Radiomics-Based Analysis in the Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Elective neck dissection (ND): which is associated with esthetic and functional morbidity and it represents a procedure that may affect negatively the quality of life of the patient; the decision on whether to perform or not ND in all cases of cN0 neck is still under debate [6];
- Watch and wait policy: this is currently disregarded as a valid option because it was substantially demonstrated that elective neck dissection resulted in longer overall and disease-free survival than did therapeutic neck dissection after nodal relapse [7];
2. Materials and Methods
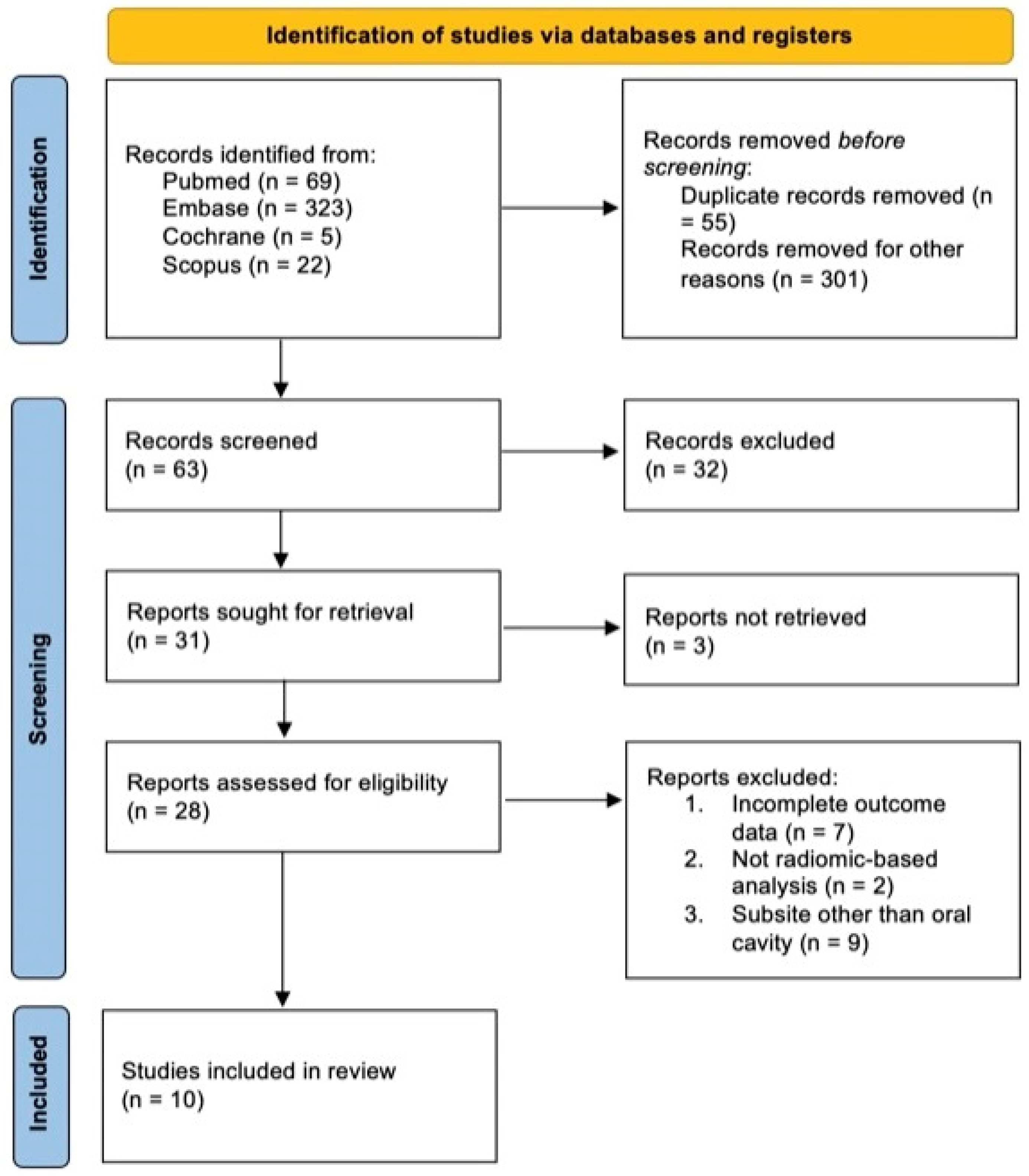
2.1. Searching Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Definition of the Outcomes, Synthesis of the Literature, and Meta-Analysis
2.4. Quality Assessment and Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elaiwy, O.; El Ansari, W.; AlKhalil, M.; Ammar, A. Epidemiology and pathology of oral squamous cell carcinoma in a multi-ethnic population: Retrospective study of 154 cases over 7 years in Qatar. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 60, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abati, S.; Bramati, C.; Bondi, S.; Lissoni, A.; Trimarchi, M. Oral Cancer and Precancer: A Narrative Review on the Relevance of Early Diagnosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, L.L.; Guimarães, Y.L.M.; Leite, A.K.; Cernea, C.R. Management of Stage III Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Light of the New Staging System: A Critical Review. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, L.V.; Acero, J.; Gulati, A.; Hölzle, F.; Hutchison, I.L.; Prabhu, S.; Testelin, S.; Wolff, K.-D.; Kalavrezos, N. Management of the clinically N0 neck in early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). An EACMFS position paper. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 48, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bree, R.; Takes, R.P.; Shah, J.P.; Hamoir, M.; Kowalski, L.P.; Robbins, K.T.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Sanabria, A.; Medina, J.E.; Rinaldo, A.; et al. Elective neck dissection in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Past, present and future. Oral Oncol. 2019, 90, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.-H.; Xu, J.-L.; Li, B.; Fan, T.-F.; Ji, T.; Zhang, C.-P. Elective versus therapeutic neck dissection in node-negative oral cancer: Evidence from five randomized controlled trials. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T.; Maheshwari, G.; Kannan, S.; Nair, S.; Agarwal, J.P. Should Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Be Considered the New Standard of Care for Early-Stage Clinically Node-Negative Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma? J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1706–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, C.; Stoeckli, S.J.; Haerle, S.K.; Broglie, M.A.; Huber, G.F.; Sorensen, J.A.; Bakholdt, V.; Krogdahl, A.; von Buchwald, C.; Bilde, A.; et al. Sentinel European Node Trial (SENT): 3-year results of sentinel node biopsy in oral cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, L.V.; Fuller, C.D. Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics in Head and Neck Cancer Care: Opportunities, Mechanics, and Challenges. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2021, 41, e225–e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Fan, R.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Application of radiomics and machine learning in head and neck cancers. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossinelli, C.; Tagliabue, M.; Ruju, F.; Cammarata, G.; Volpe, S.; Raimondi, S.; Zaffaroni, M.; Isaksson, J.L.; Garibaldi, C.; Cremonesi, M.; et al. The role of radiomics in tongue cancer: A new tool for prognosis prediction. Head Neck 2023, 45, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roepman, P.; Wessels, L.F.A.; Kettelarij, N.; Kemmeren, P.; Miles, A.J.; Lijnzaad, P.; Tilanus, M.G.J.; Koole, R.; Hordijk, G.-J.; van der Vliet, P.C.; et al. An expression profile for diagnosis of lymph node metastases from primary head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Abu Bakar, M.; Sarwar, A.; Adeel, M.; Batool, F.; Malik, K.I.; Jamshed, A.; Hussain, R. Depth of invasion (DOI) as a predictor of cervical nodal metastasis and local recurrence in early stage squamous cell carcinoma of oral tongue (ESSCOT). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.S.; Davis, M.E.; Vera, D.R.; Lai, S.Y.; Guo, T.W. Role of sentinel lymph node biopsy for oral squamous cell carcinoma: Current evidence and future challenges. Head Neck 2023, 45, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, V. Cervical lymphadenopathy: What radiologists need to know. Cancer Imaging 2004, 4, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Brekel, M.W.; Stel, H.V.; Castelijns, J.A.; Nauta, J.J.; van der Waal, I.; Valk, J.; Meyer, C.J.; Snow, G.B. Cervical lymph node metastasis: Assessment of radiologic criteria. Radiology 1990, 177, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Deep learning radiomics model related with genomics phenotypes for lymph node metastasis prediction in colorectal cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 167, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, M.; Jian, L.; Bi, F.; Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, N.; Yu, X. Radiomic Score as a Potential Imaging Biomarker for Predicting Survival in Patients with Cervical Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 706043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Shi, S.; Xie, W.; Liu, H.; Su, Y.; Huang, J.; Lin, T. A Radiomics Nomogram for the Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, M.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, J.A.; Van Der Windt, D.A.; Cartwright, J.L.; Côté, P.; Bombardier, C. Assessing Bias in Studies of Prognostic Factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. Radiomics based on magnetic resonance imaging for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer: Machine learning study. Head Neck 2022, 44, 2786–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, H.; Yamashiro, T.; Heianna, J.; Nakasone, T.; Kimura, Y.; Mimura, H.; Murayama, S. Nodal-based radiomics analysis for identifying cervical lymph node metastasis at levels I and II in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma using contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 7440–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Tan, R.; Feng, K.; Hu, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Liu, X. Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Radiomics Features Associated with Depth of Invasion Predicted Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Tongue Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, K.; Kawahara, D.; Murakami, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Katsuta, T.; Imano, N.; Nishibuchi, I.; Saito, A.; Konishi, M.; Kakimoto, N.; et al. Development of a radiomics and machine learning model for predicting occult cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with tongue cancer. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2022, 134, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.-W.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, S.; Wu, W.-J.; Wang, L.-X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, M.-W. Tumor radiomics signature for artificial neural network-assisted detection of neck metastasis in patient with tongue cancer. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 49, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committeri, U.; Fusco, R.; Di Bernardo, E.; Abbate, V.; Salzano, G.; Maglitto, F.; Orabona, G.D.; Piombino, P.; Bonavolontà, P.; Arena, A.; et al. Radiomics Metrics Combined with Clinical Data in the Surgical Management of Early-Stage (cT1–T2 N0) Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Study. Biology 2022, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudoh, T.; Haga, A.; Kudoh, K.; Takahashi, A.; Sasaki, M.; Kudo, Y.; Ikushima, H.; Miyamoto, Y. Radiomics analysis of [18F]-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography for the prediction of cervical lymph node metastasis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral. Radiol. 2023, 39, 41–50, Erratum in: Oral. Radiol. 2022, 39, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, A.; Abdalaty, A.H.; Hasan, M.; Tadic, T.; Patel, T.; Giuliani, M.; Kim, J.; Ringash, J.; Cho, J.; Bratman, S.; et al. PO-1549: Non-invasive prediction of lymph node risk in oral cavity cancer patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 152, S838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, A.; Hosni-Abdalaty, A.; Hasan, M.; Kim, J.; Ringash, J.; Cho, J.; Hope, A. Investigating Radiomics to Predict Positive Lymph Nodes in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC). Scientific Abstracts and Sessions. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e94–e670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yuan, Y.; Tao, X. Histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for predicting occult lymph node metastasis in early-stage oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Gong, G.-Z.; Qiu, Q.-T.; Han, Y.-W.; Lu, H.-M.; Yin, Y. Radiomics for Diagnosis and Radiotherapy of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 767134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajgor, A.D.; Patel, S.; McCulloch, D.; Obara, B.; Bacardit, J.; McQueen, A.; Aboagye, E.; Ali, T.; O’hara, J.; Hamilton, D.W. The application of radiomics in laryngeal cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, M.; Bonjoc, K.-J.C.; Gorlin, D.; Wong, C.W.; Salem, A.; La, V.; Filippov, A.; Chaudhry, A.; Imam, M.H.; Chaudhry, A.A. Diagnostic Utility of Radiomics in Thyroid and Head and Neck Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 639326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aringhieri, G.; Fanni, S.C.; Febi, M.; Colligiani, L.; Cioni, D.; Neri, E. The Role of Radiomics in Salivary Gland Imaging: A Systematic Review and Radiomics Quality Assessment. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitto, C.; Mercante, G.; Ammirabile, A.; Cerri, L.; De Giorgi, T.; Lofino, L.; Vatteroni, G.; Casiraghi, E.; Marra, S.; Esposito, A.A.; et al. Radiomics-based machine learning for the diagnosis of lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck cancer: Systematic review. Head Neck 2023, 45, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, V.; Cuocolo, R.; Ricciardi, C.; Ugga, L.; Cocozza, S.; Verde, F.; Stanzione, A.; Napolitano, V.; Russo, D.; Improta, G.; et al. Prediction of Tumor Grade and Nodal Status in Oropharyngeal and Oral Cavity Squamous-cell Carcinoma Using a Radiomic Approach. Anticancer. Res. 2020, 40, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brekel, M.W.; Castelijns, J.A.; Stel, H.V.; Golding, R.P.; Meyer, C.J.; Snow, G.B. Modern imaging techniques and ultrasound-guided aspiration cytology for the assessment of neck node metastases: A prospective comparative study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1993, 250, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C. 18FDG-PET/CT for the detection of regional nodal metastasis in patients with head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bree, R.; Takes, R.P.; Castelijns, J.A.; Medina, J.E.; Stoeckli, S.J.; Mancuso, A.A.; Hunt, J.L.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Triantafyllou, A.; Teymoortash, A.; et al. Advances in diagnostic modalities to detect occult lymph node metastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2015, 37, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reel, P.S.; Reel, S.; Pearson, E.; Trucco, E.; Jefferson, E. Using machine learning approaches for multi-omics data analysis: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 49, 107739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.P.; Senadeera, M.; Jacobs, S.; Coghlan, S.; Le, V. Trust and medical AI: The challenges we face and the expertise needed to overcome them. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2021, 28, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babushkina, D. Are we justified attributing a mistake in diagnosis to an AI diagnostic system? AI Ethics 2023, 3, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Country | Study Type (Retrospective R, Prospective P) | Imaging Technique (MRI 1, CT 2, PET 3) | Feature Extraction | Software | Year of Recruitment | Sample Size (n) | Primary/Train Cohort (%) | Validation/Test Cohort (%) | Subsite (%) | Staging | Positive LNs (n) | Negative LNs (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang Y et al., 2022 [24] | China | R | 1 | LN | LIFEx (EVOMICS) | 2013– 2021 | 160 | 75 | 25 | 100 oral cavity (70.1 tongue) | 61 I–II 39 III–IV | NA | NA |
| Tomita et al., 2021 [25] | Japan | R | 2 | LN | Python | 2013– 2017 | 44 | 70 | 30 | 100 oral (tongue, gingiva, floor of mouth) | I–IV | 51 | 150 |
| Wang F et al., 2022 [26] | China | R | 1 | Tumor | Python (version 3.5.2) | 2012– 2019 | 236 | 67 | 33 | 100 tongue | I–IV | 99 | 137 |
| Kubo et al., 2022 [27] | Japan | R | 2 | LN | Python (Pyradiomics software) | 2008– 2019 | 161 | NA | NA | 100 tongue | I–III | 63 | NA |
| Zhong et al., 2022 [28] | China | R | 2 | Tumor | Matlab 2018b (MathWork) | 2013– 2018 | 313 | 60 | 40 | 100 tongue | I–IV | 143 | 170 |
| Committeri et al., 2022 [29] | Italy | R | 2 | Tumor | PyRadiomics | 2016– 2020 | 81 | 80 | 20 | 100 tongue | I–II | NA | NA |
| Kudoh et al., 2022 [30] | Japan | R | 3 | Tumor | Matlab | 2015– 2019 | 40 | 80 | 20 | 100 tongue | 15 I, 30 II, 18 III, 37 IV | 19 pts | 21 pts |
| Traverso et al., 2020 [31] | Multicentric | R | 1 | NA | PyRadiomics v2.1.2 | 2003– 2017 | 243 | 70 | 30 | 100 oral | NA | NA | NA |
| Traverso et al., 2019 [32] | Multicentric | R | 1 | Tumor | PyRadiomics | NA | 134 | 80 | 20 | 100 oral | NA | NA | NA |
| Ren et al., 2022 [33] | China | R | 1 | Tumor | Pyradiomics | 2015– 2021 | 55 | NA | NA | 100 tongue | I–II | 21 pts | 34 pts |
| Study | Sensitivity | Specificity | ACC (95%CI) | AUC (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang Y et al., 2022 [24] | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.82 |
| Tomita et al., 2021 [25] | 0.74 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| Wang F et al., 2022 [26] | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| Kubo et al., 2022 [27] | NA | NA | 0.85 | 0.92 |
| Zhong et al., 2022 [28] | 0.82 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.91 |
| Committeri et al., 2022 [29] | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.93 |
| Kudoh et al., 2022 [30] | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.68 ± 0.13 | 0.79 |
| Traverso et al., 2020 [31] | NA | NA | 0.70 (0.67–0.71) | NA |
| Traverso et al., 2019 [32] | NA | NA | NA | 0.83 |
| Ren et al., 2022 [33] | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.87 (0.77–0.96) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Locatello, L.G.; Maggiore, G.; Gallo, O. Radiomics-Based Analysis in the Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154958
Jiang S, Locatello LG, Maggiore G, Gallo O. Radiomics-Based Analysis in the Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(15):4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154958
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Serena, Luca Giovanni Locatello, Giandomenico Maggiore, and Oreste Gallo. 2023. "Radiomics-Based Analysis in the Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 15: 4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154958
APA StyleJiang, S., Locatello, L. G., Maggiore, G., & Gallo, O. (2023). Radiomics-Based Analysis in the Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154958








