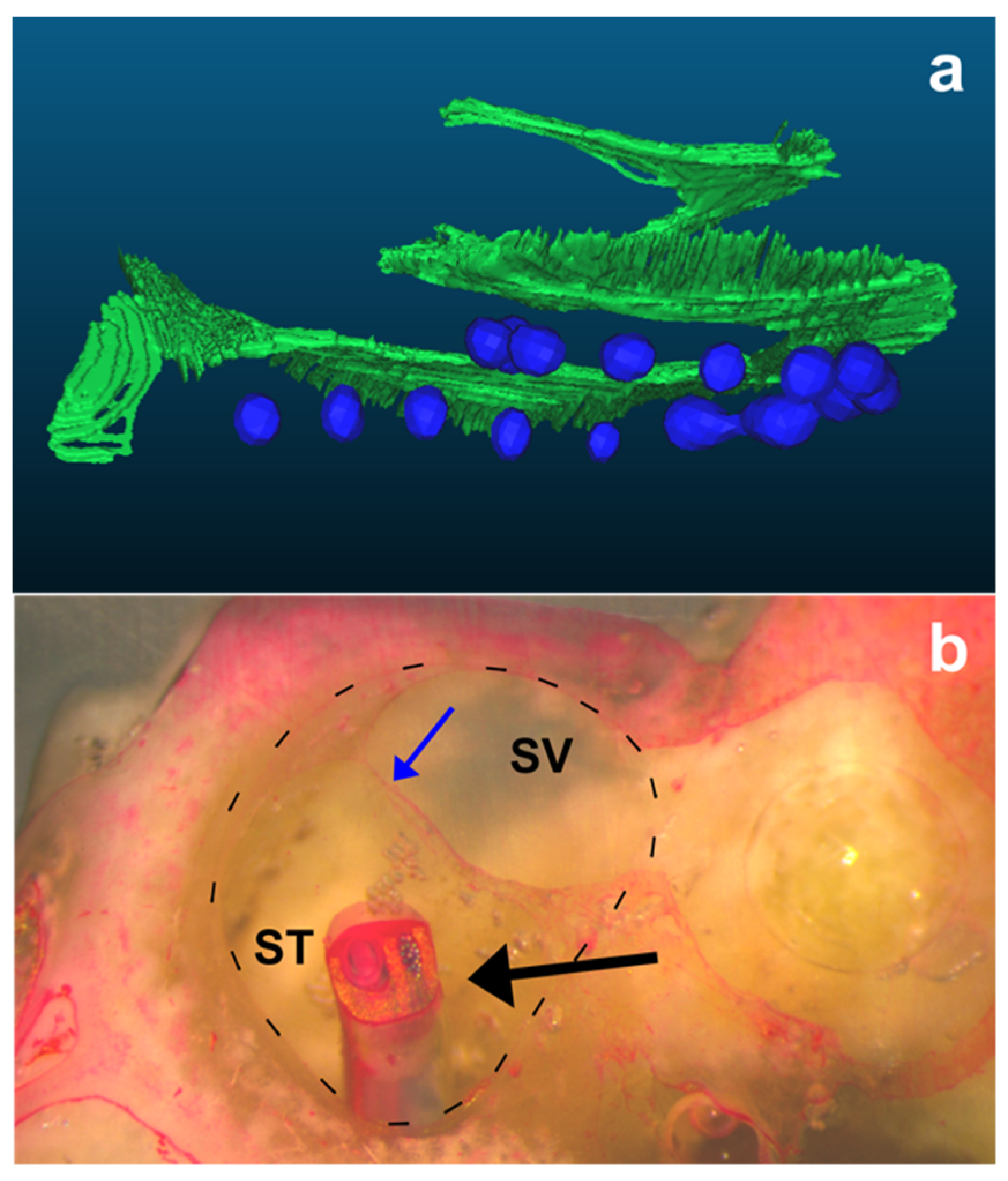
2.5. Comparing the “Basilar Membrane” Reconstruction with Histology to Determine the Intrascalar Position of the Electrode Array
- Select a “basilar membrane” template according to the index value obtained on pre-implantation CBCT.
- Obtain the reconstruction of the electrode array from the post-implantation CBCT.
- Obtain the four corresponding points from the post-implantation CBCT.
- Merge the electrode array reconstruction with the selected “basilar membrane” template according to the four landmarks.
- Determine the position of each electrode.
2.6. Description of the Histopathological Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inter-Rater Agreement in Determining the Scalar Position of Each Electrode
3.2. Different Translocation Patterns Depending on the Type of Electrode Array
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazard, D.S.; Vincent, C.; Venail, F.; Van de Heyning, P.; Truy, E.; Sterkers, O.; Skarzynski, P.H.; Skarzynski, H.; Schauwers, K.; O’Leary, S.; et al. Pre-, Per- and Postoperative Factors Affecting Performance of Postlinguistically Deaf Adults Using Cochlear Implants: A New Conceptual Model over Time. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blamey, P.; Artieres, F.; Başkent, D.; Bergeron, F.; Beynon, A.; Burke, E.; Dillier, N.; Dowell, R.; Fraysse, B.; Gallégo, S.; et al. Factors Affecting Auditory Performance of Postlinguistically Deaf Adults Using Cochlear Implants: An Update with 2251 Patients. Audiol. Neurootol. 2013, 18, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bas, E.; Bohorquez, J.; Goncalves, S.; Perez, E.; Dinh, C.T.; Garnham, C.; Hessler, R.; Eshraghi, A.A.; Van De Water, T.R. Electrode Array-Eluted Dexamethasone Protects against Electrode Insertion Trauma Induced Hearing and Hair Cell Losses, Damage to Neural Elements, Increases in Impedance and Fibrosis: A Dose Response Study. Hear. Res. 2016, 337, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanna, G.B.; Noble, J.H.; Gifford, R.H.; Dietrich, M.S.; Sweeney, A.D.; Zhang, D.; Dawant, B.M.; Rivas, A.; Labadie, R.F. Impact of Intrascalar Electrode Location, Electrode Type, and Angular Insertion Depth on Residual Hearing in Cochlear Implant Patients: Preliminary Results. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, L.K.; Finley, C.C.; Firszt, J.B.; Holden, T.A.; Brenner, C.; Potts, L.G.; Gotter, B.D.; Vanderhoof, S.S.; Mispagel, K.; Heydebrand, G.; et al. Factors Affecting Open-Set Word Recognition in Adults with Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2013, 34, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanna, G.B.; Noble, J.H.; Carlson, M.L.; Gifford, R.H.; Dietrich, M.S.; Haynes, D.S.; Dawant, B.M.; Labadie, R.F. Impact of Electrode Design and Surgical Approach on Scalar Location and Cochlear Implant Outcomes. Laryngoscope 2014, 124 (Suppl. S6), S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, B.P.; Hunter, J.B.; Wanna, G.B. The Importance of Electrode Location in Cochlear Implantation. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2016, 1, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiam, N.T.; Jiradejvong, P.; Pearl, M.S.; Limb, C.J. The Effect of Round Window vs Cochleostomy Surgical Approaches on Cochlear Implant Electrode Position: A Flat-Panel Computed Tomography Study. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laszig, R.; Ridder, G.J.; Fradis, M. Intracochlear Insertion of Electrodes Using Hyaluronic Acid in Cochlear Implant Surgery. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2002, 116, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittoria, S.; Lahlou, G.; Torres, R.; Daoudi, H.; Mosnier, I.; Mazalaigue, S.; Ferrary, E.; Nguyen, Y.; Sterkers, O. Robot-Based Assistance in Middle Ear Surgery and Cochlear Implantation: First Clinical Report. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finley, C.C.; Holden, T.A.; Holden, L.K.; Whiting, B.R.; Chole, R.A.; Neely, G.J.; Hullar, T.E.; Skinner, M.W. Role of Electrode Placement as a Contributor to Variability in Cochlear Implant Outcomes. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Seta, D.; Nguyen, Y.; Bonnard, D.; Ferrary, E.; Godey, B.; Bakhos, D.; Mondain, M.; Deguine, O.; Sterkers, O.; Bernardeschi, D.; et al. The Role of Electrode Placement in Bilateral Simultaneously Cochlear-Implanted Adult Patients. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daoudi, H.; Lahlou, G.; Torres, R.; Sterkers, O.; Lefeuvre, V.; Ferrary, E.; Mosnier, I.; Nguyen, Y. Robot-Assisted Cochlear Implant Electrode Array Insertion in Adults: A Comparative Study with Manual Insertion. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e438–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschendorff, A.; Kromeier, J.; Klenzner, T.; Laszig, R. Quality Control after Insertion of the Nucleus Contour and Contour Advance Electrode in Adults. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 75S–79S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbist, B.M.; Frijns, J.H.M.; Geleijns, J.; van Buchem, M.A. Multisection CT as a Valuable Tool in the Postoperative Assessment of Cochlear Implant Patients. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyer, E.; Karkas, A.; Attye, A.; Lefournier, V.; Escude, B.; Schmerber, S. Scalar Localization by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography of Cochlear Implant Carriers: A Comparative Study between Straight and Periomodiolar Precurved Electrode Arrays. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Seta, D.; Mancini, P.; Russo, F.Y.; Torres, R.; Mosnier, I.; Bensimon, J.L.; De Seta, E.; Heymann, D.; Sterkers, O.; Bernardeschi, D.; et al. 3D Curved Multiplanar Cone Beam CT Reconstruction for Intracochlear Position Assessment of Straight Electrodes Array. A Temporal Bone and Clinical Study. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2016, 36, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipari, S.; Iso-Mustajärvi, M.; Löppönen, H.; Dietz, A. The Insertion Results of a Mid-Scala Electrode Assessed by MRI and CBCT Image Fusion. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e1019–e1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragovic, A.S.; Stringer, A.K.; Campbell, L.; Shaul, C.; O’Leary, S.J.; Briggs, R.J. Co-Registration of Cone Beam CT and Preoperative MRI for Improved Accuracy of Electrode Localization Following Cochlear Implantation. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2018, 19, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.; Drouillard, M.; De Seta, D.; Bensimon, J.-L.; Ferrary, E.; Sterkers, O.; Bernardeschi, D.; Nguyen, Y. Cochlear Implant Insertion Axis into the Basal Turn: A Critical Factor in Electrode Array Translocation. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.W.; Holden, T.A.; Whiting, B.R.; Voie, A.H.; Brunsden, B.; Neely, J.G.; Saxon, E.A.; Hullar, T.E.; Finley, C.C. In vivo estimates of the position of advanced bionics electrode arrays in the human cochlea. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Suppl. 2007, 197, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, A.; Labadie, R.F.; Zuniga, M.G.; Dawant, B.M.; Noble, J.H. Evaluation of Rigid Cochlear Models for Measuring Cochlear Implant Electrode Position. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 1560–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biedron, S.; Prescher, A.; Ilgner, J.; Westhofen, M. The Internal Dimensions of the Cochlear Scalae with Special Reference to Cochlear Electrode Insertion Trauma. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escudé, B.; James, C.; Deguine, O.; Cochard, N.; Eter, E.; Fraysse, B. The Size of the Cochlea and Predictions of Insertion Depth Angles for Cochlear Implant Electrodes. Audiol. Neurootol. 2006, 11 (Suppl. S1), 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erixon, E.; Högstorp, H.; Wadin, K.; Rask-Andersen, H. Variational Anatomy of the Human Cochlea: Implications for Cochlear Implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, J.H.; Labadie, R.F.; Majdani, O.; Dawant, B.M. Automatic Segmentation of Intracochlear Anatomy in Conventional CT. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demarcy, T.; Vandersteen, C.; Guevara, N.; Raffaelli, C.; Gnansia, D.; Ayache, N.; Delingette, H. Automated Analysis of Human Cochlea Shape Variability from Segmented ΜCT Images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2017, 59, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerber, N.; Reyes, M.; Barazzetti, L.; Kjer, H.M.; Vera, S.; Stauber, M.; Mistrik, P.; Ceresa, M.; Mangado, N.; Wimmer, W.; et al. A Multiscale Imaging and Modelling Dataset of the Human Inner Ear. Sci. Data. 2017, 4, 170132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horos Project. Available online: https://horosproject.org (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- ITK-SNAP Home. Available online: http://www.itksnap.org (accessed on 3 April 2017).
- CloudCompare—Open Source project. Available online: https://www.cloudcompare.org (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- Blender Project—Free and Open 3D Creation Software. Available online: https://www.blender.org/ (accessed on 9 March 2019).
- Biedron, S.; Westhofen, M.; Ilgner, J. On the Number of Turns in Human Cochleae. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassepass, F.; Aschendorff, A.; Bulla, S.; Arndt, S.; Maier, W.; Laszig, R.; Beck, R. Radiologic Results and Hearing Preservation with a Straight Narrow Electrode via Round Window Versus Cochleostomy Approach at Initial Activation. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka Massuda, E.; Demarcy, T.; Hoen, M.; Danieli, F.; Arantes do Amaral, M.S.; Gnansia, D.; Hyppolito, M.A. Method to Quantitatively Assess Electrode Migration from Medical Images: Feasibility and Application in Patients with Straight Cochlear Implant Arrays. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2019, 20, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Briaire, J.J.; Siebrecht, M.; Stronks, H.C.; Frijns, J.H.M. Detection of Translocation of Cochlear Implant Electrode Arrays by Intracochlear Impedance Measurements. Ear Hear. 2021, 42, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.; Hochet, B.; Daoudi, H.; Carré, F.; Mosnier, I.; Sterkers, O.; Ferrary, E.; Nguyen, Y. Atraumatic Insertion of a Cochlear Implant Pre-Curved Electrode Array by a Robot-Automated Alignment with the Coiling Direction of the Scala Tympani. Audiol. Neurootol. 2022, 27, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient CT (n = 100) | Cadaveric CBCT (n = 30) | Micro-CT (n = 22) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Min–Max | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | |
| Distance A | 9.1 ± 0.30 | 8.0–9.6 | 9.1 ± 0.22 | 8.7–9.4 | 9.2 ± 0.33 | 8.6–9.8 |
| Distance B | 6.8 ± 0.32 | 5.8–7.6 | 6.9 ± 0.24 | 6.6–7.4 | 7.0 ± 0.31 | 6.5–7.5 |
| H360 | 2.8 ± 0.21 | 2.4–3.3 | 2.9 ± 0.17 | 2.6–3.3 | 2.9 ± 0.19 | 2.3–3.3 |
| (A)×H360 | 26 ± 2.30 | 20–33 | 26 ± 1.9 | 23–30 | 27 ± 2.4 | 22–29 |
| (A×B)×H360 | 175 ± 19.9 | 126–210 | 182 ± 17.2 | 159–211 | 194 ± 23.3 | 135–203 |
| (A/B)×H360 | 3.8 ± 0.30 | 3.0–4.7 | 3.8 ± 0.24 | 3.4–4.2 | 3.9 ± 0.29 | 3.1–4.4 |
| All Electrodes | Scala Tympani Electrode | Intermediate Electrode | Scala Vestibuli Electrode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Bionics MidScala | Expert | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.24 | 0.89 |
| Non-expert | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.06 | 0.81 | |
| Expert + Non-expert | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.12 | 0.82 | |
| Oticon EVO | Expert | 0.46 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.60 |
| Non-expert | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 0.41 | |
| Expert + Non-expert | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres, R.; Tinevez, J.-Y.; Daoudi, H.; Lahlou, G.; Grislain, N.; Breil, E.; Sterkers, O.; Mosnier, I.; Nguyen, Y.; Ferrary, E. Best Fit 3D Basilar Membrane Reconstruction to Routinely Assess the Scalar Position of the Electrode Array after Cochlear Implantation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082075
Torres R, Tinevez J-Y, Daoudi H, Lahlou G, Grislain N, Breil E, Sterkers O, Mosnier I, Nguyen Y, Ferrary E. Best Fit 3D Basilar Membrane Reconstruction to Routinely Assess the Scalar Position of the Electrode Array after Cochlear Implantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(8):2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082075
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres, Renato, Jean-Yves Tinevez, Hannah Daoudi, Ghizlene Lahlou, Neil Grislain, Eugénie Breil, Olivier Sterkers, Isabelle Mosnier, Yann Nguyen, and Evelyne Ferrary. 2022. "Best Fit 3D Basilar Membrane Reconstruction to Routinely Assess the Scalar Position of the Electrode Array after Cochlear Implantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 8: 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082075
APA StyleTorres, R., Tinevez, J.-Y., Daoudi, H., Lahlou, G., Grislain, N., Breil, E., Sterkers, O., Mosnier, I., Nguyen, Y., & Ferrary, E. (2022). Best Fit 3D Basilar Membrane Reconstruction to Routinely Assess the Scalar Position of the Electrode Array after Cochlear Implantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(8), 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082075








