Clinical Risk Factors for Dysphagia and Esophageal Dysmotility in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Ethics
2.2. Methodology
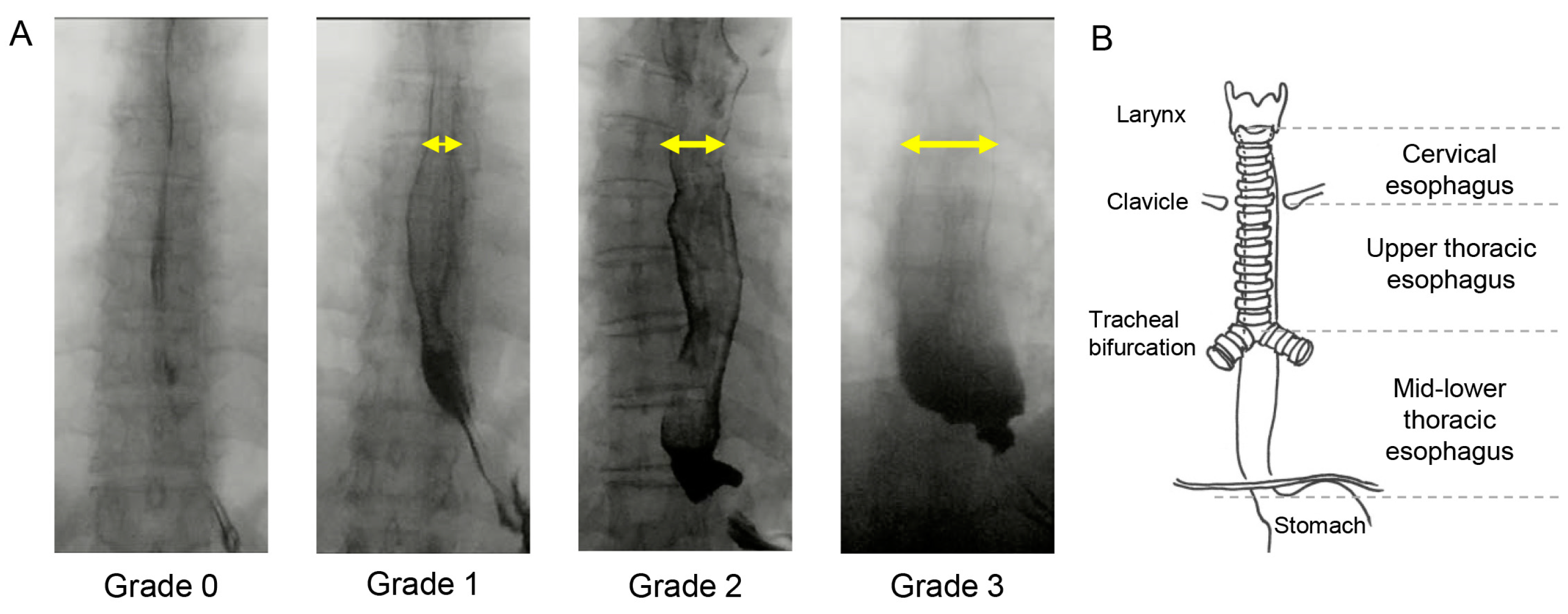
2.3. Videofluorographic Study
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
3.2. Clinical Risk Factors for Dysphagia in Patients with SSc
3.3. Clinical Risk Factors for Esophageal Dysmotility in Patients with SSc
4. Discussion
4.1. Systemic Scleroderma and Dysphagia
4.2. Autoantibodies in Systemic Scleroderma and Dysphagia
4.3. Systemic Scleroderma and Esophageal Dysmotility
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emmanuel, A. Current management of the gastrointestinal complications of systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kuwana, M.; Saito, A.; Sakamoto, W.; Raabe, C.; Saito, K. Incidence Rate and Prevalence of Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease in Japan: Analysis Using Japanese Claims Databases. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 2222–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nihtyanova, S.I.; Denton, C.P. Autoantibodies as predictive tools in systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Tang, S.; Zhu, D.; Ding, Y.; Qiao, J. Classical Disease-Specific Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: Clinical Features, Gene Susceptibility, and Disease Stratification. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 587773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaroni, M.G.; Airò, P. Anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies in patients with suspected and definite systemic sclerosis: Why and how to screen. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2018, 3, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunzelmann, N.; Genth, E.; Krieg, T.; Lehmacher, W.; Melchers, I.; Meurer, M.; Moinzadeh, P.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Pfeiffer, C.; Riemekasten, G.; et al. The registry of the German Network for Systemic Scleroderma: Frequency of disease subsets and patterns of organ involvement. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, B.; Yan, J.; Pu, J.; Tang, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, X. Esophageal Dysfunction in Systemic Sclerosis: An Update. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 1535–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.; Ghernautan, V.; Nso, N.; Nyabera, A.; Castillo, F.C.; Tu, W.; Medina, L.; Ciobanu, C.; Alfishawy, M.; Rizzo, V.; et al. Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis: An updated review. Medicine 2022, 101, e31780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, Z.H. Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, M.A.; Mann, G.D.; Groher, M.E. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbek, J.C.; Robbins, J.A.; Roecker, E.B.; Coyle, J.L.; Wood, J.L. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 1996, 11, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, K.M.; Yoshizaki, A.; Kotani, H.; Kuzumi, A.; Fukayama, M.; Fukasawa, T.; Ebata, S.; Yoshizaki-Ogawa, A.; Asano, Y.; Oba, K.; et al. Clinical Significance of Anti-U1 Ribonucleoprotein Antibody in Anti-Topoisomerase I Antibody-Positive Systemic Sclerosis Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. Arch. Clin. Biomed. Res. 2020, 5, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneoka, A.; Pisegna, J.M.; Inokuchi, H.; Ueha, R.; Goto, T.; Nito, T.; Stepp, C.E.; LaValley, M.P.; Haga, N.; Langmore, S.E. Relationship between Laryngeal Sensory Deficits, Aspiration, and Pneumonia in Patients with Dysphagia. Dysphagia 2018, 33, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse-Jarres, R.; Oldenburg, J.; Santagostino, E.; Shima, M.; Kempton, C.L.; Kessler, C.M.; Lehle, M.; Chebon, S.; Selak Bienz, N.; Asikanius, E.; et al. Bleeding and safety outcomes in persons with haemophilia A without inhibitors: Results from a prospective non-interventional study in a real-world setting. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.M.; Grace-Martin, K. Reflections on Clinical and Statistical Use of the Penetration-Aspiration Scale. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeckle, M.; Domahs, F.; Kartmann, A.; Tomandl, B.; Frank, U. Predictors of Penetration-Aspiration in Parkinson’s Disease Patients With Dysphagia: A Retrospective Analysis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 128, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Ueha, R.; Sato, T.; Goto, T.; Koyama, M.; Yamauchi, A.; Kaneoka, A.; Suzuki, S.; Yamasoba, T. Risk Factors for Aspiration Pneumonia After Receiving Liquid-Thickening Recommendations. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2022, 167, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jou, J.; Radowsky, J.; Gangnon, R.; Sadowski, E.; Kays, S.; Hind, J.; Gaumnitz, E.; Taylor, A.; Robbins, J. Esophageal clearance patterns in normal older adults as documented with videofluoroscopic esophagram. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2009, 2009, 965062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ueha, R.; Sato, T.; Goto, T.; Yamauchi, A.; Nativ-Zeltzer, N.; Mitsui, J.; Belafsky, P.C.; Yamasoba, T. Esophageal Dysmotility is Common in Patients With Multiple System Atrophy. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyigor, S.; Sezgin, B.; Kuntman, B.D.; Karabulut, G.; Zihni Yargucu, F.; Ozturk, K.; Kirazli, T. Oropharyngeal swallowing functions are impaired in patients with scleroderma. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 125), 169–170. [Google Scholar]
- Fraticelli, P.; Pisani, A.M.; Benfaremo, D.; De Marino, L.; Campioni, D.; Carboni, N.; Fischetti, C.; Manfredi, L.; Gabrielli, A.; Giovagnoni, A. Videofluorography swallow study in patients with systemic sclerosis: Correlation with clinical and radiological features. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 119), 108–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russo, S.; Lo Re, G.; Galia, M.; Reginelli, A.; Lo Greco, V.; D’Agostino, T.; La Tona, G.; Coppolino, F.; Grassi, R.; Midiri, M.; et al. Videofluorography swallow study of patients with systemic sclerosis. Radiol. Med. 2009, 114, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniecki, T.; Abdi, T.; McMahan, Z.H. A practical approach to the evaluation and management of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with systemic sclerosis. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 35, 101666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobanski, V.; Giovannelli, J.; Lynch, B.M.; Schreiber, B.E.; Nihtyanova, S.I.; Harvey, J.; Handler, C.E.; Denton, C.P.; Coghlan, J.G. Characteristics and Survival of Anti-U1 RNP Antibody-Positive Patients With Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qian, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Z.; Zeng, X. The Role of Anti-U1 RNP Positivity in Predicting Survival in Patients with Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Angel or Demon? Comment on the Article by Sobanski et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1788–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mengshoel, A.M.; Førre, O. Pain and fatigue in patients with rheumatic disorders. Clin. Rheumatol. 1993, 12, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, S.; Hot, A.; Fabien, N.; Cordier, J.F.; Miossec, P.; Ninet, J.; Mion, F. Esophageal dysmotility associated with systemic sclerosis: A high-resolution manometry study. Dis. Esophagus 2011, 24, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutka, K.; Garkowski, A.; Karaszewska, K.; Łebkowska, U. Imaging in Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepri, G.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Giani, I.; Bruni, C.; Blagojevic, J.; Carnesecchi, G.; Radicati, A.; Pucciani, F.; Marco, M.C. Evidence for oesophageal and anorectal involvement in very early systemic sclerosis (VEDOSS): Report from a single VEDOSS/EUSTAR centre. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asano, Y.; Jinnin, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kuwana, M.; Goto, D.; Sato, S.; Takehara, K.; Hatano, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Mugii, N.; et al. Diagnostic criteria, severity classification and guidelines of systemic sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 633–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ebert, E.C. Esophageal disease in progressive systemic sclerosis. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2008, 11, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowell, M.D.; Umar, S.B.; Griffing, W.L.; DiBaise, J.K.; Lacy, B.E.; Vela, M.F. Esophageal Motor Abnormalities in Patients With Scleroderma: Heterogeneity, Risk Factors, and Effects on Quality of Life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 207–213.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abozaid, H.S.M.; Imam, H.M.K.; Abdelaziz, M.M.; El-Hammady, D.H.; Fathi, N.A.; Furst, D.E. High-resolution manometry compared with the University of California, Los Angeles Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium GIT 2.0 in Systemic Sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 47, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettori, S.; Tolone, S.; Capocotta, D.; Chieffo, R.; Giacco, V.; Valentini, G.; Docimo, L. Esophageal high-resolution impedance manometry alterations in asymptomatic patients with systemic sclerosis: Prevalence, associations with disease features, and prognostic value. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | |
|---|---|
| Patients, no. | 50 |
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 61 (50, 69) |
| Female, no. (%) | 44 (88%) |
| Duration of disease, months, median (IQR) | 110 (33, 265) |
| Autoantibodies, no. (%) | |
| Anti-topoisomerase I antibodies (ATAs) | 21 (42%) |
| Anti-centromere antibodies (ACAs) | 11 (22%) |
| Anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies (ARAs) | 2 (4%) |
| Anti-U1 RNP antibodies | 9 (18%) |
| Other autoantibodies | 11 (22%) |
| Typical findings of SSc | |
| Raynaud’s phenomenon, no. (%) | 43 (86%) |
| Puffy fingers, no. (%) | 40 (80%) |
| Comorbid connective tissue diseases, no. (%) | |
| Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis | 17 (34%) |
| Sjogren’s syndrome | 12 (24%) |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 6 (12%) |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 5 (10%) |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome | 4 (8%) |
| Functional oral intake scale, median (IQR) | 7 (6, 7) |
| Oropharyngeal findings, no. (%) | |
| Xerostomia | 14 (28%) |
| Tongue mobility impairment | 9 (18%) |
| Laryngeal sensory deficits | 20 (40%) |
| Dysphagia findings, no. (%) | |
| Velopharyngeal insufficiency | 1 (2%) |
| Poor laryngeal elevation | 14 (28%) |
| Reduced pharyngeal contraction | 25 (50%) |
| Impaired UES opening | 11(22%) |
| Pharyngeal residue | 16 (32%) |
| PAS score, median (IQR) | 1 (1, 3) |
| Esophageal-dilation score, median (IQR) | 3 (2, 4) |
| Esophageal endoscopic findings, no. (%) | |
| GERD (with/without ED) | 4 (8%)/17 (34%) |
| Non-GERD (with/without ED) | 12 (24%)/17 (34%) |
| Esophageal hiatal hernia | 23 (46%) |
| Medication | |
| PPIs, no. (%) | 48 (96%) |
| Immunosuppressants, no. (%) | 39 (78%) |
| PAS Score ≤ 2 | PAS Score ≥ 3 | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, no. (%) | 37 (74%) | 13 (26%) | ||
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 60 (46, 66) | 68 (54, 73) | 0.027 * | |
| Female, no. (%) | 32 (86%) | 12 (92%) | 1.88 (0.20–17.74) | 1.000 |
| Duration of disease, months, median (IQR) | 99 (28, 236) | 255 (72, 270) | 0.521 | |
| Autoantibodies, no. (%) | ||||
| Anti-topoisomerase I antibodies (ATAs) | 12 (32%) | 9 (69%) | 4.69 (1.20–18.34) | 0.027 * |
| Anti-centromere antibodies (ACAs) | 11 (30%) | 0 (0%) | - | 0.046 * |
| Anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies (ARAs) | 2 (5.4%) | 0 (0%) | - | 1.000 |
| Anti-U1 RNP antibodies | 4 (11%) | 5 (39%) | 5.16 (1.12–23.69) | 0.040 * |
| Other autoantibodies | 10 (27%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.22 (0.026–1.96) | 0.248 |
| Comorbid connective tissue diseases, no. (%) | ||||
| Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis | 11 (30%) | 6 (46%) | 2.02 (0.55–7.42) | 0.322 |
| Sjogren’s syndrome | 7 (19%) | 5 (38%) | 2.68 (0.69–10.73) | 0.256 |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 3 (8.1%) | 3 (23%) | 3.40 (0.59–19.54) | 0.173 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 4 (11%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.69 (0.07–6.78) | 1.000 |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome | 2 (5.4%) | 2 (15%) | 3.18 (0.40–25.31) | 0.275 |
| Functional oral intake scale, median (IQR) | 7 (6, 7) | 6 (5, 7) | 0.023 * | |
| Oropharyngeal findings, no. (%) | ||||
| Xerostomia | 11 (30%) | 3 (23%) | 0.71 (0.16–3.08) | 0.734 |
| Tongue mobility impairment | 5 (14%) | 4 (31%) | 2.84 (0.63–12.86) | 0.214 |
| Laryngeal sensory deficits | 10 (27%) | 10 (77%) | 9.00 (2.05–39.55) | 0.003 ** |
| Dysphagia findings, no. (%) | ||||
| Velopharyngeal insufficiency | 0 (0%) | 1 (7.7%) | - | 0.260 |
| Poor laryngeal elevation | 4 (11%) | 10 (77%) | 27.50 (5.25–144.00) | <0.001 *** |
| Reduced pharyngeal contraction | 12 (32%) | 13 (100%) | - | <0.001 *** |
| Impaired UES opening | 4 (11%) | 7 (54%) | 9.63 (2.14–43.36) | 0.003 ** |
| Pharyngeal residue | 6 (16%) | 10 (77%) | 17.22 (3.62–81.83) | <0.001 *** |
| Esophageal-dilation score, median (IQR) | 3 (2, 4) | 4 (2, 4) | 0.397 | |
| Immunosuppressants, no. (%) | 27 (73%) | 12 (92%) | 4.44 (0.51–38.74) | 0.248 |
| ED Score ≤ 2 | ED Score ≥ 3 | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, no. (%) | 16 (32%) | 34 (68%) | ||
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 52 (44, 66) | 62 (53, 70) | 0.060 | |
| Female, no. (%) | 15 (94%) | 29 (85%) | 0.39 (0.04–3.62) | 0.650 |
| Duration of disease, months, median (IQR) | 73 (15, 227) | 123 (68, 297) | 0.167 | |
| Autoantibodies, no. (%) | ||||
| Anti-topoisomerase I antibodies (ATAs) | 7 (44%) | 14 (41%) | 0.9 (0.27 to 2.99) | 1.000 |
| Anti-centromere antibodies (ACAs) | 3 (19%) | 8 (24%) | 1.33 (0.30 to 5.88) | 1.000 |
| Anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies (ARAs) | 0 (0%) | 2 (5.9%) | - | 1.000 |
| Anti-U1 RNP antibodies | 2 (13%) | 7 (21%) | 1.81 (0.33 to 9.92) | 0.699 |
| Other autoantibodies | 3 (19%) | 8 (24%) | 1.33 (0.30–5.88) | 1.009 |
| Comorbid connective tissue diseases, no. (%) | ||||
| Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis | 6 (16%) | 11 (32%) | 0.79 (0.23–2.76) | 0.757 |
| Sjogren’s syndrome | 3 (19%) | 9 (26%) | 1.56 (0.36–6.77) | 0.728 |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 2 (13%) | 4 (12%) | 0.93 (0.15–5.71) | 1.000 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 1 (6.2%) | 4 (12%) | 2.00 (0.21–19.50) | 1.000 |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome | 1 (6.3%) | 3 (8.8%) | 1.45 (0.14–15.15) | 1.000 |
| Functional oral intake scale, median (IQR) | 7 (7, 7) | 7 (6, 7) | 0.058 | |
| Oropharyngeal findings, no. (%) | ||||
| Xerostomia | 1 (6.3%) | 13 (38%) | 9.29 (1.09–78.86) | 0.020 * |
| Tongue mobility impairment | 1 (6.3%) | 8 (24%) | 4.62 (0.53–40.58) | 0.240 |
| Laryngeal sensory deficits | 6 (38%) | 14 (41%) | 1.16 (0.34–3.96) | 1.000 |
| Dysphagia findings, no. (%) | ||||
| Velopharyngeal insufficiency | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.9%) | - | 1.000 |
| Poor laryngeal elevation | 4 (25%) | 10 (29%) | 1.25 (0.32–4.83) | 1.000 |
| Reduced pharyngeal contraction | 7 (44%) | 18 (53%) | 1.45 (0.44–4.78) | 0.762 |
| Impaired UES opening | 3 (19%) | 8 (24%) | 1.33 (0.30–5.88) | 1.000 |
| Pharyngeal residue | 5 (31%) | 11 (32%) | 1.05 (0.29–3.78) | 1.000 |
| PAS score, median (IQR) | 1 (1, 1.5) | 1 (1, 2.8) | 0.607 | |
| Esophageal endoscopic findings, no. (%) | ||||
| GERD | 4 (25%) | 17 (50%) | 3.00 (0.80–11.19) | 0.129 |
| Esophageal hiatal hernia | 5 (31%) | 18 (53%) | 2.48 (0.71–8.67) | 0.225 |
| Immunosuppressants, no. (%) | 12 (75%) | 27 (79%) | 1.29 (0.32–5.24) | 0.728 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hara, M.; Ueha, R.; Sato, T.; Goto, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Sumida, H.; Sato, S.; Yamasoba, T. Clinical Risk Factors for Dysphagia and Esophageal Dysmotility in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103448
Hara M, Ueha R, Sato T, Goto T, Yoshizaki A, Sumida H, Sato S, Yamasoba T. Clinical Risk Factors for Dysphagia and Esophageal Dysmotility in Systemic Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(10):3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103448
Chicago/Turabian StyleHara, Mariko, Rumi Ueha, Taku Sato, Takao Goto, Ayumi Yoshizaki, Hayakazu Sumida, Shinichi Sato, and Tatsuya Yamasoba. 2023. "Clinical Risk Factors for Dysphagia and Esophageal Dysmotility in Systemic Sclerosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 10: 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103448
APA StyleHara, M., Ueha, R., Sato, T., Goto, T., Yoshizaki, A., Sumida, H., Sato, S., & Yamasoba, T. (2023). Clinical Risk Factors for Dysphagia and Esophageal Dysmotility in Systemic Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(10), 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103448








