Laser Efficiency and Laser Safety: Holmium YAG vs. Thulium Fiber Laser
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laser Lithotripsy Efficiency
2.1.1. Laser Systems
2.1.2. Artificial Stones
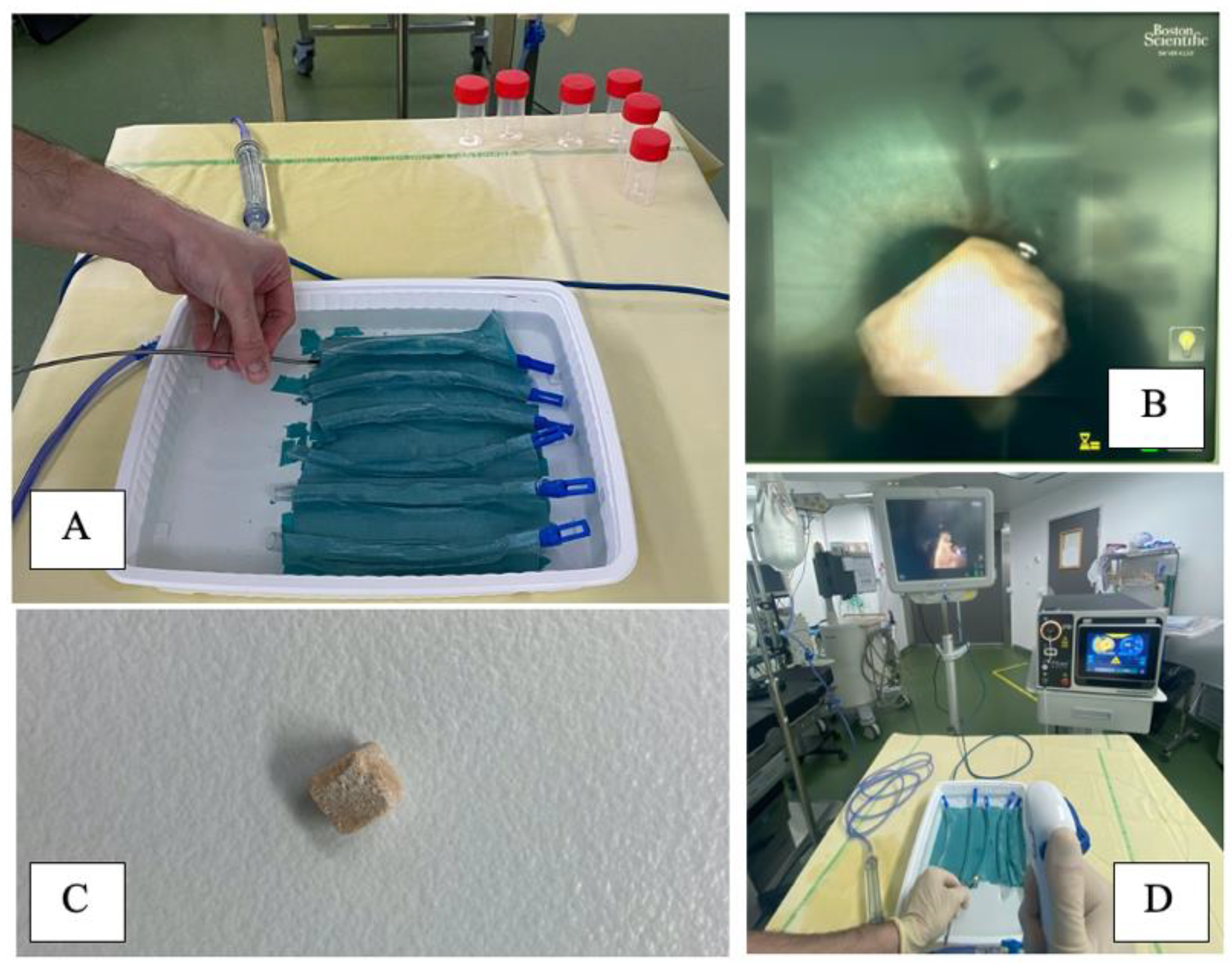
2.1.3. Experimental Setup
2.1.4. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Urothelial Damage
2.2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2.2. Laser Settings
2.2.3. Method of Temperature Measurement
2.2.4. Post-Procedure Endoscopic Control
3. Results
3.1. Laser Efficiency
3.2. Urothelial Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geraghty, R.M.; Davis, N.F.; Tzelves, L.; Lombardo, R.; Yuan, C.; Thomas, K.; Petrik, A.; Neisius, A.; Türk, C.; Gambaro, G.; et al. Best Practice in Interventional Management of Urolithiasis: An Update from the European Association of Urology Guidelines Panel for Urolithiasis 2022. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, V.; Vinarov, A.; Yaroslavsky, I.; Kovalenko, A.; Vybornov, A.; Rapoport, L.; Enikeev, D.; Sorokin, N.; Dymov, A.; Tsarichenko, D.; et al. Preclinical comparison of superpulse thulium fiber laser and a holmium: YAG laser for lithotripsy. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, A.S.; Corrales, M.; Kolvatzis, M.; Panthier, F.; Piñero, A.; Traxer, O. Thermal injury and laser efficiency with holmium: Yag and thulium fiber laser—An in vitro study. J. Endourol. 2022, 36, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventimiglia, E.; Doizi, S.; Kovalenko, A.; Andreeva, V.; Traxer, O. Effect of temporal pulse shape on urinary stone phantom retropulsion rate and ablation efficiency using holmium:YAG and super-pulse thulium fibre lasers. BJU Int. 2020, 126, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Corrales, M.; Piñero, A.; Traxer, O. Thulium fiber laser pre-settings during ureterorenoscopy: Twitter’s experts’ recommendations. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traxer, O.; Corrales, M. Managing Urolithiasis with Thulium Fiber Laser: Updated Real-Life Results—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvik, Ø.; Æsøy, M.S.; Juliebø-Jones, P.; Gjengstø, P.; Beisland, C. Thulium Fibre Laser versus Holmium:YAG for Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy: Outcomes from a Prospective Randomised Clinical Trial. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, P.; Traxer, O. The laser of the future: Reality and expectations about the new thulium fiber laser—A systematic review. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8 (Suppl. 4), S398–S417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taratkin, M.; Laukhtina, E.; Singla, N.; Kozlov, V.; Abdusalamov, A.; Ali, S.; Gabdullina, S.; Alekseeva, T.; Enikeev, D. Temperature changes during laser lithotripsy with Ho:YAG laser and novel Tm-fiber laser: A comparative in-vitro study. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 3261–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, W.R.; Carrera, R.V.; Chew, B.H.; Knudsen, B.E. Temperature rise during ureteral laser lithotripsy: Comparison of super pulse thulium fiber laser (SPTF) vs high power 120 W holmium-YAG laser (Ho:YAG). World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 3951–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, J.D.; Chen, R.; Srikureja, N.; Amasyali, A.S.; Keheila, M.; Baldwin, D.D. Does the Novel Thulium Fiber Laser Have a Higher Risk of Urothelial Thermal Injury than the Conventional Holmium Laser in an In Vitro Study? J. Endourol. 2022, 36, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, E.; Simmons, W.N.; Sankin, G.; Cocks, H.F.; Preminger, G.M.; Zhong, P. A simple method for fabricating artificial kidney stones of different physical properties. Urol. Res. 2010, 38, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthier, F.; Germain, T.; Gorny, C.; Berthe, L.; Doizi, S.; Traxer, O. Laser Fiber Displacement Velocity during Tm-Fiber and Ho:YAG Laser lithotripsy: Introducing the Concept of Optimal Displacement Velocity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, A.; Corrales, M.; Kolvatzis, M.; Traxer, O. Initial clinical experience with the thulium fiber laser from Quanta System: First 50 reported cases. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 2549–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventimiglia, E.; Villa, L.; Doizi, S.; Briganti, A.; Proietti, S.; Giusti, G.; Montorsi, F.; Montanari, E.; Traxer, O.; Salonia, A. Laser lithotripsy: The importance of peak power and pulse modulation. Eur. Urol. Focus 2021, 7, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taratkin, M.; Laukhtina, E.; Singla, N.; Tarasov, A.; Alekseeva, T.; Enikeev, M.; Enikeev, D. How Lasers Ablate Stones: In Vitro Study of Laser Lithotripsy (Ho:YAG and Tm-Fiber Lasers) in Different Environments. J. Endourol. 2021, 35, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, E.X.; De Coninck, V.; Doizi, S.; Daudon, M.; Traxer, O. Thulium fiber laser: Ready to dust all urinary stone composition types? World J. Urol. 2020, 39, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, P.; Hameed, B.Z.; Somani, B. Outcomes of thulium fibre laser for treatment of urinary tract stones: Results of a systematic review. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2021, 31, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.S.; Whiles, B.B.; Ito, W.E.; Machen, E.; Thompson, J.A.; Duchene, D.A.; Neff, D.A.; Molina, W.R. Image Distortion During Flexible Ureteroscopy: A Laboratory Model Comparing SuperPulsed Thulium Fiber Laser vs. High-Power Ho:YAG Laser. J Endourol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enikeev, D.; Shariat, S.F.; Taratkin, M.; Glybochko, P. The changing role of lasers in urologic surgery. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2020, 30, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Bobrowski, A.; Lee, J. A scoping review of the clinical efficacy and safety of the novel thulium fiber laser: The rising star of laser lithotripsy. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2020, 15, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martov, A.; Ergakov, D.; Guseynov, M.; Coninck, V.; Keller, E.; Traxer, O. VS1-2 SuperPulse Thulium Fiber Laser for UreteroscopicLithotripsy: 1 Year Experience. J. Endourol. 2018, 32, A495. [Google Scholar]
- Korolev, D.; Akopyan, G.; Tsarichenko, D.; Shpikina, A.; Ali, S.; Chinenov, D.; Corrales, M.; Taratkin, M.; Traxer, O.; Enikeev, D. Minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy with SuperPulsed Thulium-fiber laser. Urolithiasis 2021, 49, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enikeev, D.; Taratkin, M.; Klimov, R.; Alyaev, Y.; Rapoport, L.; Gazimiev, M.; Korolev, D.; Ali, S.; Akopyan, G.; Tsarichenko, D.; et al. Thulium-fiber laser for lithotripsy: First clinical experience in percutaneous nephrolithotomy. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 3069–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Coninck, V.; Defraigne, C.; Traxer, O. Watt determines the temperature during laser lithotripsy. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 1257–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollin, D.A.; Carlos, E.C.; Tom, W.R.; Simmons, W.N.; Preminger, G.M.; Lipkin, M.E. Effect of Laser Settings and Irrigation Rates on Ureteral Temperature During Holmium Laser Lithotripsy, an In Vitro Model. J. Endourol. 2018, 32, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldoukhi, A.H.; Black, K.M.; Hall, T.L.; Ghani, K.R.; Maxwell, A.D.; MacConaghy, B.; Roberts, W.W. Defining thermally safe laser lithotripsy power and irrigation parameters: In vitro model. J. Endourol. 2020, 34, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Laser Settings | ||||||||||
| 0.5 J/10 Hz * | 0.5 J/20 Hz * | 0.7 J/10 Hz * | 0.7 J/20 Hz | 1 J/12 Hz * | 1 J/20 Hz | Ureter Tested Settings | All Tested Settings | |||
| Ablation rate (mg/s) | ||||||||||
| Junior (n = 5) | Mean | Ho:YAG | 8.24 | 10.04 | 17.12 | 28.18 | 41.26 | 41.44 | 19.165 | 24.38 |
| TFL | 13.28 | 17.52 | 22.7 | 38.04 | 50.96 | 56.82 | 26.115 | 33.22 | ||
| % Difference | −52% | +61% | +74% | +32% | +35% | +23% | +37% | +36% | ||
| p value | 0.10 | 0.1 | 0.03 | <0.001 | <0.0001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0001 | ||
| Senior (n = 5) | Mean | Ho:YAG | 19.58 | 28.4 | 22.5 | 46.52 | 49.92 | 61.34 | 30.1 | 38.04 |
| TFL | 26.08 | 31.2 | 30.44 | 59 | 58.56 | 70.82 | 36.57 | 46.02 | ||
| % Difference | −19% | +33% | +10% | +35% | +27% | +17% | +15% | +21% | ||
| p value | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.15 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| Total group (n = 10) | Mean | Ho:YAG | 13.91 | 19.22 | 19.81 | 37.35 | 45.59 | 51.39 | 24.63 | 31.21 |
| TFL | 19.68 | 24.36 | 26.57 | 48.52 | 54.76 | 63.82 | 31.34 | 39.62 | ||
| % Difference | −33% | +41% | +27% | +34% | +30% | +20% | +24% | +27% | ||
| p value | 0.002 | 0.008 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| Laser Settings | ||||||||||
| 0.5 J/10 Hz * | 0.5 J/20 Hz * | 0.7 J/10 Hz * | 0.7 J/20 Hz | 1 J/12 Hz * | 1 J/20 Hz | Ureter Tested Settings | All Tested Settings | |||
| Energy/stone volume (J/mg) | ||||||||||
| Junior (n = 5) | Mean | Ho:YAG | 21.07 | 29.64 | 14.21 | 16.52 | 8.71 | 14.97 | 19.04 | 17.52 |
| TFL | 10.03 | 19.25 | 10.26 | 10.11 | 7.25 | 10.48 | 13.34 | 11.23 | ||
| % Difference | −52% | −35% | −28% | −39% | −17% | −30% | −70% | −36% | ||
| pvalue | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.24 | 0.001 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | ||
| Senior (n = 5) | Mean | Ho:YAG | 8.05 | 7.87 | 9.12 | 8.93 | 6.73 | 9.07 | 8.21 | 8.30 |
| TFL | 6.52 | 10.63 | 7.82 | 6.68 | 7.08 | 7.14 | 8.21 | 7.64 | ||
| % Difference | −19% | +35% | −14% | −25% | +5% | −21% | 0% | −19% | ||
| pvalue | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.77 | 0.04 | 0.99 | 0.07 | ||
| Total group (n = 10) | Mean | Ho:YAG | 14.77 | 19.04 | 12.61 | 13.29 | 8.06 | 12.31 | 13.62 | 13.35 |
| TFL | 9.95 | 16.14 | 9.63 | 8.66 | 7.38 | 8.94 | 10.78 | 10.12 | ||
| % Difference | −33% | −15% | −24% | −35% | −8% | −27% | −21% | −24% | ||
| pvalue | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.0008 | 0.0002 | 0.32 | 0.001 | 0.004 | <0.0001 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sierra, A.; Corrales, M.; Somani, B.; Traxer, O. Laser Efficiency and Laser Safety: Holmium YAG vs. Thulium Fiber Laser. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010149
Sierra A, Corrales M, Somani B, Traxer O. Laser Efficiency and Laser Safety: Holmium YAG vs. Thulium Fiber Laser. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010149
Chicago/Turabian StyleSierra, Alba, Mariela Corrales, Bhaskar Somani, and Olivier Traxer. 2023. "Laser Efficiency and Laser Safety: Holmium YAG vs. Thulium Fiber Laser" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010149
APA StyleSierra, A., Corrales, M., Somani, B., & Traxer, O. (2023). Laser Efficiency and Laser Safety: Holmium YAG vs. Thulium Fiber Laser. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010149







