Machine-Learning-Based Tool to Predict Target Prostate Biopsy Outcomes: An Internal Validation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. mp-MRI and Biopsy Technique
2.3. Histopathological Evaluation
2.4. ML Methods
2.5. Classification System Development
- For each class, a 4-by-4 SOM was used to cluster patients into subgroups with similar characteristics. In particular, we used a linear learning function that was equal to 1 at the winner neuron, 0.5 for neurons at distance 1 from the winner neuron, and 0 otherwise; the learning rate was set to 0.4.
- Each input variable was transformed into a binary variable by dividing it into intervals and associating each couple variable-interval to a new binary variable: for each original value that the variable assumed for a given patient, a “1” was set in the corresponding couple variable-interval. This step was introduced because the FP-growth algorithm that is applied to the next step works only on binary data.
- The FP-growth algorithm was applied to the binary matrix associated with each cluster and returned a list of “IF … THEN” rules [18].
- The number of patients matching each rule was counted for the two classes separately and the rule predominance was calculated as the ratio between the number of elements belonging to the two classes: only rules that showed a predominance of elements belonging to one class were input into the FIS.
2.6. Performance Evaluation
- Logistic regression (LR), a statistics-based model that captures the relationship between the categorical dependent variable (in this case, the patient class) and one or more of the independent variables (in this case, we used the same six prebiopsy variables used as input for our PPM);
- The standard diagnostic tools, i.e., PSA, PSA density (PSAdens), and the PI-RADS score.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Training and Validation Sets
3.2. Evaluation of Models’ Performances in Training Set
3.3. Evaluation of Models’ Performances in Validation Set
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhandari, M.; Reddiboina, M. Building artificial intelligence-based personalized predictive models. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checcucci, E.; Autorino, R.; Cacciamani, G.E.; Amparore, D.; De Cillis, S.; Piana, A.; Piazzolla, P.; Vezzetti, E.; Fiori, C.; Veneziano, D.; et al. Artificial intelligence and neural networks in Urology: Current clinical applications. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020, 72, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checcucci, E.; De Cillis, S.; Granato, S.; Chang, P.; Afyouni, A.S.; Okhunov, Z. Uro-technology and SoMe Working Group of the Young Academic Urologists Working Party of the European Association of Urology. Applications of neural networks in urology: A systematic review. Curr Opin Urol. 2020, 30, 788–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgulu, O.; Akilli, A. Use of Fuzzy Logic Based Decision Support Systems in Medicine. Stud. Ethno-Med. 2016, 10, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüllermeier, E. Fuzzy methods in machine learning and data mining: Status and prospects. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2005, 156, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, S.; Montanaro, A.; Tralli, A.; Balestra, G. Fuzzy logic applied to a Patient Classification System. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1310–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati, S.; Agostini, V.; Balestra, G.; Knaflitz, M. Basographic gait impairment score: A fuzzy classifier based on foot-floor contact parameters. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Lisboa, Portugal, 11–12 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tătaru, O.S.; Vartolomei, M.D.; Rassweiler, J.J.; Virgil, O.; Lucarelli, G.; Porpiglia, F.; Amparore, D.; Manfredi, M.; Carrieri, G.; Falagario, U.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Prostate Cancer Patient Management-Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checcucci, E.; Rosati, S.; De Cillis, S.; Vagni, M.; Giordano, N.; Piana, A.; Granato, S.; Amparore, D.; De Luca, S.; Fiori, C.; et al. Artificial intelligence for target prostate biopsy outcomes prediction the potential application of fuzzy logic. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barentsz, J.O.; Weinreb, J.C.; Verma, S.; Thoeny, H.C.; Tempany, C.M.; Shtern, F.; Padhani, A.R.; Margolis, D.; Macura, K.J.; Haider, M.A.; et al. Synopsis of the PI-RADS v2 Guidelines for Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Recommendations for Use. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checcucci, E.; Piramide, F.; Amparore, D.; De Cillis, S.; Granato, S.; Sica, M.; Verri, P.; Volpi, G.; Piana, A.; Garrou, D.; et al. Beyond the Learning Curve of Prostate MRI/TRUS Target Fusion Biopsy after More than 1000 Procedures. Urology 2021, 155, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porpiglia, F.; Manfredi, M.; Mele, F.; Cossu, M.; Bollito, E.; Veltri, A.; Cirillo, S.; Regge, D.; Faletti, R.; Passera, R.; et al. Diagnostic Pathway with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Versus Standard Pathway: Results from a Randomized Prospective Study in Biopsy-naïve Patients with Suspected Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 72, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porpiglia, F.; De Luca, S.; Passera, R.; De Pascale, A.; Amparore, D.; Cattaneo, G.; Checcucci, E.; De Cillis, S.; Garrou, D.; Manfredi, M.; et al. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance/Ultrasound Fusion Prostate Biopsy: Number and Spatial Distribution of Cores for Better Index Tumor Detection and Characterization. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Kasivisvanathan, V.; Eggener, S.; Emberton, M.; Fütterer, J.J.; Gill, I.S.; Iii, R.L.G.; Hadaschik, B.; Klotz, L.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Standards of Reporting for MRI-targeted Biopsy Studies (START) of the Prostate: Recommendations from an International Working Group. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Regge, D.; Armando, E.; Giannini, V.; Vignati, A.; Mazzetti, S.; Manfredi, M.; Bollito, E.; Correale, L.; Porpiglia, F. Detection of prostate cancer index lesions with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mp-MRI) using whole-mount histological sections as the reference standard. BJU Int. 2016, 118, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.C. A General Coefficient of Similarity and Some of Its Properties. Biometrics 1971, 27, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pei, J.; Yin, Y. Mining frequent patterns without candidate generation. ACM Sigmod Rec. 2000, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, S.; Giordano, N.; Checcucci, E.; De Cillis, S.; Porpiglia, F.; Balestra, G. Decision Support System for target prostate biopsy outcome prediction: Clustering and FP-growth algorithm for fuzzy rules extraction. In Proceedings of the 2021 Workshop on Towards Smarter Health Care: Can Artificial Intelligence Help? Virtual, 29 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Provost, F.; Fawcett, T. Robust Classification for Imprecise Environments. Mach. Learn. 2001, 42, 203–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, A.J.; Elkin, E.B. Decision Curve Analysis: A Novel Method for Evaluating Prediction Models. Med. Decis. Mak. 2006, 26, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirce, C.S. The numerical measure of the success of predictions. Science 1884, 4, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniffel, D.; Healy, G.M.; Dong, X.; Ghai, S.; Salinas-Miranda, E.; Fleshner, N.; Hamilton, R.; Kulkarni, G.; Toi, A.; van der Kwast, T.; et al. Avoiding Unnecessary Biopsy: MRI-based Risk Models versus a PI-RADS and PSA Density Strategy for Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer. Radiology 2021, 300, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washino, S.; Okochi, T.; Saito, K.; Konishi, T.; Hirai, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyagawa, T. Combination of prostate imaging reporting and data system (PI-RADS) score and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) density predicts biopsy outcome in prostate biopsy naïve patients. BJU Int. 2017, 119, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoots, I.G.; Padhani, A.R. Risk-adapted biopsy decision based on prostate magnetic resonance imaging and prostate-specific antigen density for enhanced biopsy avoidance in first prostate cancer diagnostic evaluation. BJU Int. 2020, 127, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, P.K.; Shen, X.; Wang, G.; Ho, C.L.; Leung, C.H.; Ng, C.F.; Choi, K.S.; Teoh, J.Y. Enhancement of prostate cancer diagnosis by machine learning techniques: An algorithm development and validation study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.; Yoo, S.; Park, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Cho, M.C.; Son, H.; Jeong, H. Development and validation of an explainable artificial intelligence-based decision-supporting tool for prostate biopsy. BJU Int. 2020, 126, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linardatos, P.; Papastefanopoulos, V.; Kotsiantis, S. Explainable AI: A Review of Machine Learning Interpretability Methods. Entropy 2020, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checcucci, E.; Amparore, D.; De Luca, S.; Autorino, R.; Fiori, C.; Porpiglia, F. Precision prostate cancer surgery: An overview of new technologies and techniques. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. Ital. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 71, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Emberton, M.; Moore, C.M. There Is No Longer a Role for Systematic Biopsies in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2022, 38, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porpiglia, F.; Checcucci, E.; DE Cillis, S.; Piramide, F.; Amparore, D.; Piana, A.; Volpi, G.; Granato, S.; Zamengo, D.; Stura, I.; et al. A prospective randomized controlled trial comparing target prostate biopsy alone approach vs. target plus standard in naïve patients with positive mpMRI. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2023, 75, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Overall (1629 pts) | Training Set (1448 pts) | Validation Set (181 pts) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years; mean (SD) | 69 (7.9) | 69 (8.0) | 68 (7.8) | 0.11 |
| PSA, ng/dL; mean (SD) | 8.2 (6.8) | 8.4 (7.5) | 7.6 (4.7) | 0.16 |
| PSA density, ng/mL2; mean (SD) | 0.16 (0.15) | 0.17 (0.17) | 0.13 (0.13) | 0.0025 |
| Positive DRE, number (%) | 220 (13.5) | 177 (12) | 43 (23.7) | <0.001 |
| Prostate volume, CC; mean (SD) | 54.2 (26.6) | 55.8 (27.8) | 50.8 (25.5) | 0.02 |
| Lesion volume, CC; mean (SD) | 0.96 (1.56) | 0.98 (1.91) | 0.88 (1.24) | 0.49 |
Pirads score
| 0.16 | |||
| 449 (27.6) | 403 (27.9) | 46 (25.4) | ||
| 917 (56.3) | 820 (56.6) | 97 (53.6) | ||
| 263 (16.1) | 225 (15.5) | 38 (21.0) | ||
Lesion location, number (%)
| 0.65 | |||
| 1395 (85.6) | 1238 (85.5) | 157 (86.7) | ||
| 234 (14.4) | 210 (14.5) | 24 (13.3) | ||
Biopsy approach, number (%)
| <0.001 | |||
| 470 (28.8) | 413 (29) | 57 (31.5) | ||
| 965 (59.2) | 841 (58) | 124 (68.5) | ||
| 194 (12) | 194 (13) | 0 (0) | ||
| Overall detection rate of PCa, number (%) | 942 (57.8) | 824 (56.9) | 118 (65.2) | 0.04 |
| Overall detection rate of csPCa, number (%) | 833 (51.1) | 730 (50.4) | 103 (56.9) | 0.11 |
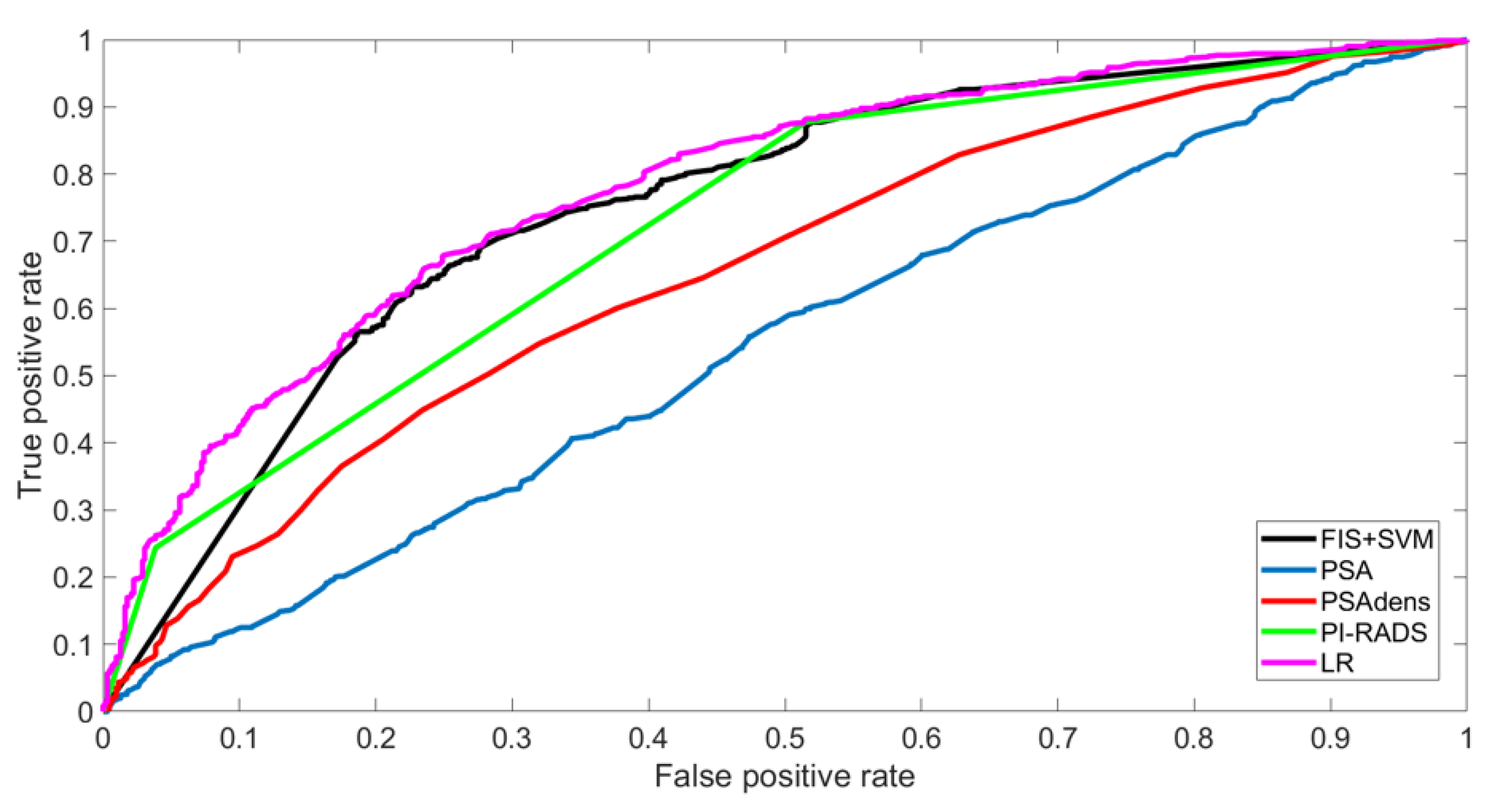
| AUC (95%CI) | TP | TN | FP | FN | NPV | PPV | Spec | Sens | Acc | Net Benefit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRAINING SET | FIS + SVM | 0.75 (0.73–0.78) | 759 | 238 | 385 | 65 | 78.5% | 66.3% | 38.2% | 92.1% | 68.9% | 0.49 |
| LR | 0.78 (0.76–0.80) | 684 | 360 | 263 | 140 | 72.0% | 72.2% | 57.8% | 83% | 72.1% | 0.45 | |
| PSA | 0.55 (0.51–0.57) | 792 | 52 | 571 | 32 | 61.9% | 58.1% | 8.3% | 96.1% | 58.3% | 0.50 | |
| PSAdens | 0.66 (0.63–0.68) | 683 | 232 | 391 | 141 | 62.2% | 63.6% | 37.2% | 82.9% | 63.2% | 0.44 | |
| PI-RADS | 0.73 (0.70–0.75) | 723 | 302 | 321 | 101 | 74.9% | 69.3% | 48.5% | 87.7% | 70.8% | 0.48 | |
| VALIDATION SET | FIS + SVM | - | 108 | 17 | 45 | 11 | 60.7% | 70.6% | 27.4% | 90.8% | 69.1% | - |
| LR | - | 93 | 28 | 34 | 26 | 51.9% | 73.2% | 45.2% | 78.2% | 66.9% | - | |
| PSA | - | 108 | 4 | 58 | 11 | 26.7% | 65.1% | 6.5% | 90.8% | 61.9% | - | |
| PSAdens | - | 96 | 19 | 43 | 23 | 45.2% | 69.1% | 30.6% | 80.7% | 63.5% | - | |
| PI-RADS | - | 98 | 25 | 37 | 21 | 54.3% | 72.6% | 40.3% | 82.4% | 68.0% | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Checcucci, E.; Rosati, S.; De Cillis, S.; Giordano, N.; Volpi, G.; Granato, S.; Zamengo, D.; Verri, P.; Amparore, D.; De Luca, S.; et al. Machine-Learning-Based Tool to Predict Target Prostate Biopsy Outcomes: An Internal Validation Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134358
Checcucci E, Rosati S, De Cillis S, Giordano N, Volpi G, Granato S, Zamengo D, Verri P, Amparore D, De Luca S, et al. Machine-Learning-Based Tool to Predict Target Prostate Biopsy Outcomes: An Internal Validation Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134358
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheccucci, Enrico, Samanta Rosati, Sabrina De Cillis, Noemi Giordano, Gabriele Volpi, Stefano Granato, Davide Zamengo, Paolo Verri, Daniele Amparore, Stefano De Luca, and et al. 2023. "Machine-Learning-Based Tool to Predict Target Prostate Biopsy Outcomes: An Internal Validation Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134358
APA StyleCheccucci, E., Rosati, S., De Cillis, S., Giordano, N., Volpi, G., Granato, S., Zamengo, D., Verri, P., Amparore, D., De Luca, S., Manfredi, M., Fiori, C., Di Dio, M., Balestra, G., & Porpiglia, F. (2023). Machine-Learning-Based Tool to Predict Target Prostate Biopsy Outcomes: An Internal Validation Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134358









