The Rate of and Factors Associated with Delivery by Caesarean Section among Women with Epilepsy: Time Trend in a Single-Centre Cohort in Mazovia, Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Sample
3.2. Comparison of CS vs. VD Deliveries in WWE
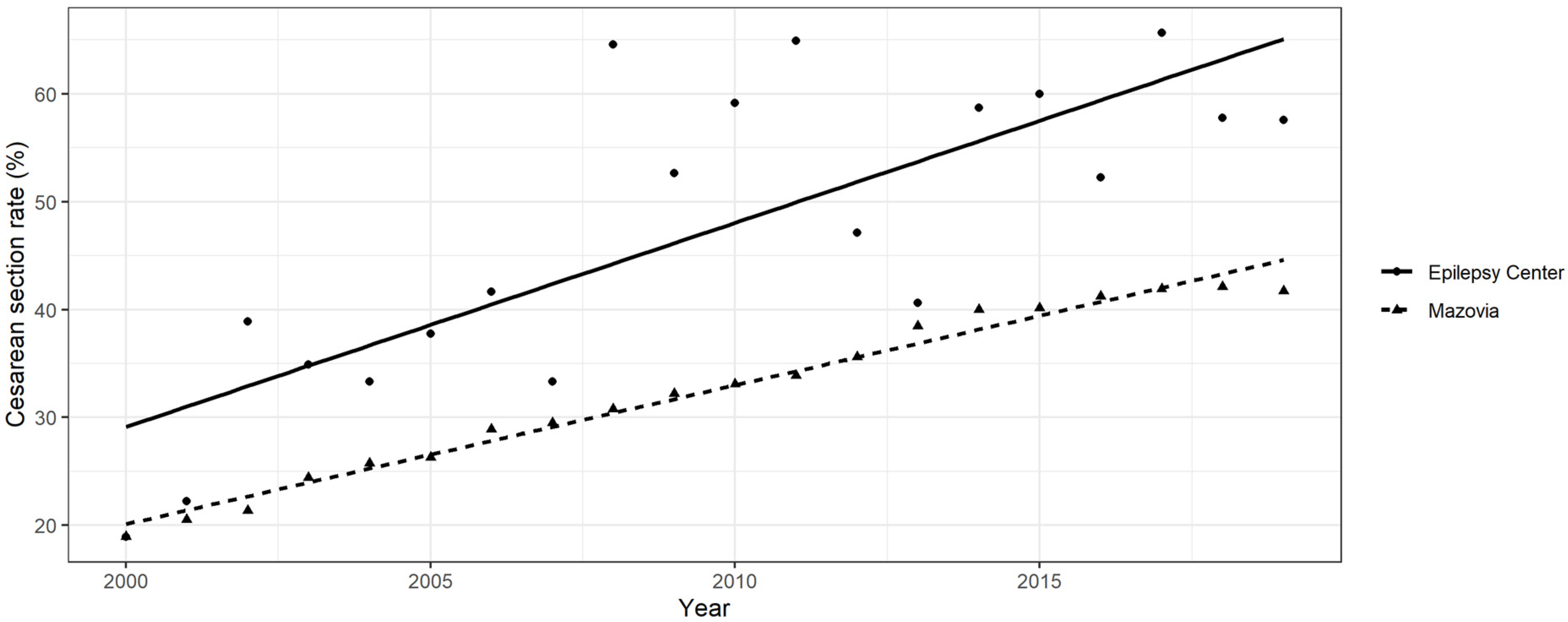
3.3. CS Rate and Its Changes over Time in WWE and the Mazovia General Population
3.4. Analysis of Factors Related to CS in WWE Deliveries
3.4.1. Seizures
3.4.2. Antiseizure Treatment
3.4.3. Gestational Week at Delivery
3.4.4. Parity
3.4.5. Twin Pregnancies
3.5. Indications for CS
Seizure Occurrence during Pregnancy According to the Group of Indications for CS
3.6. Relationship between CS Indication and Year of the Study Period from 2000–2019
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandall, J.; Tribe, R.M.; Avery, L.; Mola, G.; Visser, G.H.; Homer, C.S.; Gibbons, D.; Kelly, N.M.; Kennedy, H.P.; Kidanto, H.; et al. Short-term and long-term effects of caesarean section on the health of women and children. Lancet 2018, 392, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Statement on Caesarean Section. Available online: https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/maternal_perinatal_health/cs-statement/en/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Sveberg, L.; Svalheim, S.; Taubøll, E. The impact of seizures on pregnancy and delivery. Seizure 2015, 28, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linton, A.; Peterson, M.R. Effect of preexisting chronic disease on primary cesarean delivery rates by race for births in U.S. military hospitals 1999–2002. Birth 2004, 31, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borthen, I.; Eide, M.G.; Veiby, G.; Daltveit, A.K.; Gilhus, N.E. Complications during pregnancy in women with epilepsy: Population-based cohort study. BJOG 2009, 116, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennel, P.B. Epilepsy. In Management of High-Risk Pregnancy, 5th ed.; Queenan, J.T.S.C., Lockwood, C.J., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Malden, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Artama, M.; Gissler, M.; Malm, H.; Ritvanen, A. Drug, pregnancy G. Effects of maternal epilepsy and antiepileptic drug use during pregnancy on perinatal health in offspring: Nationwide, retrospective cohort study in Finland. Drug Saf. 2013, 36, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razaz, N.; Tomson, T.; Wikstrom, A.K.; Cnattingius, S. Association between pregnancy and perinatal outcomes among women with epilepsy. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harden, C.L.; Hopp, J.; Ting, T.Y.; Pennell, P.B.; French, J.A.; Hauser, W.A.; Wiebe, S.; Gronseth, G.S.; Thurman, D.; Meador, K.J.; et al. Management issues for women with epilepsy-focus on pregnancy (An evidence-based review): I. obstetrical complications and change in seizure frequency: Report of the quality standards subcommittee and therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American academy of neurology and the American epilepsy society. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, V.M.; Nelson, L.M.; Chakravarty, E.F. Obstetric outcomes in women with multiple sclerosis and epilepsy. Neurology 2009, 73, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, K.C.; Gilhus, N.E.; Borthen, I.; Lie, R.T.; Morken, N.H. Maternal complications in pregnancy and childbirth for women with epilepsy: Time trends in a nationwide cohort. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.V.; Jadhav, V.K. Comparative study of obstetric outcome in epileptic and non-epileptic pregnant women. Ind. Med. Gaz. 2003, 147, 352–355. [Google Scholar]
- Olafsson, E.; Hallgrimsson, J.T.; Hauser, W.A.; Ludvigsson, P.; Gudmundsson, G. Pregnancies of women with epilepsy: A population-based study in Iceland. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilo, C.; Wide, K.; Winbladh, B. Pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal complications after treatment with antiepileptic drugs. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2006, 85, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, J.R.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Andermann, E.; Benjamin, A. Epilepsy and pregnancy: An obstetric perspective. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 190, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajda, F.; O’Brien, T.J.; Graham, J.E.; Hitchcock, A.A.; Kuhn, R.J.; Lander, C.M.; Eadie, M.J. Cesarean section in Australian women with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 89, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.C.; Lussier, E.C.; Sun, Y.-T.; Lan, T.-Y.; Yu, H.-Y.; Chang, T.-Y. Antiepileptic drug use among women from the Taiwanese registry of epilepsy and pregnancy: Obstetric complications and fetal malformation outcomes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borthen, I.; Eide, M.G.; Daltveit, A.K.; Gilhus, N.E. Obstetric outcome in women with epilepsy: A hospital-based, retrospective study. BJOG 2011, 118, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soontornpun, A.; Choovanichvong, T.; Tongsong, T. Pregnancy outcomes among women with epilepsy: A retrospective cohort study. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 82, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiby, G.; Daltveit, A.K.; Engelsen, B.A.; Gilhus, N.E. Pregnancy, delivery, and outcome for the child in maternal epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikova, S.; Bagirova, H.; Magalov, S. The impact of maternal epilepsy on delivery and neonatal outcomes. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battino, D.; Tomson, T.; Bonizzoni, E.; Craig, J.; Lindhout, D.; Sabers, A.; Perucca, E.; Vajda, F.; EURAP Study Group. Seizure control and treatment changes in pregnancy: Observations from the EURAP epilepsy pregnancy registry. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chiou, H.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, H.-L. Affect of seizures during gestation on pregnancy outcomes in women with epilepsy. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mawer, G.; Briggs, M.; Baker, G.A.; Bromley, R.; Coyle, H.; Eatock, J.; Kerr, L.; Kini, U.; Kuzmyshcheva, L.; Lucas, S.B.; et al. Pregnancy with epilepsy: Obstetric and neonatal outcome of a controlled study. Seizure 2010, 19, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, S.V.; Syam, U.; Devi, J.S. Predictors of seizures during pregnancy in women with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2012, 53, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosak, M.; Song, B.H.; Dewerenda-Sikora, M.; Słowik, A.; Lasek-Bal, A. Obstetric and neonatal outcomes in women with epilepsy in Poland—A two-centre study. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2020, 54, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, H.; French, J.A.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshe, S.L.; Peltola, J.; Roulet, E.; et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the international league against epilepsy: Position paper of the ILAE commission for classification and terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pyza, I.; Rzeczkowski, T. Mazowieckie Centrum Zdrowia Publicznego: Opracowanie Dotyczące Porodów i Noworodków w Latach 2008–2009 w Województwie Mazowieckim; Mazowieckie Centrum Zdrowia Publicznego: Warszawa, Poland, 2009. (In Polish)
- Narodowy Fundusz Zdrowia. Available online: https://statystyki.nfz.gov.pl/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Borthen, I.; Eide, M.G.; Daltveit, A.K.; Gilhus, N.E. Delivery outcome of women with epilepsy: A population-based cohort study. BJOG 2010, 117, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, S.C.; Bateman, B.T.; McElrath, T.F.; Hernandez-Diaz, S. Mortality and morbidity during delivery. Hospitalization among pregnant women with epilepsy in the United States. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, L.; Allotey, J.; Cheong-See, F.; Arroyo-Manzano, D.; Mccorry, D.; Bagary, M.; Mignini, L.; Khan, K.S.; Zamora, J.; Thangaratinam, S.; et al. Epilepsy in pregnancy and reproductive outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2015, 386, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viinikainen, K.; Heinonen, S.; Eriksson, K.K.; Lviinen, R. Community-based, prospective, controlled study of obstetric and neonatal outcome of 179 pregnancies in women with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.V.; Sindhu, K.; Ajaykumar, B.; Sulekha Devi, P.B.; Sujamol, J. Maternal and obstetric outcome of women with epilepsy. Seizure 2009, 18, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairgrieve, S.D.M.; Jackson, P.; Jonas, D.; Walshaw, K.; White, T.L.; Montgomery, J.; Burn, S.A.; Lynch, S.A. Population based, prospective study of the care of women with epilepsy in pregnancy. BMJ 2000, 321, 674–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Europeristat. The European Perinatal Health Report 2015. Available online: https://www.europeristat.com/index.php/reports/european-perinatal-health-report-2015.html (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Allotey, J.; Aroyo-Manzano, D.; Lopez, P.; Viale, L.; Zamora, J.; Thangaratinam, S. Global variation in pregnancy complications in women with epilepsy: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 215, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitturi, B.K.; Cabral, F.B.; Cukiert, C.M. Outcomes of pregnant women with refractory epilepsy. Seizure 2019, 69, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCOG. Epilepsy in Pregnancy (Green-Top Guidlines No. 68). 2016. Available online: https://www.rcog.org.uk/en/guidelines-research-services/guidelines/gtg68 (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Aguglia, U.; Barboni, G.; Battino, D.; Battista Cavazzuti, G.; Citernesi, A.; Corosu, R.; Maria Guzzetta, F.; Iannetti, P.; Mamoli, D.; Patella, A.; et al. Italian consensus conference on epilepsy and pregnancy, labor and puerperium. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. 1), 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jędrzejczak, J.; Bomba-Opoń, D.; Jakiel, G.; Kwaśniewska, A.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. Managing epilepsy in women of childbearing age—Polish society of epileptology and Polish gynecological society guidelines. Ginekol. Pol. 2017, 88, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donaldson, J.O. Neurological disorders. In Medical Disorders in Obstetric Practice, 4th ed.; Swiet, M.D., Ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: London, UK, 2002; pp. 486–489. [Google Scholar]
- Jędrzejczak, J.; Kopytek-Beuzen, M.; Gawłowicz, J.; Stanosz-Sankowska, J.; Majkowska-Zwolińska, B. Knowledge of pregnancy and procreation in women with epilepsy of childbearing age: A 16-year comparative study in Poland. Epilepsy Res. 2020, 164, 106372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejczak, J.; Kozik, A.; Kozik, T.; Rebeś, Z. Ocena stanu wiedzy kobiet chorych na padaczkę w Polsce. Wyn. Wstępne. Epileptol. 2004, 12, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Tadevosyan, M.; Ghazaryan, A.; Harutyunyan, A.; Petrosyan, V.; Atherly, A.; Hekimian, K. Factors contributing to rapidly increasing rates of cesarean section in Armenia: A partially mixed concurrent quantitative-qualitative equal status study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, M.A.; Leahy-Warren, P.; Khashan, A.S.; Kenny, L.C.; O’Neill, S.M. Worldwide prevalence of tocophobia in pregnant women: Systematic review and meta—Analysis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2017, 96, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Vaginal Delivery | Caesarean Section | p | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | n | Mean | SD | n | Mean | SD | ||||||
| Maternal age at delivery (years) | 521 | 28.04 | 4.91 | 500 | 29.02 | 4.51 | 0.002 1 | |||||
| Gestation week | 521 | 39.14 | 1.95 | 500 | 38.41 | 2.14 | <0.001 1 | |||||
| Total deliveries | n | % | n | % | ||||||||
| n | % | |||||||||||
| Treatment at conception | No ASMs | 144 | 14.1 | 85 | 16.3 | 59 | 11.8 | 0.057 0.019 | ||||
| Monotherapy | 711 | 69.6 | 360 | 69.1 | 351 | 70.2 | ||||||
| polytherapy | 166 | 16.3 | 76 | 14.6 | 90 | 18 | ||||||
| Treatment in 1st trimester | No ASMs | 131 | 12.8 | 80 | 15.4 | 51 | 10.2 | 0.019 0.008 | ||||
| Monotherapy | 724 | 70.9 | 365 | 70.1 | 359 | 71.8 | ||||||
| polytherapy | 166 | 16.3 | 76 | 14.6 | 90 | 18 | ||||||
| Treatment in 2nd trimester | No ASMs | 142 | 13.9 | 86 | 16.5 | 56 | 11.2 | 0.02 0.004 | ||||
| Monotherapy | 724 | 70.9 | 366 | 70.2 | 358 | 71.6 | ||||||
| polytherapy | 155 | 15.2 | 69 | 13.2 | 86 | 17.2 | ||||||
| Treatment in 3rd trimester | No ASMs | 131 | 12.9 | 79 | 15.2 | 52 | 10.4 | 0.042 0.003 | ||||
| Monotherapy | 728 | 71.3 | 373 | 71.6 | 355 | 71.2 | ||||||
| polytherapy | 161 | 15.8 | 69 | 13.2 | 92 | 18.4 | ||||||
| Any type of seizures 1 year prior to conception | No | 165 | 53.0 | 89 | 56 | 76 | 50 | 0.273 | ||||
| Yes | 146 | 47.0 | 70 | 44 | 76 | 50 | ||||||
| Generalized seizures 1 year prior to conception | No | 498 | 88.0 | 262 | 90.7 | 236 | 85.2 | 0.044 | ||||
| Yes | 68 | 12.0 | 27 | 9.3 | 41 | 14.8 | ||||||
| Any type of seizures during pregnancy | No | 488 | 48.0 | 278 | 53.5 | 210 | 42 | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 532 | 52.0 | 242 | 46.5 | 290 | 58 | ||||||
| Generalized seizures during pregnancy | No | 731 | 71.7 | 401 | 77.1 | 330 | 66 | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 289 | 28.3 | 119 | 22.9 | 170 | 34 | ||||||
| Generalized seizures in the 3rd trimester | No | 787 | 89.0 | 430 | 93.9 | 357 | 83.8 | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 97 | 11.0 | 28 | 6.1 | 69 | 16.2 | ||||||
| Twin pregnancy | No | 1007 | 98.6 | 519 | 51.5 | 488 | 48.5 | 0.006 2 | ||||
| Yes | 14 | 1.4 | 2 | 14.3 | 12 | 85.7 | ||||||
| Malformations | No | 948 | 92.9 | 485 | 94.5 | 463 | 91.3 | 0.1314 3 | ||||
| Major | 24 | 2.4 | 9 | 1.8 | 15 | 3 | ||||||
| Minor | 48 | 4.7 | 19 | 3.7 | 29 | 5.7 | ||||||
| Variable | Odds Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
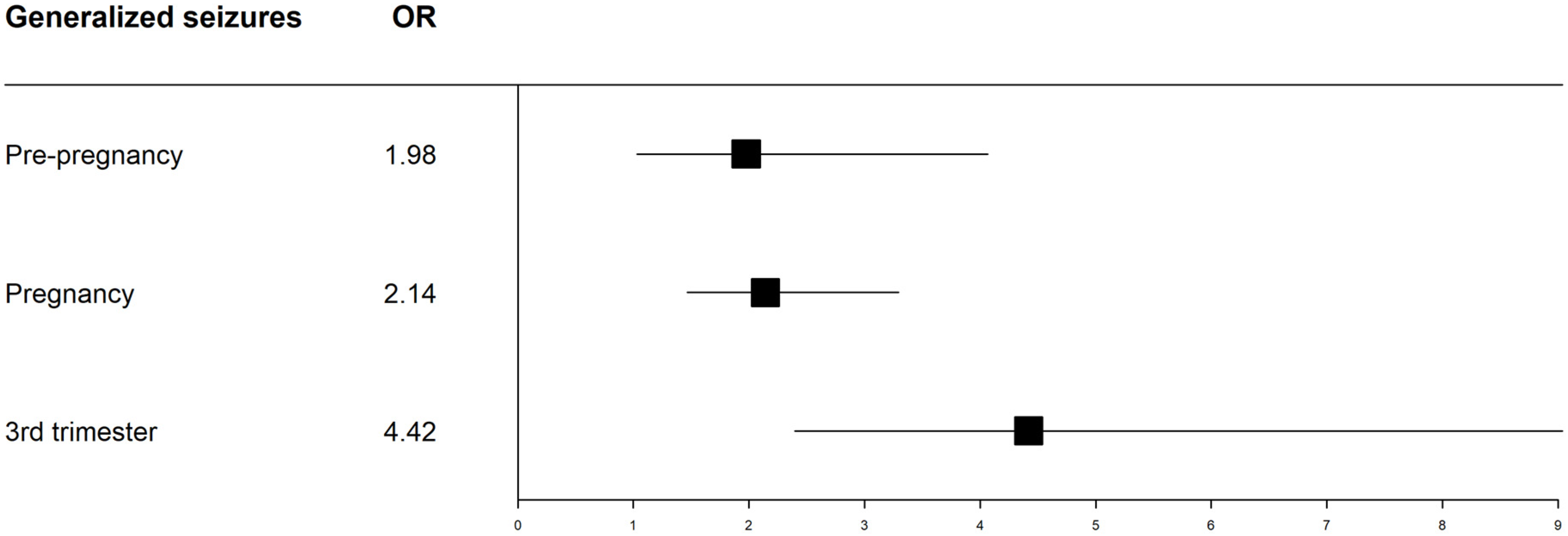
| Generalized seizures in the 3rd trimester | 4.42 | <0.001 |
| Twin pregnancy | 4.10 | 0.022 |
| Polytherapy in the 3rd trimester | 2.71 | 0.003 |
| Polytherapy in the 2nd trimester | 2.55 | 0.004 |
| Polytherapy in the 1st trimester | 2.38 | 0.008 |
| Generalized seizures any time during pregnancy | 2.13 | <0.001 |
| Polytherapy at conception | 2.08 | 0.019 |
| Generalized seizures 1 year prior to pregnancy | 1.97 | 0.044 |
| Monotherapy in the 1st trimester | 1.85 | 0.019 |
| Any seizure any time during pregnancy | 1.82 | <0.001 |
| Monotherapy in the 2nd trimester | 1.81 | 0.020 |
| Monotherapy in the 3rd trimester | 1.70 | 0.042 |
| Monotherapy at conception | 1.60 | 0.057 |
| Seizures 1 year prior to pregnancy | 1.32 | 0.273 |
| Parity | 0.96 | 0.821 |
| Primiparity | 0.89 | 0.703 |
| Gestational week | 0.78 * | <0.001 |
| Indications for Caesarean Section | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obstetric | Other | ||||
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Prolonged and obstructed labour | 86 | 30.5 | Neurological: cerebral palsy, aneurysm, tumour, brain/brainstem cavernoma, hemiparesis, haemorrhage Arnold-Chiari syndrome | 31 | 36.5 |
| Foetal distress | 54 | 19.1 | Orthopaedic: hip dislocation/joint dysplasia/instability, spine defect | 17 | 20 |
| Abnormal positioning | 36 | 12.8 | Ophthalmic: myopia, retinal detachment | 16 | 18.8 |
| Cephalic-pelvic disproportion | 27 | 9.6 | Internal/metabolic | 8 | 9.4 |
| Previous caesarean section | 25 | 8.9 | Psychiatric/mental state: psychosis, psychogenic seizures, mental impairment, uncooperativeness | 8 | 9.4 |
| Urogenital tract infections, uterine defects, in vitro fertilization | 14 | 5.0 | Cardiac: heart defect, circulatory failure, hypertension | 5 | 5.9 |
| Placenta/amniotic fluid disorder | 12 | 4.3 | |||
| Preeclampsia/eclampsia | 11 | 3.9 | |||
| Multiparity | 10 | 3.5 | |||
| Foetal malformation/stillbirth | 4 | 1.4 | |||
| Abnormal intrauterine growth | 3 | 1.0 | |||
| Total | 282 | 100 | 85 | 100 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majkowska-Zwolińska, B.; Jędrzejczak, J. The Rate of and Factors Associated with Delivery by Caesarean Section among Women with Epilepsy: Time Trend in a Single-Centre Cohort in Mazovia, Poland. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092622
Majkowska-Zwolińska B, Jędrzejczak J. The Rate of and Factors Associated with Delivery by Caesarean Section among Women with Epilepsy: Time Trend in a Single-Centre Cohort in Mazovia, Poland. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(9):2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092622
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajkowska-Zwolińska, Beata, and Joanna Jędrzejczak. 2022. "The Rate of and Factors Associated with Delivery by Caesarean Section among Women with Epilepsy: Time Trend in a Single-Centre Cohort in Mazovia, Poland" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 9: 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092622
APA StyleMajkowska-Zwolińska, B., & Jędrzejczak, J. (2022). The Rate of and Factors Associated with Delivery by Caesarean Section among Women with Epilepsy: Time Trend in a Single-Centre Cohort in Mazovia, Poland. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(9), 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092622






