A JAK Inhibitor for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Baricitinib Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Properties of Baricitinib
1.2. Dose Flexibility
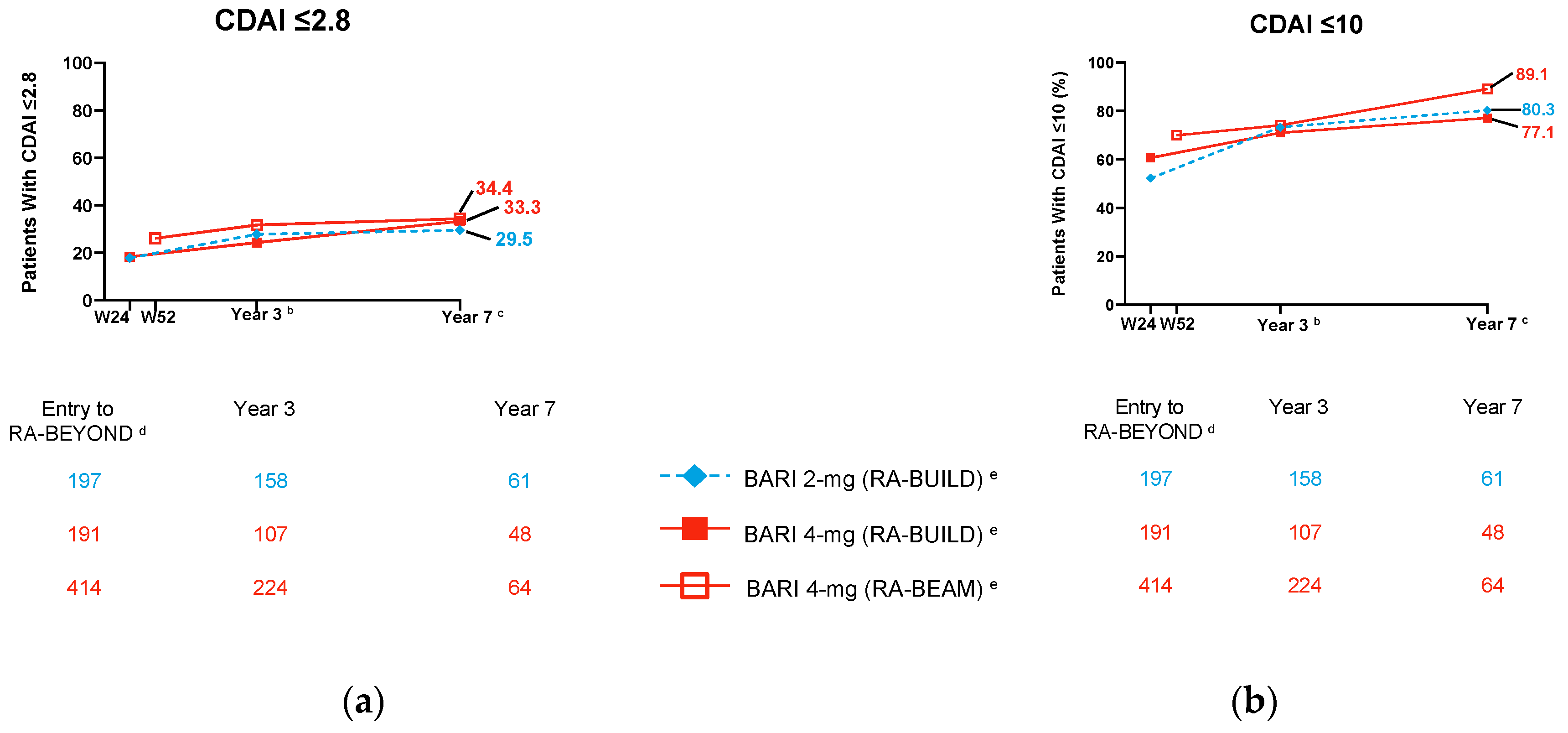
2. Efficacy across RA Populations in Randomised Controlled Trials (RCTs)
2.1. RA Populations
2.2. Clinical Outcomes
2.3. Radiographic Outcomes
2.4. Patient-Reported Outcomes: Pain and Physical Function
2.5. Temporary Treatment Interruption and Tapering
3. Baricitinib in Real-World Settings
3.1. Characteristics of Baricitinib-Treated Patients in Real-World Settings
3.2. Treatment Outcomes for Baricitinib in Real-Life Settings
3.2.1. Factors Affecting Treatment Outcomes—Drug Discontinuation, Drug Survival and Effectiveness
3.2.2. Effectiveness of Baricitinib Monotherapy in RWE Settings
3.2.3. Effect of Baricitinib on Glucocorticoid Tapering
3.2.4. Effect of Baricitinib on Ultrasound-Assessed Inflammation
3.2.5. RWE Effectiveness and Drug Survival of Baricitinib Compared to TNFi and Other Mode of Action bDMARDs
3.2.6. To Cycle or to Switch?
3.3. Safety
3.3.1. Baricitinib Safety in RCTs
3.3.2. New EULAR Recommendations for Risk Management Regarding JAKi Safety
3.3.3. Baricitinib Safety from RWE
3.3.4. Baricitinib vs. TNFi Safety from RWE
3.3.5. JAKi Safety from RWE
3.3.6. Risk Assessment for Personalised Medicine for Patients with RA
4. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; England, B.R.; St Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Luo, Y.; O’Shea, J.J.; Nakayamada, S. Janus kinase-targeting therapies in rheumatology: A mechanisms-based approach. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Baricitinib: First global approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougados, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Chen, Y.C.; Greenwald, M.; Drescher, E.; Liu, J.; Beattie, S.; Witt, S.; de la Torre, I.; Gaich, C.; et al. Baricitinib in patients with inadequate response or intolerance to conventional synthetic DMARDs: Results from the RA-BUILD study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Keystone, E.C.; van der Heijde, D.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Del Carmen Morales, L.; Reyes Gonzaga, J.; Yakushin, S.; Ishii, T.; Emoto, K.; Beattie, S.; et al. Baricitinib versus placebo or adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, R.; Schiff, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Ramos-Remus, C.; Spindler, A.; Stanislav, M.; Zerbini, C.A.; Gurbuz, S.; Dickson, C.; de Bono, S.; et al. Baricitinib, methotrexate, or combination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and no or limited prior disease-modifying antirheumatic drug treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.C.; Kremer, J.; Zamani, O.; Ludivico, C.; Krogulec, M.; Xie, L.; Beattie, S.D.; Koch, A.E.; Cardillo, T.E.; Rooney, T.P.; et al. Baricitinib in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Olumiant (Baricitinib) Film-Coated Tablets: EU Summary of Product Characteristics. 2017. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/olumiant-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- OLUMIANT (Baricitinib): US Prescribing Information. 2022. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/207924s006lbl.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- McInnes, I.B.; Byers, N.L.; Higgs, R.E.; Lee, J.; Macias, W.L.; Na, S.; Ortmann, R.A.; Rocha, G.; Rooney, T.P.; Wehrman, T.; et al. Comparison of baricitinib, upadacitinib, and tofacitinib mediated regulation of cytokine signaling in human leukocyte subpopulations. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thudium, C.S.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Cahya, S.; Dow, E.R.; Karsdal, M.A.; Koch, A.E.; Zhang, W.; Benschop, R.J. The Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor baricitinib reduces biomarkers of joint destruction in moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, S.; Simon, N.; Steffen, U.; Andes, F.T.; Scholtysek, C.; Müller, D.I.H.; Weidner, D.; Andreev, D.; Kleyer, A.; Culemann, S.; et al. JAK inhibition increases bone mass in steady-state conditions and ameliorates pathological bone loss by stimulating osteoblast function. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Minopoulou, I.; Kemenes, S.; Bayat, S.; Tascilar, K.; Mutlu, M.Y.; Valor-Méndez, L.; Krönke, G.; Hueber, A.J.; Schett, G.; et al. Baricitinib improves bone properties and biomechanics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—Results of the prospective interventional BARE BONE trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, J.S.; Scherle, P.A.; Collins, R.; Burn, T.C.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Covington, M.B.; Thomas, B.; Collier, P.; Favata, M.F.; et al. Selective inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 is efficacious in rodent models of arthritis: Preclinical characterization of INCB028050. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5298–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Xeljanz, INN-Tofacitinib Citrate. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/xeljanz-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- XELJANZ (Tofacitinib): US Prescribing Information. 2018. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/203214s018lbl.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Meyer, D.M.; Jesson, M.I.; Li, X.; Elrick, M.M.; Funckes-Shippy, C.L.; Warner, J.D.; Gross, C.J.; Dowty, M.E.; Ramaiah, S.K.; Hirsch, J.L.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity and neutrophil reductions mediated by the JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor, CP–690,550, in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. J. Inflamm. 2010, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Rinvoq, INN-Upadacitinib. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/rinvoq-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- RINVOQ (Upadacitinib): US Prescribing Information. 2019. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/211675s003lbl.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Parmentier, J.M.; Voss, J.; Graff, C.; Schwartz, A.; Argiriadi, M.; Friedman, M.; Camp, H.S.; Padley, R.J.; George, J.S.; Hyland, D.; et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the JAK1 selectivity of upadacitinib (ABT-494). BMC Rheumatol. 2018, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Jyseleca, INN-Filgotinib. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/jyseleca-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Van Rompaey, L.; Galien, R.; van der Aar, E.M.; Clement-Lacroix, P.; Nelles, L.; Smets, B.; Lepescheux, L.; Christophe, T.; Conrath, K.; Vandeghinste, N.; et al. Preclinical characterization of GLPG0634, a selective inhibitor of JAK1, for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, J.; Talotta, R.; Roncato, R.; Fornasier, G.; Barbiero, G.; Dal Cin, L.; Brancati, S.; Scaglione, F. JAK-Inhibitors for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Focus on the Present and an Outlook on the Future. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astellas Pharma. Smyraf® Tablets 50 mg and 100 mg, Peficitinib Hydrobromide: Review Report. Available online: https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000233074.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Markham, A.; Keam, S.J. Peficitinib: First global approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, M.M.; Cannady, E.A.; Payne, C.D.; Zhang, X.; Bacon, J.A.; Pak, Y.A.; Higgins, J.W.; Shahri, N.; Hall, S.D.; Hillgren, K.M. Prediction of transporter-mediated drug-drug interactions for baricitinib. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Cardillo, T.; Schlichting, D.; Rooney, T.; Beattie, S.; Helt, C.; Smolen, J.S. Temporary interruption of baricitinib: Characterization of interruptions and effect on clinical outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.J.; Mount, J.; Meeks, A.; Gulati, T.; Zaremba-Pechmann, L.; Sheesh, M.; Larsson, E.; Dennison, E. Characteristics of patients initiating treatment with baricitinib and outcomes at follow-up: Analysis of BSRBR-RA registry data. Rheumatology 2023, kead074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Alam, J.; Arora, V.; Bradley, J.; Schlichting, D.E.; Muram, D.; Smolen, J.S. Safety and efficacy of baricitinib in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Meeting Highlights from the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) 9–12 January 2023. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/meeting-highlights-pharmacovigilance-risk-assessment-committee-prac-9-12-january-2023 (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mikuls, T.R.; Koch, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.; Rivas, J.L.; Germino, R.; Menon, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, C.A.; Louder, A.; Polinski, J.; Zhang, T.C.; Bower, H.; Phillips, S.; Song, Y.; Rashidi, E.; Bosan, R.; Chang, H.C.; et al. Evaluation of VTE, MACE, and serious infections among patients with RA treated with baricitinib compared to TNFi: A multi-database study of patients in routine care using disease registries and claims databases. Rheumatol. Ther. 2023, 10, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, X.; Bao, C.D.; Hu, J.K.; Xu, J.H.; Li, X.P.; Xu, J.; He, D.Y.; Li, Z.J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib in Chinese rheumatoid arthritis patients and the subgroup analyses: Results from study RA-BALANCE. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Hu, J.K.; Li, X.P.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.F.; Xu, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Bao, C.D.; He, D.Y.; et al. Rapid onset of efficacy of baricitinib in Chinese patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: Results from study RA-BALANCE. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, M.C.; Kremer, J.M.; Kartman, C.E.; Schlichting, D.E.; Xie, L.; Carmack, T.; Pantojas, C.; Sanchez Burson, J.; Tony, H.P.; Macias, W.L.; et al. Response to baricitinib based on prior biologic use in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, R.; Aletaha, D.; Sanmartí, R.; Takeuchi, T.; Mo, D.; Haladyj, E.; Zaremba-Pechmann, L.; Taylor, P.C. POS0701 Long-term efficacy of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have had inadequate response to csDMARDs: Results from RA-beyond up to 7 years of treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, R.; Aletaha, D.; Sanmartí, R.; Takeuchi, T.; Mo, D.; Haladyj, E.; Zaremba-Pechmann, L.; Taylor, P.C. POS0682 Long-term efficacy of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with inadeqaute response to bDMARDs: Results from RA-beyond following 6.9 years of treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 617–618. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann, R.; Pangan, A.L.; Song, I.H.; Mysler, E.; Bessette, L.; Peterfy, C.; Durez, P.; Ostor, A.J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Upadacitinib Versus Placebo or Adalimumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate: Results of a Phase III, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, R.; Mysler, E.; Hall, S.; Kivitz, A.J.; Moots, R.J.; Luo, Z.; DeMasi, R.; Soma, K.; Zhang, R.; Takiya, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib monotherapy, tofacitinib with methotrexate, and adalimumab with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (ORAL Strategy): A phase 3b/4, double-blind, head-to-head, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combe, B.; Kivitz, A.; Tanaka, Y.; van der Heijde, D.; Simon, J.A.; Baraf, H.S.B.; Kumar, U.; Matzkies, F.; Bartok, B.; Ye, L.; et al. Filgotinib versus placebo or adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to methotrexate: A phase III randomised clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijde, D.; Durez, P.; Schett, G.; Naredo, E.; Østergaard, M.; Meszaros, G.; De Leonardis, F.; de la Torre, I.; López-Romero, P.; Schlichting, D.; et al. Structural damage progression in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate, baricitinib, or baricitinib plus methotrexate based on clinical response in the phase 3 RA-BEGIN study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Romero, P.; de la Torre, I.; Haladyj, E.; Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Baricitinib further enhances disease-modifying effects by uncoupling the link between disease activity and joint structural progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Han, C.; van der Heijde, D.M.; Emery, P.; Bathon, J.M.; Keystone, E.; Maini, R.N.; Kalden, J.R.; Aletaha, D.; Baker, D.; et al. Radiographic changes in rheumatoid arthritis patients attaining different disease activity states with methotrexate monotherapy and infliximab plus methotrexate: The impacts of remission and tumour necrosis factor blockade. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Avila, J.C.M.; Aletaha, D. Tocilizumab inhibits progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis irrespective of its anti-inflammatory effects: Disassociation of the link between inflammation and destruction. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Alasti, F.; Smolen, J.S. Rituximab dissociates the tight link between disease activity and joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijde, D.; Kartman, C.E.; Xie, L.; Beattie, S.; Schlichting, D.; Mo, D.; Durez, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Fleischmann, R. Radiographic progression of structural joint damage over 5 years of baricitinib treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from RA-BEYOND. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Spencer, H.J.; Abda, E.; Aggarwal, A.; Alten, R.; Ancuta, C.; Andersone, D.; Bergman, M.; Craig-Muller, J.; Detert, J.; et al. Determinants of discordance in patients’ and physicians’ rating of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Elst, K.; Meyfroidt, S.; De Cock, D.; De Groef, A.; Binnard, E.; Moons, P.; Verschueren, P.; Westhovens, R. Unraveling patient-preferred health and treatment outcomes in early rheumatoid arthritis: A longitudinal qualitative study. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Nassikas, N.J.; Clauw, D.J. The role of the central nervous system in the generation and maintenance of chronic pain in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Kuroiwa, Y.; Yoshida, E.; Sato, M.; Krupa, D.; Henry, N.; Ikeda, K.; Kaneko, Y. Residual symptoms and disease burden among patients with rheumatoid arthritis in remission or low disease activity: A systematic literature review. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifbjerg-Madsen, S.; Christensen, A.W.; Christensen, R.; Hetland, M.L.; Bliddal, H.; Kristensen, L.E.; Danneskiold-Samsøe, B.; Amris, K. Pain and pain mechanisms in patients with inflammatory arthritis: A Danish nationwide cross-sectional DANBIO registry survey. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Alten, R.; Álvaro Gracia, J.M.; Kaneko, Y.; Walls, C.; Quebe, A.; Jia, B.; Bello, N.; Terres, J.R.; Fleischmann, R. Achieving pain control in early rheumatoid arthritis with baricitinib monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate versus methotrexate monotherapy. RMD Open 2022, 8, e001994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautrel, B.; Zhu, B.; Taylor, P.C.; van de Laar, M.; Emery, P.; De Leonardis, F.; Kannowski, C.L.; Nicolay, C.; Kadziola, Z.; De La Torre, I.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of improvement in pain and physical function for baricitinib versus adalimumab, tocilizumab and tofacitinib monotherapies in rheumatoid arthritis patients who are naïve to treatment with biologic or conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A matching-adjusted indirect comparison. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, K.; Pope, J.E.; Emery, P.; Zhu, B.; Gaich, C.L.; DeLozier, A.M.; Zhang, X.; Dickson, C.L.; Smolen, J.S. Relative impact of pain and fatigue on work productivity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from the RA-BEAM baricitinib trial. Rheumatol. Ther. 2019, 6, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Fleischmann, R.; Takeuchi, T.; Perkins, E.L.; Fautrel, B.; Zhu, B.; Quebe, A.K.; Gaich, C.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Achieving pain control in rheumatoid arthritis with baricitinib or adalimumab plus methotrexate: Results from the RA-BEAM trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautrel, B.; Kirkham, B.; Pope, J.E.; Takeuchi, T.; Gaich, C.; Quebe, A.; Zhu, B.; de la Torre, I.; De Leonardis, F.; Taylor, P.C. Effect of baricitinib and adalimumab in reducing pain and improving function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in low disease activity: Exploratory analyses from RA-BEAM. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Kremer, J.M.; Gaich, C.L.; DeLozier, A.M.; Schlichting, D.E.; Xie, L.; Stoykov, I.; Rooney, T.; Bird, P.; Sánchez Bursón, J.M.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes from a randomised phase III study of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to biological agents (RA-BEACON). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Genovese, M.C.; Haraoui, B.; Li, Z.; Xie, L.; Klar, R.; Pinto-Correia, A.; Otawa, S.; López-Romero, P.; de la Torre, I.; et al. Dose reduction of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis achieving sustained disease control: Results of a prospective study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Cruz, B.; Rosas, J.; Díaz-Torné, C.; Belzunegui, J.; García-Vicuña, R.; Inciarte-Mundo, J.; Pons, A.; Millán, A.M.; Jeria-Navarro, S.; Valero, J.A.; et al. Real-world treatment patterns and clinical outcomes of baricitinib in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Spain: Results of a multicenter, observational study in routine clinical practice (The ORBIT-RA study). Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, J.; Pons, A.; Barber, X.; Seabre-Gallego, J.M.; Santos Soler, G.; Soler-Giner, E.; Bernal, J.A.; Raga, A.; Raya-Santos, C.; Cortés-Quiroz, J.C.; et al. POS0657 Survival of baricitinib vs anti-TNF as the first biological drug in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, in clinical practice: Results of a local registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 600–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, B.; Courvoisier, D.; Mongin, D.; Lauper, K.; Perrier, C.; Müller, R.; Finckh, A. POS0668 Real-world effectiveness of baricitinib in the Swiss rheumatoid arthiritis register (SCQM-RA). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, B.; Mongin, D.; Nham, E.; Courvoisier, D.; Lauper, K.; Laedermann, C.; Müller, R.; Finckh, A. POS0435 Impact of combination therapy with csDMARDs on the effectiveness of biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs in a real-life setting: Results from the Swiss rheumatoid arthritis register (SCQM-RA). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 472–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelli, G.M.; Viapiana, O.; Luciano, N.; De Santis, M.; Boffini, N.; Quartuccio, L.; Birra, D.; Conticini, E.; Chimenti, M.S.; Bazzani, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib in 446 patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A real-life multicentre study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbulescu, A.; Askling, J.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Kastbom, A.; Lindström, U.; Turesson, C.; Frisell, T. Effectiveness of baricitinib and tofacitinib compared with bDMARDs in RA: Results from a cohort study using nationwide Swedish register data. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 3952–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeberg, A.; Rosenø, N.A.L.; Aagaard, D.; Lørup, E.H.; Nielsen, M.L.; Nymand, L.; Kristensen, L.E.; Thyssen, J.P.; Thomsen, S.F.; Cordtz, R.L.; et al. Drug survival of biologics and novel immunomodulators for rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and psoriasis—A nationwide cohort study from the DANBIO and DERMBIO registries. Sem. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 53, 151979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, Y.; Kekow, J.; Klopsch, T.; Kühne, C.; Zink, A.; Strangfeld, A. Erste Erfahrungen mit baricitinib aus dem rheumatologischen alltag. RA.05. Kongress der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Rheumatologie (DGRh). In Proceedings of the Congress Center Rosengarten, Mannheim, Germany, 19–22 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, Y.; Albrecht, K.; Kekow, J.; Zinke, S.; Tony, H.P.; Schaefer, M.; Strangfeld, A. OP0135 Risk of cardiovascular events under Janus kinase inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthririts: Observational data from the German RABBIT register. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeb, B.F.; Spellitz, F.; Eichbauer-Sturm, G.; Herold, M.; Stetter, M.; Puchner, R.; St. Singer, F.; Fritsch-Stork, R. Januskinase inhibitors to treat rheumatoid arthritis: Real world data match clinical trial results an evaluation by BioReg, the Austrian registry for biologicals, biosimilars, and targeted synthetic DMARDS in the treatment of inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol. Curr. Res. 2021, 11, 1–7. Available online: https://www.longdom.org/open-access/januskinase-inhibitors-to-treat-rheumatoid-arthritis-real-world-data-match-clinical-trial-results-an-evaluation-by-biore.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Ebina, K.; Hirano, T.; Maeda, Y.; Yamamoto, W.; Hashimoto, M.; Murata, K.; Onishi, A.; Jinno, S.; Hara, R.; Son, Y.; et al. Drug retention of sarilumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The ANSWER cohort study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Nakano, K.; Nakayamada, S.; Kubo, S.; Inoue, Y.; Fujino, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib versus baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in real clinical practice: Analyses with propensity score-based inverse probability of treatment weighting. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Nakayamada, S.; Kubo, S.; Sonomoto, K.; Inoue, Y.; Fukuyo, S.; Hanami, K.; Tanaka, Y. Characteristics and treatment-selection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and with inadequate response to Janus kinase inhibitors. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 0296. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-and-treatment-selection-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-with-inadequate-response-to-janus-kinase-inhibitors/ (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Asai, S.; Takahashi, N.; Kobayakawa, T.; Kaneko, A.; Watanabe, T.; Kato, T.; Nishiume, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kanayama, Y.; et al. Comparison of the effects of baricitinib and tocilizumab on disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A propensity score matching analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3143–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Asai, S.; Kobayakawa, T.; Kaneko, A.; Watanabe, T.; Kato, T.; Nishiume, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kanayama, Y.; et al. Predictors for clinical effectiveness of baricitinib in rheumatoid arthritis patients in routine clinical practice: Data from a Japanese multicenter registry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, N.; Sato, S.; Kurushima, S.; Michitsuji, T.; Nishihata, S.; Okamoto, M.; Tsuji, Y.; Endo, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Sumiyoshi, R.; et al. Real-world comparative effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib and baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, M.; Atsumi, T.; Matsuno, H.; Tamura, N.; Fujii, T.; Okamoto, N.; Takahashi, N.; Nakajima, A.; Nakajima, A.; Tsujimoto, N.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of baricitinib for rheumatoid arthritis in Japanese clinical practice: 24-week results of all-case post-marketing surveillance. Mod. Rheumatol. 2022, 6, roac089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alten, R.; Burmester, G.R.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Salmon, J.H.; López-Romero, P.; Fakhouri, W.; de la Torre, I.; Zaremba-Pechmann, L.; Holzkämper, T.; Fautrel, B. The RA-BE-REAL multinational, prospective, observational study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving baricitinib, targeted synthetic, or biologic disease-modifying therapies: A 6-month interim analysis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2023, 10, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, F.R.; Ceccarelli, F.; Garufi, C.; Duca, I.; Mancuso, S.; Cipriano, E.; Dell’Unto, E.; Alessandri, C.; Di Franco, M.; Perricone, C.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of baricitinib in rheumatoid arthritis: A monocentric, longitudinal, real-life experience. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisell, T.; Bower, H.; Morin, M.; Baecklund, E.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Delcoigne, B.; Feltelius, N.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Lindqvist, E.; Lindström, U.; et al. Safety of biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis as used in clinical practice: Results from the ARTIS programme. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molander, V.; Bower, H.; Frisell, T.; Delcoigne, B.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Askling, J.; ARTIS Study Group. Venous thromboembolism with JAK inhibitors and other immune-modulatory drugs: A Swedish comparative safety study among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitton, J.; Melville, A.R.; Emery, P.; Nam, J.L.; Buch, M.H. Real-world single centre use of JAK inhibitors across the rheumatoid arthritis pathway. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 4048–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, S.; Tascilar, K.; Bohr, D.; Krönke, G.; Simon, D.; Knitza, J.; Hartmann, F.; Schett, G.; Kleyer, A. Efficacy and drug persistence of baricitinib monotherapy is similar to combination therapy in patients with active RA: A prospective observational study. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesei, G.; Cometi, L.; Nacci, F.; Terenzi, R.; Tofani, L.; Capassoni, M.; Bartoli, F.; Fiori, G.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Bruni, C. Baricitinib in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Clinical and ultrasound evaluation of a real-life single-centre experience. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X211014019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprez, V.; Le Monnier, L.; Sobhy-Danial, J.M.; Grados, F.; Henry-Desailly, I.; Salomon-Goëb, S.; Rabin, T.; Ristic, S.; Fumery, M.; Fardellone, P.; et al. Therapeutic maintenance of baricitinib and tofacitinib in real life. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, M.N.; Holroyd, C.; Edwards, C.J. O10 Characteristics of patients who discontinued baricitinib treatment within 12 months and reasons for discontinuation: Real-world data. Rheumatology 2021, 60, keab246.009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Jung, U.H.; Kim, J.W.; Choe, J.Y. The beneficial effect of baricitinib on ultrasound-detected synovial inflammation and bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis: Preliminarily data from single center-based observational study for 24 weeks. Medicine 2021, 100, e26739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, V.; Losi, S.; Rogai, V.; Antonelli, S.; Fakhouri, W.; Giovannitti, M.; Giacomini, E.; Sangiorgi, D.; Degli Esposti, L. Real-world analysis of therapeutic patterns in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis in Italy: A focus on baricitinib. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, V.; Losi, S.; Rogai, V.; Antonelli, S.; Fakhouri, W.; Giovannitti, M.; Giacomini, E.; Sangiorgi, D.; Degli Esposti, L. Treatment patterns and pharmacoutilization in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis in Italian settings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrejon, I.; Molina Collada, J.; Perez-garcia, C.; Vela-Casasempere, P.; Díaz-Torné, C.; Bohórquez, C.; Blanco, J.M.; Sánchez-Alonso, F.; on behalf of BIOBADASER. POS1439 Cancer in patients with rheumatic diseases exposed to different biologic and targeted synthetic DMARDS in real-world clinical practice: Data from a multicenter register. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigante, A.; Quintana, R.; Isnardi, C.; Roberts, K.; Gomez, G.; Haye Salinas, M.; Soriano, E.; Pons-Estel, G.; De la Vega, M.; Kerzberg, O.; et al. Cardiovascular and oncologic outcomes of anti-TNF alfa and JAK inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. Real world data and insights of BIOBADASAR 3.0 registry. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 0722. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-and-oncologic-outocomes-of-anti-tnf-alfa-and-jak-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-and-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-data-and-insights-of-biobadasar-3-0-registry/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Amstad, A.; Papagiannoulis, E.; Scherer, A.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Finckh, A.; Mueller, R.; Dudler, J.; Möller, B.; Villiger, P.M.; Schulz, M.M.P.; et al. Comparison of drug retention of TNF inhibitors, other biologics and JAK inhibitors in RA patients who discontinued JAK inhibitor therapy. Rheumatology 2022, 62, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciciriello, S.; Smith, T.; O’Sullivan, C.; Tymms, K.; Youssef, P.; Mathers, D.; Deakin, C.; Griffiths, H.; Littlejohn, G. POS0223 Patterns of Janus kinase inhibitor cycling for the management of rheumatoid arthritis in real-world clinical practice: An analysis of the OPAL dataset. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 330–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangfeld, A.; Manger, B.; Worsch, M.; Schmeiser, T.; Zink, A.; Schaefer, M. OP0116 Elderly patients are not at increased risk of serious infections when receiving bDMARDS or JAK inhibitors compared to csDMARD treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauper, K.; Aymon, R.; Mongin, D.; Bergstra, S.A.; Choquette, D.; Codreanu, C.; Cordtz, R.; De Cock, D.; Dreyer, L.; Elkayam, O.; et al. Evaluation of treatment discontinuation due to adverse events, and the effect of cardiovascular risk factors or type of JAK-inhibitors: An international collaboration of registries of rheumatoid arthritis patients (the ‘JAK-pot‘ study) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 0290. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-treatment-discontinuation-due-to-adverse-events-and-the-effect-of-cardiovascular-risk-factors-or-type-of-jak-inhibitors-an-international-collaboration-of-registries-of-rheumatoid-arthr/ (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Pombo-Suarez, M.; Sanchez-Piedra, C.; Gómez-Reino, J.; Lauper, K.; Mongin, D.; Iannone, F.; Pavelka, K.; Nordström, D.C.; Inanc, N.; Codreanu, C.; et al. After JAK inhibitor failure: To cycle or to switch, that is the question–Data from the JAK-pot collaboration of registries. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montastruc, F.; Flumian, C.; Degboe, Y.; Constantin, A.; Ruyssen-Witrand, A. OP0268 Comparison of major cardiovascular and thromboembolic events in safety reports between rheumatoid arthriritis patients treated with JAK inhibitors versus anti-TNF: Results from VigiBase. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 178–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoisnard, L.; Pina Vegas, L.; Dray-Spira, R.; Weill, A.; Zureik, M.; Sbidian, E. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular and venous thromboembolism events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis exposed to JAK inhibitors versus adalimumab: A nationwide cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouverneur, A.; Avouac, J.; Prati, C.; Cracowski, J.L.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Pariente, A.; Truchetet, M.E. JAK inhibitors and risk of major cardiovascular events or venous thromboembolism: A self-controlled case series study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodenrijs, N.M.T.; de Hair, M.J.H.; van der Goes, M.C.; Jacobs, J.W.G.; Welsing, P.M.J.; van der Heijde, D.; Aletaha, D.; Dougados, M.; Hyrich, K.L.; McInnes, I.B.; et al. Characteristics of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: Results of an international survey. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenic, P.; Radner, H.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Discrepancies between patients and physicians in their perceptions of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, S.; Sonomoto, K.; Nakayamada, S.; Tanaka, Y. Preferable outcome of Janus kinase inhibitors for a group of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis patients: From the FIRST Registry. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Reed, G.W.; Kremer, J.M.; Curtis, J.R.; Farkouh, M.E.; Harrold, L.R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Tsao, P.; Greenberg, J.D. Disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of cardiovascular events. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molander, V.; Bower, H.; Frisell, T.; Askling, J. Risk of venous thromboembolism in rheumatoid arthritis, and its association with disease activity: A nationwide cohort study from Sweden. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecklund, E.; Iliadou, A.; Askling, J.; Ekbom, A.; Backlin, C.; Granath, F.; Catrina, A.I.; Rosenquist, R.; Feltelius, N.; Sundström, C.; et al. Association of chronic inflammation, not its treatment, with increased lymphoma risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, B.; Pedro, S.; Ozen, G.; Kalil, A.; Wolfe, F.; Mikuls, T.; Michaud, K. Serious infection risk in rheumatoid arthritis compared with non-inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: A US national cohort study. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Carmona, L.; BIOBADASER Group. Switching TNF antagonists in patients with chronic arthritis: An observational study of 488 patients over a four-year period. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Combe, B.; Curtis, J.R.; Hall, S.; Haraoui, B.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Cioffi, C.; Ecoffet, C.; Gervitz, L.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of certolizumab pegol versus adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year efficacy and safety results from the randomised EXXELERATE study. Lancet 2016, 388, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, P.; Keystone, E.; Tony, H.P.; Cantagrel, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Sanchez, A.; Alecock, E.; Lee, J.; Kremer, J. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: Results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, M.C.; Becker, J.C.; Schiff, M.; Luggen, M.; Sherrer, Y.; Kremer, J.; Birbara, C.; Box, J.; Natarajan, K.; Nuamah, I.; et al. Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottenberg, J.E.; Brocq, O.; Perdriger, A.; Lassoued, S.; Berthelot, J.M.; Wendling, D.; Euller-Ziegler, L.; Soubrier, M.; Richez, C.; Fautrel, B.; et al. Non-TNF-targeted biologic vs a second anti-TNF drug to treat rheumatoid arthritis in patients with insufficient response to a first anti-TNF drug: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, A.; Pompilio, G.; Integlia, D.; Zhuo, J.; Alemao, E. Cycling of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors versus switching to different mechanism of action therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X211002682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Fautrel, B.; Keystone, E.C.; Ortmann, R.A.; Xie, L.; Zhu, B.; Issa, M.; Patel, H.; Gaich, C.L.; de Bono, S.; et al. Clinical outcomes in patients switched from adalimumab to baricitinib due to non-response and/or study design: Phase III data in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.; Thomas, S.; Gorantla, V. Accelerated atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. F1000Research 2022, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketfi, C.; Boutigny, A.; Mohamedi, N.; Bouajil, S.; Magnan, B.; Amah, G.; Dillinger, J.G. Risk of venous thromboembolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilton, K.M.; Matteson, E.L. Malignancy incidence, management, and prevention in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2017, 4, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listing, J.; Gerhold, K.; Zink, A. The risk of infections associated with rheumatoid arthritis, with its comorbidity and treatment. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.C.; Takeuchi, T.; Burmester, G.R.; Durez, P.; Smolen, J.S.; Deberdt, W.; Issa, M.; Terres, J.R.; Bello, N.; Winthrop, K.L. Safety of baricitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis over a median of 4.6 and up to 9.3 years of treatment: Final results from long-term extension study and integrated database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T.; Feist, E.; Irvine, A.D.; Harigai, M.; Haladyj, E.; Ball, S.; Deberdt, W.; Issa, M.; Grond, S.; Taylor, P.C. A review of safety outcomes from clinical trials of baricitinib in rheumatology, dermatology and COVID-19. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 4910–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.; Vassilopoulos, D. Infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the era of targeted synthetic therapies. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 31, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.; Askling, J.; Berglind, N.; Franzen, S.; Frisell, T.; Garwood, C.; Greenberg, J.D.; Ho, M.; Holmqvist, M.; Novelli Horne, L.; et al. Infection rates in patients from five rheumatoid arthritis (RA) registries: Contextualising an RA clinical trial programme. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, D.; Callegaro, A.; Fahrbach, K.; Neupane, B.; Vroling, H.; van Oorschot, D.; Yawn, B.P. Meta-regression of herpes zoster incidence worldwide. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, J.; Harigai, M.; Rancourt, J.; Dickson, C.; Melby, T.; Issa, M.; de la Torre, I.; Isaka, Y.; Cardoso, A.; Saifan, C.; et al. Changes in selected haematological parameters associated with JAK1/JAK2 inhibition observed in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with baricitinib. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.C.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Burmester, G.R.; Rooney, T.P.; Witt, S.; Walls, C.D.; Issa, M.; Salinas, C.A.; Saifan, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Cardiovascular safety during treatment with baricitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, M.; Mootoo, A.; Adas, M.; Bechman, K.; Rampes, S.; Patel, V.; Qureshi, S.; Cope, A.P.; Norton, S.; Galloway, J.B. Venous thromboembolism risk with JAK inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, M.H.; Weber, B.N.; Haberman, R.H.; Lo Sicco, K.I.; Bangalore, S.; Garshick, M.S. Cardiovascular and venous thromboembolic risk with Janus kinase inhibitors in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022, 4, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Bieber, T.; Alten, R.; Witte, T.; Galloway, J.; Deberdt, W.; Issa, M.; Haladyj, E.; De La Torre, I.; Grond, S.; et al. Baricitinib safety for events of special interest in populations at risk: Analysis from randomised trial data across rheumatologic and dermatologic indications. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 1867–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Janus Kinase Inhibitors (JAKi). 2023. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/referrals/janus-kinase-inhibitors-jaki (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Requires Warnings about Increased Risk of Serious Heart-Related Events, Cancer, Blood Clots, and Death for JAK Inhibitors that Treat Certain Chronic Inflammatory Conditions. 2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safetyand-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increasedrisk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clotsand-death (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; Buch, M.H.; Dougados, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Giles, J.T.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Koch, G.G.; Vranic, I.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular events with tofacitinib versus tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with or without a history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A post hoc analysis from ORAL Surveillance. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 82, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpouzas, G.; Szekanecz, Z.; Baecklund, E.; Mikuls, T.; Bhatt, D.; Shi, H.; Wang, C.; Sawyerr, G.; Chen, Y.; Menon, S.; et al. Relationship between disease activity and adverse events of interest in patients with RA on tofacitinib or TNF inhibitors: Post hoc analysis of a phase 3b/4 randomized safety study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1401. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-disease-activity-and-adverse-events-of-interest-in-patients-with-ra-on-tofacitinib-or-tnf-inhibitors-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-3b-4-randomized-safety-study/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Frisell, T.; Baecklund, E.; Bengtsson, K.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Askling, J.; on behalf of the ARTIS Study Group. Patient characteristics influence the choice of biological drug in RA, and will make non-TNFi biologics appear more harmful than TNFi biologics. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.M.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Cappelli, L.C.; Greenberg, J.D.; Madsen, A.M.; Geier, J.; Rivas, J.L.; Onofrei, A.M.; Barr, C.J.; Pappas, D.A.; et al. Postapproval comparative safety study of tofacitinib and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 5-year results from a United States-based rheumatoid arthritis registry. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrow-Khavar, F.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.B.; Desai, R.J. Tofacitinib and risk of cardiovascular outcomes: Results from the Safety of TofAcitinib in Routine care patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (STAR-RA) study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouverneur, A.; Avouac, J.; Prati, C.; Cracowski, J.L.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Pariente, A.; Truchetet, M.E. JAK inhibitors and risk of cancer. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 2216. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-inhibitors-and-risk-of-cancer/ (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Khosrow-Khavar, F.; Desai, R.J.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, S.C. Tofacitinib and risk of malignancy: Results from the Safety of Tofacitinib in Routine Care patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (STAR-RA) study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.R.; Shin, A.; Ha, Y.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, E.B.; Kang, E.H. Risk of infections between JAK inhibitors and TNF inhibitors among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 0302. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-infections-between-jak-inhibitors-and-tnf-inhibitors-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/ (accessed on 14 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Heutz, J.; de Jong, P.H.P. Possibilities for personalised medicine in rheumatoid arthritis: Hype or hope. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, A.I.; Patarata, E.; Subesinghe, S.; Hyrich, K.L.; Galloway, J.B. Opportunistic infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to biologic therapy: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Humira, INN-Adalimumab. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/humira-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Enbrel, INN-Etanercept. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/enbrel-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Remicade, INN-Infliximab. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/remicade-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics, Cimzia, INN-Certolizumab Pegol. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/cimzia-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- European Medicine Agency. SIMPONI (Golimumab). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/simponi (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Tardella, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Carotti, M.; Ceccarelli, L.; Giovagnoni, A.; Salaffi, F. A retrospective study of the efficacy of JAK inhibitors or abatacept on rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcher, G.; Hummel, N.; Didden, E.M.; Egger, M.; Reichenbach, S.; GetReal Work Package 4. Rheumatoid arthritis patients treated in trial and real world settings: Comparison of randomized trials with registries. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voshaar, M.O.; Ten Klooster, P.; Tedjo, D.; Van de Laar, C.; Van de Laar, M. Baricitinib versus TNF-inhibitors in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to csDMARDs: 12 weeks results of a pragmatic, multicenter, open label, noninferiority trial. POS0830. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Laar, C.J.; Oude Voshaar, M.A.H.; Fakhouri, W.K.H.; Zaremba-Pechmann, L.; De Leonardis, F.; De La Torre, I.; Van De Laar, M.A.F.J. Cost-effectiveness of a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor vs a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) in a treat-to-target strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. ClinicoEconomics Outcomes Res. 2020, 12, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Baricitinib | Tofacitinib | Upadacitinib | Filgotinib | Peficitinib | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4,9,10,15] | [16,17,18] | [19,20,21] | [22,23,24] | [25,26] | |
| Chemical structure |  |  |  |  |  |
| Dose | 2 or 4 mg QD | 5 mg BID | 15 mg XR QD | 200 mg QD | 150 mg QD (100 mg QD a) |
| (5 mg QD a) | |||||
| (100 mg QD a) | |||||
| 11 mg XR QD | |||||
| JAK selectivity (in vitro), IC50, nM | JAK1: 5.9, | JAK1: 3.2, | JAK1: 47, | JAK1: 10, | JAK1: 3.9, |
| JAK2: 5.7, | JAK2: 4.1, | JAK2: 120, | JAK2: 28, | JAK2: 5.0, | |
| JAK3: 560, | JAK3: 1.6, | JAK3: 2304, | JAK3: 810, | JAK3: 0.7, | |
| TYK2: 53 | TYK2: 34 | TYK2: 4690 | TYK2: 116 | TYK2: 4.8 | |
| Half-life (hours) | 12.5 | ~3 | 8–14 | 7 b | 10–18 |
| Excretion | Parent and metabolites: 75% renal, 20% faeces | Unchanged parent: 70% hepatic, 30% renal | Parent and metabolites: 24% urine, 38% faeces | Parent and metabolites: 87% urine, 15% faeces | Parent and metabolites: ~37% urine, 57% faeces |
| Drug–drug interactions | Strong (OAT3) inhibitors | Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers, moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors with strong CYP2C19 inhibitors, immunosuppressants | Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers | CES2 inhibitors, CYP1A2 or P-gp or BCRP substrates | P-gp inhibitor verapamil |
| BIO-1 (Bio-naïve) [61] | SCQM-RA [62] | RA-BE-REAL [77] | ARTIS [65] | DANBIO [66] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | BARI | TNFi | BARI a | TNFi | BARI | b/tsDMARD b | BARI | TNFi | BARI | ETN | ADA |
| 63 | 33 | 273 | 408 | 509 | 565 | 1420 | 6036 | 275 | 1830 | 1332 | |
| Age (years) | 60 | 56 c | 59 | 52 ** | 59 | 57 * | 61 | 58 d | 59 | 57 d | 57 d |
| Disease duration (years) | 8 e | 7 d,e | 13 | 8 ** | 10 | 9 * | 13 | 8 d | 14 | 10 d | 10 d |
| Disease activity (CDAI) | NR | NR d | 15 | 14 c | 24 | 24 c | 20 | 18 d | 4.35 f | 3.75 d,f | 3.65 d,f |
| Smokers (%) | NR | NR d | NR | NR d | NR | NR d | 11 | 12 d | 17 | 22 d | 23 d |
| Bio-naïve (%) | 100 | 100 d | 17 | 48 **,g | 48 | 61 d | Mostly d,h | 3 | 42 d | 55 d | |
| ≥2 DMARDs (%) | NR | NR d | 63 | 29 **,d,g | 39 | 29 d | Mostly d,h | 86 | 26 d | 22 d | |
| Comorbidities (%) | NR | NR d | NR | NR d | NR | NRd | 3 (VTE) | 2 (VTE) d | NR e | NR d | NR d |
| Real-World Study | Effectiveness | Survival (Kaplan–Meier) | Survival (Adjusted HR) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| or % Discontinuation (Crude) | ||||||
| CDAI | DAS28-ESR | Overall | Bio-Naïve | Overall | Bio-Naïve | |
| ARTIS [65] | BARI >> TNFi | BARI > TNFi | BARI = TNFi | NR | BARI >> TNFi | NR |
| at 3 and | at 3 mo | |||||
| 12 mo | ||||||
| SCQM-RA [62] | BARI = TNFi at 12 mo | NR | BARI > TNFi | BARI > TNFi | BARI >> TNFi | BARI >> TNFi |
| DANBIO [66] | NR | NR | BARI = TNFi | NR a | BARI >> TNFi b | NR a |
| RA-BE-REAL [77] | BARI > b/tsDMARD c at 6 mo d | NR | BARI > b/tsDMARD c at 6 mo d | BARI > b/tsDMARD c at 6 mo d | NR | NR |
| BIO-1 (Bio-naïve) [61] | NR | NR | NR | BARI > TNFi e | NR | BARI >> TNFi |
| SNDS (Hoisnard et al., 2023) [97] | SNDS (Salinas et al., 2022) [33] | ARTIS (Salinas et al., 2022) [33] | ARTIS (Frisell et al., 2023; [79] Molander et al., 2023 [80]) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | Cohort study comparing new users of JAKis (tofacitinib or baricitinib) and TNFi (adalimumab) | Focused analysis on data from SNDS: reanalysis of data from the SNDS cohort study comparing new users of baricitinib and TNFi | Focused analysis on data from ARTIS: reanalysis of data from the ARTIS cohort study comparing new users of baricitinib and TNFi | Nationwide register-based cohort study comparing individual b/tsDMARDs (baricitinib vs. individual TNFi) |
| Study population | Eligible patients included in the SNDS data between 1 Jul 2017 and 31 May 2021 | Eligible patients included in the SNDS data between 1 September 2017 and 31 December 2019 | Eligible patients were identified between February 2017 and December 2020 | All patients with RA in Sweden who started any b/tsDMARD between 1 January 2010 and 31 December 2020 |
| Patients, n | 8481 JAKi recipients (5065 baricitinib); 7354 TNFi recipients | 2859 baricitinib recipients’ propensity score matched with TNFi recipients | 1685 baricitinib recipients’ propensity score matched with TNFi patients | 1837 baricitinib recipients; 20,117 b/tsDMARD recipients in total (MACE); 1825 baricitinib recipients; 19,950 TNFi recipients (VTE) |
| Exposure | JAKi median follow-up b 1.2 years in SNDS | Baricitinib median exposure 0.47 years in SNDS | Baricitinib mean exposure 1.38 years in ARTIS | Baricitinib mean exposure 1.9 years in ARTIS (MACE); NR (VTE) |
| Statistical analysis | Analysis results based on propensity score weighted (IPTW) Cox regression | Analysis based on propensity score matched cohorts evaluated with modified Poisson regression | Analysis based on propensity score matched cohorts evaluated with modified Poisson regression | Crude and adjusted incidence rates and Cox regressions (VTE) adjusted with stabilised IPTW (MACE) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, P.C.; Laedermann, C.; Alten, R.; Feist, E.; Choy, E.; Haladyj, E.; De La Torre, I.; Richette, P.; Finckh, A.; Tanaka, Y. A JAK Inhibitor for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Baricitinib Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134527
Taylor PC, Laedermann C, Alten R, Feist E, Choy E, Haladyj E, De La Torre I, Richette P, Finckh A, Tanaka Y. A JAK Inhibitor for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Baricitinib Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134527
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Peter C., Cedric Laedermann, Rieke Alten, Eugen Feist, Ernest Choy, Ewa Haladyj, Inmaculada De La Torre, Pascal Richette, Axel Finckh, and Yoshiya Tanaka. 2023. "A JAK Inhibitor for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Baricitinib Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134527
APA StyleTaylor, P. C., Laedermann, C., Alten, R., Feist, E., Choy, E., Haladyj, E., De La Torre, I., Richette, P., Finckh, A., & Tanaka, Y. (2023). A JAK Inhibitor for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Baricitinib Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134527








