Comparison of the Ability of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) Systems and Endoscopists to Detect Colorectal Neoplastic Lesions on Endoscopy Video
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
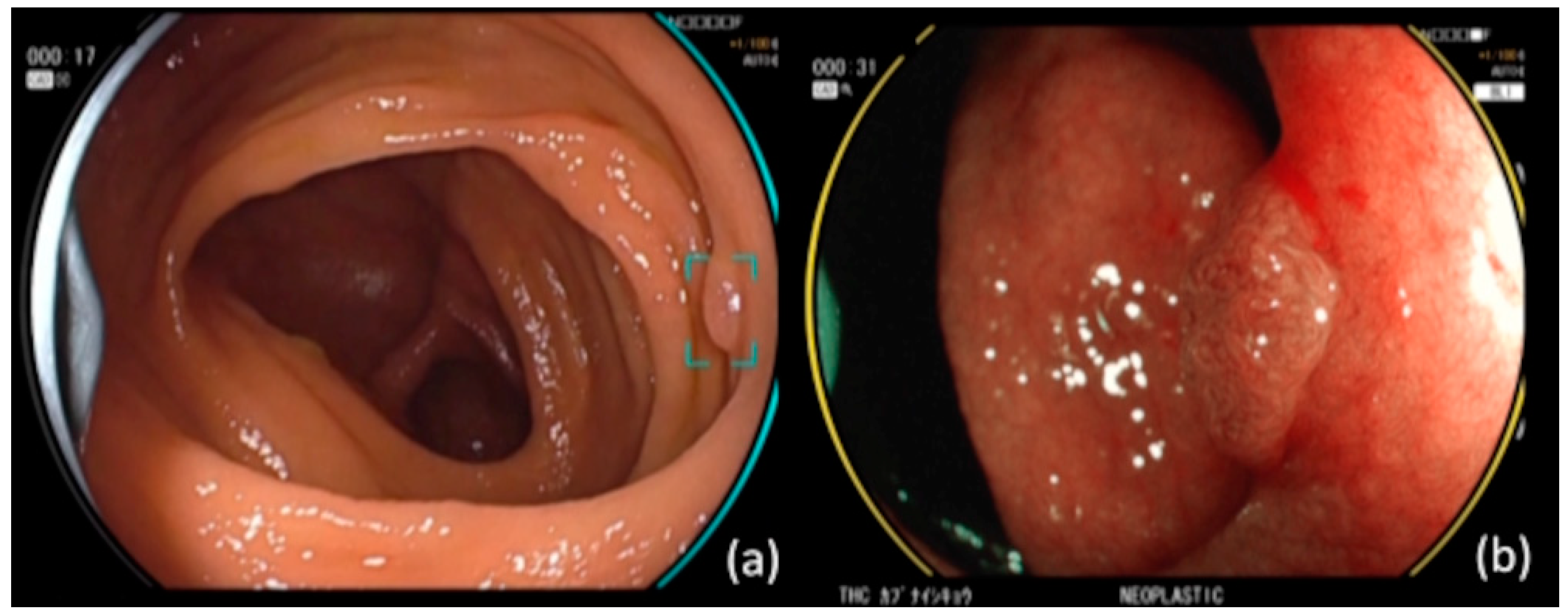
2.2. CAD EYE (CADe and CADx)
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Preparation of the Colonoscopy Videos
2.5. Time Measurement and Comparison
2.5.1. Basis for Setting Time X of Win/Loss Decision
2.5.2. False Positives
2.6. Polyp Characteristics
2.7. Outcome Measures
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
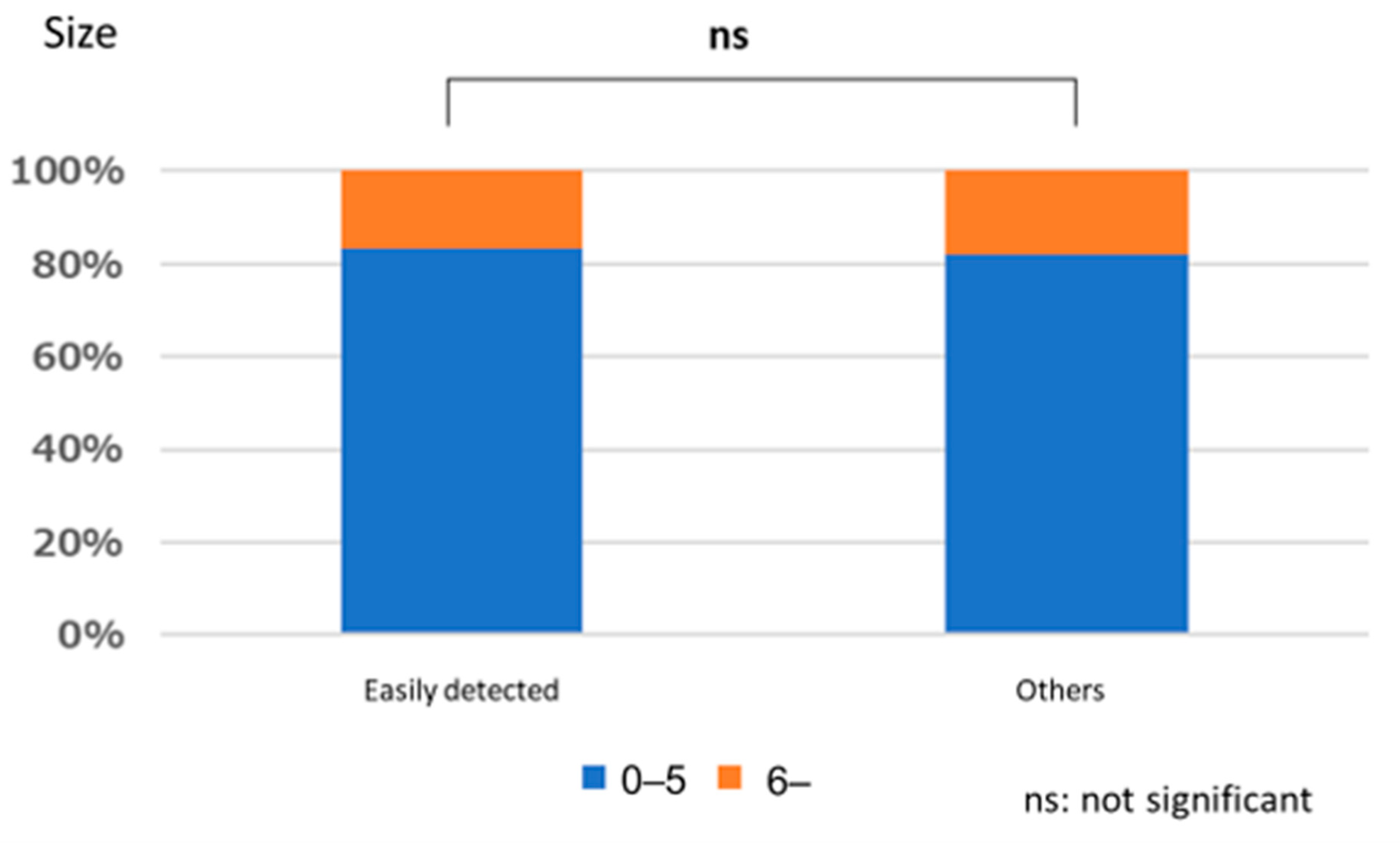
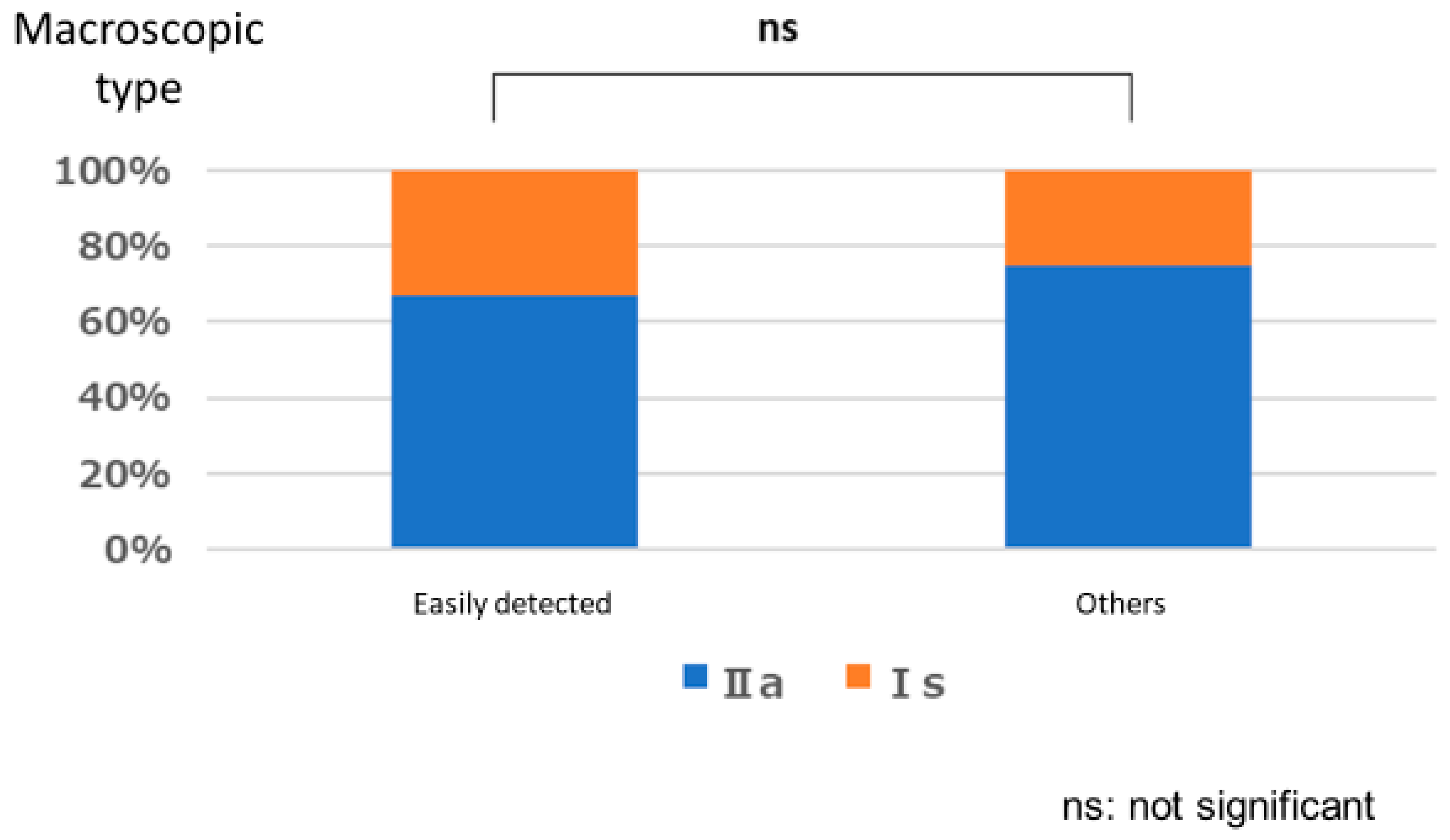
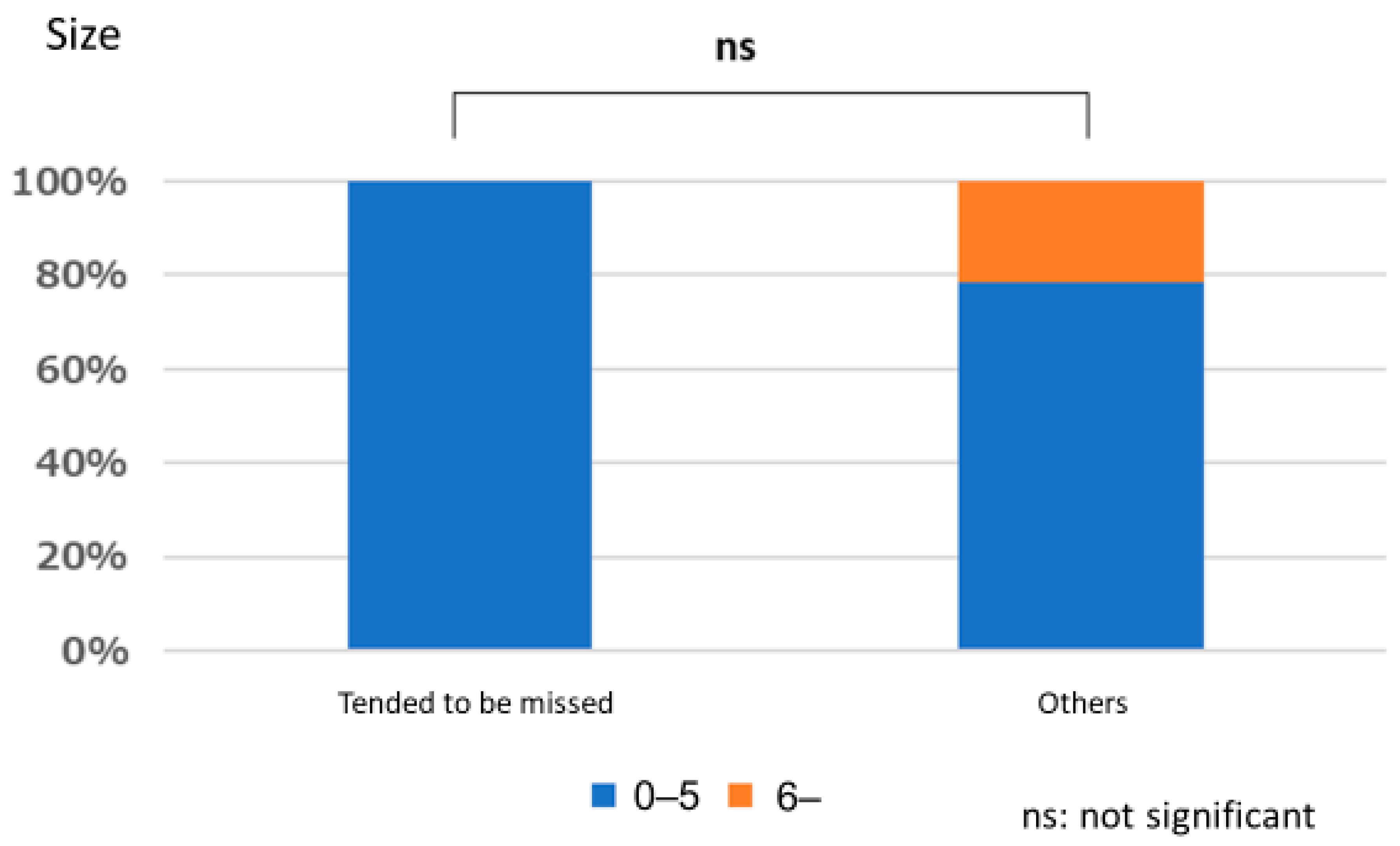
3.1. Lesion Characteristic
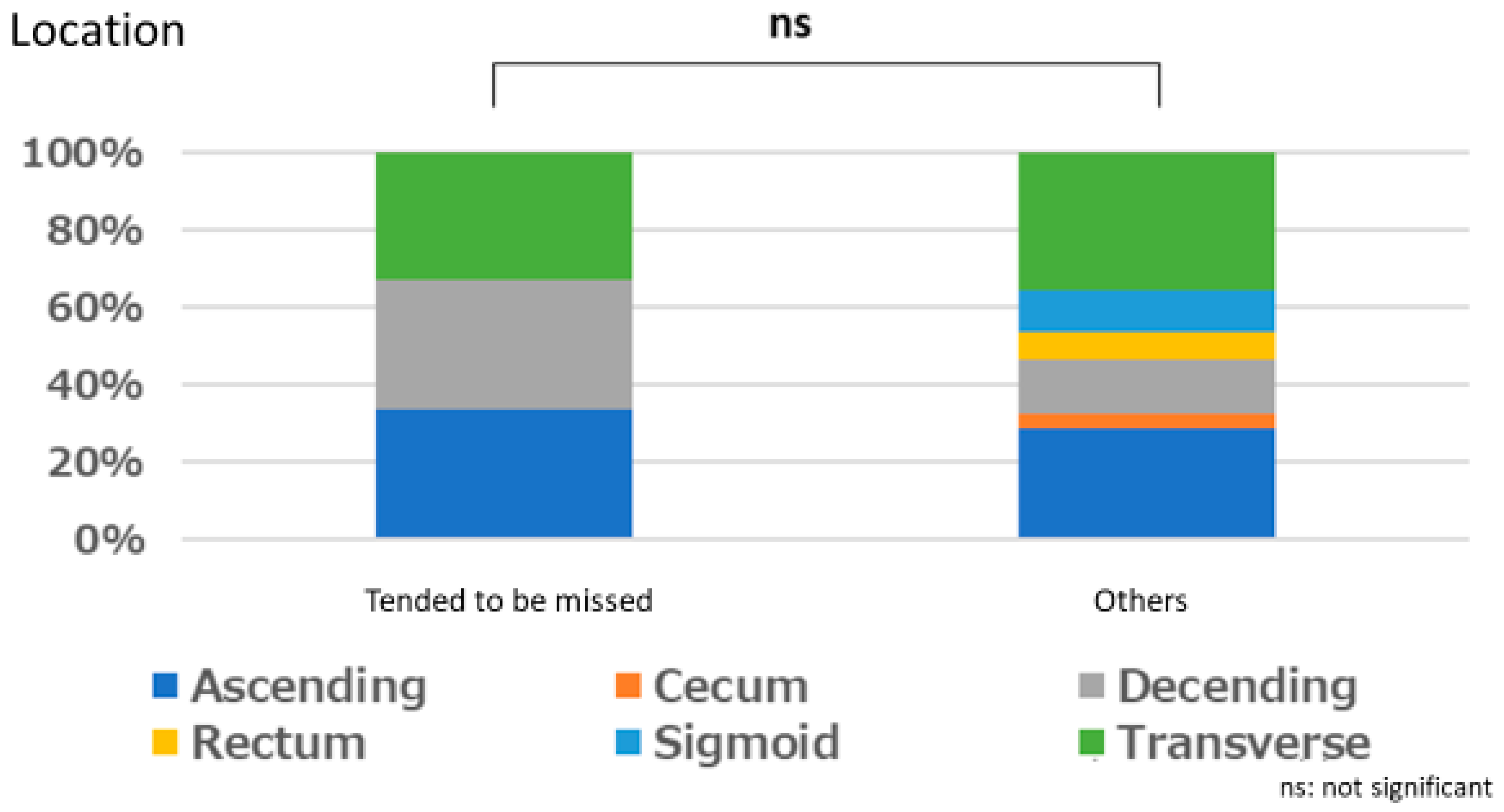
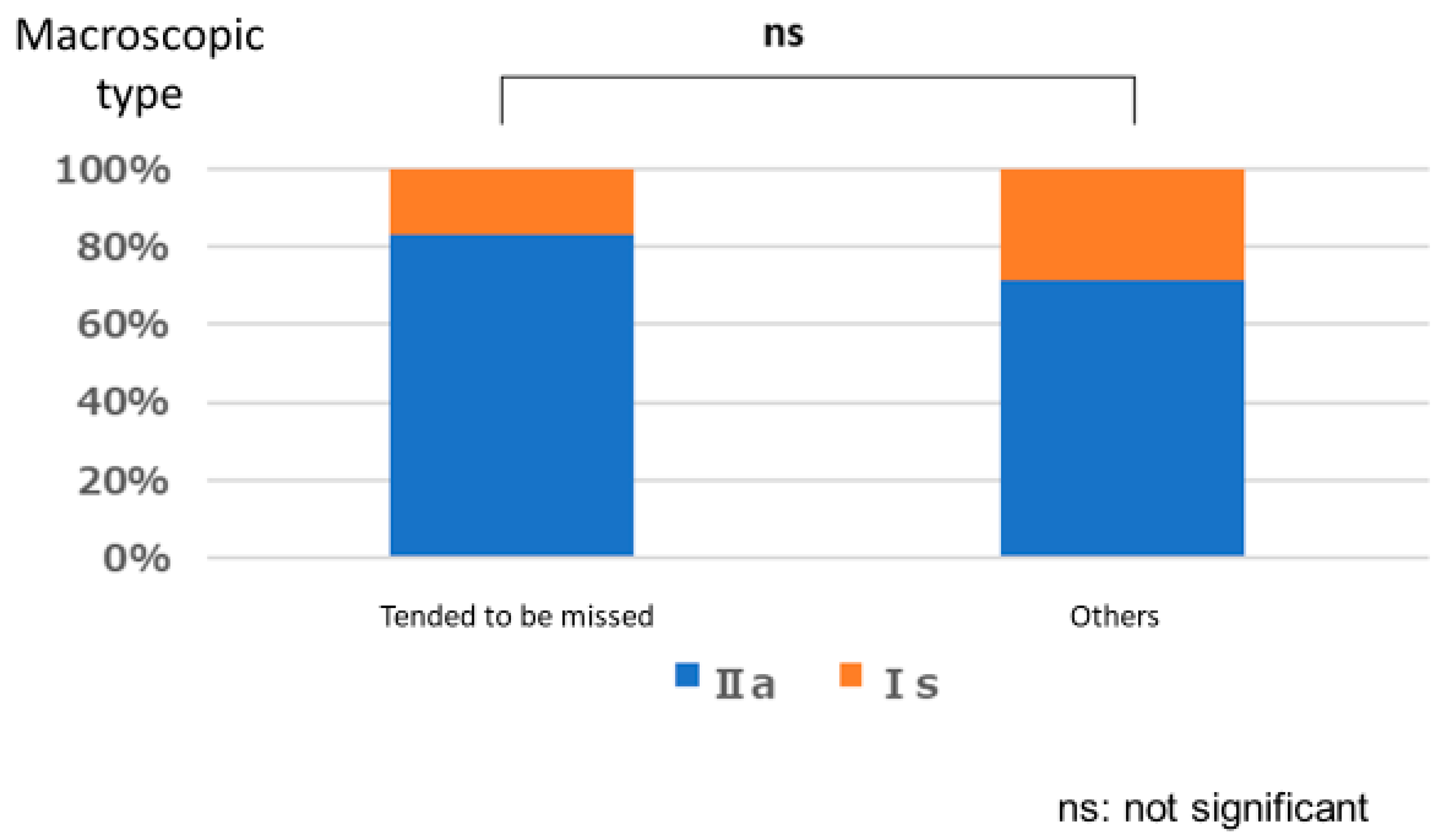
Polyps That are Easy for Endoscopists to Detect or Those They Tend to Miss
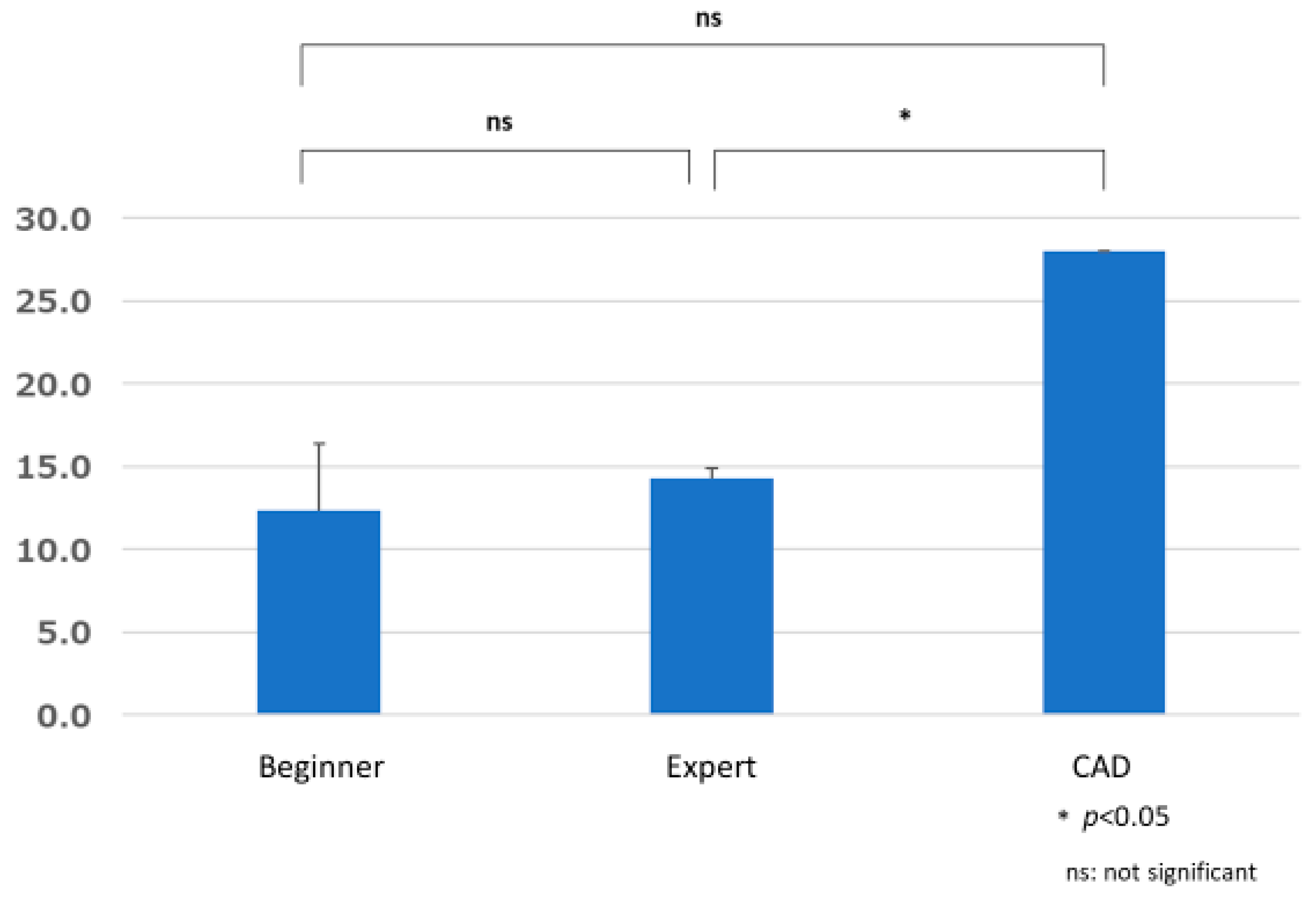
3.2. Lesion Detection Time
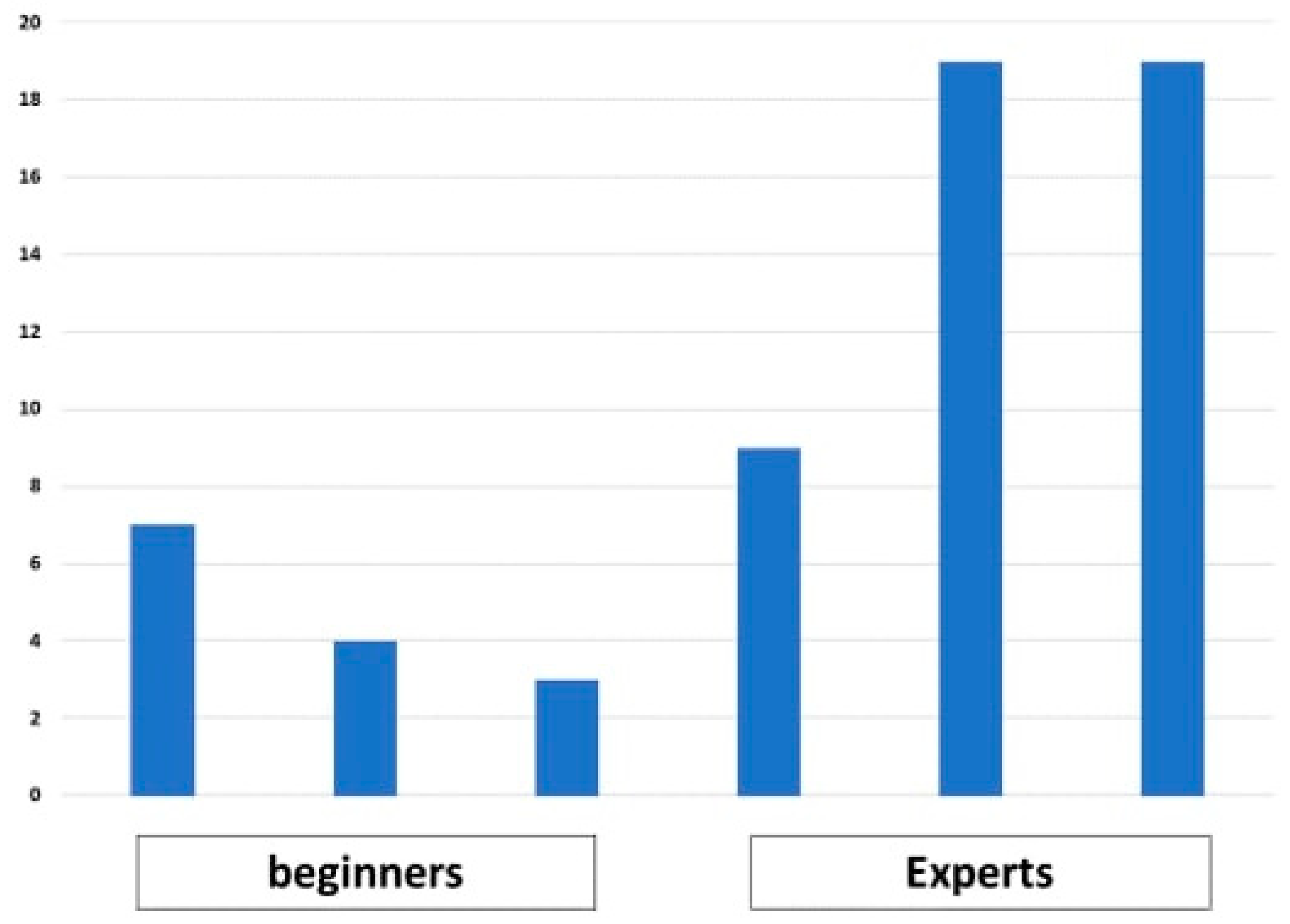
3.2.1. Number of Endoscopist Wins
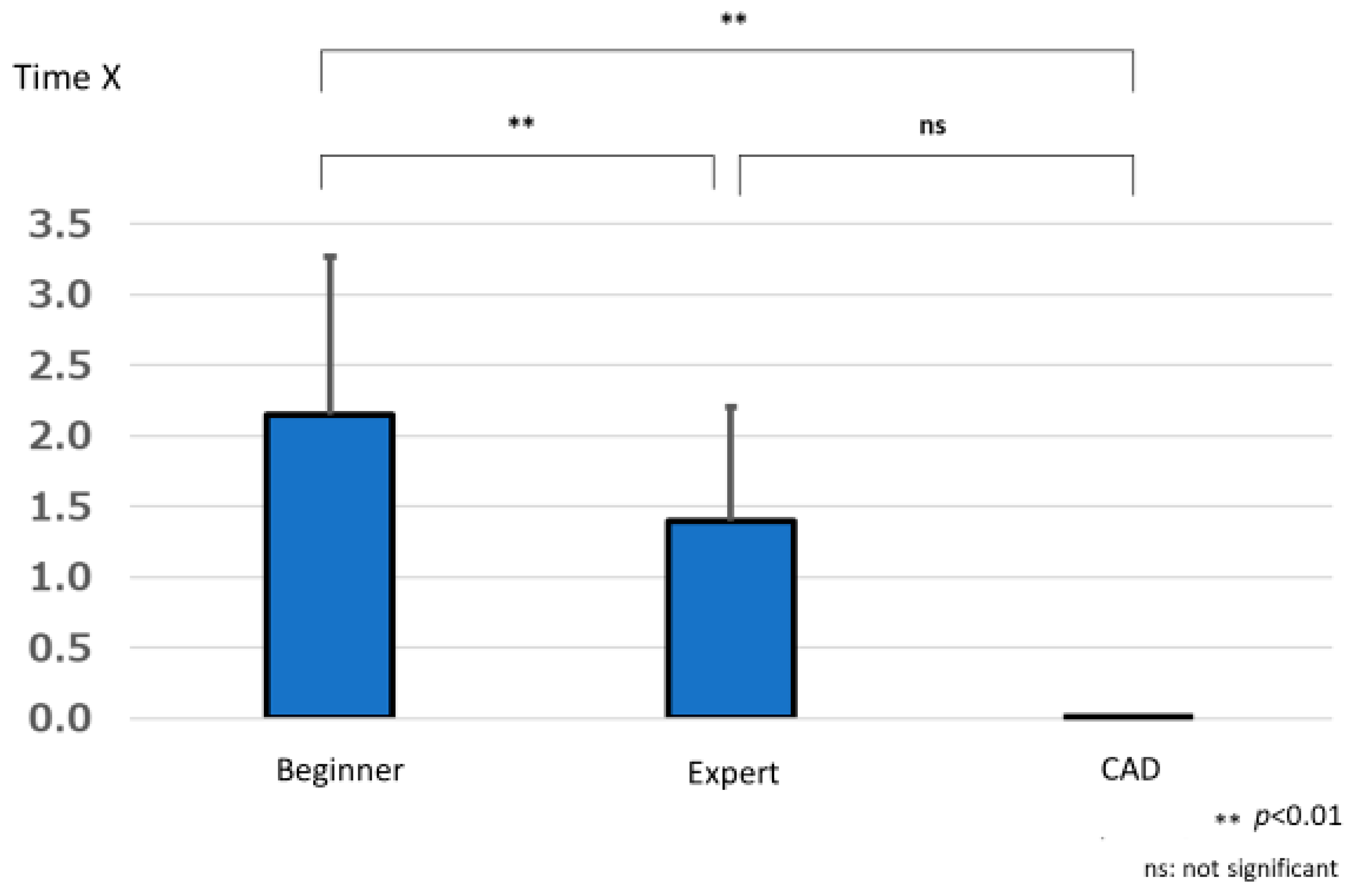
3.2.2. Group Comparisons of Time Required to Detect Lesions (Time X)
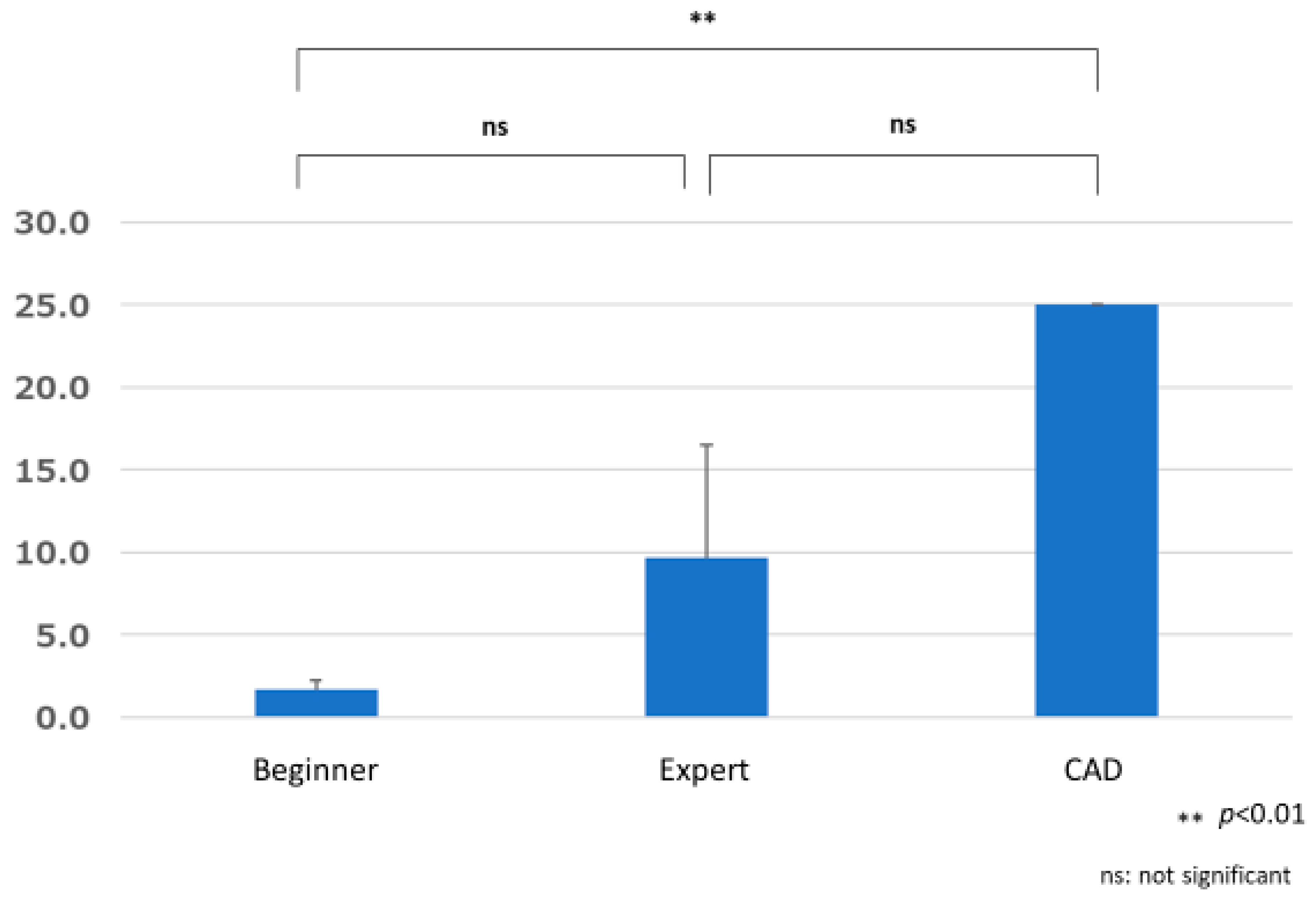
3.3. Number of False Positives
3.3.1. Comparison of the Number of False Positives by Group
3.3.2. Comparison of False Positive A by Group
3.3.3. Comparison of False Positive B by Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, D.W.; Morson, B.C. The adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Major Probl. Pathol. 1978, 10, 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zauber, A.G.; Winawer, S.J.; O’Brien, M.J.; Lansdorp-Vogelaar, I.; van Ballegooijen, M.; Hankey, B.F.; Shi, W.; Bond, J.H.; Schapiro, M.; Panish, J.F.; et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, H.; Chang-Claude, J.; Jansen, L.; Knebel, P.; Stock, C.; Hoffmeister, M. Reduced risk of colorectal cancer up to 10 years after screening, surveillance, or diagnostic colonoscopy. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doubeni, C.A.; Corley, D.A.; Quinn, V.P.; Jensen, C.D.; Zauber, A.G.; Goodman, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Mehta, S.J.; Becerra, T.A.; Zhao, W.K.; et al. Effectiveness of screening colonoscopy in reducing the risk of death from right and left colon cancer: A large community-based study. Gut 2018, 67, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Clercq, C.M.; Bouwens, M.W.; Rondagh, E.J.; Bakker, C.M.; Keulen, E.T.; de Ridder, R.J.; Winkens, B.; Masclee, A.A.; Sanduleanu, S. Postcolonoscopy colorectal cancers are preventable: A population-based study. Gut 2014, 63, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, D.A.; Jensen, C.D.; Marks, A.R.; Zhao, W.K.; Lee, J.K.; Doubeni, C.A.; Zauber, A.G.; de Boer, J.; Fireman, B.H.; Schottinger, J.E.; et al. Adenoma detection rate and risk of colorectal cancer and death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, G.; Tripathi, P.; Alkayali, T.; Mittal, M.; Jalali, F.; Karnes, W.; Baldi, P. Deep learning localizes and identifies polyps in real time with 96% accuracy in screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1069–1078.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, M.F.; Regula, J.; Kraszewska, E.; Polkowski, M.; Wojciechowska, U.; Didkowska, J.; Zwierko, M.; Rupinski, M.; Nowacki, M.P.; Butruk, E. Quality indicators for colonoscopy and the risk of interval cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.Y.; Chiu, H.M. Can image-enhanced endoscopy improve adenoma detection rate? Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Berzin, T.M.; Glissen Brown, J.R.; Liu, P.; Zhou, C.; Lei, L.; Li, L.; Guo, Z.; Lei, S.; et al. Effect of a deep-learning computer-aided detection system on adenoma detection during colonoscopy (CADe-DB trial): A double-blind randomised study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Berzin, T.M.; Glissen Brown, J.R.; Bharadwaj, S.; Becq, A.; Xiao, X.; Liu, P.; Li, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Real-time automatic detection system increases colonoscopic polyp and adenoma detection rates: A prospective randomised controlled study. Gut 2019, 68, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, T.; Nakashima, H.; Nakamura, K.; Nagahama, R.; Saito, Y. Performance of computer-aided detection and diagnosis of colorectal polyps compares to that of experienced endoscopists. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 3976–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigt, J.; Repici, A.; Antonelli, G.; Afifi, A.; Kliegis, L.; Correale, L.; Hassan, C.; Neumann, H. Performance of a new integrated computer-assisted system (CADe/CADx) for detection and characterization of colorectal neoplasia. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, H.; Sivanathan, V.; Rahman, K.F.; Galle, P.R. Sa2042 Artificial intelligence combined with lci yields in highest accuracy and detection of colorectal polyps, including sessile serrated lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, AB255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.E.; Misawa, M.; Mori, Y.; Hotta, K.; Ohtsuka, K.; Ikematsu, H.; Saito, Y.; Takeda, K.; Nakamura, H.; Ichimasa, K.; et al. Artificial intelligence-assisted system improves endoscopic identification of colorectal neoplasms. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1874–1881.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donders, F.C. On the speed of mental processes. Acta Psychol. 1969, 30, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, F.H.; Ladlad, J.; Teo, E.K.; Lin, C.L.; Foo, F.J. Real-time artificial intelligence (AI)-aided endoscopy improves adenoma detection rates even in experienced endoscopists: A cohort study in Singapore. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tang, R.S.; Lam, T.Y.; Zhao, G.; Lau, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Rong, L.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 337–346.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repici, A.; Spadaccini, M.; Antonelli, G.; Correale, L.; Maselli, R.; Galtieri, P.A.; Pellegatta, G.; Capogreco, A.; Milluzzo, S.M.; Lollo, G.; et al. Artificial intelligence and colonoscopy experience: Lessons from two randomised trials. Gut 2022, 71, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitz, R.P. The speed-accuracy tradeoff: History, physiology, methodology, and behavior. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, C.; Badalamenti, M.; Maselli, R.; Correale, L.; Iannone, A.; Radaelli, F.; Rondonotti, E.; Ferrara, E.; Spadaccini, M.; Alkandari, A.; et al. Computer-aided detection-assisted colonoscopy: Classification and relevance of false positives. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 900–904.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klare, P.; Sander, C.; Prinzen, M.; Haller, B.; Nowack, S.; Abdelhafez, M.; Poszler, A.; Brown, H.; Wilhelm, D.; Schmid, R.M.; et al. Automated polyp detection in the colorectum: A prospective study (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 576–582.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Shen, J.; Hong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, S.; Du, N.; Zhang, M.; Guo, D. Effect of artificial intelligence-aided colonoscopy for adenoma and polyp detection: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2022, 37, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Size | |
| 0–5 mm | 8 |
| 6–10 mm | 26 |
| Location | |
| Cecum | 1 |
| Ascending colon | 10 |
| Transverse colon | 12 |
| Descending colon | 6 |
| Sigmoid colon | 3 |
| Rectum | 2 |
| Shape | |
| Is | 9 |
| IIa | 25 |
| Hyperplastic Polyp | 25 |
| Lipoma | 2 |
| Angioectasia | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Misumi, Y.; Nonaka, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Kamitani, Y.; Uechi, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Kishino, M.; Omori, T.; Yonezawa, M.; Isomoto, H.; et al. Comparison of the Ability of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) Systems and Endoscopists to Detect Colorectal Neoplastic Lesions on Endoscopy Video. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144840
Misumi Y, Nonaka K, Takeuchi M, Kamitani Y, Uechi Y, Watanabe M, Kishino M, Omori T, Yonezawa M, Isomoto H, et al. Comparison of the Ability of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) Systems and Endoscopists to Detect Colorectal Neoplastic Lesions on Endoscopy Video. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(14):4840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144840
Chicago/Turabian StyleMisumi, Yoshitsugu, Kouichi Nonaka, Miharu Takeuchi, Yu Kamitani, Yasuhiro Uechi, Mai Watanabe, Maiko Kishino, Teppei Omori, Maria Yonezawa, Hajime Isomoto, and et al. 2023. "Comparison of the Ability of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) Systems and Endoscopists to Detect Colorectal Neoplastic Lesions on Endoscopy Video" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 14: 4840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144840
APA StyleMisumi, Y., Nonaka, K., Takeuchi, M., Kamitani, Y., Uechi, Y., Watanabe, M., Kishino, M., Omori, T., Yonezawa, M., Isomoto, H., & Tokushige, K. (2023). Comparison of the Ability of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) Systems and Endoscopists to Detect Colorectal Neoplastic Lesions on Endoscopy Video. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(14), 4840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144840









