Cross-Sectional Study on Lateral Skull Radiographs to Design a New Nasopharyngeal Swab for Simplified COVID-19 and Respiratory Infections Diagnostic Testing in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Laboratory Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Suspected Human Cases: Interim Guidance. 2 March 2020. World Health Organization, 2020. Available online: https://data.oecd.org/healthcare/computed-tomography-ct-exams.htm (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- Azzi, L.; Maurino, V.; Baj, A.; Dani, M.; d’Aiuto, A.; Fasano, M.; Lualdi, M.; Sessa, F.; Alberio, T. Diagnostic Salivary Tests for SARS-CoV-2. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torretta, S.; Zuccotti, G.; Cristofaro, V.; Ettori, J.; Solimeno, L.; Battilocchi, L.; D’Onghia, A.; Bonsembiante, A.; Pignataro, L.; Marchisio, P.; et al. Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR Using Different Sample Sources: Review of the Literature. Ear. Nose Throat J. 2021, 100 (Suppl. 2), 131S–138S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.; Moon, J.W.; Chae, S.W.; Rhyu, I.J. Complications of Nasopharyngeal Swabs and Safe Procedures for COVID-19 Testing Based on Anatomical Knowledge. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2022, 37, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pondaven-Letourmy, S.; Alvin, F.; Boumghit, Y.; Simon, F. How to perform a nasopharyngeal swab in adults and children in the COVID-19 era. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head. Neck Dis. 2020, 137, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, F.M.; Chen, K.; Verrill, K.A. How to Obtain a Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NEJM Procedure: Collection of Nasopharyngeal Specimens with the Swab Technique. 2021. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DVJNWefmHjE (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- COVID-19: Nasal and Oropharyngeal Swab. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/action/downloadSupplement?doi=10.1002%2Fhed.26212&file=hhe26212-sup-0001-Video.mp4 (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- Torretta, S.; Zuccotti, G.; Cristofaro, V.; Ettori, J.; Solimeno, L.; Battilocchi, L.; D’Onghia, A.; Pignataro, L.; Capaccio, P. Nonserologic test for COVID-19: How to manage? Head Neck 2020, 42, 1552–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasopharyngeal Swab for COVID-19. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SEEYEDMug8E (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- COVID-19 Specimen Collection Nasopharyngeal (NP) Specimens Only. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J7lLZEZ6u_w (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- Pruidze, P.; Mincheva, P.; Weninger, J.T.; Reissig, L.F.; Hainfellner, A.; Weninger, W.J. Performing nasopharyngeal swabs-Guidelines based on an anatomical study. Clin. Anat. 2021, 34, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, A.; Rizzo, D.; Longoni, E.; Turra, N.; Urru, S.; Saba, P.P.; Musumano, L.; Bussu, F. Nasopharyngeal swab collection in the suspicion of COVID-19. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, A.; Rizzo, D.; Uzzau, S.; De Riu, G.; Rubino, S.; Bussu, F. Inappropriate Nasopharyngeal Sampling for SARS-CoV-2 Detection Is a Relevant Cause of False- Negative Reports. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maio, P.; Iocca, O.; Cavallero, A.; Giudice, M. Performing the nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swab for 2019-novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) safely: How to dress, undress, and technical notes. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1548–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzzi, G.; De Virgilio, A.; Pichi, B.; Mazzola, F.; Zocchi, J.; Mercante, G.; Spriano, G.; Pellini, R. COVID-19: Nasal and oropharyngeal swab. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, A.C.; Brewster, R.; Rajasekaran, K. How to Perform a Nasopharyngeal Swab—An Otolaryngology Perspective. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coden, E.; Russo, F.; Arosio, A.D.; Castelnuovo, P.; Karligkiotis, A.; Volpi, L. Optimum Naso-oropharyngeal Swab Procedure for COVID-19: Step-by-Step Preparation and Technical Hints. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 2564–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Son, K.K.; Han, Y.J.; Ko, S. A method for optimal depth of the nasopharyngeal temperature probe: The philtrum to tragus distance. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2014, 66, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callesen, R.E.; Kiel, C.M.; Hovgaard, L.H.; Jakobsen, K.K.; Papesch, M.; von Buchwald, C.; Todsen, T. Optimal Insertion Depth for Nasal Mid-Turbinate and Nasopharyngeal Swabs. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feres, M.F.; Hermann, J.S.; Pignatari, S.S. Cephalometric evaluation of adenoids: An analysis of current methods and a proposal of a new assessment tool. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2012, 142, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feres, M.F.; Hermann, J.S.; Sallum, A.C.; Pignatari, S.S. Radiographic adenoid evaluation: Proposal of an objective parameter. Radiol. Bras. 2014, 47, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, P.; Castriciano, S.; Chernesky, M.; Smieja, M. Comparison of flocked and rayon swabs for collection of respiratory epithelial cells from uninfected volunteers and symptomatic patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2265–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungnak, W.; Huang, N.; Bécavin, C.; Berg, M.; Queen, R.; Litvinukova, M.; Talavera-López, C.; Maatz, H.; Reichart, D.; Sampaziotis, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torretta, S.; Capaccio, P.; Gaffuri, M.; Gaini, L.M.; Borin, M.; Maruca, A.; Battilocchi, L.; Nitro, L.; Marchisio, P.; Pignataro, L. ENT management of children with adenotonsillar disease during COVID-19 pandemic. Ready to start again? Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 138, 110145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
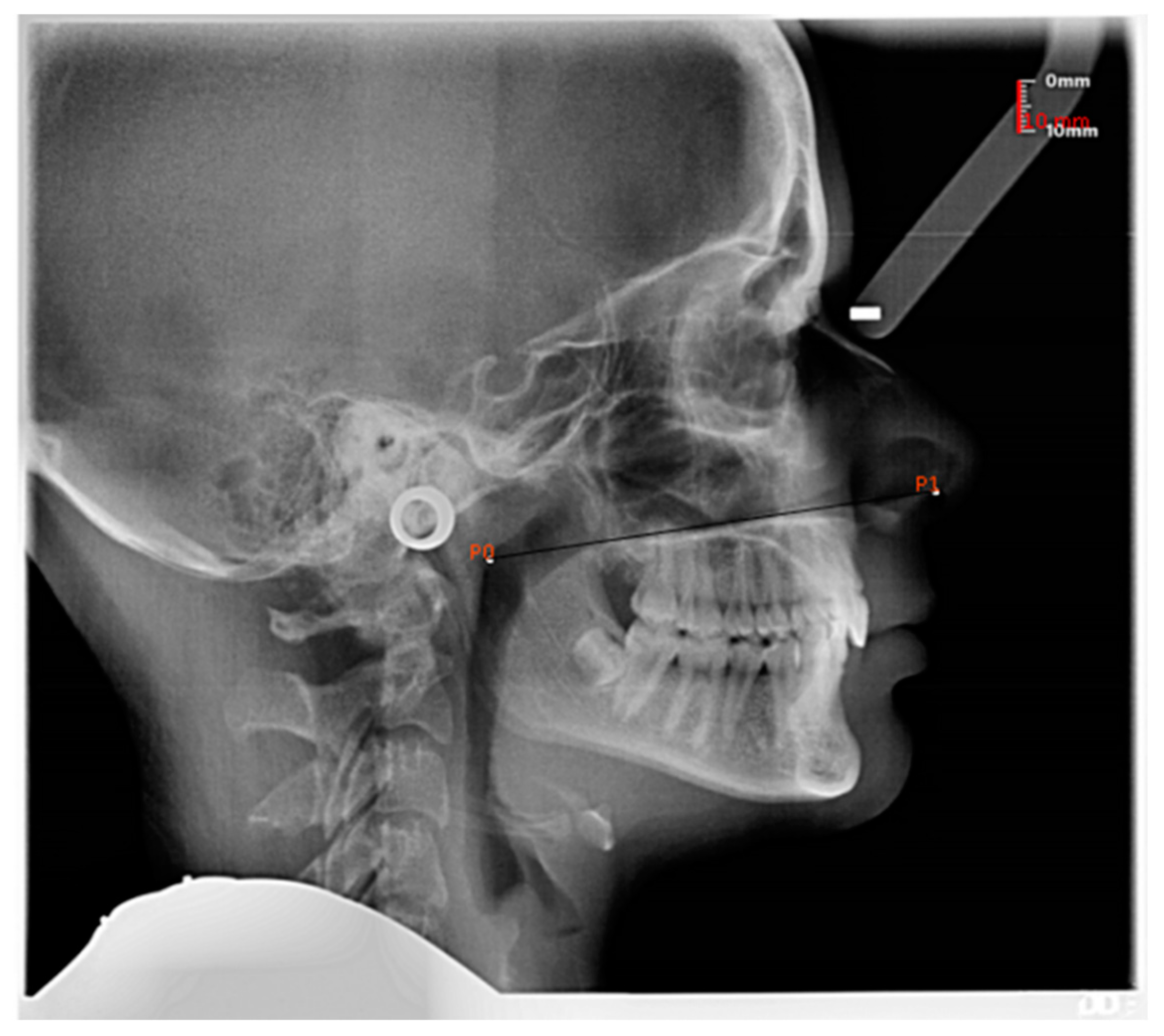
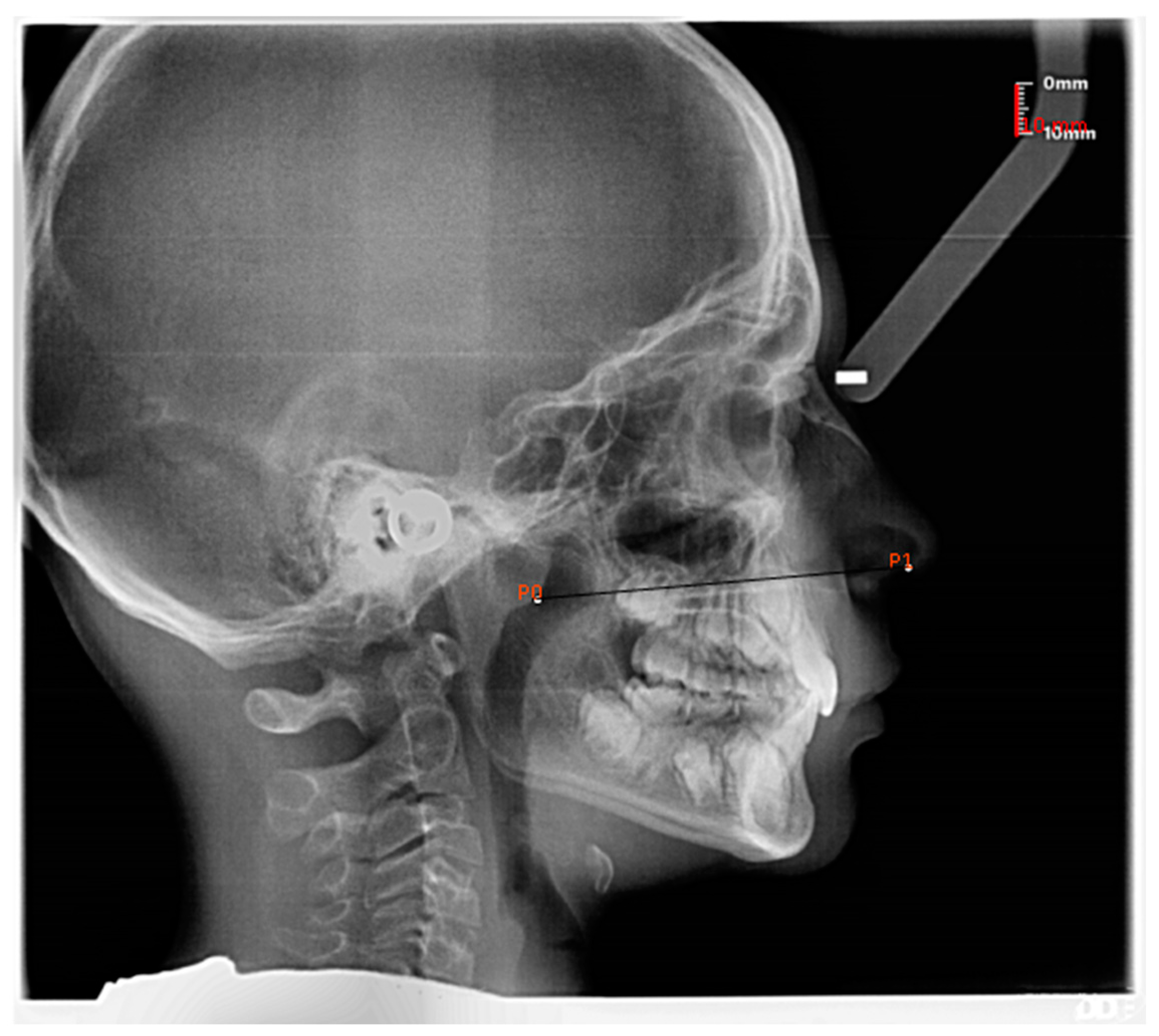


| Age Group (Years.Months) | n | Mean | SD | 95% Confidence Interval | Landmark on Swab Stick |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical Significance of between Gender Difference | |||||
| 4–4.11 | 16 | 56.86 | 13.41 | 49.71–64.00 | 4: At 50 mm distance from the tip |
| Male | 5 | 65.56 | 12.81 | p = 0.054 | |
| Female | 11 | 52.90 | 12.21 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 8 | 65.51 | 13.19 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 8 | 48.21 | 6.36 | ||
| 5–5.11 | 28 | 60.75 | 10.40 | 56.71–64.78 | 5: At 57 mm distance from the tip |
| Male | 13 | 62.03 | 10.98 | p = 0.55 | |
| Female | 15 | 59.64 | 10.13 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 19 | 61.3 | 11.32 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 9 | 59.6 | 8.65 | ||
| 6–6.11 | 32 | 66.43 | 10.17 | 62.76–70.10 | 6: At 63 mm distance from the tip |
| Male | 13 | 66.30 | 8.19 | p = 0.95 | |
| Female | 19 | 66.52 | 11.56 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 22 | 67.35 | 11.51 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 10 | 64.41 | 6.37 | ||
| 7–7.11 | 52 | 71.26 | 6.07 | 69.57–72.95 | 7: At 70 mm distance from the tip |
| Male | 19 | 70.24 | 6.42 | p = 0.36 | |
| Female | 33 | 71.85 | 5.88 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 23 | 73.82 | 6.46 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 29 | 69.23 | 4.97 | ||
| 8–8.11 | 50 | 73.63 | 6.38 | 71.81–75.44 | |
| Male | 28 | 75.75 | 5.83 | p = 0.007 | |
| Female | 22 | 70.93 | 6.15 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 23 | 76.11 | 6.05 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 27 | 71.52 | 5.98 | ||
| 9–9.11 | 47 | 76.76 | 6.65 | 74.81–78.71 | 9: At 75 mm distance from the tip |
| Male | 24 | 78.81 | 6.17 | p = 0.029 | |
| Female | 23 | 74.62 | 6.58 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 33 | 78.60 | 6.27 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 14 | 72.42 | 5.55 | ||
| 10–10.11 | 37 | 76.69 | 7.18 | 74.30–76.69 | |
| Male | 21 | 76.40 | 6.58 | p = 0.78 | |
| Female | 16 | 77.08 | 8.11 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 23 | 78.80 | 6.78 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 14 | 73.23 | 6.65 | ||
| 11–11.11 | 23 | 83.76 | 4.50 | 81.82–85.71 | 11: At 80 mm distance from the tip |
| Male | 8 | 85.46 | 5.76 | p = 0.195 | |
| Female | 15 | 82.88 | 3.57 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 23 | 78.80 | 6.78 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 0 | 73.23 | 6.65 | ||
| 12–12.11 | 22 | 79.45 | 8.81 | 75.53–83.36 | |
| Male | 11 | 80.08 | 10.70 | p = 0.746 | |
| Female | 11 | 78.81 | 6.91 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 16 | 82.29 | 5.75 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 6 | 71.86 | 7.73 | ||
| 13–14 | 15 | 82.95 | 6.41 | 79.40–86.50 | |
| Male | 9 | 83.10 | 7.50 | p = 0.91 | |
| Female | 6 | 82.73 | 5.01 | ||
| no adenoid hypertrophy | 14 | 83.37 | 6.44 | ||
| adenoid hypertrophy | 1 | 77.1 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goracci, C.; Volpe, A.; Salerni, L.; Paolini, E.; Vichi, A.; Franchi, L. Cross-Sectional Study on Lateral Skull Radiographs to Design a New Nasopharyngeal Swab for Simplified COVID-19 and Respiratory Infections Diagnostic Testing in Children. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010213
Goracci C, Volpe A, Salerni L, Paolini E, Vichi A, Franchi L. Cross-Sectional Study on Lateral Skull Radiographs to Design a New Nasopharyngeal Swab for Simplified COVID-19 and Respiratory Infections Diagnostic Testing in Children. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010213
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoracci, Cecilia, Alessandra Volpe, Lorenzo Salerni, Elisabetta Paolini, Alessandro Vichi, and Lorenzo Franchi. 2023. "Cross-Sectional Study on Lateral Skull Radiographs to Design a New Nasopharyngeal Swab for Simplified COVID-19 and Respiratory Infections Diagnostic Testing in Children" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010213
APA StyleGoracci, C., Volpe, A., Salerni, L., Paolini, E., Vichi, A., & Franchi, L. (2023). Cross-Sectional Study on Lateral Skull Radiographs to Design a New Nasopharyngeal Swab for Simplified COVID-19 and Respiratory Infections Diagnostic Testing in Children. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010213








