Clinical Features and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Definitions and Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Acute Kidney Injury
3.3. Factors Associated with AKI
3.4. Predictors of ICU Mortality in AKI Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)—World Health Organization. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- Tunisia: WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Fominskiy, E.V.; Scandroglio, A.M.; Monti, G.; Calabrò, M.G.; Landoni, G.; Dell’Acqua, A.; Beretta, L.; Moizo, E.; Ravizza, A.; Monaco, F.; et al. Prevalence, Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Invasively Ventilated COVID-19 Patients with Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Replacement Therapy. Blood Purif. 2020, 50, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, P.; Russo, E.; Picciotto, D.; Cappadona, F.; Battaglia, Y.; Traverso, G.B.; Viazzi, F. Changes of Acute Kidney Injury Epidemiology during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19: The Chinese Experience. Semin. Nephrol. 2020, 40, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenezi, F.K.; Almeshari, M.A.; Mahida, R.; Bangash, M.N.; Thickett, D.R.; Patel, J.M. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients with and without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during the first wave of COVID-19: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; Chaudhary, K.; Saha, A.; Chauhan, K.; Vaid, A.; Zhao, S.; Paranjpe, I.; Somani, S.; Richter, F.; Miotto, R.; et al. AKI in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 32, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Hayek, S.S.; Wang, W.; Chan, L.; Mathews, K.S.; Melamed, M.L.; Brenner, S.K.; Leonberg-Yoo, A.; Schenck, E.J.; Radbel, J.; et al. Factors Associated with Death in Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in the US. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifi, A.; Abdellatif, S.; Masseoudi, Y.; Mehdi, A.; Benjima, O.; Seghir, E.; Cherif, F.; Touil, Y.; Jeribi, B.; Daly, F.; et al. COVID-19–induced acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: Epidemiology, risk factors, and outcome. Acute Crit. Care 2021, 36, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Aeddula, N.R. Chronic Renal Failure; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- NCI Comorbidity Index Overview. Available online: https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/seermedicare/considerations/comorbidity.html (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Le Gall, J.-R. A New Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) Based on a European/North American Multicenter Study. JAMA 1993, 270, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SOFA Score What It Is and How to Use It in Triage|Technical Resources. Available online: https://asprtracie.hhs.gov/technical-resources/resource/3981/sofa-score-what-it-is-and-how-to-use-it-in-triage (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Aspelin, P.; Barsoum, R.S.; Burdmann, E.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Herzog, C.A.; Joannidis, M.; Kribben, A.; Levey, A.S.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ARDS Definition of Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Symptoms and Severity. Available online: https://www.who.int/westernpacific/emergencies/covid-19/information/asymptomatic-covid-19 (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Green, R.S.; Edwards, J.; Sabri, E.; Fergusson, D. Evaluation of the incidence, risk factors, and impact on patient outcomes of postintubation hemodynamic instability. Can. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 14, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanelli, V.; Fiorentino, M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; Ronco, C.; Castellano, G. Acute kidney injury in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farouk, S.S.; Fiaccadori, E.; Cravedi, P.; Campbell, K.N. COVID-19 and the kidney: What we think we know so far and what we don’t. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaly, Z.; Kinaneh, S.; Skorecki, K. Renal Manifestations of Covid-19: Physiology and Pathophysiology. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, U.; Ramachandran, P.; Spitalewitz, S.; Alasadi, L.; Chakraborti, A.; Azhar, M.; Mikhalina, G.; Sherazi, A.; Narh, J.T.; Khattar, P.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19 Patients: An Inner City Hospital Experience and Policy Implications. Am. J. Nephrol. 2020, 51, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; On behalf of the University Hospital Southampton Critical Care Team and the REACT COVID Investigators; Ferrari, M.; Nasim-Mohi, M.; Jackson, A.; Beecham, R.; Veighey, K.; Cusack, R.; Richardson, D.; Grocott, M.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of critically ill COVID-19 patients with acute kidney injury: A single centre cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, M.; Attallah, N.; Badr, M.; Abdallah, K.; De Oliveira, B.; Nadeem, A.; Varghese, Y.; Munde, D.; Salam, S.; Abduljawad, B.; et al. Severe Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 Admitted to ICU: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumlertgul, N.; Pirondini, L.; Cooney, E.; Kok, W.; Gregson, J.; Camporota, L.; Lane, K.; Leach, R.; Ostermann, M. Acute kidney injury prevalence, progression and long-term outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A cohort study. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansrivijit, P.; Qian, C.; Boonpheng, B.; Thongprayoon, C.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Ghahramani, N. Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury and Its Association with Mortality in Patients with Covid-19: A Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Med. 2020, 68, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienza, N.; Puntillo, F.; Romagnoli, S.; Tritapepe, L. Acute Kidney Injury in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infected Patients: A Meta-Analytic Study. Blood Purif. 2020, 50, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doher, M.P.; de Carvalho, F.R.T.; Scherer, P.F.; Matsui, T.N.; Ammirati, A.L.; da Silva, B.C.; Barbeiro, B.G.; Carneiro, F.D.; Corrêa, T.D.; Ferraz, L.J.R.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Risk Factors and Outcomes: A Single-Center Experience in Brazil. Blood Purif. 2020, 50, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Den Akker, J.P.; Egal, M.; Groeneveld, J.A.B. Invasive mechanical ventilation as a risk factor for acute kidney injury in the critically ill: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Shao, S.-C.; Hsu, C.-K.; Wu, I.-W.; Hung, M.-J.; Chen, Y.-C. Incidence of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmon, M.; Clec’H, C.; Adrie, C.; Argaud, L.; Allaouchiche, B.; Azoulay, E.; Bouadma, L.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Haouache, H.; Schwebel, C.; et al. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Risk of AKI among Critically Ill Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joannidis, M.; Forni, L.G.; Klein, S.J.; Honore, P.M.; Kashani, K.; Ostermann, M.; Prowle, J.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Darmon, M.; et al. Lung–kidney interactions in critically ill patients: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 21 Workgroup. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 654–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evrard, B.; Goudelin, M.; Montmagnon, N.; Fedou, A.-L.; Lafon, T.; Vignon, P. Cardiovascular phenotypes in ventilated patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Straaten, H.M.O.-V.; Forni, L.G. Fluid overload and acute kidney injury: Cause or consequence? Crit. Care 2015, 19, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salunke, B.G. Fluid Overload and Acute Kidney Injury. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 24, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finfer, S.; Myburgh, J.; Bellomo, R. Intravenous fluid therapy in critically ill adults. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prowle, J.R.; Echeverri, J.E.; Ligabo, E.V.; Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R. Fluid balance and acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 6, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testani, J.M.; Khera, A.V.; Sutton, M.G.S.J.; Keane, M.; Wiegers, S.E.; Shannon, R.P.; Kirkpatrick, J.N. Effect of Right Ventricular Function and Venous Congestion on Cardiorenal Interactions During the Treatment of Decompensated Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bansal, S.; Prasad, A.; Linas, S. Right Heart Failure—Unrecognized Cause of Cardiorenal Syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1795–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lee, J.; Johnson, A.E.; Mark, R.G.; Celi, L.A.; Danziger, J. Right Ventricular Function, Peripheral Edema, and Acute Kidney Injury in Critical Illness. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchino, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R.; Doig, G.S.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; et al. Acute Renal Failure in Critically Ill PatientsA Multinational, Multicenter Study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezerra, R.; Teles, F.; Mendonca, P.B.; Damte, T.; Likaka, A.; Ferrer-Miranda, E.; de Albuquerque, J.O.; Filho, J.L.D.L. Outcomes of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury in COVID-19 infection: An observational study. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumayyaleh, M.; Nuñez-Gil, I.J.; El-Battrawy, I.; Estrada, V.; Becerra-Muñoz, V.M.; Uribarri, A.; Fernández-Rozas, I.; Feltes, G.; Arroyo-Espliguero, R.; Trabattoni, D.; et al. Sepsis of Patients Infected by SARS-CoV-2: Real-World Experience from the International HOPE-COVID-19-Registry and Validation of HOPE Sepsis Score. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.H.; Kim, C.S.; Choi, J.S.; Bae, E.H.; Ma, S.K.; Kim, S.W. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Sepsis and Septic Shock: Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, E.; Jo, S.-K. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Septic Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients. Korean J. Nephrol. 2011, 30, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Septic Shock with Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in Wuhan, China. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/av/2022/3178283/ (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Starke, K.R.; Reissig, D.; Petereit-Haack, G.; Schmauder, S.; Nienhaus, A.; Seidler, A. The isolated effect of age on the risk of COVID-19 severe outcomes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.; Gameiro, J.; Oliveira, J.; Fonseca, J.A.; Duarte, I.; Bernardo, J.; Branco, C.; Costa, C.; Carreiro, C.; Braz, S.; et al. Acute Kidney Disease and Mortality in Acute Kidney Injury Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, H.; Schwarz, G.L.; Flaatten, H.; De Lange, D.W.; Guidet, B.; Dechartres, A. Mortality of Older Patients Admitted to an ICU: A Systematic Review. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 49, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carteaux, G.; Parfait, M.; Combet, M.; Haudebourg, A.-F.; Tuffet, S.; Dessap, A.M. Patient-Self Inflicted Lung Injury: A Practical Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.J.; Gattinoni, L.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet 2021, 398, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pun, B.T.; Badenes, R.; La Calle, G.H.; Orun, O.M.; Chen, W.; Raman, R.; Simpson, B.-G.K.; Wilson-Linville, S.; Olmedillo, B.H.; de la Cueva, A.V.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors for delirium in critically ill patients with COVID-19 (COVID-D): A multicentre cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Backer, D.; Aissaoui, N.; Cecconi, M.; Chew, M.S.; Denault, A.; Hajjar, L.; Hernandez, G.; Messina, A.; Myatra, S.N.; Ostermann, M.; et al. How can assessing hemodynamics help to assess volume status? Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1482–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network; Brower, R.G.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; Wheeler, A. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelosi, P.; Ball, L.; Barbas, C.S.V.; Bellomo, R.; Burns, K.E.A.; Einav, S.; Gattinoni, L.; Laffey, J.G.; Marini, J.J.; Myatra, S.N.; et al. Personalized mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, J.R.; Jones, B.J.; Fernandes, B.M.; Law, D.J.; Cooper, J.A.; Wise, M.P. Mechanical ventilation variables associated with high pulmonary artery pressures in ARDS patients: A post hoc analysis. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Tonetti, T.; Cressoni, M.; Cadringher, P.; Herrmann, P.; Moerer, O.; Protti, A.; Gotti, M.; Chiurazzi, C.; Carlesso, E.; et al. Ventilator-related causes of lung injury: The mechanical power. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.V.; Munroe, E.; Weirauch, A.J.; Fiorino, K.; Culter, C.A.; Nelson, K.; Labaki, W.W.; Choi, P.J.; Co, I.; Standiford, T.J.; et al. Electric impedance tomography-guided PEEP titration reduces mechanical power in ARDS: A randomized crossover pilot trial. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzzo, G.; Spadaro, S.; Waldmann, A.D.; Böhm, S.H.; Ragazzi, R.; Marangoni, E.; Alvisi, V.; Spinelli, E.; Mauri, T.; Volta, C.A. Heterogeneity of regional inflection points from pressure-volume curves assessed by electrical impedance tomography. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Qin, S.; Chen, C.; Mei, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Gao, Y. Emerging Trends and Hot Spots of Electrical Impedance Tomography Applications in Clinical Lung Monitoring. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 813640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerichs, I.; Amato, M.B.P.; Van Kaam, A.H.; Tingay, D.; Zhao, Z.; Grychtol, B.; Bodenstein, M.; Gagnon, H.; Böhm, S.H.; Teschner, E.; et al. Chest electrical impedance tomography examination, data analysis, terminology, clinical use and recommendations: Consensus statement of the TRanslational EIT developmeNt stuDy group. Thorax 2016, 72, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomicic, V.; Cornejo, R. Lung monitoring with electrical impedance tomography: Technical considerations and clinical applications. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 3122–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumulative Fluid Accumulation Is Associated with the Development of Acute Kidney Injury and Non-Recovery of Renal Function: A Retrospective Analysis|Critical Care|Full Text. Available online: https://ccforum.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13054-019-2673-5 (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Fluid Management in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury—A Post-Hoc Analysis of the FINNAKI Study|Elsevier Enhanced Reader. Available online: https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S0883944121000812?token=E1BF5FB65ABEDA3BEFCC294A7435E3C4B3BAF5BEFF3D7151D1A7AF879B1F80AC719BB6CED16C587290A7145881AB0A83&originRegion=eu-west-1&originCreation=20230306191350 (accessed on 6 March 2023).


| Total (n = 465) | AKI (n = 229) | No AKI (n = 236) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64 [54–71] | 65 [55–71] | 64 [53–71] | 0.546 |
| Male | 290 (62.4) | 137 (59.8) | 151 (63.9) | 0.356 |
| CCI | 3 [1–4] | 3 [2–4] | 2 [1–3] | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Hypertension | 219 (47.1) | 116 (50.7) | 100 (42.4) | 0.073 |
| Diabetes | 210 (45.2) | 123 (53.7) | 86 (36.4) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 178 (38.2) | 106 (46.3) | 72 (30.5) | <0.001 |
| Coronary disease | 50 (10.8) | 19 (8.3) | 29 (12.3) | 0.157 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 53 (11.4) | 35 (15.3) | 18 (7.6) | 0.009 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 17 (3.7) | 7 (3.1) | 12 (5.1) | 0.269 |
| Neoplasia | 13 (2.8) | 6 (2.6) | 6 (2.5) | 0.958 |
| Immunosuppression | 29 (6.2) | 18 (7.9) | 10 (4.2) | 0.101 |
| Illness severity scores | ||||
| SOFA | 3 [2–5] | 4 [3–5] | 3 [2–4] | <0.001 |
| SAPS II | 31 [24–38] | 33 [27–42] | 29 [23–35] | <0.001 |
| Pre-ICU management delay (days) | 11 [8–14] | 11 [8–14] | 11 [8–14] | 0.307 |
| Intensive care unit course | ||||
| IMV on admission | 14 (3) | 10 (4.4) | 4 (1.7) | 0.123 |
| Shock on admission | 35 (7.5) | 25 (10.9) | 10 (4.3) | 0.007 |
| P/F ratio at admission | 120 [90–160] | 120 [84–160] | 118 [85–160] | 0.287 |
| Use of invasive ventilation | 244 (52.5) | 144 (62.9) | 100 (42.4) | <0.001 |
| Duration of IMV, (days) | 7 [4–11] | 8 [4–12] | 7 [4–12] | 0.422 |
| Use of vasopressors | 253 (54.4) | 150 (65.5) | 103 (43.6) | <0.001 |
| Duration of vasopressor use, (days) | 7 [4–11] | 7 [5–12] | 7 [4–12] | 0.074 |
| Positive fluid balance on day 3 | 219 (47.1) | 139 (60.7) | 80 (34.3) | <0.001 |
| Cumulative fluid balance at day 3, (mL) | −135 [−2000/+2162] | 690 [−1275/+3275] | −550 [−2450/+800] | <0.001 |
| ICU LOS, (days) | 8 [5–13] | 9 [6–16] | 7.5 [5–12] | 0.001 |
| Adverse events | ||||
| Shock during ICU stay | 212 (45.5) | 132 (57.6) | 80 (33.9) | <0.001 |
| Post-intubation hypotension | 93 (20) | 58 (25.3) | 35 (14.8) | 0.005 |
| Septic shock | 143 (30.8) | 87 (38) | 56 (23.7) | 0.001 |
| Right heart failure | 103 (22.2) | 71 (31) | 32 (13.6) | <0.001 |
| Hemorrhagic shock | 9 (1.9) | 4 (1.7) | 5 (2.1) | - |
| ICU mortality | 228 (49) | 135 (59.2) | 93 (40.8) | <0.001 |
| Admission laboratory profile | ||||
| Creatinine (µmol/L), (n = 420) | 70 [54–96] | 70 [57–100] | 69 [57–89] | 0.499 |
| Urea (mmol/L), (n = 420) | 7 [5–10.5] | 7.7 [5–11] | 7 [5–10] | 0.014 |
| CRP (mg/L), (n = 109) | 130 [74–176] | 154 [116–238] | 112 [62–162] | 0.005 |
| WBC (109/L), (n = 328) | 10.3 [7.7–14.6] | 11.2 [7.9–15.1] | 9.8 [7.4–14] | 0.167 |
| Hb (g/dL), (n = 328) | 12 [10.2–13] | 11.8 [10–12.8] | 12 [10.8–13] | 0.090 |
| Lymphocytes (109/L), (n = 328) | 0.7 [0.5–1] | 0.7 [0.5–1] | 0.8 [0.5–1] | 0.737 |
| D-dimer (µg/mL), (n = 49) | 1000 [507–2234] | 1300 [511–2238] | 838 [506–1921] | 0.244 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL), (n = 93) | 664 [238–2734] | 410 [224–2111] | 930 [414–3280] | 0.429 |
| pH, (n = 393) | 7.43 [7.36–7.46] | 7.42 [7.36–7.46] | 7.43 [7.37–7.46] | 0.276 |
| Bicarbonates (mmol/L), (n = 393) | 23 [20–25] | 23 [20–25] | 23.6 [21–26] | 0.795 |
| All AKI Patients (n = 229) | Survivors (n = 94) | Non Survivors (n = 135) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, (years) | 65 [55–71] | 58 [47–67] | 68 [62–73] | <0.001 |
| Male | 137 (59.8) | 51 (54.3) | 86 (63.7) | 0.151 |
| CCI | 3 [2–4] | 2 [1–4] | 3 [2–4] | 0.009 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Hypertension | 116 (50.7) | 40 (42.6) | 76 (56.3) | 0.041 |
| Diabetes | 123 (53.7) | 41 (43.6) | 82 (60.7) | 0.011 |
| Obesity | 106 (46.3) | 35 (37.2) | 71 (52.6) | 0.022 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 7 (3.1) | 2 (2.1) | 5 (3.7) | 0.496 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 35 (15.3) | 9 (9.6) | 26 (19.3) | 0.045 |
| Neoplasia | 6 (2.6) | 0 (0) | 6 (4.4) | - |
| Immunosuppression | 18 (7.9) | 6 (6.4) | 12 (8.9) | 0.488 |
| Illness severity scores | ||||
| SOFA | 4 [3–5] | 4 [2–5] | 4 [3–5] | 0.179 |
| SAPS II | 33 [27–42] | 27.5 [24–38.5] | 34 [29–44] | 0.001 |
| KDIGO stages | ||||
| Stage 1 | 30 (13.1) | 17 (18.1) | 13 (9.6) | 0.062 |
| Stage 2 | 27 (11.8) | 15 (16) | 12 (8.9) | 0.103 |
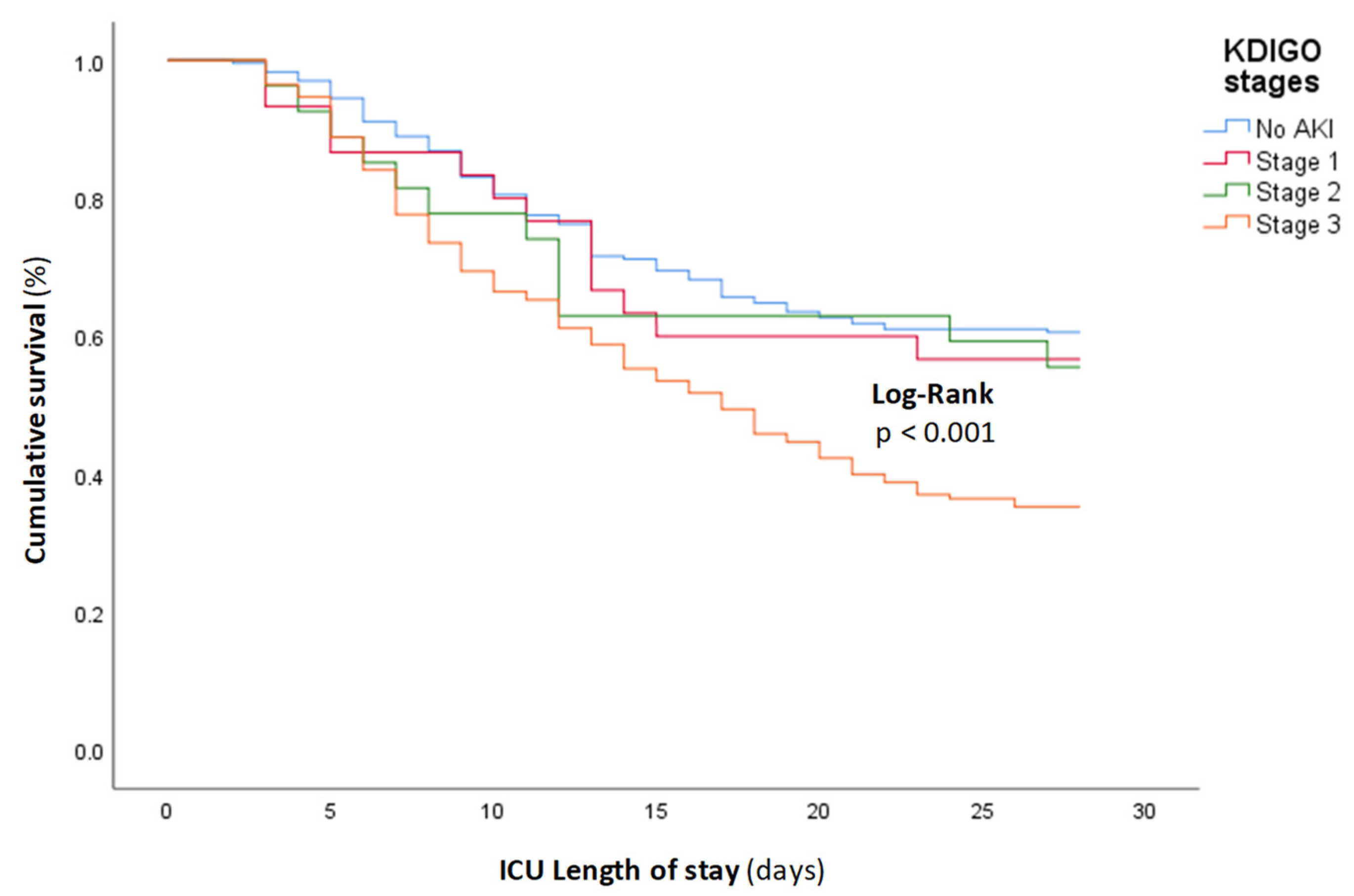
| Stage 3 | 172 (75.1) | 62 (66) | 110 (81.5) | 0.008 |
| Etiology of AKI | ||||
| Prerenal | 67 (29.2) | 17 (18.1) | 50 (37) | 0.002 |
| Type 1 CRS | 37 (16.2) | 0 | 37 (27.4) | - |
| Other than CRS | 30 (13.1) | 17 (18.1) | 13 (9.6) | - |
| Intrinsic renal | 162 (70.7) | 77 (81.9) | 85 (63) | 0.002 |
| ICU course | ||||
| IMV use | 144 (62.9) | 17 (18.1) | 127 (94.1) | <0.001 |
| Duration of IMV (days) | 8 [4–12] | 6 [3–9] | 8 [4–12] | 0.426 |
| RRT | 47 (20.5) | 3 (3.2) | 44 (32.6) | <0.001 |
| Cumulative fluid balance at day 3 (mL/3 days) | 690 [−1275/+3275] | 750 [−1275/+3750] | 650 [−1350/+3000] | 0.618 |
| Positive fluid balance | 139 (60.7) | 56 (59.6) | 83 (61.5) | 0.771 |
| ICU LOS, (days) | 9 [6–16] | 8 [5–13] | 10 [7–17] | 0.185 |
| Adverse events | ||||
| Shock | 132 (57.6) | 9 (9.6) | 123 (91.1) | <0.001 |
| Post-intubation hypotension | 58 (25.3) | 16 (17) | 42 (31.1) | 0.016 |
| Septic shock | 87 (38) | 9 (9.6) | 78 (57.8) | <0.001 |
| Right heart failure | 71 (31) | 0 | 71 (52.6) | - |
| Hemorrhagic shock | 4 (1.7) | 0 | 4 (3) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouguezzi, N.; Ben Saida, I.; Toumi, R.; Meddeb, K.; Ennouri, E.; Bedhiafi, A.; Hamdi, D.; Boussarsar, M. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155127
Bouguezzi N, Ben Saida I, Toumi R, Meddeb K, Ennouri E, Bedhiafi A, Hamdi D, Boussarsar M. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(15):5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155127
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouguezzi, Nabil, Imen Ben Saida, Radhouane Toumi, Khaoula Meddeb, Emna Ennouri, Amir Bedhiafi, Dhouha Hamdi, and Mohamed Boussarsar. 2023. "Clinical Features and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 15: 5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155127
APA StyleBouguezzi, N., Ben Saida, I., Toumi, R., Meddeb, K., Ennouri, E., Bedhiafi, A., Hamdi, D., & Boussarsar, M. (2023). Clinical Features and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155127






