Perception of the Regulatory Change for Zolpidem Prescription by French General Practitioners and Its Relation to Prescription Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Oversight
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Procedures
- Nothing changed;
- A supplementary difficulty (writing on secured prescription pads);
- Awareness of risks of zolpidem;
- Awareness of risks of hypnotics;
- Helpful for zolpidem discontinuation.
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Population and Perceptions of the New Regulation
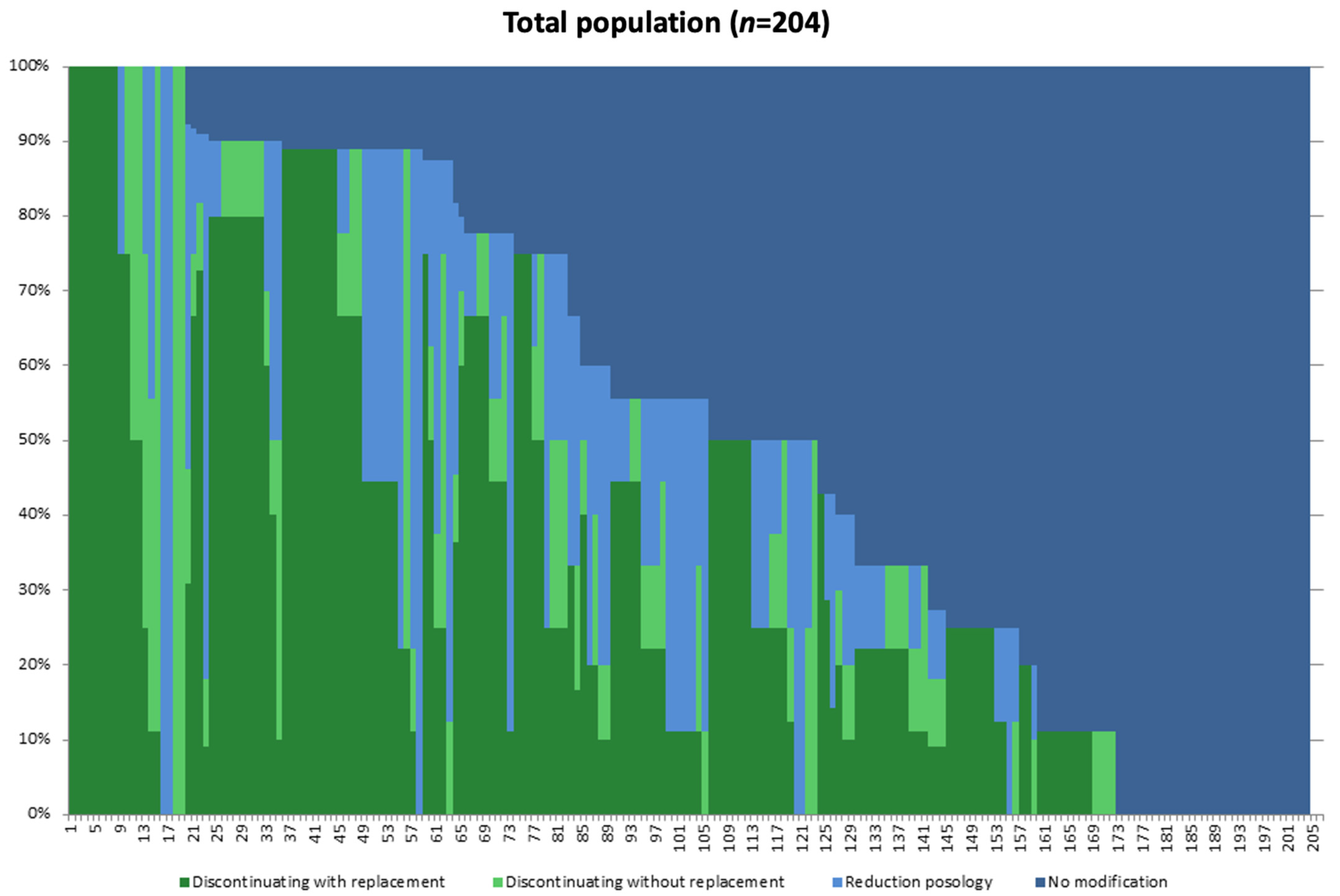
3.2. Description of the Different Strategies Applied with Regard to the New Regulation
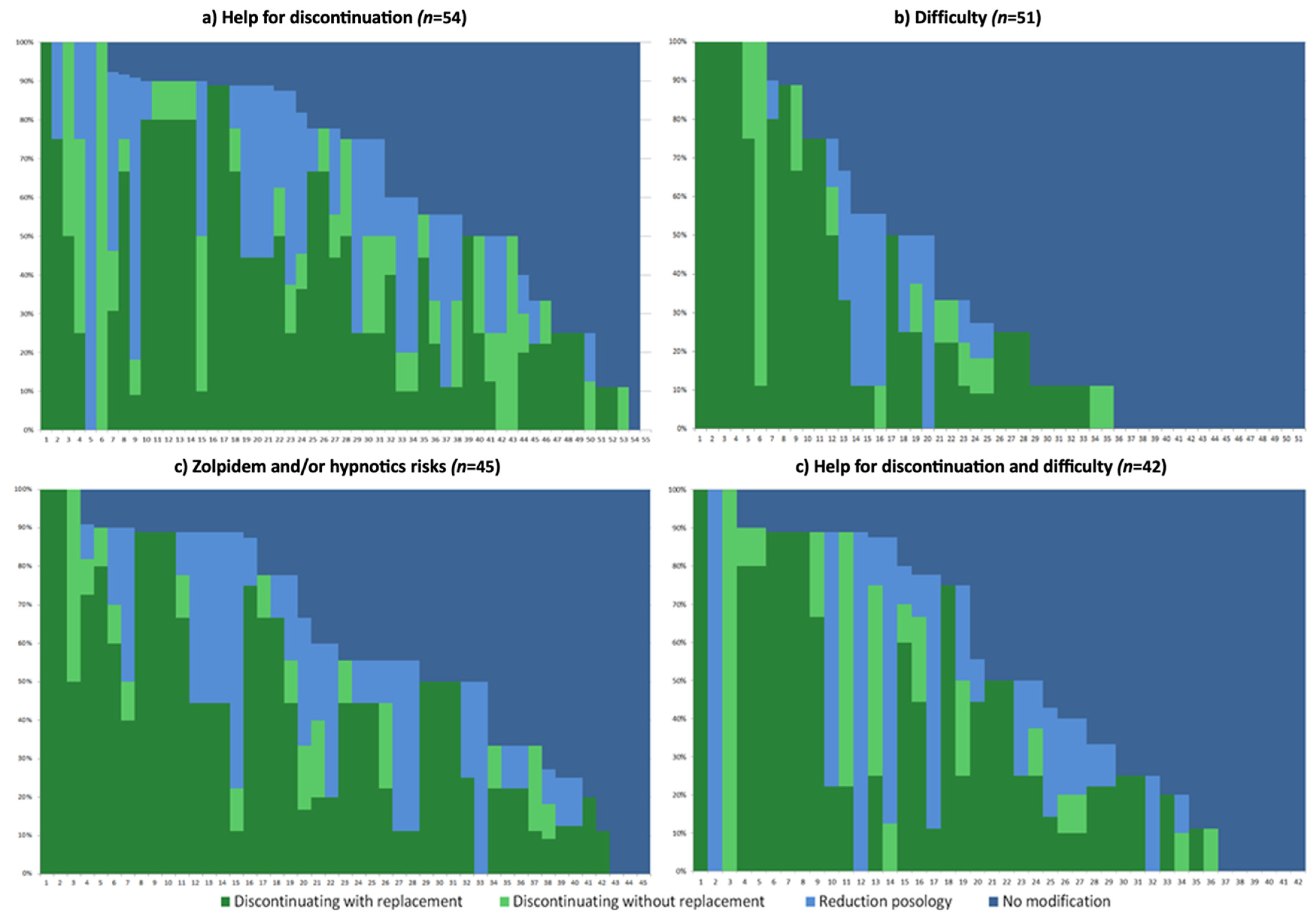
3.3. Different Strategies Applied towards Zolpidem Prescription Based on Perceptions towards the New Regulation
- Helpful for discontinuation (only), n = 54.
- Difficulty (only), n = 51.
- Awareness of risks of zolpidem and/or hypnotics (and potentially other answers), n = 45.
- Helpful for discontinuation and difficulty, n = 42.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ANSM: Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé. Etat des Lieux de la Consommation des Benzodiazépines—Point D’Information—ANSM: Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé. 2017. Available online: https://ansm.sante.fr/S-informer/Points-d-information-Points-d-information/Etat-des-lieux-de-la-consommation-des-benzodiazepines-Point-d-Information (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Victorri-Vigneau, C.; Dailly, E.; Veyrac, G.; Jolliet, P. Evidence of zolpidem abuse and dependence: Results of the French Centre for Evaluation and Information on Pharmacodependence (CEIP) network survey. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 64, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victorri-Vigneau, C.; Gérardin, M.; Rousselet, M.; Guerlais, M.; Grall-Bronnec, M.; Jolliet, P. An update on zolpidem abuse and dependence. J. Addict. Dis. 2014, 33, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Hayasaka, Y.; Furukawa, T.A. Continuation and discontinuation of benzodiazepine prescriptions: A cohort study based on a large claims database in Japan. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 237, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jouanjus, E.; Gibaja, V.; Kahn, J.-P.; Haramburu, F.; Daveluy, A. Signal identification in addictovigilance: The functioning of the French system. Therapie 2015, 70, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanjus, E.; Guernec, G.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M.; Network, T.F.A. Medical prescriptions falsified by the patients: A 12-year national monitoring to assess prescription drug diversion. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselet, M.; Feuillet, F.; Gerardin, M.; Jolliet, P.; Hardouin, J.-B.; Victorri-Vigneau, C. The French addictovigilance network clinical assessment: Z-drugs, true false twins. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2017, 16, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, M.; Feuillet, F.; Gerardin, M.; Jolliet, P.; Hardouin, J.-B.; Victorri-Vigneau, C. Pharmacoepidemiological characterisation of zolpidem and zopiclone usage. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence. Thirty-second report. World Health Organ. Technol. Rep. Ser. 2001, 903, i–v,1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires lower dosing of zolpidem. Med. Lett. Drugs Ther. 2013, 55, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Base de Données Publique des Médicaments. Résumé des Caractéristiques du Produit—STILNOX 10 mg, Comprimé Pelliculé Sécable. 2021. Available online: https://base-donnees-publique.medicaments.gouv.fr/affichageDoc.php?specid=63179285&typedoc=R (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- ANSM: Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé. STILNOX et Génériques. 2017. Available online: https://archiveansm.integra.fr/Activites/Surveillance-des-stupefiants-et-des-psychotropes/Medicaments-a-risque-d-usage-detourne-ou-de-dependance/Medicaments-a-risque-d-usage-detourne-ou-de-dependance/STILNOX-et-generiques (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Gérardin, M.; Rousselet, M.; Caillet, P.; Grall-Bronnec, M.; Loué, P.; Jolliet, P.; Victorri-Vigneau, C. French national health insurance database analysis and field study focusing on the impact of secure prescription pads on zolpidem consumption and sedative drug misuse: ZORRO study protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, P.; Rousselet, M.; Gerardin, M.; Jolliet, P.; Victorri-Vigneau, C. Prevalence of zolpidem use in France halved after secure prescription pads implementation in 2017: A SNDS database nested cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istvan, M.; Caillet, P.; Rousselet, M.; Guerlais, M.; Laforgue, E.-J.; Gérardin, M.; Jolliet, P.; Feuillet, F.; Victorri-Vigneau, C. Change in the regulatory framework for zolpidem: What is the impact on the landscape of the prescription of sedative medications? The French national ZORRO study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, bcp.14753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, G.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M.; Micallef, J. Combatting the misuse of benzodiazepines and related Z drugs in French general practice: A clinical review. BJGP Open 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedecke, T.; Morales, D.R.; Pacurariu, A.; Kurz, X. Measuring the impact of medicines regulatory interventions—Systematic review and methodological considerations: Methods for measuring impact of medicines regulatory interventions. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebo, P.; Cerutti, B.; Fournier, J.-P.; Rat, C.; Rougerie, F.; Senn, N.; Haller, D.M.; Maisonneuve, H. How do general practitioners put preventive care recommendations into practice? A cross-sectional study in Switzerland and France. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caisse Autonome de Retraite des Médecins de France. Site internet de la CARMF. 2019. Available online: https://www.carmf.fr/page.php?page=chiffrescles/stats/2019/demographie.htm (accessed on 6 July 2021).
- Bedson, J.; Belcher, J.; Martino, O.; Ndlovu, M.; Rathod, T.; Walters, K.; Dunn, K.; Jordan, K. The effectiveness of national guidance in changing analgesic prescribing in primary care from 2002 to 2009: An observational database study. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daveluy, A.; Sauvaget, L.; Bastien, A.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M.; Collin, C.; Richard, N.; Haramburu, F. Tamper-resistant prescription forms for narcotics in France: Should we generalize them? Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F. Perceptions of German GPs on benefits and risks of benzodiazepines and Z-drugs. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2013, 143, w13745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardena, A.N.; Qureshi, Z.; Gibson, S.; Collier, S.; Latham, M. GPs’ attitudes to benzodiazepine and ‘Z-drug’ prescribing: A barrier to implementation of evidence and guidance on hypnotics. Br. J. Gen. Pract. J. R. Coll. Gen. Pract. 2006, 56, 964–967. [Google Scholar]
- Victorri-Vigneau, C.; Marais, M.; Veyrac, G.; Chaslerie, A.; Pivette, J.; Jolliet, P. Réactivité et communication des décisions de pharmacovigilance des autorités de santé vers les professionnels de santé: Exemples du pergolide et du célécoxib. Therapies 2007, 62, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victorri-Vigneau, C.; Basset, G.; Jolliet, P. How a novel programme for increasing awareness of health professionals resulted in a 14% decrease in patients using excessive doses of psychotropic drugs in western France. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laforgue, E.; Jobert, A.; Rousselet, M.; Grall-Bronnec, M.; Jolliet, P.; Feuillet, F.; Victorri-Vigneau, C.; Network, F. Do older people know why they take benzodiazepines? A national french cross-sectional survey of long-term consumers. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogunovic, O.J.; Greenfield, S.F. Practical geriatrics: Use of benzodiazepines among elderly patients. Psychiatr. Serv. 2004, 55, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victorri-Vigneau, C.; Laforgue, E.; Grall-Bronnec, M.; Guillou-Landreat, M.; Rousselet, M.; Guerlais, M.; Feuillet, F.; Jolliet, P.; Network, F. Are seniors dependent on benzodiazepines? A national clinical survey of substance use disorder. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobert, A.; Laforgue, E.-J.; Grall-Bronnec, M.; Rousselet, M.; Péré, M.; Jolliet, P.; Barjoux, C.; Batisse, A.; Boucher, A.; Caous, A.-S.; et al. Benzodiazepine withdrawal in older people: What is the prevalence, what are the signs, and which patients? Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorvatn, B.; Meland, E.; Flo, E.; Mildestvedt, T. High prevalence of insomnia and hypnotic use in patients visiting their general practitioner. Fam. Pract. 2017, 34, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hohagen, F.; Käppler, C.; Schramm, E.; Riemann, D.; Weyerer, S.; Berger, M. Sleep onset insomnia, sleep maintaining insomnia and insomnia with early morning awakening--temporal stability of subtypes in a longitudinal study on general practice attenders. Sleep 1994, 17, 551–554. [Google Scholar]
- Hohagen, F.; Rink, K.; Käppler, C.; Schramm, E.; Riemann, D.; Weyerer, S.; Berger, M. Prevalence and treatment of insomnia in general practice. A longitudinal study. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1993, 242, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, F.C.; Morin, C.M.; Boisclair, A.; Grenier, V.; Guay, B. Insomnia. Prevalence and treatment of patients in general practice. Can. Fam. Physician 2001, 47, 759–767. [Google Scholar]
- Creupelandt, H.; Anthierens, S.; Habraken, H.; Declercq, T.; Sirdifield, C.; Siriwardena, A.N.; Christiaens, T. Teaching young GPs to cope with psychosocial consultations without prescribing: A durable impact of an e-module on determinants of benzodiazepines prescribing. BMC Med. Educ. 2017, 17, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Weiß, V.; Nau, R.; Glaeske, G.; Hummers, E.; Himmel, W. The interplay of context factors in hypnotic and sedative prescription in primary and secondary care—A qualitative study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthey, L.; van Veen, T.; Giltay, E.J.; Stoop, J.E.; Neven, A.K.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Zitman, F.G. Correlates of (inappropriate) benzodiazepine use: The Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA). Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 71, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HAS: Haute Autorité de Santé. Épisode Dépressif Caractérisé de L’adulte: Prise en Charge en Premier Recours. 2017. Available online: https://www.has-sante.fr/portail/jcms/c_1739917/fr/episode-depressif-caracterise-de-l-adulte-prise-en-charge-en-premier-recours (accessed on 7 August 2018).
| Duration of Practice | n = 204 | |
|---|---|---|
| <5 years | 34 (16.7%) | |
| 6–10 years | 24 (11.8%) | |
| 11–20 years | 35 (17.2%) | |
| 21–30 years | 49 (24.0%) | |
| >30 years | 62 (30.4%) | |
| Location of practice | n = 206 | |
| Urban | 183 (88.8%) | |
| Rural | 23 (11.2%) | |
| Perception | n = 205 | |
| Difficulty | 114 (55.3%) | |
| Awareness of risks of zolpidem | 36 (17.5%) | |
| Awareness of risks of hypnotics | 26 (12.6%) | |
| Helpful for discontinuation | 125 (60.7%) | |
| Nothing changed | 11 (5.4%) |
| Helpful for Discontinuation Only | Difficulty Only | Awareness of Risks of Zolpidem and/or Hypnotics | Helpful for Discontinuation and Difficulty | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 54 | n = 51 | n = 45 | n = 42 | ||
| Strategy employed | Proportion of patients concerned, mean [IC95] | ||||
| Discontinuation with replacement | 39% (30–49) | 24% (15–35) | 42% (31–53) | 31% (21–43) | |
| Discontinuation without replacement | 10% (5–15) | 3% (0.5–10) | 2% (0–6) | 8% (3–17) | |
| Reduction posology | 19% (13–27) | 5% (2–10) | 14% (8–22) | 14% (7–26) | |
| No modification | 33% (24–42) | 68% (56–78) | 42% (31–53) | 47% (35–58) | |
| GPs who have applied this strategy for >50% of their patients, number (%) | p-value | ||||
| No modification | 11 (20.4%) | 31 (60.8%) | 12 (26.7%) | 18 (42.9%) | <0.001 |
| GPs’ characteristics, number (%) | |||||
| Duration of practice | p-value | ||||
| <5 years | 16 (29.6%) | 3 (5.9%) | 7 (15.6%) | 6 (14.3%) | |
| 6–10 years | 7 (13.0%) | 2 (3.9%) | 5 (11.1%) | 9 (21.4%) | |
| 11–20 years | 10 (18.5%) | 7 (13.7%) | 6 (13.3%) | 8 (19.0%) | 0.01 |
| 21–30 years | 11 (20.4%) | 15 (29.4%) | 10 (22.2%) | 12 (28.6%) | |
| >30 years | 10 (18.5%) | 24 (47.1%) | 17 (37.8%) | 7 (16.7%) | |
| Area of practice | |||||
| Urban | 48 (87.3%) | 45 (88.2%) | 42 (93.3%) | 37 (88.1%) | 0.776 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laforgue, E.-J.; Istvan, M.; Schreck, B.; Mainguy, M.; Jolliet, P.; Grall-Bronnec, M.; Victorri-Vigneau, C. Perception of the Regulatory Change for Zolpidem Prescription by French General Practitioners and Its Relation to Prescription Behavior. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082176
Laforgue E-J, Istvan M, Schreck B, Mainguy M, Jolliet P, Grall-Bronnec M, Victorri-Vigneau C. Perception of the Regulatory Change for Zolpidem Prescription by French General Practitioners and Its Relation to Prescription Behavior. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(8):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082176
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaforgue, Edouard-Jules, Marion Istvan, Benoit Schreck, Marie Mainguy, Pascale Jolliet, Marie Grall-Bronnec, and Caroline Victorri-Vigneau. 2022. "Perception of the Regulatory Change for Zolpidem Prescription by French General Practitioners and Its Relation to Prescription Behavior" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 8: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082176
APA StyleLaforgue, E.-J., Istvan, M., Schreck, B., Mainguy, M., Jolliet, P., Grall-Bronnec, M., & Victorri-Vigneau, C. (2022). Perception of the Regulatory Change for Zolpidem Prescription by French General Practitioners and Its Relation to Prescription Behavior. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(8), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11082176








