Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate whether a large paraumbilical vein (L-PUV) was independently associated with the occurrence of overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) after the implantation of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS). Methods: This bi-center retrospective study included patients with cirrhotic variceal bleeding treated with a TIPS between December 2015 and June 2021. An L-PUV was defined in line with the following criteria: cross-sectional areas > 83 square millimeters, diameter ≥ 8 mm, or greater than half of the diameter of the main portal vein. The primary outcome was the 2-year OHE rate, and secondary outcomes included the 2-year mortality, all-cause rebleeding rate, and shunt dysfunction rate. Results: After 1:2 propensity score matching, a total of 27 patients with an L-PUV and 54 patients without any SPSS (control group) were included. Patients with an L-PUV had significantly higher 2-year OHE rates compared with the control group (51.9% vs. 25.9%, HR = 2.301, 95%CI 1.094–4.839, p = 0.028) and similar rates of 2-year mortality (14.8% vs. 11.1%, HR = 1.497, 95%CI 0.422–5.314, p = 0.532), as well as variceal rebleeding (11.1% vs. 13.0%, HR = 0.860, 95%CI 0.222–3.327, p = 0.827). Liver function parameters were similar in both groups during the follow-up, with a tendency toward higher shunt patency in the L-PUV group (p = 0.067). Multivariate analysis indicated that having an L-PUV (HR = 2.127, 95%CI 1.050–4.682, p = 0.037) was the only independent risk factor for the incidence of 2-year OHE. Conclusions: Having an L-PUV was associated with an increased risk of OHE after a TIPS. Prophylaxis management should be considered during clinical management.
1. Introduction
Aggravated portal hypertension triggers complications, such as esophagogastric variceal bleeding and refractory ascites, in the decompensated stage of cirrhosis. In addition, it drives the development of spontaneous portosystemic shunts (SPSSs) and the formation of collateral circulation, including splenorenal shunts (SRSs), gastrorenal shunts (GRSs), paraumbilical veins (PUVs), and portocaval or mesorenal/caval shunts [1,2]. This compensatory decompression mechanism was recently found to decrease hepatic portal perfusion and increase the risk of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) and death [3,4].
By significantly reducing portal vein pressure, the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is an effective therapy for acute variceal bleeding, as well as for the prevention of rebleeding in patients with cirrhosis [5,6]. Post-TIPS HE is one of the major complications after TIPS creation, with a 1-year incidence of 23–54.5% [7,8]. Recent studies [1,4,9] demonstrated that the embolization of large SPSSs may be a therapeutic target to reduce the risk of HE after a TIPS, whereas the definitions of large SPSSs are under debate. The major reported types of SPSSs are mostly SRSs or GRSs, whereas PUVs are less discussed [9,10,11].
In the Baveno VI Cooperation Group cohort [4], large SPSSs were observed in 28% of cirrhotic patients, with SRSs and GRSs accounting for more than half of these (55%), and PUVs approaching one-third (27%). Other rare examples included mesocaval shunts (5%), inferior mesenteric vein-caval shunts (4%), and mesorenal shunts (3%). PUVs are located in the falciform ligament and originate from the left portal vein (LPV), which anastomoses with the anterior subcutaneous vein of the abdominal wall. The typical presentation is the formation of a caput medusae appearance [3]. Unlike other extrahepatic collateral circulation systems, PUVs are rarely a source of bleeding associated with portal hypertension but tend to increase the main portal vein (MPV) blood flow [12]. In cirrhotic patients without TIPS placement, PUVs lead to increases in the portal flow volume, HVPG, and grade of esophageal varices but not do increase the risk of death [13]. However, the impact of PUVs, particularly those meeting large SPSS criteria, on clinical outcomes after TIPS implementation is not yet known. Identifying large PUVs (L-PUVs) may have potential significance for patient management.
Therefore, this retrospective study was carried out to compare the differences in primary clinical outcomes, such as overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE), death, rebleeding, and shunt dysfunction after TIPS implementation in patients with L-PUVs and those without any SPSSs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
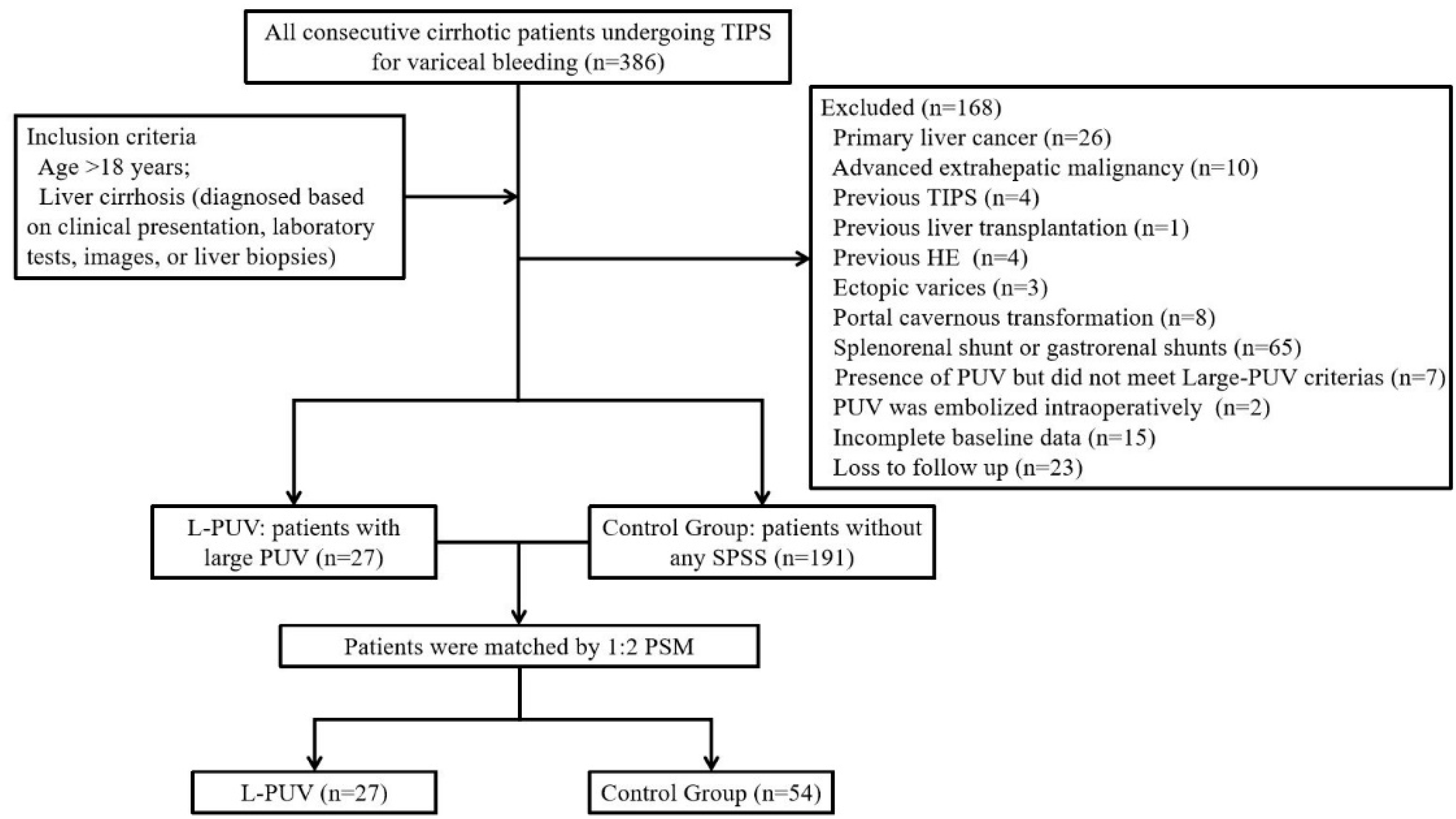
In total, 386 patients who received a TIPS for acute variceal bleeding or to prevent variceal rebleeding from December 2015 to June 2021 were screened in this study. Two hundred and eighteen patients were included in the analysis (Figure 1). Of these, 78 (35.8%) had received β-blockers combined with endoscopic therapy, while the remaining received an emergency TIPS [14].
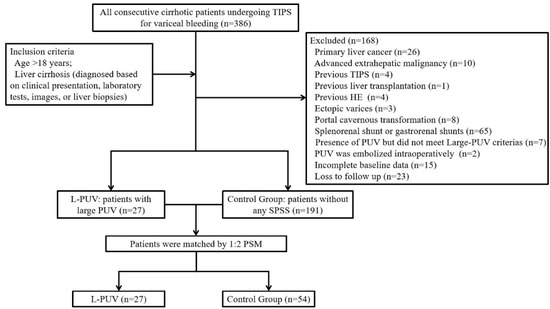
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram.
Regarding the definition of a large SPSS from previous studies [1,4,9], a PUV is defined as large when it satisfies any of the following criteria: cross-sectional areas > 83 square millimeters, diameter ≥ 8 mm, or greater than half of the diameter of the MPV. The patients were classified into two groups: large PUV (L-PUV) and no SPSS (control group).
The inclusion criteria were as follows: age > 18 years and liver cirrhosis (diagnosed based on clinical presentation, laboratory tests, images, or liver biopsies). The exclusion criteria were as follows: previous HE, the presence of PUV but did not meet large PUV criteria, the presence of other SPSS detected using enhanced CT and portal venography, PUV synchronously embolized intraoperatively, bleeding from ectopic varices, previous treatments with a TIPS or surgical shunt, primary liver cancer or extrahepatic tumors, portal cavernous transformation, or incomplete baseline data or loss to follow up.
2.2. Radiological Data Acquisition
Preoperative enhanced abdominal CT scans (Revolution CT, GE Healthcare and SOMATOM Force, Siemens Healthcare) were reviewed by a radiologist (at least 10 years experience in the diagnosis of abdominal diseases, such as liver, biliary, and pancreas) and an interventionalist. The preferred portal phase was observed from a top-down perspective in the axial plane images for the presence of SPSSs and verified in the coronal and sagittal planes. It was recorded only when the PUV diameter exceeded 5 mm. The starting point or the position where the vessel leaves the liver was usually chosen, and the maximum diameter of the PUV was measured in the axis position. Then, the cross-sectional area of the PUV was calculated using the formula πr2 [1].
The diameter of the MPV was measured at the junction of the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein, and the diameters of the LPV and the right portal vein (RPV) were determined at the junctures of the LPV and RPV, respectively. The presence and grade [15] of the esophageal varices were observed and recorded in the axial plane.
2.3. Outcomes and Definitions
The primary outcome was the 2-year OHE rate, and secondary outcomes included the 2-year mortality, all-cause rebleeding rate, and shunt dysfunction rate.
HE was diagnosed and graded according to the West Haven criteria [16]. OHE was defined as grade 2 and above, and severe HE was defined as grade 3 and above. Refractory HE was defined as recurrent (at least 3 episodes of HE in the past 3 months) or persistent symptoms (persistently detectable mental status changes with further episodic deterioration) despite sufficient pharmacological treatment [16,17]. Rebleeding was defined as the occurrence of persistent or new clinical symptoms of bleeding according to the Baveno VI consensus [18]. Shunt dysfunction was defined as a very slow (<40 cm/s) or rapid (>200 cm/s) flow velocity in the stent or a low flow velocity in the portal vein (<20 cm/s) according to ultrasonography or as shunt stenosis > 50% according to the portography procedure [19]. Technical success, clinical success, and complications (major and minor) are referenced in the SIR standards [20].
2.4. TIPS Procedure and Follow-Up
The TIPS procedures (Figure S1) in both centers were performed by a team leader with over 10 years of experience in TIPS creation. The angiographic equipment comprised Artis one and Artis zee (Siemens, Munich, Germany). The procedure was performed under sedation and local anesthesia. The 10F guiding sheath was inserted through the jugular vein and the Rups-100 suite (Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA) was introduced into the hepatic vein along the guidewire. After puncturing the portal vein, portal venography clarified the blood flow, location, and classification of the gastroesophageal varices. Embolization of the varices with coils (Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA, or Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) and/or n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA, BME, Guangzhou, China) was performed. NBCA was mixed with lipiodol in a ratio of 1:2 to 1:3. A 6 or 8 mm-diameter balloon (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, Massachusetts, USA, or Abbott, Chicago, IL, USA) was then selected to dilate the shunt until the incision had completely disappeared. All patients were implanted with an 8 mm e-polytetrafluoroethylene (e-PTFE)-covered stent (Viatorr TIPS endoprosthesis, W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc, Newark, USA). The placement of an additional covered stent (Vanbahn, W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc., Newark, NJ, USA, and Wallstent, Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) was evaluated depending on the portal vein and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis. Measurement of the portal pressure gradient (ppg) pre- and post-stenting was an essential step.
Patients with viral hepatitis were treated with antiviral therapy after the TIPS placement. HE prophylaxis was not routinely performed after the TIPS implementation. When symptomatic HE was detected, pharmacological treatments with lactulose (10 mL, TID, PO) combined with l-ornithine l-aspartate granules (3 g, TID, PO) or lactulose (400 mg, BID, PO) were generally used. Patients with a suspected TIPS stenosis/occlusion based on imaging or the recurrence of symptoms of portal hypertension (e.g., ascites, variceal bleeding) were hospitalized for TIPS venography and pressure measurement to confirm whether the shunt was revised.
Follow-up visits included laboratory work and an abdominal ultrasound after 1 and 3 months, as well as ultrasound or enhanced CT after 6 months, and every 6 months thereafter. Evaluations were conducted by at least one physician and one nurse via hospitalization, outpatient service, and telephone calls. The follow-up period was defined as the time interval between the initial TIPS placement to death, liver transplantation, or the end of this study.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables are presented as the mean ± standard deviation or median and IQR and were compared with Student’s t-test or the Mann–Whitney U test depending on whether they were normally distributed. Categorical variables are expressed as frequencies (percentages) and were compared using the chi-square test or Kruskal–Wallis H test.
Univariate analysis was performed to identify variables that were potentially related to OHE. Cox regression analysis (forward step-wise likelihood quotient) was performed using the significant predictors in the univariate analysis (p < 0.1) to determine the independent predictors of 2-year OHE after a TIPS placement. Cumulative rates of time free of OHE and survival were expressed with Kaplan–Meier curves and compared using the log-rank test. The contribution of each parameter to the risk of developing the outcome was recorded as the HR with a 95% confidence interval (CI). To reduce the baseline differences and the probability of selection bias, we performed (1:2) propensity score matching (PSM) for the L-PUV and control groups. Having had a splenectomy or the presence of gastric varices, platelets, or white blood cells were adjusted with a maximum propensity score distance (caliper) of 0.1.
All tests were two-sided, and significance was established at p < 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 26.0 (IBM Corporation, Somers, NY, USA) or R 4.2.2 (http://www.R-project.org/, accessed on 20 October 2022) software packages.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
The characteristics of the patients at baseline are shown in Table S1. To accurately describe the practical application of the TIPS, it is reported for the pre-matched cohort. In total, 218 patients had a technical success rate of 100% and a clinical success rate of 95.0% (11 cases (5.0%) of variceal rebleeding were confirmed via endoscopy 2 years after the TIPS). According to the incidence, the main complications were as follows: HE (26/218, 11.9%), hepatic failure (8/218, 3.7%), biliary bleeding (3/218, 1.4%), hepatic artery injury (2/218, 0.9%), pneumonia (2/218, 0.9%), vomiting (2/218, 0.9%), abdominal pain (2/218, 0.9%), fever (1/218, 0.4%), and malignant arhythmia (1/218, 0.4%). Minor complications included HE (43/218, 19.7%), abdominal pain (15/218, 6.9%), vomiting (9/218, 4.1%), fever (5/218, 2.3%), transient pulmonary edema (1/218, 0.4%), and enter site hematoma (1/218, 0.4%), sequentially.
L-PUVs were present in 27 (12.4%) patients with a median diameter of 9.8 mm (IQR: 8.8–14.0), of which 23 (10.2%) patients showed a diameter ≥ 8 mm and 25 (11.1%) patients showed a diameter greater than half the diameter of the MPV. The median of the cross-sectional areas was 75.4 square millimeters (IQR: 55.4–158.4), with 13 (5.8%) patients showing an area > 83 square millimeters (Table S2).
Overall, the pre-matched L-PUV group had larger diameters of the LPV and a high presence of gastric varices. None of these patients underwent a splenectomy and had lower platelet and white blood cell counts. There were no statistically significant differences in terms of liver function, imaging parameters, esophageal vein grading, PPG, the diameter of the balloon, or follow-up time in either group.
3.2. Propensity Score Matching
To reduce the effect of imbalanced baseline information, 27 patients with L-PUVs were matched to 54 patients without any SPSSs after propensity matching for having had a splenectomy and the presence of gastric varices, platelets, and white blood cells.
As described in Table 1, the baseline characteristics of the two groups were comparable after matching when considering the diameter of the LPV. The median follow-up times were 22.0 months (IQR: 12.0–43.0) and 23.0 months (IQR: 14.7–39.0) in the L-PUV and control groups, respectively (p = 0.996). One patient developed primary liver cancer during follow-up in the control group.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients after PSM.
3.3. Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy
Fourteen patients in each of the L-PUV and the control groups (51.9% vs. 25.9%, p = 0.022) experienced at least one episode of OHE within 2 years (Table 2). The average numbers of OHE episodes were 0.9 ± 1.2 and 0.7 ± 1.3 in the two groups, respectively (p = 0.426). Severe HE (grade III/IV) occurred in three (11.1%) patients in the L-PUV group and seven (13.0%) patients in the control group (p = 0.810), of which one (3.7%) and five (9.3%) patients, respectively, developed refractory HE (p = 0.342). All OHE patients were hospitalized for treatment. No patient received additional PUV embolization during the follow-up. Except for one patient in the control group who received shunt reduction, the remaining patients were treated with lactulose combined with ornithine methylate pellets or rifaximin after discharge.

Table 2.
Summary of outcome measurements within 2 years.
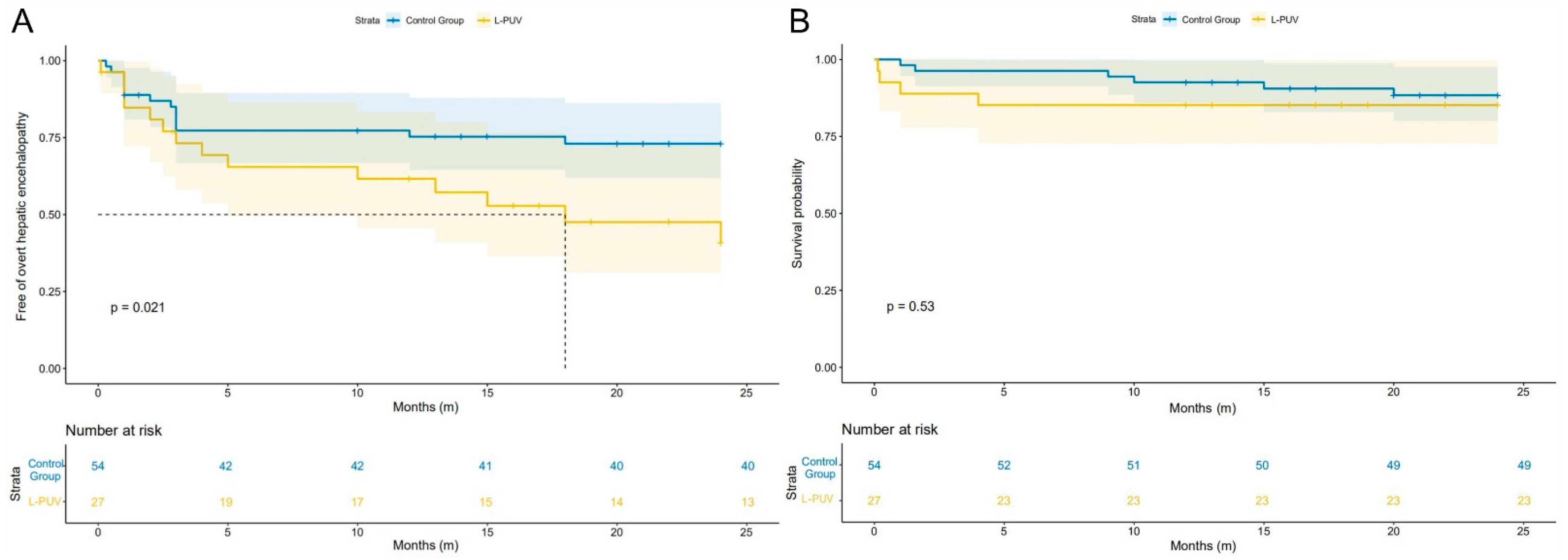
As shown in Figure 2A, the 1-year actuarial probability of OHE in the L-PUV group was similar to the control group (33.3% vs. 25.9%, HR = 1.413, 95%CI 0.612–3.266, log-rank test: p = 0.406), but the 2-year actuarial probability of OHE was significantly higher (51.9% vs. 25.9%, HR = 2.301, 95%CI 1.094–4.839, log-rank test: p = 0.021).
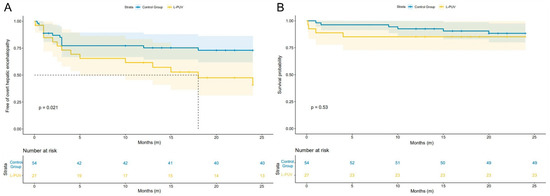
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curves of overt hepatic encephalopathy (A) and survival (B) after TIPS implementation according to the L-PUV and the control groups.
Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed on all matched patients (Table 3). Factors affecting the occurrence of OHE at 2 years included total bilirubin and L-PUV. Multifactorial analysis adjusted for confounders showed L-PUV (HR = 2.600, 95%CI 1.148–5.889, p = 0.022) was the only independent influencing factor for 2-year OHE.

Table 3.
COX regression analysis for 2-year OHE after PSM.
3.4. Mortality, Rebleeding, and Shunt Dysfunction
Compared with the control group, the L-PUV group showed no significant difference between the 1-year (14.8% vs. 7.4%, HR = 2.155, 95%CI 0.539–8.618, log-rank test: p = 0.256) and 2-year (14.8% vs. 11.1%, HR = 1.497, 95%CI 0.422–5.314, log-rank test: p = 0.529) actuarial mortality probabilities (Figure 2B). The detailed causes of death are listed in Table 2. There was no statistical difference between the 1-year (7.4% vs. 13.3%, HR = 0.703, 95%CI 0.142–3.483, log-rank test: p = 0.664) and 2-year (11.1% vs. 13.3%, HR = 0.860, 95%CI 0.222–3.327, log-rank test: p = 0.827) actuarial rebleeding probabilities between the L-PUV and control groups. Reasons for rebleeding are shown in Table 2.
Two (3.7%) and four (5.6%) patients in the control group had shunt dysfunction at 1 and 2 years, respectively; however, no dysfunction occurred in the L-PUV group during the follow-up. Of these four patients, one was treated with balloon dilation combined with thrombolysis, and three were treated with stent implantation. All of them had normalized shunt blood flow after the procedure. Except for these patients, no ascites deterioration was found.
3.5. Changes in Liver Function and L-PUV Diameter
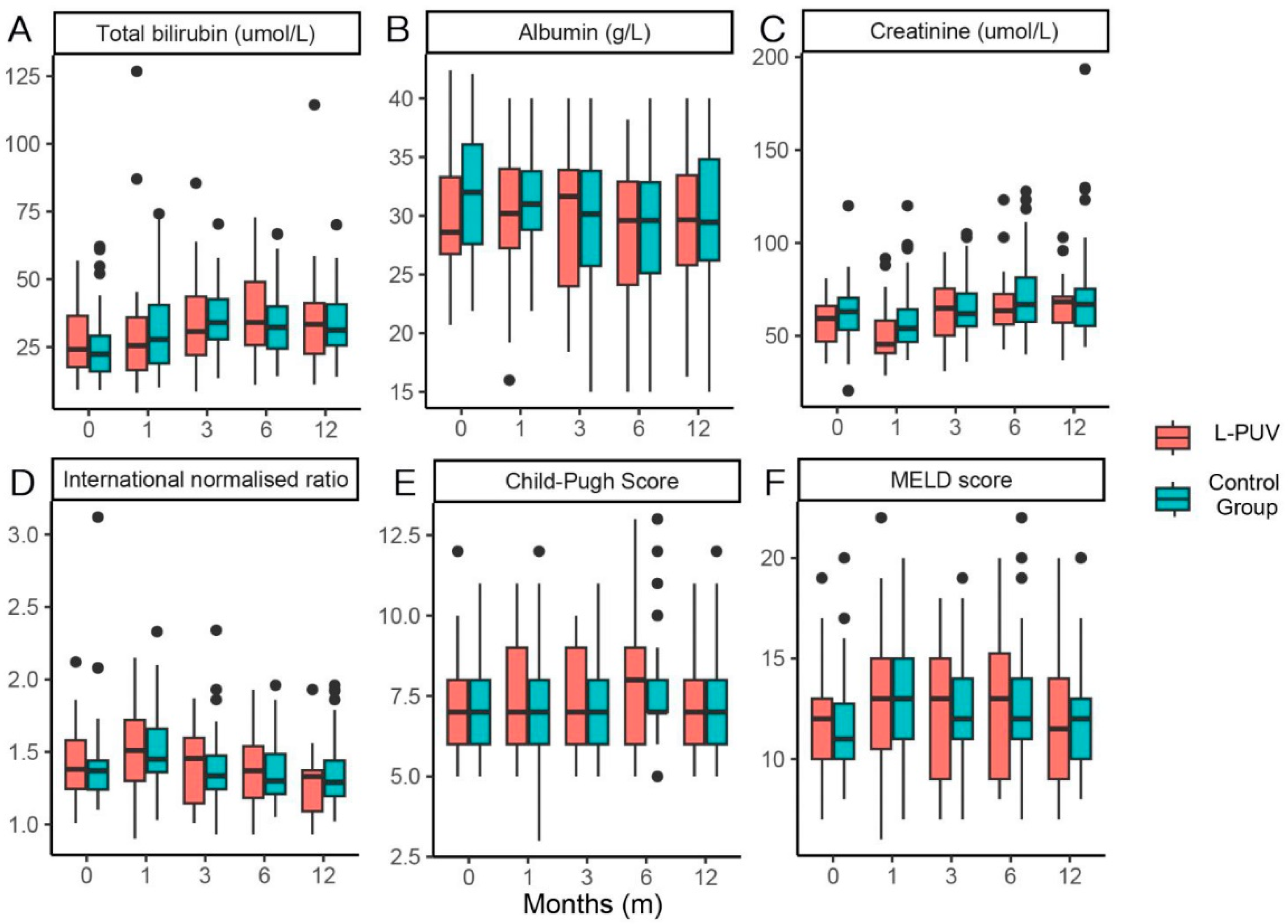
The total bilirubin, Child–Pugh score, and MELD score in both groups showed overall elevated and then decreased changes, and albumin improved ineffectively after the procedure. Creatinine was high in the control cohort 1 month after the TIPS. Overall, there was no significant difference in liver function indicators between the two groups at each time point of observation (Figure 3).
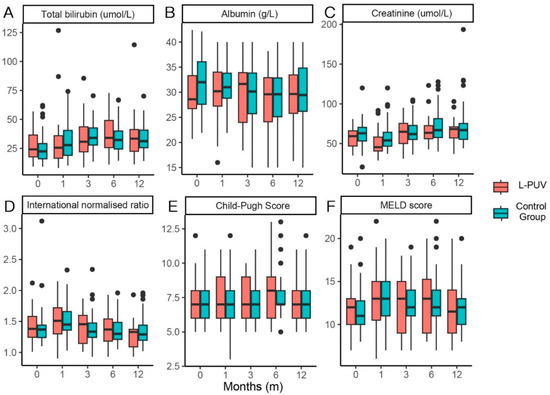
Figure 3.
Box plots of total bilirubin (A): the p-values were 0.344, 0.512, 0.506, 0.624, and 0.913 for pre-TIPS and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-TIPS, respectively), albumin (B): the p-values were 0.110, 0.311, 0.964, 0.729, and 0.817 for pre-TIPS and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-TIPS, respectively), creatinine (C): the p-values were 0.233, 0.032, 0.938, 0.390, and 0.760 for pre-TIPS and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-TIPS, respectively), international normalized ratio (D): the p-values were 0.455, 0.863, 0.599, 0.917, and 0.429 for pre-TIPS and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-TIPS, respectively), Child–Pugh score (E): the p-values were 0.236, 0.645, 0.264, 0.500, and 0.628 for pre-TIPS and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-TIPS, respectively), and MELD score (F): the p-values were 0.279, 0.709, 0.715, 0.573, and 0.701 for pre-TIPS and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-TIPS, respectively) in the L-PUV and control groups.
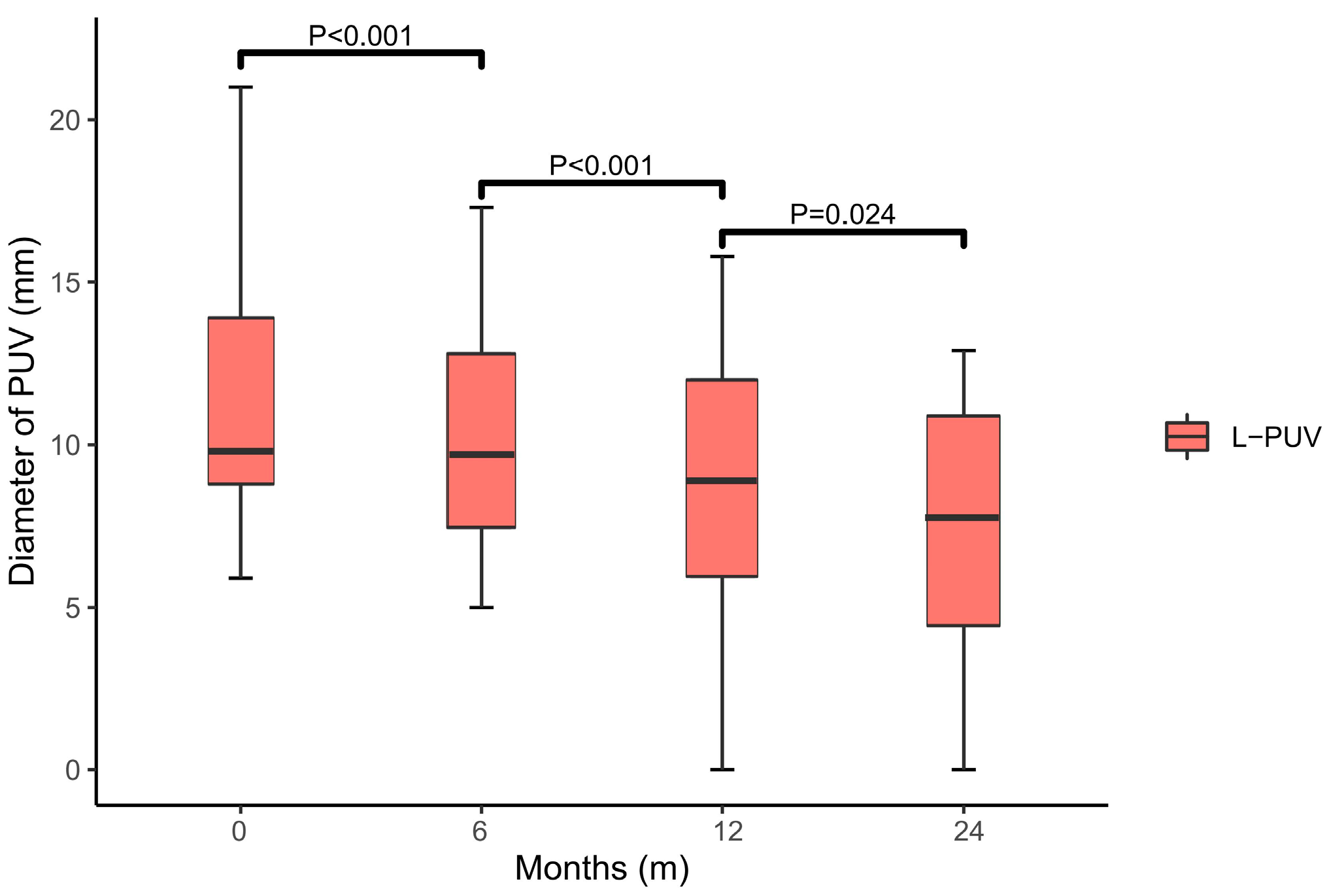
At 6 months (9.7 (7.0–13.6), p < 0.001), 1 year (8.9 (5.9–12.3), p < 0.001), and 2 years (7.8 (3.0–11.1), p = 0.024) after TIPS implantation, statistically significant changes in the L-PUV diameter were observed compared with the previous follow-up (Figure 4). There was no new or increased diameter of the PUV in either group by the end of the study. The L-PUV showed a gradual collapse post-TIPS, but only completely disappeared in five (18.5%) patients (Figures S2 and S3).
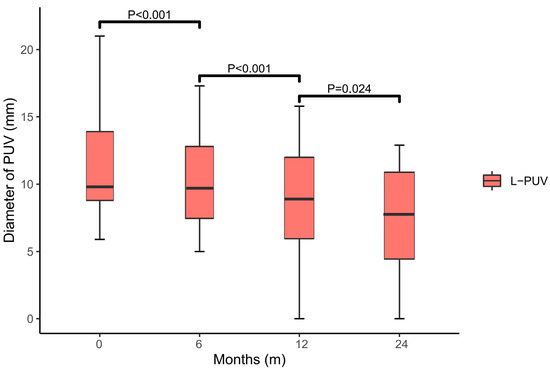
Figure 4.
Box plot of the L-PUV diameter variation. There was a significant collapse in the diameter of the L-PUV at 6 (p < 0.001), 12 (p < 0.001), and 24 (p = 0.024) months post-TIPS compared with the previous data.
4. Discussion
Our study demonstrated that patients with variceal bleeding in unembolized L-PUVs had no increased risk of death, rebleeding, or worsening liver function 2 years after TIPS implementation, but did have a 2.2-fold increased risk of OHE 2 years after the operation. This study highlighted the robustness of L-SPSSs in predicting OHE, further refined the impact of the L-SPSS classification on clinical outcomes after TIPS implementation, and provided a reference for the prophylactic treatment of patients at high risk of OHE.
Yi F. et al. [21] found that SRSs may narrow portal vein diameter (RPV and MPV) and shrink liver volume, impairing hepatic function and survival. In contrast, we found a larger LPV diameter in L-PUV patients, which may have been caused by different hemodynamic characteristics. Unlike SRSs, the PUV allows blood to pass through the MPV rather than leave it, hence the term right-sided shunt [22]. The current recognition of PUVs is still controversial. One idea is that the PUV benefits the maintenance of MPV volume and velocity, preserves MPV diameter, and reduces the risk of portal thrombosis [23]. The other is that the PUV has no protective effect on hepatic perfusion, but deteriorates liver function [12,24]. However, whether from the perspective of increasing portal perfusion or worsening liver function, PUV may increase the risk of OHE after TIPS implementation.
Similar to several previous studies [9,10,25], we confirmed that there was indeed an association between an L-PUV and OHE. This indicated that even if the anatomical drainage of the PUV is different from other collateral circulation, a large shunt can still affect OHE after TIPS. Decreases in L-PUV diameter were mainly caused by the normalization of portal vein pressure after the TIPS. This change may be relatively rapid after TIPS placement. However, the collapse of the L-PUV diameter did not occur as quickly as expected, and it only completely disappeared in a quarter of patients by the end of the study. This moderate change may have resulted in liver function and mortality being comparable in both groups. Interestingly, OHE was gradually induced in the L-PUV group. We hypothesized that this may have been related to covert HE (CHE), as some reports [26] discovered that the deterioration of CHE to OHE may be influenced by this shunt.
Notably, an L-PUV did not aggravate the OHE grading. Furthermore, the symptoms of OHE were manageable through routine medical care and did not require additional PUV embolization. Therefore, we cannot recommend L-PUV embolization based on the present study; in previous studies, the short- and long-term benefits of embolizing large SPSSs are lacking, except in patients with refractory or recurrent HE [27]. Moreover, after receiving large SPSS embolization, a significant proportion of patients still did not completely avoid HE [9]. Moreover, a cost–benefit analysis is required.
After controlling for consistent risk factors [28,29,30], such as age, liver function, history of HE, stent diameter, and diabetes, half of the patients in the L-PUV group still experienced OHE. This suggested that in addition to familiar factors, having an L-PUV was a relatively reliable predictor, which reminded us to consider the necessity of prophylactic treatment for these patients in the absence of embolization of the PUV. Elevated serum bilirubin was a direct indicator of hepatocellular dysfunction and generally tended to increase and then decrease after TIPS implementation. Coinciding with the findings of Fonio P [31] and Lin X [32], we found that bilirubin was associated with post-TIPS OHE but was not an independent risk factor. Our study also assessed under-dilated and completely dilated TIPSs; it may be that under-dilated stent grafts still expand to the nominal diameter with time [33], and thus, we did not find any effect on long-term OHE.
Additionally, L-SPSSs did not cause a decreased survival rate in TIPS patients compared with the cirrhotic cohort without TIPS placement [9,10], and the same results were observed in our study, which could be a survival benefit of TIPS implementation. Although some studies [13,34,35] showed that PUV is associated with alcoholic cirrhosis, esophageal varices grading, and esophageal variceal bleeding, probably limited by case size, in general, we did not find these associations. Moreover, the majority of patients in our study had a punctured LPV. Although choosing a puncture site to reduce the risk of OHE is unreliable [36], it is unclear whether there is a hemodynamic difference between a large shunt and a stent located ipsilateral and heterolateral.
The study had several limitations. First, the sample size of the study was small, which could have led to selection bias. Second, limited by the invasive nature of the assay, we were unable to assess the changes in PPG after the collapse of the L-PUV. Third, the study lacked the measurement of flow rates at different sites in the portal vein, as well as liver perfusion, which needs to be improved in future studies. Fourth, we did not compare our results with other SPSSs. However, this is one of the research directions we are currently exploring. Finally, we only selected patients with variceal bleeding and did not include refractory ascites, and thus, the conclusions drawn need to be interpreted with caution.
5. Conclusions
In summary, L-PUVs increased the risk of post-TIPS OHE. Even if the overall symptoms are manageable, the prophylactic treatment of OHE in such patients still needs to be considered.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded from https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm12010158/s1. Figure S1: Detailed TIPS procedure figures. Figure S2: A 66-year-old patient with hepatitis B cirrhosis, where the diameter of the L-PUV was reduced from 10.6 mm to 5.2 mm 17 months after a TIPS. Figure S3: A 47-year-old patient with hepatitis B cirrhosis; 24 months after a TIPS, the diameter of the L-PUV was reduced from 8.1 mm to 2.7 mm, approaching complete collapse. Table S1: Baseline characteristics of patients before PSM. Table S2: Characteristics of the PUV.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.-L.Z. and W.-D.W.; data curation, B.-Y.Z. and C.F.; formal analysis, H.-H.T. and Z.-C.Z.; investigation, Z.-L.Z. and C.F.; methodology, H.-H.T. and Z.-C.Z.; resources, X.-L.Z. and W.-D.W.; software, Z.-C.Z. and Z.-L.Z.; supervision, X.-L.Z. and W.-D.W.; validation, Z.-L.Z. and B.-Y.Z.; visualization, H.-H.T. and Z.-C.Z.; writing—original draft, H.-H.T. and Z.-C.Z.; writing—review and editing, H.-H.T. and Z.-C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Suzhou Livelihood Science and Technology Projects (SS202059) and Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program (Social Development) Projects (BE2021648).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was waived due to its retrospective nature.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used and analyzed in the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Praktiknjo, M.; Simón-Talero, M.; Römer, J.; Roccarina, D.; Martínez, J.; Lampichler, K.; Baiges, A.; Low, G.; Llop, E.; Maurer, M.H.; et al. Total area of spontaneous portosystemic shunts independently predicts hepatic encephalopathy and mortality in liver cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turco, L.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Portal Hypertension: Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-González, J.; Quiroga, S.; Simón-Talero, M.; Genescà, J. Spontaneous portosystemic shunts in liver cirrhosis: New approaches to an old problem. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1320571904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simón-Talero, M.; Roccarina, D.; Martínez, J.; Lampichler, K.; Baiges, A.; Low, G.; Llop, E.; Praktiknjo, M.; Maurer, M.H.; Zipprich, A.; et al. Association Between Portosystemic Shunts and Increased Complications and Mortality in Patients With Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, K.; He, C.; Wang, Z.; Bai, W.; Guo, W.; Yu, T.; Yuan, X.; et al. Early TIPS with covered stents versus standard treatment for acute variceal bleeding in patients with advanced cirrhosis: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. 2019, 4, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Abraldes, J.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Bosch, J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 2017, 65, 310–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanny, B.; Winters, A.; Boutros, S.; Saab, S. Hepatic Encephalopathy Challenges, Burden, and Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gairing, S.J.; Müller, L.; Kloeckner, R.; Galle, P.R.; Labenz, C. Review article: Post-TIPSS hepatic encephalopathy—Current knowledge and future perspectives. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, H.; Luo, B.; Bai, W.; Li, K.; Wang, Z.; Xia, D.; Guo, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Concurrent large spontaneous portosystemic shunt embolization for the prevention of overt hepatic encephalopathy after TIPS: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 2022, 76, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W.; Tie, J.; Li, K.; Niu, J.; Zuo, L.; Yu, T.; Yuan, X.; et al. Association between non-variceal spontaneous portosystemic shunt and outcomes after TIPS in cirrhosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; Yin, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, X.; Zhuge, Y. Comparison of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for treatment of variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis with or without spontaneous portosystemic shunt. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacerdoti, D.; Bolognesi, M.; Bombonato, G.; Gatta, A. Paraumbilical vein patency in cirrhosis: Effects on hepatic hemodynamics evaluated by Doppler sonography. Hepatology 1995, 22, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Maruyama, H.; Sekimoto, T.; Shimada, T.; Takahashi, M.; Okugawa, H.; Yokosuka, O.; Yamaguchi, T. Influence of paraumbilical vein patency on the portal hemodynamics of patients with cirrhosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.C.; Zhong, B.Y.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, X.L. Emergent TIPS as a first-line therapy in advanced cirrhotic patients with acute gastroesophageal variceal bleeding. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Raman, S.S.; Yu, N.C.; To’o, K.J.; Jutabha, R.; Lu, D.S. Esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients: Evaluation with liver CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, O.; Nardelli, S.; Moscucci, F.; Pasquale, C.; Ridola, L.; Merli, M. Hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franchis, R.; Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicka, J.; Bastgen, D.; Byrtus, J.; Praktiknjo, M.; Terstiegen, S.; Meyer, C.; Thomas, D.; Fimmers, R.; Treitl, M.; Euringer, W.; et al. Smaller-Diameter Covered Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Stents Are Associated With Increased Survival. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2793–2799.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariushnia, S.R.; Haskal, Z.J.; Midia, M.; Martin, L.G.; Walker, T.G.; Kalva, S.P.; Clark, T.W.; Ganguli, S.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Saiter, C.K.; et al. Quality Improvement Guidelines for Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; An, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tacke, F.; Arora, A.; Qi, X. Impact of spontaneous splenorenal shunt on liver volume and long-term survival of liver cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Radiological Intervention for Shunt Related Encephalopathy. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.K.; Mitchell, D.G.; Lakhman, Y.; Bergin, D.; Dolin, R.J.; Doria, C.; Parker, L. Paraumbilical collateral veins on MRI as possible protection against portal venous thrombosis in candidates for liver transplantation. Abdom. Imaging. 2008, 33, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Morin, C.; Lafortune, M.; Pomier, G.; Robin, M.; Breton, G. Patent paraumbilical vein: Anatomic and hemodynamic variants and their clinical importance. Radiology 1992, 185, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borentain, P.; Soussan, J.; Resseguier, N.; Botta-Fridlund, D.; Dufour, J.C.; Gérolami, R.; Vidal, V. The presence of spontaneous portosystemic shunts increases the risk of complications after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2016, 97, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinert, R.; Zipprich, A.; Simón-Talero, M.; Stangl, F.; Ludwig, C.; Wienke, A.; Praktiknjo, M.; Höhne, K.; Trebicka, J.; Genescà, J.; et al. Covert hepatic encephalopathy and spontaneous portosystemic shunts increase the risk of developing overt hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, C.A.; Rajesh, S.; Augustine, P.; Padsalgi, G.; Ahamed, R. Portosystemic shunts and refractory hepatic encephalopathy: Patient selection and current options. Hepatic Med.-Evid. Res. 2019, 11, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Qi, X.; Yang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Nie, Y.; Yuan, S.; Wu, K.; Han, G.; Fan, D. Predictors of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhotic patients: A systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Zhu, H.; Leng, X.; Zou, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhuge, Y. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of hepatic encephalopathy after a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhotic patients. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, L. Clinical Efficacy of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Created with Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered Stent-Grafts: 8-mm Versus 10-mm. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonio, P.; Discalzi, A.; Calandri, M.; Breatta, A.D.; Bergamasco, L.; Martini, S.; Ottobrelli, A.; Righi, D.; Gandini, G. Incidence of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) according to its severity and temporal grading classification. Radiol. Med. 2017, 122, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Gao, F.; Wu, X.; Cai, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z. Efficacy of albumin-bilirubin score to predict hepatic encephalopathy in patients underwent transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, C.; Huang, S.; Shi, Q.; Xiong, B. Potential Benefits of Underdilation of 8-mm Covered Stent in Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Creation. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calame, P.; Ronot, M.; Bouveresse, S.; Cervoni, J.P.; Vilgrain, V.; Delabrousse, É. Predictive value of CT for first esophageal variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: Value of para-umbilical vein patency. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 87, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Wang, J.H.; Lu, S.N.; Tung, W.C.; Hung, C.H.; Lee, C.M.; Changchien, C.S. Comparison of prevalence for paraumbilical vein patency in patients with viral and alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.H.; Chu, J.G.; Huang, H.; Zhao, G.R.; Yao, K.C. Targeted puncture of left branch of intrahepatic portal vein in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt to reduce hepatic encephalopathy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).