Chronotropic Incompetence after Heart Transplantation Is Associated with Increased Mortality and Decreased Functional Capacity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Metrics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
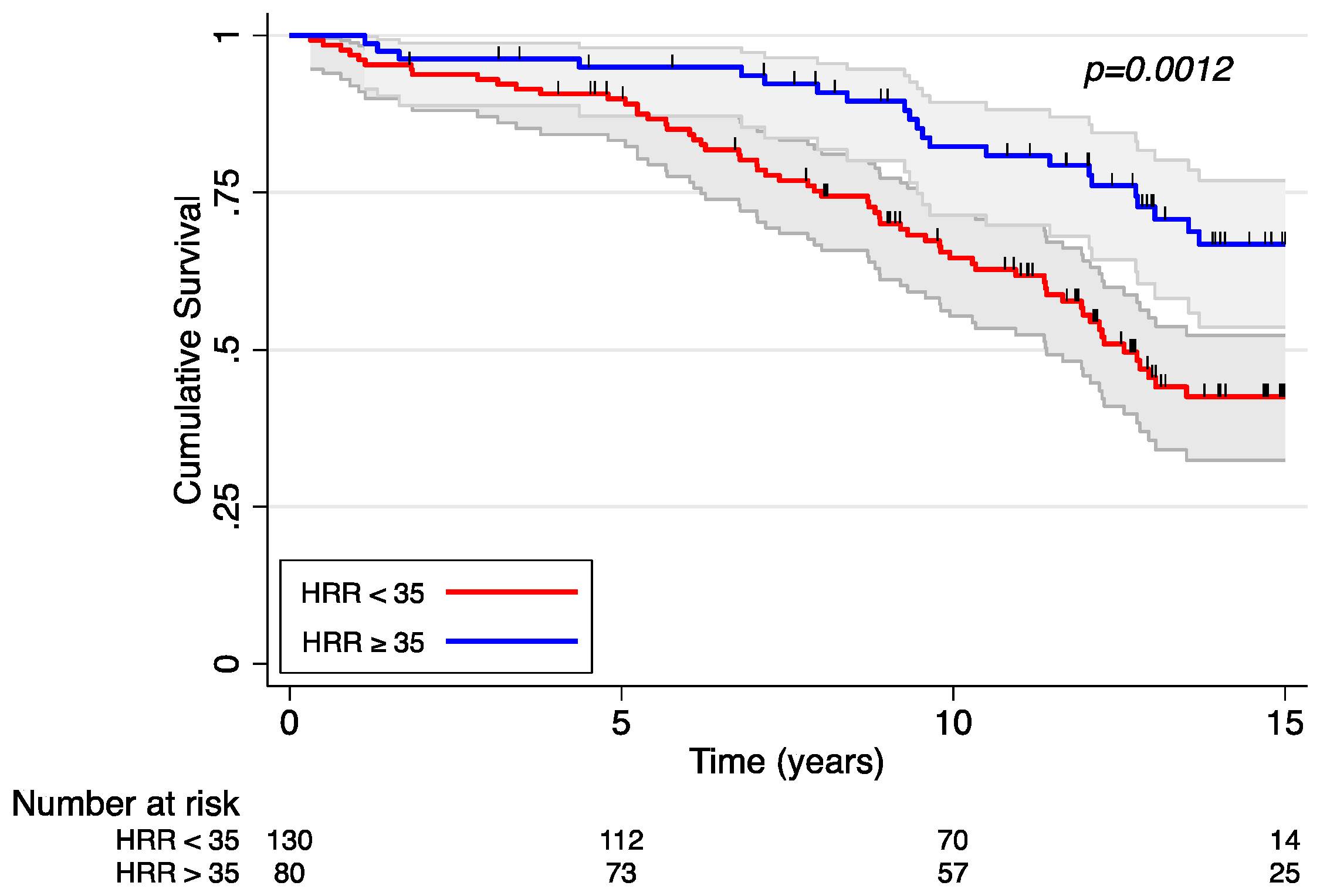
3. Results
Heart Rate Response and Survival
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPET | cardiopulmonary exercise test |
| HTR | heart transplant recipients |
| HRR | heart rate response |
| CI | chronotropic incompetence |
| APMHR | age-predicted maximum heart rate |
| OHT | orthotopic heart transplantation |
| MVV | maximum voluntary ventilation |
| PETCO2 | peak end-tidal carbon dioxide |
| RER | respiratory exchange ratio |
| VCO2 | carbon dioxide production |
| VE | minute ventilation |
| VO2 | oxygen consumption |
| VT | ventilatory threshold |
References
- Kittleson, M.M.; Kobashigawa, J.A. Cardiac Transplantation: Current Outcomes and Contemporary Controversies. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, T.-C.; Ballman, K.V.; Allison, T.G.; Wagner, J.A.; Olson, L.J.; Frantz, R.P.; Edwards, B.S.; Dearani, J.A.; Daly, R.C.; McGregor, C.G.; et al. Clinical predictors of exercise capacity 1 year after cardiac transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2003, 22, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brubaker, P.H.; Kitzman, D.W. Chronotropic Incompetence: Causes, consequences, and management. Circulation 2011, 123, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åstrand, P.-O. Physical Performance as a Function of Age. JAMA 1968, 205, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullestad, L.; Haywood, G.; Ross, H.; Bjornerheim, R.; Geiran, O.; Kjekshus, J.; Simonsen, S.; Fowler, M. Exercise capacity of heart transplant recipients: The importance of chronotropic incompetence. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 1996, 15, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Marconi, C.; Marzorati, M. Exercise after heart transplantation. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 90, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanff, T.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.S.; Genuardi, M.V.; Molina, M.; McLean, R.C.; Mazurek, J.A.; Tanna, M.S.; Wald, J.W.; Atluri, P.; et al. Early Cardiopulmonary Fitness after Heart Transplantation as a Determinant of Post-Transplant Survival. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweerink, A.; van der Lingen, A.-L.C.; Handoko, M.L.; van Rossum, A.C.; Allaart, C.P. Chronotropic Incompetence in Chronic Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, M.R.; Canter, C.E.; Hannan, M.M.; Semigran, M.J.; Uber, P.A.; Baran, D.A.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Kirklin, J.K.; Kirk, R.; Kushwaha, S.S.; et al. The 2016 International Society for Heart Lung Transplantation listing criteria for heart transplantation: A 10-year update. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2016, 35, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, N.; Chaitman, B.R.; Donohue, T.J.; Wolford, T.L.; Stelken, A.M.; Miller, L.W. Long-Term Cardiopulmonary Exercise Performance After Heart Transplantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 79, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givertz, M.M.; Hartley, L.H.; Colucci, W. Long-term Sequential Changes in Exercise Capacity and Chronotropic Responsiveness After Cardiac Transplantation. Circulation 1997, 96, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käser, A.; Martinelli, M.; Feller, M.; Carrel, T.; Mohacsi, P.; Hullin, R. Heart rate response determines long term exercise capacity after heart transplantation. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2009, 139, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.J.; McKenna, M.J. Exercise Limitation Following Transplantation. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1937–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero-Ferrer, J.L.; Sánchez-Lázaro, I.J.; Almenar-Bonet, L.; Martínez-Dolz, L.; Buendía-Fuentes, F.; Portolés-Sanz, M.; Rivera-Otero, M.; Salvador-Sanz, A. Impact of basal heart rate on long-term prognosis of heart transplant patients. Transpl. Int. 2013, 26, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel, M.; Roig, E.; Ríos, J.; Tomas, C.; Mirabet, S.; Cardona, M.; Brossa, V.; López, L.; Vargas, L.; Sionis, A.; et al. Long-term prognostic value of elevated heart rate one year after heart transplantation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 2003–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, M.S.; Okin, P.M.; Larson, M.G.; Evans, J.C.; Levy, D. Impaired Heart Rate Response to Graded Exercise. Prognostic implications of chronotropic incompetence in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1996, 93, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, D.; Zannad, F.; Keteyian, S.J.; Stevens, S.R.; Rossignol, P.; Kitzman, D.W.; Landzberg, J.; Howlett, J.; Kraus, W.E.; Ellis, S.J. Association between resting heart rate, chronotropic index, and long-term outcomes in patients with heart failure receiving β-blocker therapy: Data from the HF-ACTION trial. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrì, D.; Corrà, U.; Di Lenarda, A.; Cattadori, G.; Maruotti, A.; Iorio, A.; Mezzani, A.; Giannuzzi, P.; Mantegazza, V.; Gondoni, E.; et al. Cardiovascular mortality and chronotropic incompetence in systolic heart failure: The importance of a reappraisal of current cut-off criteria. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 16, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.F.; Johnson, T.H.; Haidet, G.C.; Kubo, S.H.; Mianuelli, M. Sympathetic Reinnervation of the Sinus Node and Exercise Hemodynamics After Cardiac Transplantation. Circulation 2000, 101, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.; Prakash, M.; Froelicher, V.; Do, D.; Partington, S.; Atwood, J.E. Exercise Capacity and Mortality among Men Referred for Exercise Testing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, D.M.; Walter, G.; Reichek, N.; Lenkinski, R.; McCully, K.K.; Mullen, J.L.; Wilson, J.R. Contribution of skeletal muscle atrophy to exercise intolerance and altered muscle metabolism in heart failure. Circulation 1992, 85, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| HRR < 35 Beats/min | HRR ≥ 35 Beats/min | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Characteristics | N = 130 | N = 80 | |
| Age at CPET, years | 52.5 (12.1) | 52.2 (13.2) | 0.86 |
| Sex, male | 108 (83.1%) | 68 (85.0%) | 0.71 |
| Race | 0.30 | ||
| Caucasian | 104 (80.0%) | 57 (71.2%) | |
| African American | 20 (15.4%) | 19 (23.8%) | |
| Other | 6 (4.6%) | 4 (5.0%) | |
| Pre-Transplant BMI, kg/m2 | 27.1 (4.6) | 28.8 (5.1) | 0.018 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.0 (4.7) | 28.6 (4.9) | 0.021 |
| Diabetes Pre-Transplant | 55 (42.3%) | 27 (34.2%) | 0.24 |
| COPD Pre-Transplant | 12 (9.2%) | 1 (1.2%) | 0.020 |
| Ischemic Cardiomyopathy | 57 (53.3%) | 29 (47.5%) | 0.47 |
| Hemoglobin at CPET (g/dL) | 12.8 (1.8) | 13.0 (1.8) | 0.37 |
| Creatinine at CPET (mg/dL) | 1.5 (0.8) | 1.5 (0.6) | 0.86 |
| Beta Blocker Use at CPET | 25 (19.2%) | 18 (23.1%) | 0.51 |
| LVEDd, cm | 4.6 (0.6) | 4.5 (0.5) | 0.49 |
| EF, % | 65.2 (9.8) | 65.1 (8.5) | 0.96 |
| Post-transplant RV dilation (% of patients) | 41 (32%) | 37 (46%) | 0.009 |
| Post-transplant RV dysfunction (% of patients) | 28 (22%) | 22 (28%) | 0.23 |
| Post-transplant PASP, mmHg | 35 (7.8) | 36 (7.9) | 0.43 |
| Ischemic time (hours) | 3 (0.9) | 3 (0.8) | 0.91 |
| CPET Parameters | |||
| Months from transplant to CPET | 3.2 (2.7) | 4.0 (3.6) | 0.062 |
| Resting heart rate (bpm) | 90.8 (11.1) | 91.5 (12.6) | 0.69 |
| Peak heart rate (bpm) | 112.4 (14.7) | 137.4 (14.0) | <0.001 |
| Resting systolic BP, mmHg | 127.0 (15.6) | 128.7 (15.1) | 0.44 |
| Peak systolic BP, mmHg | 148 (22) | 157(22) | 0.003 |
| Peak VO2, ml/kg/min | 14.6 (3.2) | 17.8 (3.5) | <0.001 |
| Total exercise time, min | 7.7 (2.7) | 9.6 (2.9) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory exchange ratio | 1.16 (0.1) | 1.18 (0.1) | 0.022 |
| Ventilatory threshold L/min | 0.9 (0.3) | 1.0 (0.3) | <0.001 |
| O2 pulse, ml/beat | 11.0 (3.0) | 11.5 (3.0) | 0.33 |
| Heart rate reserve (%) | 29.3 (13.1) | 62.8 (18.8) | <0.001 |
| Peak respiratory exchange ratio | 1.2 (0.1) | 1.2 (0.1) | 0.022 |
| VE/VCO2 | 40.1 (5.9) | 37.9 (5.2) | 0.008 |
| Maximum voluntary ventilation, L | 103.1 (27.6) | 115.3 (34.6) | 0.005 |
| Breathing reserve (%) | 38.2 (16.3) | 33.9 (17.7) | 0.081 |
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Heart rate reserve | 0.99 (0.98, 1.0) | 0.10 | ||
| Heart rate response | 0.98 (0.97, 0.99) | 0.01 | 0.97 (0.96, 0.99) | 0.002 |
| Peak heart rate | 0.98 (0.97, 0.99) | 0.02 | 0.98 (0.97, 1.0) | 0.06 |
| Resting heart rate | 0.99 (0.98, 1.01) | 0.79 | ||
| Resting heart rate * | 0.99 (0.98, 1.01) | 0.30 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.S.; Hanff, T.C.; Zhang, Y.; Genuardi, M.V.; Peters, C.J.; Levin, A.; Molina, M.; McLean, R.C.; Mazurek, J.A.; Zamani, P.; et al. Chronotropic Incompetence after Heart Transplantation Is Associated with Increased Mortality and Decreased Functional Capacity. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103487
Zhang RS, Hanff TC, Zhang Y, Genuardi MV, Peters CJ, Levin A, Molina M, McLean RC, Mazurek JA, Zamani P, et al. Chronotropic Incompetence after Heart Transplantation Is Associated with Increased Mortality and Decreased Functional Capacity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(10):3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103487
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Robert S., Thomas C. Hanff, Yuhui Zhang, Michael V. Genuardi, Carli J. Peters, Allison Levin, Maria Molina, Rhondalyn C. McLean, Jeremy A. Mazurek, Payman Zamani, and et al. 2023. "Chronotropic Incompetence after Heart Transplantation Is Associated with Increased Mortality and Decreased Functional Capacity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 10: 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103487
APA StyleZhang, R. S., Hanff, T. C., Zhang, Y., Genuardi, M. V., Peters, C. J., Levin, A., Molina, M., McLean, R. C., Mazurek, J. A., Zamani, P., Tanna, M. S., Wald, J., Santangeli, P., Atluri, P., Goldberg, L. R., & Birati, E. Y. (2023). Chronotropic Incompetence after Heart Transplantation Is Associated with Increased Mortality and Decreased Functional Capacity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(10), 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103487






