Risk Factors for the In-Hospital Mortality in Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Cross-Sectional Study on 9753 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Ethical Considerations
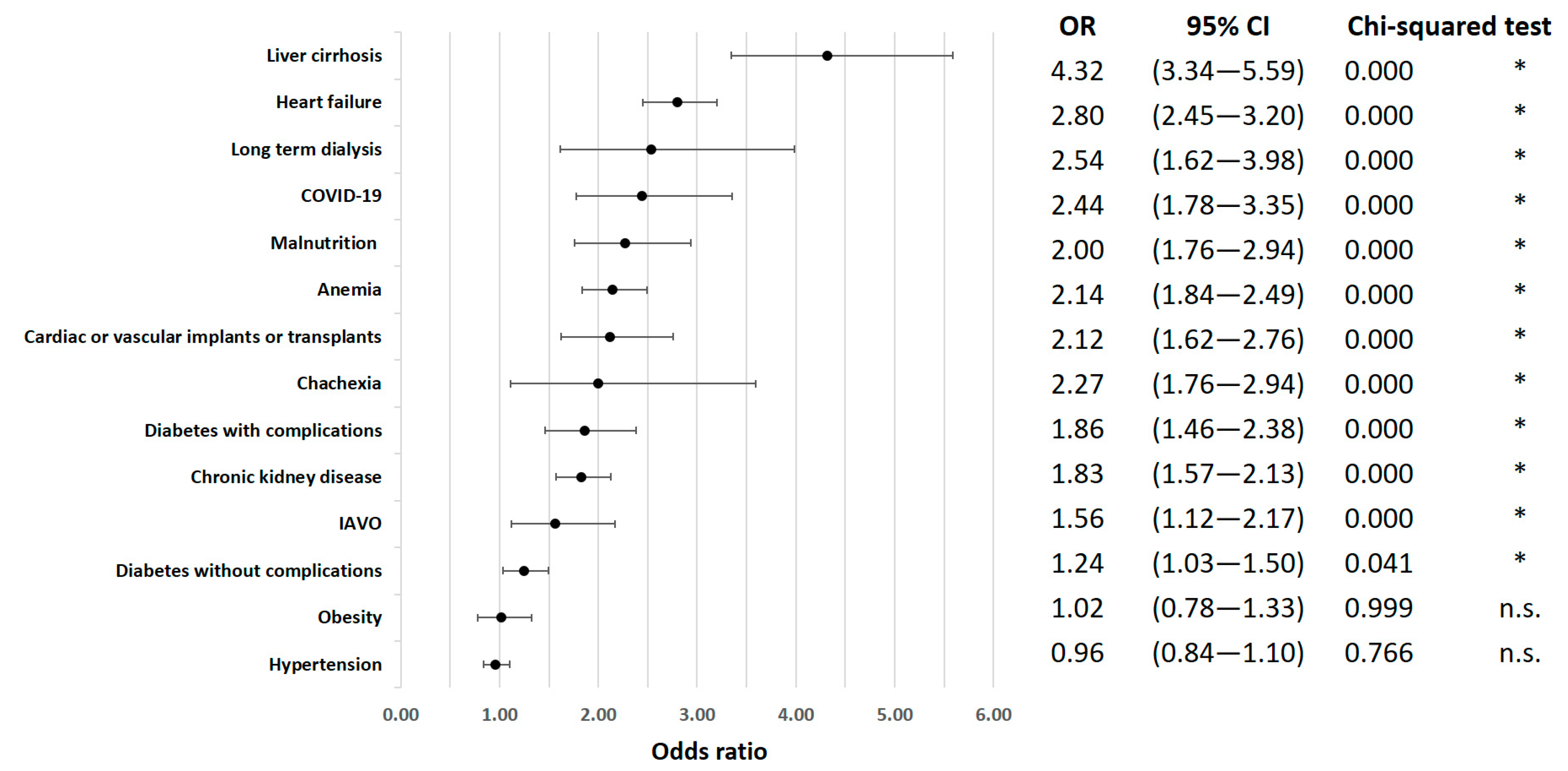
3. Results
Risk Factors for In-Hospital Mortality
4. Discussion
4.1. The Risk Factors for Mortality after VO
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alt, V.; Giannoudis, P.V. Musculoskeletal infections—A global burden and a new subsection in Injury. Injury 2019, 50, 2152–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, M.; Walter, N.; Baertl, S.; Lang, S.; Lowenberg, D.W.; Alt, V. Terminology of bone and joint infection. Bone Joint Res. 2021, 10, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W. Clinical practice. Vertebral osteomyelitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHenry, M.C.; Easley, K.A.; Locker, G.A. Vertebral osteomyelitis: Long-term outcome for 253 patients from 7 Cleveland-area hospitals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-H.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, M.S.; Kang, K.-C.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, S.Y.; Moon, C.; Chong, Y.P.; Kim, S.-H.; et al. Selection of an appropriate empiric antibiotic regimen in hematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Frömming, A.; Walter, N.; Freigang, V.; Neumann, C.; Loibl, M.; Ehrenschwender, M.; Alt, V.; Rupp, M. Is There a Difference in Clinical Features, Microbiological Epidemiology and Effective Empiric Antimicrobial Therapy Comparing Healthcare-Associated and Community-Acquired Vertebral Osteomyelitis? Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, N.; Haupenthal, J.; Schuetz, M.A.; Trampuz, A. Hematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis associated with intravascular device-associated infections—A retrospective cohort study. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 88, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conan, Y.; Laurent, E.; Belin, Y.; Lacasse, M.; Amelot, A.; Mulleman, D.; Rosset, P.; Bernard, L.; Grammatico-Guillon, L. Large increase of vertebral osteomyelitis in France: A 2010–2019 cross-sectional study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021, 149, e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatico, L.; Baron, S.; Rusch, E.; Lepage, B.; Surer, N.; Desenclos, J.C.; Besnier, J.M. Epidemiology of vertebral osteomyelitis (VO) in France: Analysis of hospital-discharge data 2002–2003. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, K.; Diebo, B.G.; Faloon, M.; Naziri, Q.; Pourtaheri, S.; Paulino, C.B.; Emami, A. The Epidemiology of Vertebral Osteomyelitis in the United States From 1998 to 2013. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, E102–E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, M.; Walter, N.; Pfeifer, C.; Lang, S.; Kerschbaum, M.; Krutsch, W.; Baumann, F.; Alt, V. The Incidence of Fractures Among the Adult Population of Germany-an Analysis From 2009 through 2019. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2021, 118, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouijzer, I.J.E.; Scheper, H.; de Rooy, J.W.J.; Bloem, J.L.; Janssen, M.J.R.; van den Hoven, L.; Hosman, A.J.F.; Visser, L.G.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; et al. The diagnostic value of 18F-FDG-PET/CT and MRI in suspected vertebral osteomyelitis—A prospective study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, M.; Lazzeri, E.; Palestro, C.J. Imaging of Spondylodiscitis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 48, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aagaard, T.; Roed, C.; Dahl, B.; Obel, N. Long-term prognosis and causes of death after spondylodiscitis: A Danish nationwide cohort study. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puth, M.-T.; Weckbecker, K.; Schmid, M.; Münster, E. Prevalence of multimorbidity in Germany: Impact of age and educational level in a cross-sectional study on 19,294 adults. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, E.; Scarborough, M.; Bowden, G.; McNally, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Athanasou, N.A. The role of histology in the diagnosis of spondylodiscitis: Correlation with clinical and microbiological findings. Bone Joint J. 2019, 101-B, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Rupp, M.; Hanses, F.; Neumann, C.; Loibl, M.; Alt, V. Infektionen der Wirbelsäule: Pyogene Spondylodiszitis und implantatassoziierte vertebrale Osteomyelitis. Unfallchirurg 2021, 124, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, C.; Höh, N. von der. Zusammenfassung der S2K-Leitlinie “Diagnostik und Therapie der Spondylodiszitis” (Stand 08/2020). Die Wirbelsäule 2021, 5, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doutchi, M.; Seng, P.; Menard, A.; Meddeb, L.; Adetchessi, T.; Fuentes, S.; Dufour, H.; Stein, A. Changing trends in the epidemiology of vertebral osteomyelitis in Marseille, France. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Walter, N.; Schindler, M.; Baertl, S.; Szymski, D.; Loibl, M.; Alt, V.; Rupp, M. The Epidemiology of Spondylodiscitis in Germany: A Descriptive Report of Incidence Rates, Pathogens, In-Hospital Mortality, and Hospital Stays between 2010 and 2020. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettivel, J.; Bortz, C.; Passias, P.G.; Baker, J.F. Pyogenic Vertebral Column Osteomyelitis in Adults: Analysis of Risk Factors for 30-Day and 1-Year Mortality in a Single Center Cohort Study. Asian Spine J. 2019, 13, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, V.; Gras, J.; Dubée, V.; de Lastours, V.; Lopes, A.; Leflon, V.; Allaham, W.; Guigui, P.; Fantin, B. Increased mortality in patients aged 75 years or over with pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Infect. Dis. 2018, 50, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagdiran, A.; Otto-Lambertz, C.; Lingscheid, K.M.; Sircar, K.; Samel, C.; Scheyerer, M.J.; Zarghooni, K.; Eysel, P.; Sobottke, R.; Jung, N.; et al. Quality of life and mortality after surgical treatment for vertebral osteomyelitis (VO): A prospective study. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, H.; Vogelmann, T.; Preissing, F.; Stiefel, J.; Adam, D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia between 2009 and 2019—Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Evans, R.G.; Iguchi, N.; Tare, M.; Parkington, H.C.; Bellomo, R.; May, C.N.; Lankadeva, Y.R. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: A disease of the microcirculation. Microcirculation 2019, 26, e12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Bouchard, J.; Soroko, S.B.; Ikizler, T.A.; Paganini, E.P.; Chertow, G.M.; Himmelfarb, J. Sepsis as a cause and consequence of acute kidney injury: Program to Improve Care in Acute Renal Disease. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizier, S.; Forel, J.-M.; Ayzac, L.; Richard, J.-C.; Hraiech, S.; Lehingue, S.; Loundou, A.; Roch, A.; Guerin, C.; Papazian, L. Early Hepatic Dysfunction Is Associated with a Worse Outcome in Patients Presenting with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Post-Hoc Analysis of the ACURASYS and PROSEVA Studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strnad, P.; Tacke, F.; Koch, A.; Trautwein, C. Liver—Guardian, modifier and target of sepsis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-J.; Jang, H.-C.; Jung, S.-I.; Choe, P.G.; Park, W.B.; Kim, C.-J.; Song, K.-H.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.B.; Oh, M.-D.; et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of pyogenic spondylitis caused by gram-negative bacteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husabø, G.; Nilsen, R.M.; Flaatten, H.; Solligård, E.; Frich, J.C.; Bondevik, G.T.; Braut, G.S.; Walshe, K.; Harthug, S.; Hovlid, E. Early diagnosis of sepsis in emergency departments, time to treatment, and association with mortality: An observational study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Belkum, A.; Bachmann, T.T.; Lüdke, G.; Lisby, J.G.; Kahlmeter, G.; Mohess, A.; Becker, K.; Hays, J.P.; Woodford, N.; Mitsakakis, K.; et al. Developmental roadmap for antimicrobial susceptibility testing systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, D.P.; Waldvogel, F.A. Osteomyelitis. Lancet 2004, 364, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Secondary Diagnosis | ICD-10 Code | [n] | Percentage of All Cases | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comorbidity | Arterial Hypertension | I10.- | 5424 | 55.6% |
| Type II diabetes | E11.- | 2819 | 28.9% | |
| Congestive heart failure | I50.- | 2522 | 25.9% | |
| Atrial fibrillation | I48.- | 2365 | 24.3% | |
| Chronic kidney disease | N18.1-; N19 | 2325 | 23.8% | |
| Coronary arterial disease | I25.0; I25.10-.19 | 1655 | 17.0% | |
| Hypothyreosis | E03.8; -.9 | 1264 | 13.0% | |
| Adipositas | E66.0-.99 | 997 | 10.2% | |
| Malignancy | C01; C10.–C97 | 736 | 7.6% | |
| Malnutrition | E43–E46 | 559 | 5.7% | |
| Implant-associated vertebral osteomyelitis | T81.4 | 431 | 4.4% | |
| Liver cirrhosis | K74.6; .-70-72 | 365 | 3.7% | |
| Dialysis | Z99.2 | 154 | 1.6% | |
| Cachexia | R64 | 107 | 1.1% | |
| Complications | Hypokalemia | E87.6 | 3408 | 34.9% |
| Anemia, bleeding | D62 | 2039 | 20.9% | |
| Spinal abscess | G06.1; -.2 | 1612 | 16.5% | |
| Urinal tract infection | N39.0 | 1595 | 16.4% | |
| Pleural infusion | J90; J91 | 1576 | 16.2% | |
| Acute respiratory insufficiency | J96.01; J96.00 | 1441 | 14.8% | |
| Acute kidney failure | N17.0-; N17.81-3, -9-; N17.91-3, -9 | 1185 | 12.2% | |
| Pneumonia | J12.8–J18.9 | 1066 | 10.9% | |
| Infectious myositis | M60.05 | 1010 | 10.4% | |
| SIRS | R65.0-.3 | 980 | 10.1% | |
| Sepsis | A40.1–8; A41.1–9 | 854 | 8.8% | |
| COVID-19 | U07.1, .2 | 332 | 3.4% | |
| Infective Endocarditis | I33.0 | 222 | 2.3% | |
| Acute liver failure | K72.0 | 59 | 0.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziarko, T.P.; Walter, N.; Schindler, M.; Alt, V.; Rupp, M.; Lang, S. Risk Factors for the In-Hospital Mortality in Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Cross-Sectional Study on 9753 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144805
Ziarko TP, Walter N, Schindler M, Alt V, Rupp M, Lang S. Risk Factors for the In-Hospital Mortality in Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Cross-Sectional Study on 9753 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(14):4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144805
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiarko, Tomasz Piotr, Nike Walter, Melanie Schindler, Volker Alt, Markus Rupp, and Siegmund Lang. 2023. "Risk Factors for the In-Hospital Mortality in Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Cross-Sectional Study on 9753 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 14: 4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144805
APA StyleZiarko, T. P., Walter, N., Schindler, M., Alt, V., Rupp, M., & Lang, S. (2023). Risk Factors for the In-Hospital Mortality in Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Cross-Sectional Study on 9753 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(14), 4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144805







