The Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Type II (DMII) in the Multiple Sclerosis Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design, Search Strategy, and Selection Criteria
2.2. Quality Control and Bias Assessment
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
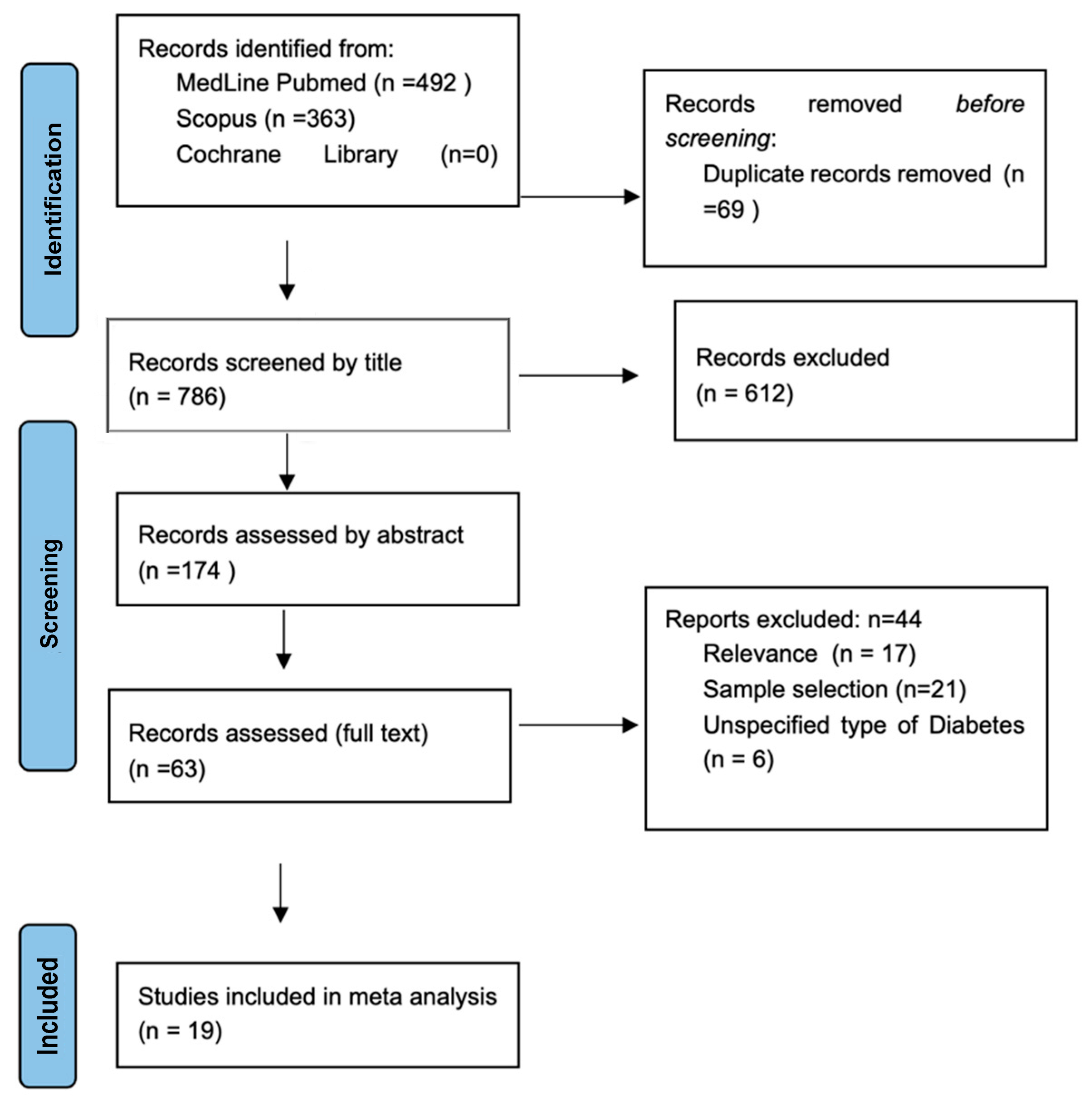
3.1. Literature Search and Included Studies
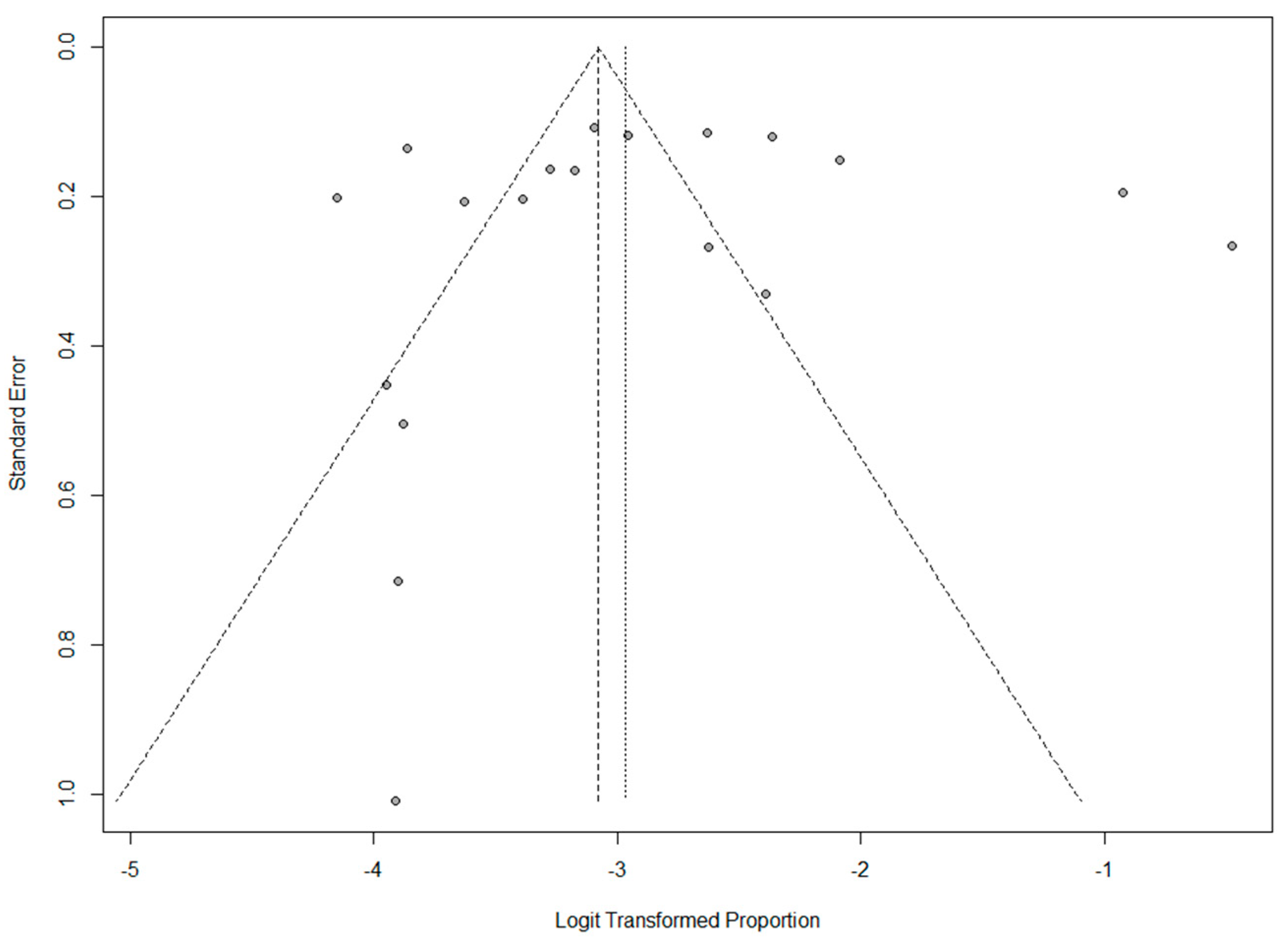
3.2. Quality Control of Included Studies
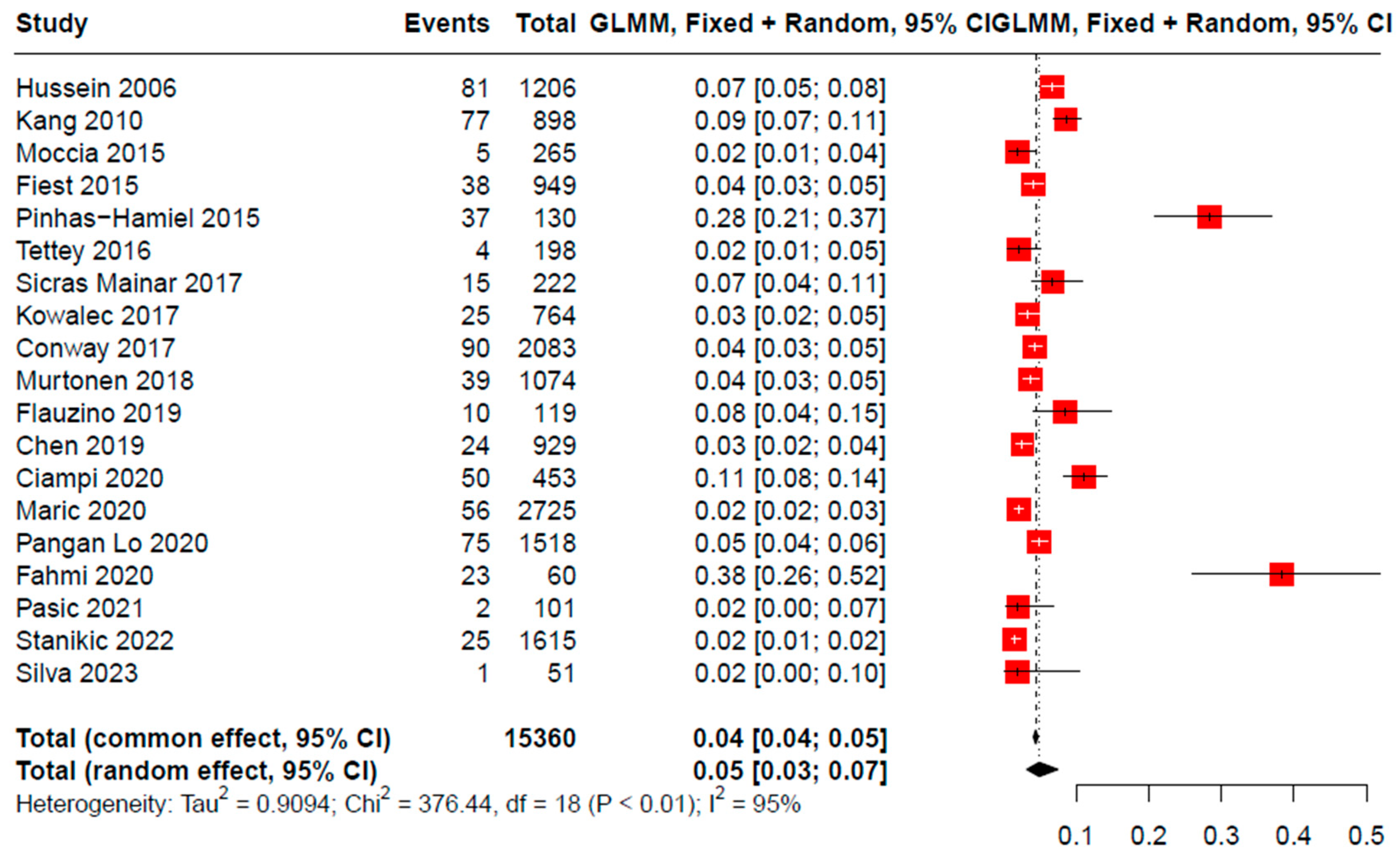
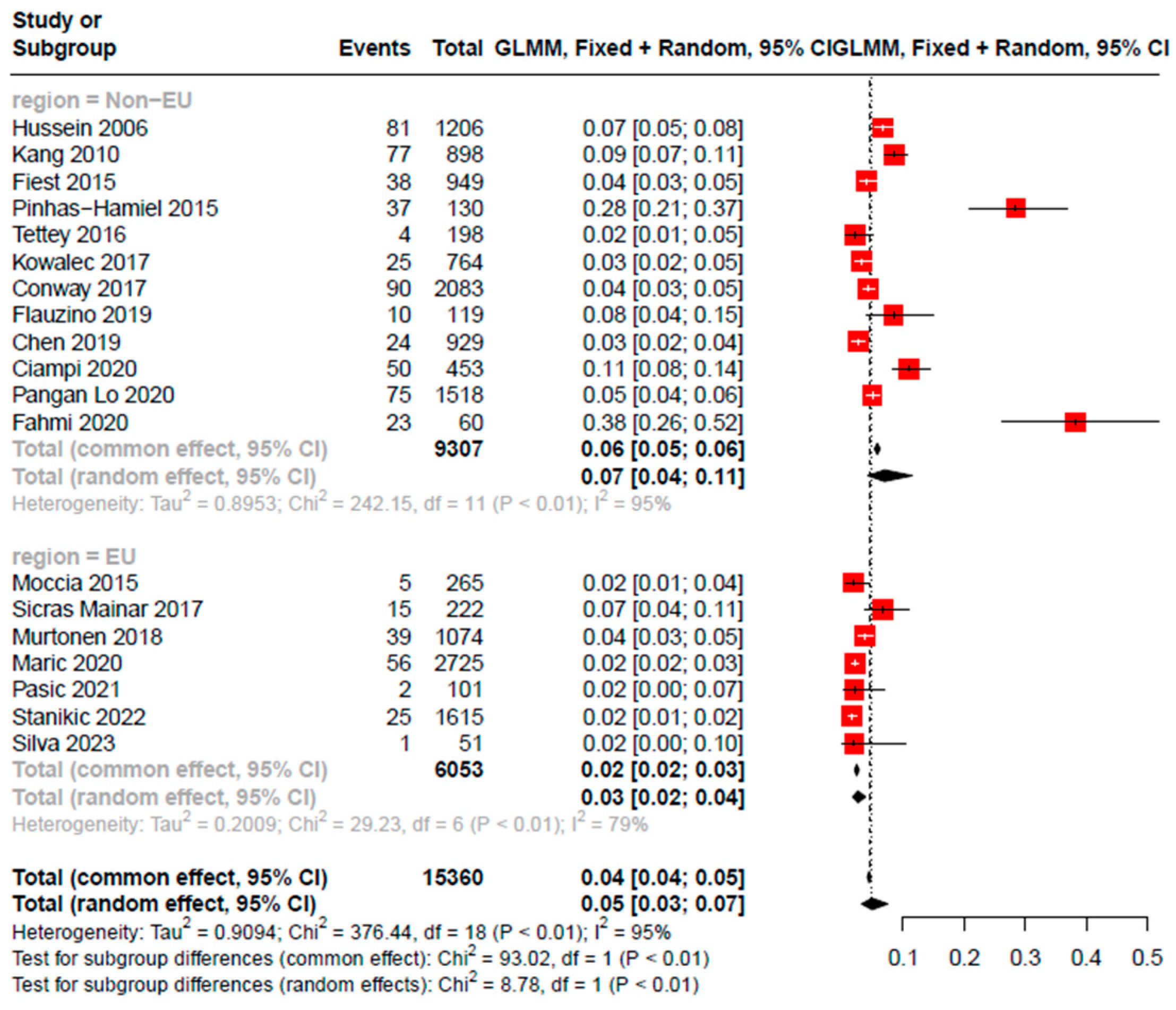
3.3. Overall and Subgroup Analyses
4. Preventive and Management Strategies
4.1. Multiple Sclerosis
4.2. Diabetes Mellitus Type II
4.3. Vitamin D
4.4. Lifestyle Factors
5. Strength and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauer, L.; Perneczky, J.; Sellner, J. A global view of comorbidity in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review with a focus on regional differences, methodology, and clinical implications. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4066–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maric, G.; Pekmezovic, T.; Tamas, O.; Veselinovic, N.; Jovanovic, A.; Lalic, K.; Mesaros, S.; Drulovic, J. Impact of comorbidities on the disability progression in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 145, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DF Diabetes Atlas 2021, 10th ed.; Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/ (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Singh, R.; Teel, C.; Sabus, C.; McGinnis, P.; Kluding, P. Fatigue in Type 2 Diabetes: Impact on Quality of Life and Predictors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165652. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.; Backholer, K.; Gearon, E.; Harding, J.; Freak-Poli, R.; Stevenson, C.; Peeters, A. Diabetes and risk of physical disability in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giannopapas, V.; Stavrogianni, K.; Christouli, N.; Kitsos, D.; Sideri, E.; Bakalidou, D.; Voumvourakis, K.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Tzartos, J.; Paraskevas, G.; et al. Do cardiovascular disease comorbidities affect the cognitive function of Multiple Sclerosis patients? J. Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 112, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Cruz, J.N.; Manuel-Apolinar, L.; Arellano-Flores, M.L.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, A.; Najera-Ahumada, A.G.; Cisneros-González, N. Health and quality of life outcomes impairment of quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2018, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.J.; Brennan, M.L.; Williams, H.C.; Dean, R.S. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; et al. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; The Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, South Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Evid.-Based Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W.G. The comparison of percentages in matched samples. Biometrika 1950, 37, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2018, 74, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Hussein, W.I.; Reddy, S.S. Prevalence of Diabetes in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1984–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H. Comorbidities amongst patients with multiple sclerosis: A population-based controlled study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moccia, M.; Lanzillo, R.; Palladino, R.; Maniscalco, G.T.; De Rosa, A.; Russo, C.; Carotenuto, A.; Allegorico, L.; Palladino, R.; Brescia Morra, V.; et al. The Framingham cardiovascular risk score in multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiest, K.; Fisk, J.; Patten, S.; Tremlett, H.; Wolfson, C.; Warren, S.; McKay, K.A.; Berrigan, L.; Marrie, R.A. Comorbidity is associated with pain-related activity limitations in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2015, 4, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Livne, M.; Harari, G.; Achiron, A. Prevalence of overweight, obesity and metabolic syndrome components in multiple sclerosis patients with significant disability. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Tettey, P.; Siejka, D.; Simpson, S., Jr.; Taylor, B.; Blizzard, L.; Ponsonby, A.; Dwyer, T.; van der Mei, I. Frequency of Comorbidities and Their Association with Clinical Disability and Relapse in Multiple Sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 2016, 46, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicras-Mainar, A.; Ruíz-Beato, E.; Navarro-Artieda, R.; Maurino, J. Comorbidity and metabolic syndrome in patients with multiple sclerosis from Asturias and Catalonia, Spain. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalec, K.; McKay, K.A.; Patten, S.B.; Fisk, J.D.; Evans, C.; Tremlett, H.; Marrie, R.A. Comorbidity increases the risk of relapse in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2017, 89, 2455–2461. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, D.S.; Thompson, N.R.; Cohen, J.A. Influence of hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obstructive lung disease on multiple sclerosis disease course. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtonen, A.; Kurki, S.; Hänninen, K.; Soilu-Hänninen, M.; Sumelahti, M. Common comorbidities and survival in MS: Risk for stroke, type 1 diabetes and infections. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 19, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flauzino, T.; Simão, A.N.C.; de Carvalho Jennings Pereira, W.L.; Alfieri, D.F.; Oliveira, S.R.; Kallaur, A.P.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Kaimen-Maciel, D.R.; Maes, M.; Reiche, E.M.V. Disability in multiple sclerosis is associated with age and inflammatory, metabolic and oxidative/nitrosative stress biomarkers: Results of multivariate and machine learning procedures. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Taylor, B.; Winzenberg, T.; Palmer, A.J.; Kirk-Brown, A.; van Dijk, P.; Simpson, S., Jr.; Blizzard, L.; Van Der Mei, I. Comorbidities are prevalent and detrimental for employment outcomes in people of working age with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, E.; Uribe-San-Martin, R.; Soler, B.; Molnar, K.; Reyes, D.; Keller, K.; Carcamo, C. Prevalence of comorbidities in Multiple Sclerosis and impact on physical disability according to disease phenotypes. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 46, 102565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maric, G.D.; Pekmezovic, T.D.; Mesaros, S.T.; Tamas, O.S.; Ivanovic, J.B.; Martinovic, V.N.; Andabaka, M.M.; Jovanovic, A.L.; Veselinovic, N.D.; Kisic-Tepavcevic, D.B.; et al. The prevalence of comorbidities in patients with multiple sclerosis: Population-based registry data. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, L.M.P.; Taylor, B.V.; Winzenberg, T.; Palmer, A.J.; Blizzard, L.; van der Mei, I. Change and onset-type differences in the prevalence of comorbidities in people with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmi, R.M.; El Ebeary, M.E.S.; Abd Alrasheed, E.M.; Elkhatib, T.H. Metabolic syndrome components and disease disability in egyptian multiple sclerosis patients. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 44, 102336. [Google Scholar]
- Bošnjak Pašić, M.; Tudor, K.I.; Mustač, F.; Rajič, F.; Pašić, H.; Vujević, L.; Šarac, H.; Vidrih, B. Comorbidities in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis in Croatia. Psychiatr. Danub. 2021, 33 (Suppl. S4), 475–479. [Google Scholar]
- Stanikić, M.; Salmen, A.; Chan, A.; Kuhle, J.; Kaufmann, M.; Ammann, S.; Schafroth, S.; Rodgers, S.; Haag, C.; Pot, C.; et al. Association of age and disease duration with comorbidities and disability: A study of the Swiss Multiple Sclerosis Registry. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 67, 104084. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.S.; Guimarães, J.; Sousa, C.; Mendonça, L.; Soares-dos-Reis, R.; Mendonça, T.; Abreu, P.; Sequeira, L.; Sá, M.J. Metabolic syndrome parameters and multiple sclerosis disease outcomes: A Portuguese cross-sectional study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 69, 104370. [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHLBI Obesity Education Initiative Expert Panel on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Obesity in Adults (US). Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report; NIH publication 98-4083; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1998. Available online: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2003 (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Park, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, M.H.; Oh, Y.H. Sedentary Lifestyle: Overview of Updated Evidence of Potential Health Risks. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2020, 41, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, F.; Bardoutsos, A.; Vidra, N. Obesity Prevalence in the Long-Term Future in 18 European Countries and in the USA. Obes. Facts 2020, 13, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivadinov, R.; Raj, B.; Ramanathan, M.; Teter, B.; Durfee, J.; Dwyer, M.; Bergsland, N.; Kolb, C.; Hojnacki, D.; Benedict, R.H. Autoimmune Comorbidities Are Associated with Brain Injury in Multiple Sclerosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Argüelles, A.; Méndez-Huerta, M.A.; Lozano, C.D.; Ruiz-Argüelles, G.J. Metabolomic profile of insulin resistance in patients with multiple sclerosis is associated to the severity of the disease. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 25, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Wens, I.; Dalgas, U.; Deckx, N.; Cools, N.; Eijnde, B. Does multiple sclerosis affect glucose tolerance? Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. DMSO 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, S.; Park, M.K. Glucocorticoid-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: An Important but Overlooked Problem. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 32, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Goodin, D.S. Glucocorticoid treatment of multiple sclerosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 122, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, Z.; Leung, C.; Sternberg, D.; Yu, J.; Hojnacki, D. Disease Modifying Therapies Modulate Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2014, 32, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hamid, N.; Jubori, T.; Farhan, A.; Mahrous, M.; Gouri, A.; Awad, E.; Breuss, J. Underlying Pathways for Interferon Risk to Type II Diabetes Mellitus. CDR 2013, 9, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Rao, X.; Zhong, J. Role of T Lymphocytes in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetes-Associated Inflammation. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 6494795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzartos, J.S.; Friese, M.A.; Craner, M.J.; Palace, J.; Newcombe, J.; Esiri, M.M.; Fugger, L. Interleukin-17 production in central nervous system-infiltrating T cells and glial cells is associated with active disease in multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitsch, A.; Schuchardt, J.; Bunkowski, S.; Kuhlmann, T.; Bruck, W. Acute axonal injury in multiple sclerosis. Correlation with demyelination and inflammation. Brain 2000, 123, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaskow, B.J.; Baecher-Allan, C. Effector T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a029025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wens, I.; Dalgas, U.; Stenager, E.; Eijnde, B.O. Risk factors related to cardiovascular diseases and the metabolic syndrome in multiple sclerosis—A systematic review. Mult. Scler. J. 2013, 19, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Kosowan, L.; Singer, A. Management of diabetes and hypertension in people with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 40, 101987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, T.; Barcellos, L.F.; Alfredsson, L. Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Lips, P.; Eekhoff, M.; van Schoor, N.; Oosterwerff, M.; de Jongh, R.; Krul-Poel, Y.; Simsek, S. Vitamin D and type 2 diabetes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 173, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Hjorth, M.F.; Astrup, A. Diet and exercise in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Country | DMII Cases | N | Age | EDSS | Disease Duration | Female % | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hussein [15] | 2006 | Saudi Arabia | 81 | 1206 | - | - | 9.9 | 64.1 | |
| Kang [16] | 2010 | Taiwan | 77 | 898 | - | - | 61 | ||
| Moccia [17] | 2015 | Naples | 5 | 265 | 42.2 | - | 8.2 | ||
| Fiest [18] | 2015 | Canada | 38 | 949 | 48.6 | 2.5 | 15.4 | 75.2 | median EDSS |
| Pinhas-Hamiel [19] | 2015 | Israel | 37 | 130 | 55.8 | 5.5 | 18.2 | 72.3 | |
| Tettey [20] | 2016 | Australia | 4 | 198 | 47.4 | 3 | 6 | 72 | median EDSS |
| Sicras Mainar [21] | 2017 | Catalonia | 15 | 222 | 45.5 | 3.2 | 13.4 | 64 | |
| Kowalec [22] | 2017 | Canada | 25 | 764 | 48.2 | 2.5 | 15.5 | 76.6 | median EDSS |
| Conway [23] | 2017 | USA | 90 | 2083 | 43 | - | 6.1 | 74.4 | PDSS instead of EDSS |
| Murtonen [24] | 2018 | Finland | 39 | 1074 | - | - | - | 70.6 | |
| Flauzino [25] | 2019 | Brazil | 10 | 119 | 42.8 | 3.2 | 43.1 | 68 | |
| Chen [26] | 2019 | Australia | 24 | 929 | 51.6 | - | 13 | 80.6 | PDSS instead of EDSS |
| Ciampi [27] | 2020 | Chile | 50 | 453 | 41 | 2 | 10.3 | 70.6 | median EDSS |
| Maric [28] | 2020 | Serbia | 56 | 2725 | 55.8 | 4 | 21.6 | 69.8 | median EDSS |
| Pangan Lo [29] | 2020 | Australia | 75 | 1518 | 55.7 | - | 20.5 | 79.6 | |
| Fahmi [30] | 2020 | Egypt | 23 | 60 | 31.4 | 2.8 | 4.3 | 68.3 | |
| Pasic [31] | 2021 | Croatia | 2 | 101 | 42.9 | 3.1 | 13.5 | 74.2 | |
| Stanikic [32] | 2022 | Swiss | 25 | 1615 | 47 | 11 | 73.3 | median age & duration, SDRSS instead of EDSS | |
| Silva [33] | 2023 | Portugal | 1 | 51 | 38.2 | 1 | 3 | 66.7 | median disease duration & EDSS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannopapas, V.; Palaiodimou, L.; Kitsos, D.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Stavrogianni, K.; Chasiotis, A.; Kosmidou, M.; Tzartos, J.S.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Bakalidou, D.; et al. The Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Type II (DMII) in the Multiple Sclerosis Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154948
Giannopapas V, Palaiodimou L, Kitsos D, Papagiannopoulou G, Stavrogianni K, Chasiotis A, Kosmidou M, Tzartos JS, Paraskevas GP, Bakalidou D, et al. The Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Type II (DMII) in the Multiple Sclerosis Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(15):4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154948
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannopapas, Vasileios, Lina Palaiodimou, Dimitrios Kitsos, Georgia Papagiannopoulou, Konstantina Stavrogianni, Athanasios Chasiotis, Maria Kosmidou, John S. Tzartos, George P. Paraskevas, Daphne Bakalidou, and et al. 2023. "The Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Type II (DMII) in the Multiple Sclerosis Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 15: 4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154948
APA StyleGiannopapas, V., Palaiodimou, L., Kitsos, D., Papagiannopoulou, G., Stavrogianni, K., Chasiotis, A., Kosmidou, M., Tzartos, J. S., Paraskevas, G. P., Bakalidou, D., Tsivgoulis, G., & Giannopoulos, S. (2023). The Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Type II (DMII) in the Multiple Sclerosis Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154948









