Extended List of Warning Signs in Qualification to Diagnosis and Treatment of Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children and Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
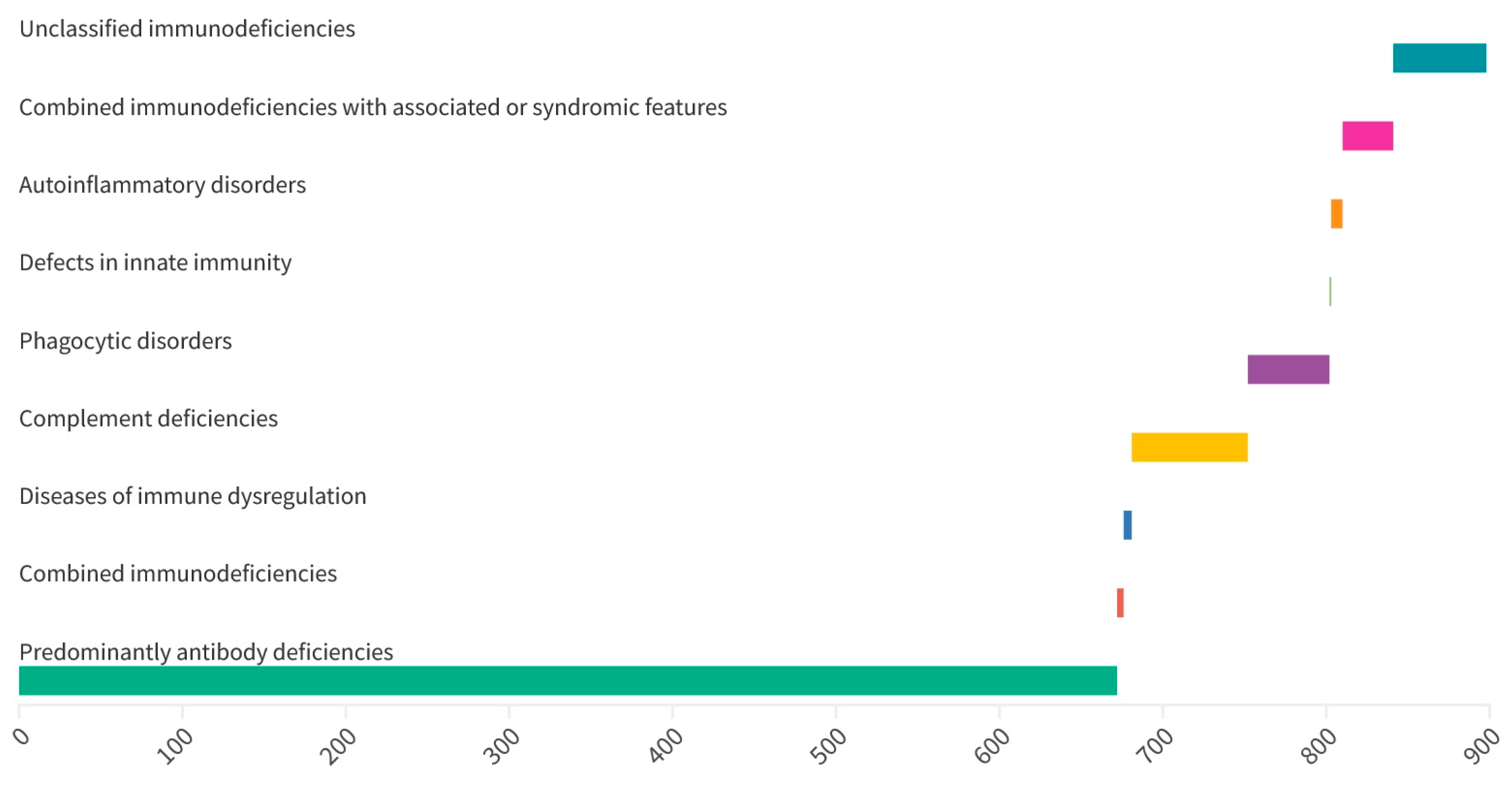
3.1. Distribution of Inborn Errors of Immunity
3.2. Sex, Age and Consanguinity
3.3. Frequency of the 14 Warning Signs in the Study Population
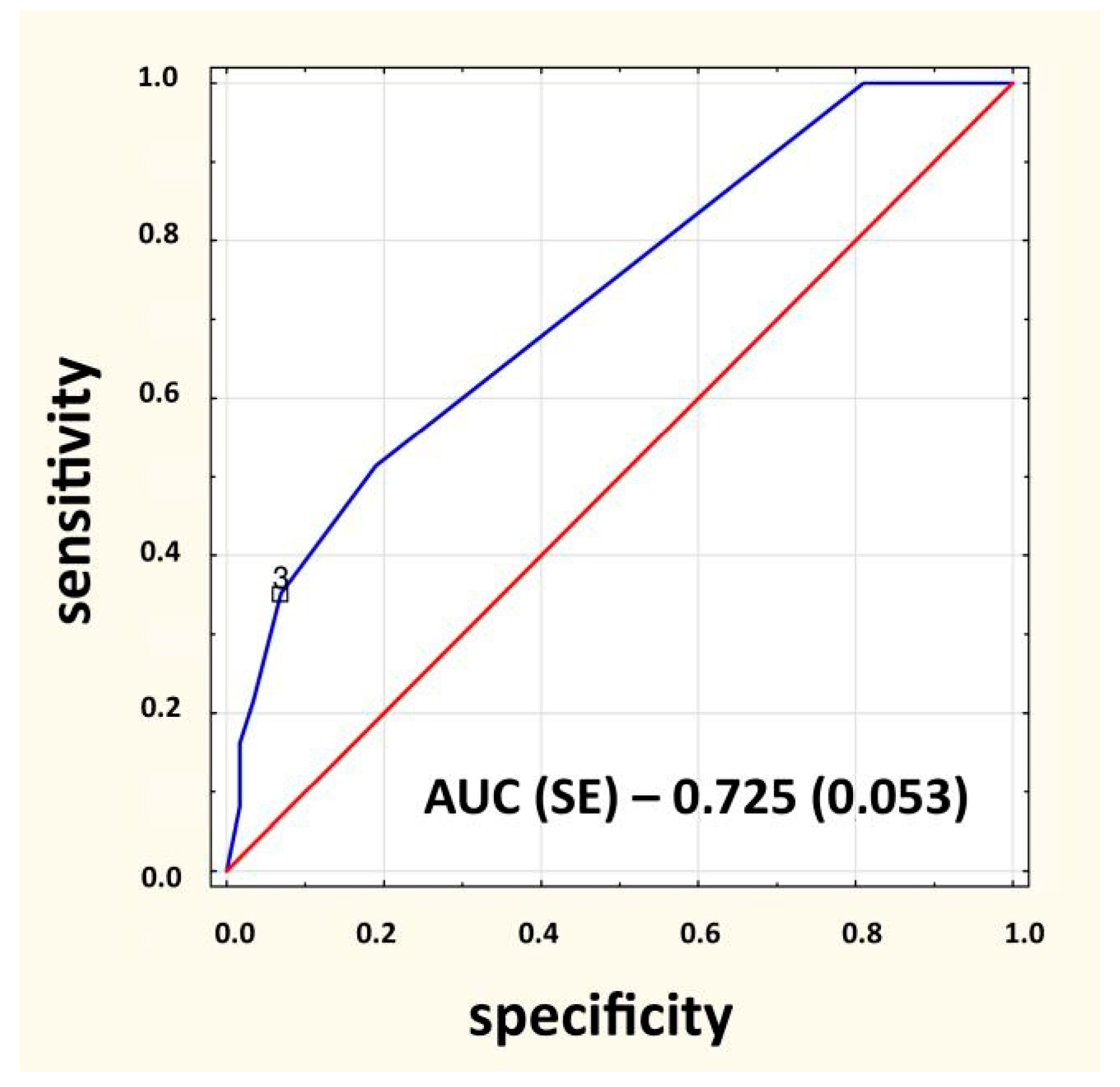
3.4. Diagnostic Value of the 14 Warning Signs in Predicting IEI
- (1)
- haematological symptoms and neoplastic diseases (OR 89.26, 95% CI 48.18–165.34, p < 0.001)
- (2)
- family history IEI (OR 25.24. 95% CI 12.84–49.58, p < 0.001)
- (3)
- autoimmune diseases (OR 16.89, 95% CI 5.50–51.86, p < 0.001)
- (4)
- inhibition of normal child development or weight gain (OR 6.16, 95% CI 3.60–10.52, p < 0.001)
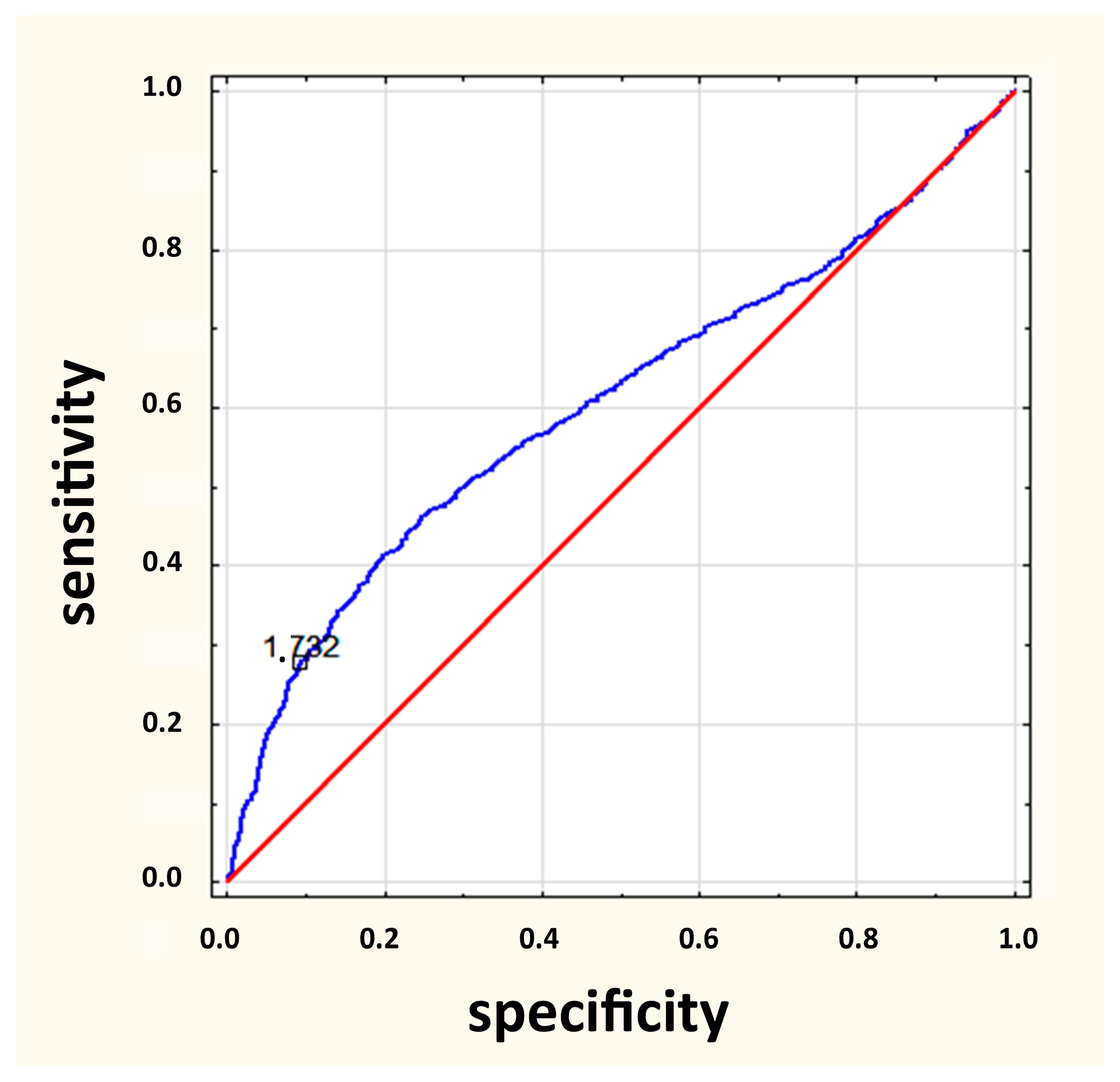
3.5. The List of 10 vs. 14 Warning Signs
- (1)
- for a list of 10 symptoms when one symptom is met (OR = 1.15; p = 0.020)
- (2)
- for a list of 14 symptoms when three symptoms are met (OR = 1.11; p = 0.020)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jesenak, M.; Banovcin, P.; Jesenakova, B.; Babusikova, E. Pulmonary manifestations of primary immunodeficiency disorders in children. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarangelo, L.D. Primary immunodeficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S182–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessach, I.; Walter, J.; Notarangelo, L.D. Recent advances in primary immunodeficiencies: Identification of novel genetic defects and unanticipated phenotypes. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 3R–12R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousfiha, A.; Jeddane, L.; Al-Herz, W.; Ailal, F.; Casanova, J.L.; Chatila, T.; Conley, M.E.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Etzioni, A.; Franco, J.L.; et al. The 2015 IUIS Phenotypic Classification for Primary Immunodeficiencies. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arason, G.J.; Jorgensen, G.H.; Ludviksson, B.R. Primary Immunodeficiency and Autoimmunity: Lessons from Human Diseases. Scand. J. Immunol. 2010, 71, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewertowska, M.; Grześk, E.; Urbańczyk, A.; Dąbrowska, A.; Bąbol-Pokora, K.; Łęcka, M.; Kołtan, S. Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta syndrome 1 and 2 (APDS 1 and APDS 2): Similarities and differences based on clinical presentation in two boys. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.E.; Grimbacher, B.; Witte, T. Autoimmunity and primary immunodeficiency: Two sides of the same coin? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 19, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelac, J.A.; Yonkof, J.R.; Fernandez, J. Differing Performance of the Warning Signs for immunodeficiency in the Diagnosis of Pediatric Versus Adult Patients in a Two-Center Tertiary Referral Population. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, C.; Atay, S.; Clark, K.E.N.; Ong, V.; Denton, C.P. Autoimmunity and immunodeficiency at the crossroad: Autoimmune disorders as the presenting feature of selective IgM deficiency. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e223180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousfiha, A.; Jeddane, L.; Picard, C.; Al-Herz, W.; Ailal, F.; Chatila, T.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Etzioni, A.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; et al. Human inborn errors of immunity: 2019 update of the IUIS Phenotypical Classification. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousfiha, A.; Moundir, A.; Tangye, S.G.; Picard, C.; Jeddane, L.; Al-Herz, W.; Rundles, C.C.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; et al. The 2022 Update of IUIS Phenotypical Classification for Human Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, E.; Driessen, G. Educational paper: Primary immunodeficiencies in children: A diagnostic challenge. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condino-Neto, A.; Espinosa-Rosales, F.J. Changing the Lives of People with Primary Immunodeficiencies (PI) with Early Testing and Diagnosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grześk, E.; Dąbrowska, A.; Urbańczyk, A.; Ewertowska, M.; Wysocki, M.; Kołtan, S. Common variable immunodeficiency: Different faces of the same disease. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grześk, E.; Kołtan, S.; Dąbrowska, A.; Urbańczyk, A.; Małdyk, J.; Małkowski, B.; Bogiel, T.; Dębski, R.; Czyżewski, K.; Wysocki, M.; et al. Case report: Cellular therapy for hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder in pediatric common variable immunodeficiency with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 915986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, S.; Lissauer, S.; Welch, S.; Hackett, S. Immune deficiencies in children: An overview. Postgrad. Med. J. 2013, 89, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INFO4PI.org. Primary Immunodeficiency Resource Center. Available online: www.info4pi.org (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Arkwright, P.D.; Gennery, A.R. Ten Warning Signs of Primary Immunodeficiency: A New Paradigm Is Needed for the 21st Century. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1238, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M.D.; Cant, A.J. The 10 warning signs: A time for a change? Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toms, K.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Kumararatne, D. Analysis of scoring systems for primary immunodeficiency diagnosis in adult immunology clinics. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 203, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro-Sampaio, M.; Jacob, C.M.; Rodrigues Leone, C. A proposal of warning signs for primary immunodeficiencies in the first year of life. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 22, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Society of Immunodeficiencies. Available online: http://esid.org (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Arslan, S.; Ucar, R.; Caliskaner, A.Z.; Reisli, I.; Guner, S.N.; Sayar, E.H.; Baloglu, I. How effective are the 6 European Society of Immunodeficiency warning signs for primary immunodeficiency disease? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 116, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeniz, F.C.; Gul, Y.; Yorulmaz, A.; Guner, S.N.; Keles, S.; Reisli, I. Evaluation of the 10 Warning Signs in Primary and Secondary Immunodeficient Patients. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 900055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbarayan, A.; Colarusso, G.; Hughes, S.M.; Gennery, A.R.; Slatter, M.; Cant, A.J.; Arkwright, P.D. Clinical features that identify children with primary immunodeficiency diseases. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacGinnitie, A.; Frank Aloi, F.; Mishra, S. Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients evaluated for primary immunodeficiency. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 22, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, S.M.; El-Ghoneimy, D.H.; Afifi, H.M. Clinical Predictors of Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases in Children. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2013, 5, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.Y.; Iyer, V.N.; Hagan, J.B.; St Sauver, J.L.; Boyce, T.G. Incidence and temporal trends of primary immunodeficiency: A population-based cohort study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2009, 84, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamohammadi, A.; Mohammadinejad, P.; Abolhassani, H.; Mirminachi, B.; Movahedi, M.; Gharagozlou, M.; Parvaneh, N.; Zeiaee, V.; Mirsaeed-Ghazi, B.; Chavoushzadeh, Z.; et al. Primary immunodeficiency disorders in Iran: Update and new insights from the third report of the National Registry. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlayel, M.S.; Bener, A.; Laban, M.A. Primary immunodeficiency diseases in children: 15 year experience in a Tertiary Care Medical Center in Qatar. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Pudifin, D.J.; Armstrong, D.; Good, R.A. Selective IgA deficiency and neoplasia. Vox Sang. 1980, 38, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.I.; Holzel, A. Wilm’s-aniridia syndrome with transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy. Arch. Dis. Child. 1973, 48, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapel, H.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Update in understanding Common Variable Immunodeficiency Disorders (CVIDs) and the management of patients with these Conditions. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor, P.C.; Eng, K.H.; Singel, K.L.; Abrams, S.I.; Odunsi, K.; Moysich, K.B.; Fuleihan, R.; Garabedian, E.; Lugar, P.; Ochs, H.D.; et al. Cancer in primary immunodeficiency diseases: Cancer incidence in the United States Immune Deficiency Network Registry. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajdic, C.M.; Mao, L.; van Leeuwen, M.T.; Kirkpatrick, P.; Grulich, A.E.; Riminton, S. Are antibody deficiency disorders associated with a narrower range of cancers than other forms of immunodeficiency? Blood 2010, 116, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarangelo, L.D.; Bacchetta, R.; Casanova, J.L.; Su, H.C. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: An Expanding Universe. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabb1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebudi, R.; Kiykim, A.; Sahin, M.K. Primary immunodeficiency and cancer in children; A Review of the Literature. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 15, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo Reyes, S.O.; Ramirez-Vazquez, G.; Cruz Hernández, A.; Medina-Torres, E.A.; Ramirez-Lopez, A.B.; España-Cabrera, C.; Hernandez-Lopez, C.A.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A.; Espinosa-Rosales, F.J.; Espinosa-Padilla, S.E.; et al. Clinical features, non-infectious manifestations and survival analysis of 161 Children with primary immunodeficiency in Mexico: A single center experience over two decades. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazina, Š.; Markelj, G.; Jeverica, A.K.; Toplak, N.; Bratanič, N.; Jazbec, J.; Kopač, P.; Debeljak, M.; Ihan, A.; Avčin, T. Autoimmune and inflammatory manifestations in 247 Patients with primary immunodeficiency—A report from the Slovenian National Registry. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podjasek, J.C.; Abraham, R.S. Autoimmune cytopenias in common variable immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivalta, B.; Zama, D.; Pancaldi, G.; Facchini, E.; Cantarini, M.E.; Miniaci, A.; Prete, A.; Pession, A. Evans Syndrome in Childhood: Long Term follow-up and the Evolution in Primary Immunodeficiency or Rheumatological Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Valdez, L.; Deya-Martinez, A.; Giner, M.T.; Berrueco, R.; Esteve-Solé, A.; Juan, M.; Plaza-Martín, A.M.; Alsina, L. Evans Syndrome as First Manifestation of Primary Immunodeficiency in Clinical Practise. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 39, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankish, P.; Schiffner, J.; Ghosh, S.; Babor, F.; Borkhardt, A.; Laws, H.J. The Duesseldorf Warning Signs for Primary Immunodeficiency: Is it time to change the rules? J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sign | |
|---|---|
| 1. | ≥4 new ear infections within 1 year |
| 2. | ≥2 serious sinus infections within 1 year |
| 3. | ≥2 months of oral antibiotic treatment with little effect |
| 4. | ≥2 episodes of pneumonia within 1 year |
| 5. | Failure of an infant to gain weight or grow normally. |
| 6. | Recurrent, deep skin or organ abscesses |
| 7. | Persistent thrush in mouth or fungal infection on skin |
| 8. | Need for intravenous antibiotics to clear infections |
| 9. | ≥2 deep-seated infections, including septicemia |
| 10. | A family history of primary immunodeficiency |
| Sign | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Severe eczema |
| 2. | Allergies |
| 3. | Hematologic and oncologic disorders |
| 4. | Autoimmunity |
| Primary Immunodeficiency | Number | % |
|---|---|---|
| Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy | 189 | 21.1 |
| IgG hypogammaglobulinemia | 160 | 17.8 |
| IgA deficiency | 120 | 13.4 |
| Selective IgA deficiency | 88 | 9.8 |
| C3, C4 complement deficiencies | 67 | 7.5 |
| IgM deficiency | 63 | 7.0 |
| Unclassified primary immunodeficiencies | 57 | 6.4 |
| IgG subclass deficiency | 43 | 4.8 |
| Common variable immunodeficiency disorders | 19 | 2.1 |
| DiGeorge syndrome | 15 | 1.7 |
| IgG subclass deficiency associated with IgA deficiency | 14 | 1.6 |
| IgA and IgM deficiency | 8 | 0.9 |
| Autoinflammatory diseases | 7 | 0.8 |
| Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome | 6 | 0.7 |
| Nijmegen breakage syndrome | 5 | 0.6 |
| Ataxia telangiectasia | 5 | 0.6 |
| CD19+ deficiency | 5 | 0.6 |
| Severe combined immunodeficiency | 4 | 0.4 |
| Shwachman-Diamond syndrome | 4 | 0.4 |
| Agammaglobulinemia | 3 | 0.3 |
| Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome | 3 | 0.3 |
| Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis | 2 | 0.2 |
| Chronic granulomatous disease | 2 | 0.2 |
| Severe congenital neutropenia | 2 | 0.2 |
| IgG and IgM deficiency | 2 | 0.2 |
| Interferon-gamma receptor deficiency | 1 | 0.1 |
| Warning Sign | IEI n (%): 896 (31.4%) | No IEI n (%): 1955 (68.6%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≥4 new ear infections within 1 year | 607 (68%) | 1575 (81%) | <0.001 |
| ≥2 serious sinus infections within 1 year | 55 (6%) | 195 (10%) | <0.001 |
| ≥2 months of oral antibiotic treatment with little effect | 135 (15%) | 290 (15%) | 0.871 |
| ≥2 episodes of pneumonia within 1 year | 281 (31.4%) | 669 (34%) | 0.132 |
| Failure of an infant to gain weight or grow normally. | 81 (9.0%) | 138 (7%) | 0.065 |
| Recurrent, deep skin or organ abscesses | 14 (2%) | 56 (3%) | 0.037 |
| Persistent thrush in mouth or fungal infection on skin | 101 (11%) | 276 (14%) | 0.037 |
| Need for intravenous antibiotics to clear infections | 303 (33.8%) | 631 (32%) | 0.415 |
| ≥2 deep-seated infections, including septicemia | 49 (5%) | 61 (3%) | 0.002 |
| A family history of primary immunodeficiency | 41 (5%) | 25 (1%) | <0.001 |
| Severe eczema 1 | 180 (20%) | 429 (22%) | 0.262 |
| Allergies 1 | 112 (12.5%) | 287 (15%) | 0.119 |
| Hematologic and oncologic disorders 1 | 114 (13%) | 25 (1%) | <0.001 |
| Autoimmunity 1 | 31 (3.5%) | 9 (0.5%) | <0.001 |
| Hematologic Disorders | IEI (n) |
|---|---|
| Cytopenias | CVID (19) DiGerorge syndrome (8) Hipogamm. (8) sIgAD (6) IgMD (6) WAS (6) AT (5) NBS (5) SCID (4) Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (3) HLH (2) |
| Non-malignant hepatomegaly | SCID (4) CGD (2) ALPS (1) AT (2) CVID (1) IgMD (1) |
| Non-malignant splenomegaly | ALPS (3) HLH (2) SCID (4) |
| Non-malignant lymphadenopathy | CVID (8) ALPS (2) CGD (2) |
| Total number of hematologic disorders | 105 |
| Autoimmunity | IEI (n) |
|---|---|
| Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis | sIgAD (6) IgAD (2) Hipogamm. (2) IgMD (1) |
| Hashimoto disease | sIgAD (3) Subclass deficiency (2) CVID (1) |
| Diabetes mellitus type 1 | sIgAD (2) Hipogamm. (1) |
| Immune thrombocytopenia | CVID (1) Hipogamm. (1) ALPS (1) |
| Ulcerative colitis | sIgAD (2) CVID (1) |
| Celiac disease | sIgAD (2) |
| Psoriasis | THI (1) |
| Autoimmune hemolytic anemia | THI (1) ALPS (1) |
| Total number of autoimmune disorders | 31 |
| IEI | Cancer | Number of Cancers |
|---|---|---|
| THI | Wilms tumor | 1 |
| Plexiform neurofibroma | 2 | |
| CVID | Seminoma testis | 1 |
| Pulmonary cancer | 1 | |
| Hypogammaglobulinemia | AML | 2 |
| NBS | T-ALL | 2 |
| Total number of cancers | 9 |
| Warning Sign | Odds Ratio | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≥4 new ear infections within 1 year | 0.50 | <0.001 | 0.42–0.60 |
| ≥2 serious sinus infections within 1 year | 0.59 | <0.001 | 0.43–0.80 |
| ≥2 months of oral antibiotic treatment with little effect | 1.01 | 0.871 | 0.81–1.27 |
| ≥2 episodes of pneumonia within 1 year | 0.87 | 0.132 | 0.74–1.04 |
| Failure of an infant to gain weight or grow normally | 1.30 | 0.065 | 0.98–1.73 |
| Recurrent, deep skin or organ abscesses | 0.53 | 0.037 | 0.29–0.97 |
| Persistent thrush in mouth or fungal infection on skin | 0.77 | 0.037 | 0.60–0.98 |
| Need for intravenous antibiotics to clear infections | 1.07 | 0.415 | 0.90–1.26 |
| ≥2 deep-seated infections, including septicemia | 1.79 | 0.002 | 1.22–2.63 |
| A family history of primary immunodeficiency | 3.70 | <0.001 | 2.23–6.12 |
| Severe eczema 1 | 0.89 | 0.262 | 0.73–1.08 |
| Allergies 1 | 0.83 | 0.119 | 0.65–1.05 |
| Hematologic and oncologic disorders 1 | 11.25 | <0.001 | 7.23–17.50 |
| Autoimmunity 1 | 7.74 | <0.001 | 3.66–16.36 |
| Warning Sign | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥4 new ear infections within 1 year | 67.7 | 19.4 | 27.8 | 56.8 |
| ≥2 serious sinus infections within 1 year | 6.1 | 90.0 | 22.0 | 67.7 |
| ≥2 months of oral antibiotic treatment with little effect | 15.1 | 85.2 | 31.8 | 68.6 |
| ≥2 episodes of pneumonia within 1 year | 31.4 | 65.8 | 29.6 | 67.6 |
| Failure of an infant to gain weight or grow normally | 9.0 | 92.9 | 37.0 | 69.0 |
| Recurrent, deep skin or organ abscesses | 1.6 | 97.1 | 20.0 | 68.3 |
| Persistent thrush in mouth or fungal infection on skin | 11.3 | 85.9 | 26.8 | 67.9 |
| Need for intravenous antibiotics to clear infections | 33.8 | 67.7 | 32.4 | 69.1 |
| ≥2 deep-seated infections, including septicemia | 5.5 | 96.9 | 44.5 | 69.1 |
| A family history of primary immunodeficiency | 4.6 | 98.7 | 62.1 | 69.3 |
| Severe eczema 1 | 20.1 | 78.1 | 29.6 | 68.1 |
| Allergies 1 | 12.5 | 85.3 | 28.1 | 68.0 |
| Hematologic and oncologic disorders 1 | 12.7 | 98.7 | 82.0 | 71.2 |
| Autoimmunity 1 | 3.5 | 99.5 | 77.5 | 69.2 |
| Warning Sign | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Failure of an infant to gain weight or grow normally | 31.9 | 92.9 | 13.8 | 97.5 | 6.16 |
| A family history of primary immunodeficiency | 24.6 | 98.7 | 40.5 | 97.4 | 25.24 |
| Hematologic and oncologic disorders 1 | 53.6 | 98.7 | 59.7 | 98.4 | 89.26 |
| Autoimmunity 1 | 7.2 | 99.5 | 35.7 | 96.8 | 16.89 |
| Warning Sign | Hypogammaglobulinemia n (%): 138 (15.4) | Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy n (%): 189 (21.1) | IgM Deficiency n (%): 63 (7.0) | Selective IgA Deficiency n (%): 88 (9.8) | CVID n (%): 19 (2.1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥4 new ear infections within 1 year | 0.55 ** | 0.30 ** | 0.62 | 0.57* | 1.20 |
| ≥2 serious sinus infections within 1 year | 0.48 | 0.09 ** | 0.21 | 0.31 | 3.22 * |
| ≥2 months of oral antibiotic treatment with little effect | 1.14 | 0.83 ** | 0.09* | 0.99 | 3.34 * |
| ≥2 episodes of pneumonia within 1 year | 1.47 * | 0.71 * | 1.00 | 0.76 | 2.00 |
| Failure of an infant to gain weight or grow normally | 1.36 | 1.21 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 0.50 |
| Recurrent, deep skin or organ abscesses | 0.49 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.30 |
| Persistent thrush in mouth or fungal infection on skin | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.20 | 1.15 | 0.50 |
| Need for intravenous antibiotics to clear infections | 1.08 | 1.71 ** | 1.2 * | 0.61 | 2.07 |
| ≥2 deep-seated infections, including septicemia | 1.65 | 2.29 ** | 0.8 | 1.09 | 1.01 |
| A family history of primary immunodeficiency | 6.03 ** | 1.66 | 0.89 | 2.72 | 9.08 * |
| Severe eczema 1 | 1.16 | 0.56 ** | 1.05 | 1.18 | 0.55 |
| Allergies 1 | 0.70 | 0.57 * | 1.70 | 0.74 | 1.63 |
| Hematologic and oncologic disorders 1 | 8.71 ** | 6.17 ** | 6.65 ** | 4.65 ** | 45.03 ** |
| Autoimmunity 1 | 4.80 * | 1.15 | 1.20 | 30.88 ** | 25.44 ** |
| Diagnostic Parameter | 1 of 10 | 2 of 10 | 3 of 10 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 27.0 | 24.2 | 18.0 |
| Specificity (%) | 75.8 | 72.5 | 80.2 |
| Odds ratio | 1.15 | 0.84 | 0.88 |
| Positive predictive value (%) | 32.2 | 28.8 | 29.4 |
| Negative predictive value (%) | 70.8 | 67.6 | 68.1 |
| Diagnostic Parameter | 1 of 14 | 2 of 14 | 3 of 14 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 19.6 | 23.4 | 20.6 |
| Specificity (%) | 79.6 | 73.8 | 79.6 |
| Odds ratio | 0.95 | 0.86 | 1.11 |
| Positive predictive value (%) | 30.7 | 29.1 | 31.5 |
| Negative predictive value (%) | 68.4 | 67.8 | 68.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dąbrowska, A.; Grześk, E.; Urbańczyk, A.; Mazalon, M.; Grześk, G.; Styczyński, J.; Kołtan, S. Extended List of Warning Signs in Qualification to Diagnosis and Treatment of Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children and Young Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103401
Dąbrowska A, Grześk E, Urbańczyk A, Mazalon M, Grześk G, Styczyński J, Kołtan S. Extended List of Warning Signs in Qualification to Diagnosis and Treatment of Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children and Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(10):3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103401
Chicago/Turabian StyleDąbrowska, Anna, Elżbieta Grześk, Anna Urbańczyk, Marta Mazalon, Grzegorz Grześk, Jan Styczyński, and Sylwia Kołtan. 2023. "Extended List of Warning Signs in Qualification to Diagnosis and Treatment of Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children and Young Adults" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 10: 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103401
APA StyleDąbrowska, A., Grześk, E., Urbańczyk, A., Mazalon, M., Grześk, G., Styczyński, J., & Kołtan, S. (2023). Extended List of Warning Signs in Qualification to Diagnosis and Treatment of Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children and Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(10), 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103401





