Current Evidence for Biological Biomarkers and Mechanisms Underlying Acute to Chronic Pain Transition across the Pediatric Age Spectrum
Abstract
1. Introduction
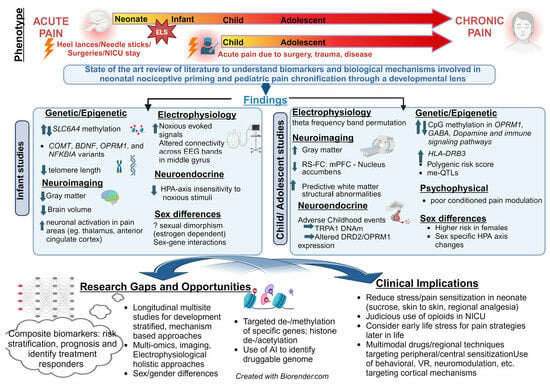
2. State-of-the-Art Review
2.1. Importance of Objective Biomarkers
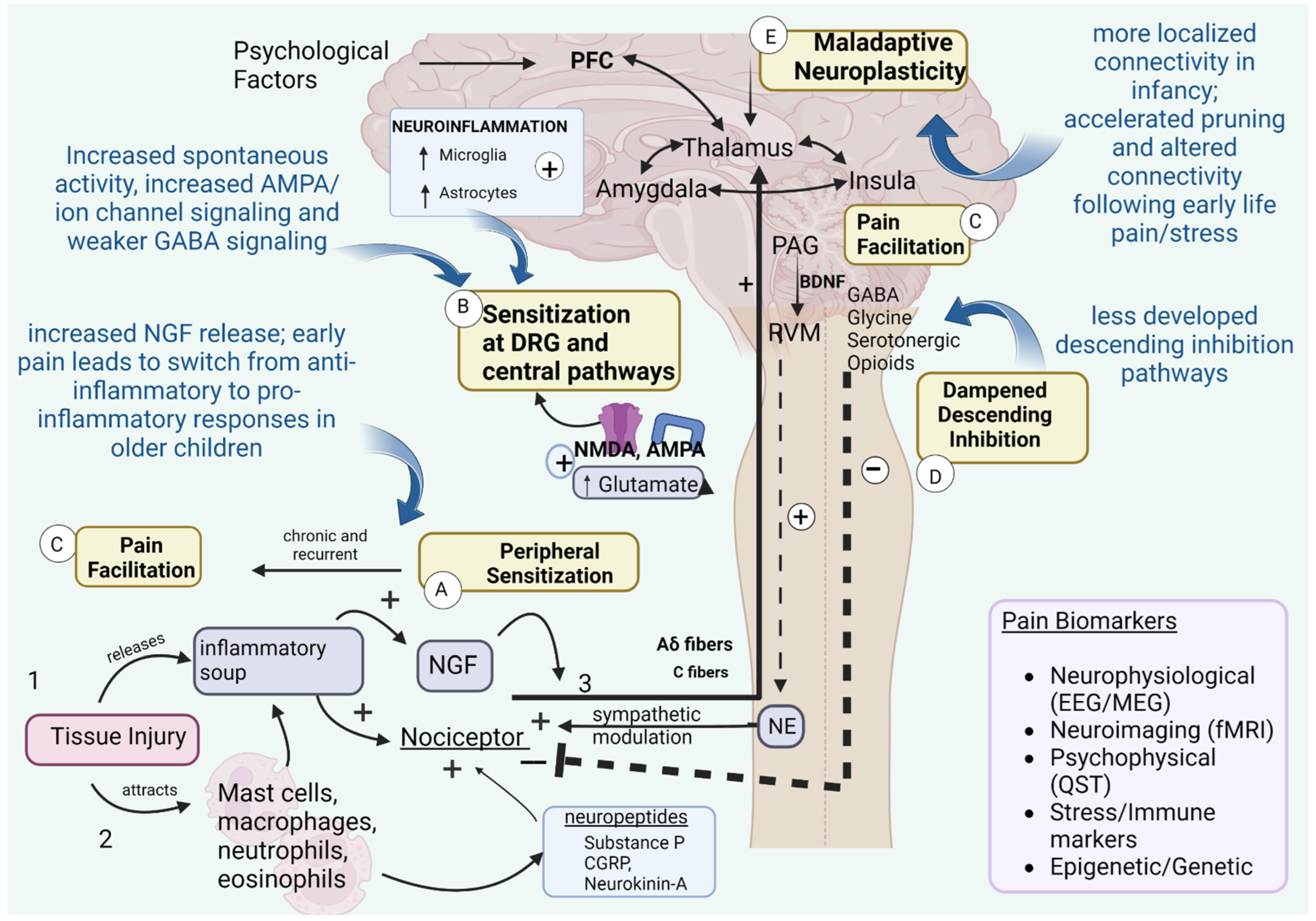
2.2. Developmental Mechanisms of Pain Chronification
2.3. Acute to Chronic Pain Transitions in Infants
2.3.1. Does Neonatal Pain Lead to Chronic Pain Later in Life?
2.3.2. Mechanistic Evidence and Biomarkers for Pain Chronification in INFANTS
2.4. Pain Chronification in Children and Adolescents
2.5. Mechanisms and Biomarkers for Pain Chronification in Children and Adolescents
3. Future Directions for Research
4. Future Directions for Clinical Practice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassett, A.L.; Hilliard, P.E.; Goesling, J.; Clauw, D.J.; Harte, S.E.; Brummett, C.M. Reports of chronic pain in childhood and adolescence among patients at a tertiary care pain clinic. J. Pain 2013, 14, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Metwally, A.; Salminen, J.J.; Auvinen, A.; Kautiainen, H.; Mikkelsson, M. Lower limb pain in a preadolescent population: Prognosis and risk factors for chronicity—A prospective 1- and 4-year follow-up study. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobina, I.; Villberg, J.; Välimaa, R.; Tynjälä, J.; Whitehead, R.; Cosma, A.; Brooks, F.; Cavallo, F.; Ng, K.; de Matos, M.G.; et al. Prevalence of self-reported chronic pain among adolescents: Evidence from 42 countries and regions. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 23, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaran, V.; Zhang, X.; Martin, L.; Ding, L.; Weirauch, M.; Geisler, K.; Stubbeman, B.; Sadhasivam, S.; Ji, H. DNA methylation at the mu-1 opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) promoter predicts preoperative, acute, and chronic postsurgical pain after spine fusion. Pharmacogenom. Pers. Med. 2017, 10, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaran, V.; Pilipenko, V.; Jegga, A.G.; Geisler, K.; Martin, L.J. Systems Biology Guided Gene Enrichment Approaches Improve Prediction of Chronic Post-surgical Pain After Spine Fusion. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 594250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbitts, J.A.; Fisher, E.; Rosenbloom, B.N.; Palermo, T.M. Prevalence and Predictors of Chronic Postsurgical Pain in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pain 2017, 18, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattberg, G. Do pain problems in young school children persist into early adulthood? A 13-year follow-up. Eur. J. Pain 2004, 8, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewald, C.B.; Essner, B.S.; Wright, D.; Fesinmeyer, M.D.; Palermo, T.M. The Economic Costs of Chronic Pain Among a Cohort of Treatment-Seeking Adolescents in the United States. Pain 2014, 15, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Schenk, S.; Genent, D.; Zernikow, B.; Wager, J. A scoping review of chronic pain in emerging adults. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashikar-Zuck, S.; Goldschneider, K.R.; Powers, S.W.; Vaught, M.H.; Hershey, A.D. Depression and functional disability in chronic pediatric pain. Clin. J. Pain 2001, 17, 341–349. [Google Scholar]
- Kucyi, A.; Davis, K.D. The dynamic pain connectome. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliki, M.N.; Mansour, A.R.; Baria, A.T.; Apkarian, A.V. Functional reorganization of the default mode network across chronic pain conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2019, 160, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wager, J.; Fabrizi, L.; Tham, S.W. Need for pediatric specifications for chronic pain diagnoses in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2023, 164, 1705–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbitts, J.A.; Palermo, T.M.; Lang, E.A. A Conceptual Model of Biopsychosocial Mechanisms of Transition from Acute to Chronic Postsurgical Pain in Children and Adolescents. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 3071–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieberg, C.B.; Karunakaran, K.D.; Kussman, B.; Borsook, D. Preventing pediatric chronic postsurgical pain: Time for increased rigor. Can. J. Pain 2022, 6, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, M.A.; Baliki, M.N.; Apkarian, A.V. A dynamic network perspective of chronic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 520, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, P.J.; Walco, G.A.; Turk, D.C.; Dworkin, R.H.; Brown, M.T.; Davidson, K.; Eccleston, C.; Finley, G.A.; Goldschneider, K.; Haverkos, L.; et al. Core outcome domains and measures for pediatric acute and chronic/recurrent pain clinical trials: PedIMMPACT recommendations. J. Pain 2008, 9, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, T.M.; Walco, G.A.; Paladhi, U.R.; Birnie, K.A.; Crombez, G.; de la Vega, R.; Eccleston, C.; Kashikar-Zuck, S.; Stone, A.L. Core outcome set for pediatric chronic pain clinical trials: Results from a Delphi poll and consensus meeting. Pain 2021, 162, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and other Tools) Resource; Food and Drug Administration (US) National Institutes of Health (US): Silver Spring, MD, USA; Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016.
- Douglas, S.R.; Shenoda, B.B.; Qureshi, R.A.; Sacan, A.; Alexander, G.M.; Perreault, M.; Barrett, J.E.; Aradillas-Lopez, E.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Ajit, S.K. Analgesic Response to Intravenous Ketamine Is Linked to a Circulating microRNA Signature in Female Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2015, 16, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.M.; Vassos, E. Polygenic risk scores: From research tools to clinical instruments. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchenbaecker, K.; Telkar, N.; Reiker, T.; Walters, R.G.; Lin, K.; Eriksson, A.; Gurdasani, D.; Gilly, A.; Southam, L.; Tsafantakis, E.; et al. The transferability of lipid loci across African, Asian and European cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, Z.; Lv, C.; Dong, Q.; He, Q.; Yi, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, B. Kinetics and mechanisms of mitotic inheritance of DNA methylation and their roles in aging-associated methylome deterioration. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, J.F.; Cecil, C.A.M. Population DNA methylation studies in the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD) framework. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2019, 10, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branham, E.M.; McLean, S.A.; Deliwala, I.; Mauck, M.C.; Zhao, Y.; McKibben, L.A.; Lee, A.; Spencer, A.B.; Zannas, A.S.; Lechner, M.; et al. CpG Methylation Levels in HPA Axis Genes Predict Chronic Pain Outcomes Following Trauma Exposure. J. Pain 2023, 24, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaran, V.; Ashton, M.; Martin, L.J.; Jegga, A.G. Systems biology-based approaches to summarize and identify novel genes and pathways associated with acute and chronic postsurgical pain. J. Clin. Anesth. 2020, 62, 109738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosak, N.; Branco, P.; Kuperman, P.; Buxbaum, C.; Cohen, R.M.; Fadel, S.; Zubeidat, R.; Hadad, R.; Lawen, A.; Saadon-Grosman, N.; et al. Brain Connectivity Predicts Chronic Pain in Acute Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 92, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiadakis, G.K.; Gaudillière, B.; Ganio, E.A.; Aghaeepour, N.; Tingle, M.; Nolan, G.P.; Angst, M.S. Patient-specific Immune States before Surgery Are Strong Correlates of Surgical Recovery. Anesthesiology 2015, 123, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.R.; Vierck, C.J. The Transition of Acute Postoperative Pain to Chronic Pain: An Integrative Overview of Research on Mechanisms. J. Pain 2017, 18, 359.e1–359.e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Morlion, B.; Perrot, S.; Dahan, A.; Dickenson, A.; Kress, H.G.; Wells, C.; Bouhassira, D.; Drewes, A.M. Assessment and manifestation of central sensitisation across different chronic pain conditions. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 216–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.R.; Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A.; Zeltzer, L.K. Chronic pain in children: Structural and resting-state functional brain imaging within a developmental perspective. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 88, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinou, J.; Reynolds, M.L.; Woolf, C.J.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Fitzgerald, M. Nerve growth factor levels in developing rat skin: Upregulation following skin wounding. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 2281–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, R.F.; Walker, S.M.; Mota, M.P.; Fitzgerald, M. The ontogeny of neuropathic pain: Postnatal onset of mechanical allodynia in rat spared nerve injury (SNI) and chronic constriction injury (CCI) models. Pain 2005, 115, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.M. Neuropathic pain in neonatal rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 209, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, R.; Berta, T.; Old, E.; Ji, R.R.; Fitzgerald, M. Neuropathic pain is constitutively suppressed in early life by anti-inflammatory neuroimmune regulation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourson, A.J.; Willits, A.; Raut, N.G.R.; Kader, L.; Young, E.; Jankowski, M.P.; Chidambaran, V. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms influencing acute to chronic postsurgical pain transitions in pediatrics: Preclinical to clinical evidence. Can. J. Pain 2022, 6, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anseloni, V.C.; He, F.; Novikova, S.I.; Turnbach Robbins, M.; Lidow, I.A.; Ennis, M.; Lidow, M.S. Alterations in stress-associated behaviors and neurochemical markers in adult rats after neonatal short-lasting local inflammatory insult. Neuroscience 2005, 131, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria, N.C.; Inoue, K.; Young, L.J.; Murphy, A.Z. A single neonatal injury induces life-long deficits in response to stress. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 35, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Kentner, A.C. Mechanical allodynia corresponds to OPRM1 downregulation within the descending pain network of male and female rats exposed to neonatal immune challenge. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 63, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, G.A.; Wang, S.; Weisshaar, C.L.; Winkelstein, B.A. Developmental Changes in Pain and Spinal Immune Gene Expression after Radicular Trauma in the Rat. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.; Beggs, S.; Vega-Avelaira, D.; Costigan, M.; Hathway, G.J.; Salter, M.W.; Fitzgerald, M. Spinal microglia and neuropathic pain in young rats. Pain 2007, 128, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichon, J.; Sun, L.; Yang, G. Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Bio-Protocol 2018, 8, e2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaepen, L.; Patijn, J.; van Kleef, M.; Mulder, M.; Tibboel, D.; Joosten, E.A. Neonatal repetitive needle pricking: Plasticity of the spinal nociceptive circuit and extended postoperative pain in later life. Dev. Neurobiol. 2013, 73, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burenkova, O.V.; Aleksandrova, E.A.; Zarayskaya, I.Y. Effects of early-life stress and HDAC inhibition on maternal behavior in mice. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 133, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizzo, S.; Campana, G.; Vella, S.; Fortuna, A.; Galietta, G.; Guarino, I.; Costa, L.; Capasso, A.; Renzi, P.; Frajese, G.V.; et al. Post-natal stress-induced endocrine and metabolic alterations in mice at adulthood involve different pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides. Peptides 2010, 31, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuke, J.T.; Rice, M.; Rudlong, J.; Paquin, T.; Russo, E.; Burman, M.A. The Effects of Acute Neonatal Pain on Expression of Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone and Juvenile Anxiety in a Rodent Model. eNeuro 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, O.; Tu, Y.; Sengar, A.S.; Salter, M.W.; Beggs, S.; Walker, S.M. Priming of Adult Incision Response by Early-Life Injury: Neonatal Microglial Inhibition Has Persistent But Sexually Dimorphic Effects in Adult Rats. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liang, Y.J.; Su, L.; Liao, F.F.; Fang, D.; Tai, J.; Xing, G.G. BDNF contributes to the neonatal incision-induced facilitation of spinal long-term potentiation and the exacerbation of incisional pain in adult rats. Neuropharmacology 2018, 137, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segelcke, D.; Reichl, S.; Neuffer, S.; Zapp, S.; Rüther, T.; Evers, D.; Zahn, P.K.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.M. The role of the spinal cyclooxygenase (COX) for incisional pain in rats at different developmental stages. Eur. J. Pain 2020, 24, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.J.; Coskun, V.; Thrivikraman, K.V.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Plotsky, P.M. Long-term behavioral effects of repetitive pain in neonatal rat pups. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Anseloni, V.; Zou, S.P.; Wade, B.E.; Novikova, I.S.; Ennis, M.; Traub, J.R.; Gold, S.M.; Dubner, R.; Lidow, S.M. Characterization of basal and re-inflammation-associated long-term alteration in pain responsivity following short-lasting neonatal local inflammatory insult. Pain 2004, 110, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, D.; Torsney, C.; Beland, B.; Reynolds, M.; Fitzgerald, M. Modelling the prolonged effects of neonatal pain. Prog. Brain Res. 2000, 129, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, A.T.; Rovnaghi, C.; Simpson, P.M.; Gossett, J.M.; Scalzo, F.M.; Anand, K.J. Interactions of inflammatory pain and morphine in infant rats: Long-term behavioral effects. Physiol. Behav. 2001, 73, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, W.F.; Ridgway, C.G. Effects of gestational stress and neonatal handling on pain, analgesia, and stress behavior of adult mice. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 78, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Chaer, E.D.; Kawasaki, M.; Pasricha, P.J. A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Baccei, M.L. Neonatal tissue damage facilitates nociceptive synaptic input to the developing superficial dorsal horn via NGF-dependent mechanisms. Pain 2011, 152, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Baccei, M.L. Excitatory synapses in the rat superficial dorsal horn are strengthened following peripheral inflammation during early postnatal development. Pain 2009, 143, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Walker, S.M.; Fitzgerald, M.; Baccei, M.L. Activity-dependent modulation of glutamatergic signaling in the developing rat dorsal horn by early tissue injury. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 102, 2208–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Baccei, M.L. Neonatal Tissue Damage Promotes Spike Timing-Dependent Synaptic Long-Term Potentiation in Adult Spinal Projection Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5405–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccei, M.L.; Fitzgerald, M. Development of GABAergic and glycinergic transmission in the neonatal rat dorsal horn. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4749–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldenström, A.; Thelin, J.; Thimansson, E.; Levinsson, A.; Schouenborg, J. Developmental learning in a pain-related system: Evidence for a cross-modality mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7719–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouikr, I.; Karshikoff, B. Lifetime Modulation of the Pain System via Neuroimmune and Neuroendocrine Interactions. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.L.; Baccei, M.L. The development of pain circuits and unique effects of neonatal injury. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathway, G.J.; Koch, S.; Low, L.; Fitzgerald, M. The changing balance of brainstem-spinal cord modulation of pain processing over the first weeks of rat postnatal life. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.M.; Tochiki, K.K.; Fitzgerald, M. Hindpaw incision in early life increases the hyperalgesic response to repeat surgical injury: Critical period and dependence on initial afferent activity. Pain 2009, 147, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duff, E.P.; Moultrie, F.; van der Vaart, M.; Goksan, S.; Abos, A.; Fitzgibbon, S.P.; Baxter, L.; Wager, T.D.; Slater, R. Inferring pain experience in infants using quantitative whole-brain functional MRI signatures: A cross-sectional, observational study. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e458–e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliki, M.N.; Petre, B.; Torbey, S.; Herrmann, K.M.; Huang, L.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Fields, H.L.; Apkarian, A.V. Corticostriatal functional connectivity predicts transition to chronic back pain. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V. Developmental pathways to functional brain networks: Emerging principles. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, D.A.; Cohen, A.L.; Power, J.D.; Dosenbach, N.U.; Church, J.A.; Miezin, F.M.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Functional brain networks develop from a “local to distributed” organization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolles, D.D.; van Buchem, M.A.; Crone, E.A.; Rombouts, S.A. A comprehensive study of whole-brain functional connectivity in children and young adults. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourson, A.; Hofmann, M.; Jankowski, M. Early life neuroimmune interactions modulate neonatal nociceptive priming. Pain 2021, 22, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourson, A.J.; Fadaka, A.O.; Warshak, A.M.; Paranjpe, A.; Weinhaus, B.; Queme, L.F.; Hofmann, M.C.; Evans, H.M.; Donmez, O.A.; Forney, C.; et al. Macrophage epigenetic memories of early life injury drive neonatal nociceptive priming. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, S.; Tajerian, M.; Suderman, M.; Machnes, Z.; Pierfelice, S.; Millecamps, M.; Stone, L.S.; Szyf, M. An epigenetic hypothesis for the genomic memory of pain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbajal, R.; Rousset, A.; Danan, C.; Coquery, S.; Nolent, P.; Ducrocq, S.; Saizou, C.; Lapillonne, A.; Granier, M.; Durand, P.; et al. Epidemiology and treatment of painful procedures in neonates in intensive care units. JAMA 2008, 300, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.W.B.; Schouw, R.; Anand, K.J.S.; van Dijk, M.; Duivenvoorden, H.J.; Tibboel, D. Does neonatal surgery lead to increased pain sensitivity in later childhood? Pain 2005, 114, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bosch, G.E.; White, T.; El Marroun, H.; Simons, S.H.; van der Lugt, A.; van der Geest, J.N.; Tibboel, D.; van Dijk, M. Prematurity, Opioid Exposure and Neonatal Pain: Do They Affect the Developing Brain? Neonatology 2015, 108, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, M.; Gouyon, B.; Hirt, D.; Carbajal, R.; Gouyon, J.B.; Brunet, A.C.; Ortala, M.; Goro, S.; Jung, C.; Durrmeyer, X. Frequencies, Modalities, Doses and Duration of Computerized Prescriptions for Sedative, Analgesic, Anesthetic and Paralytic Drugs in Neonates Requiring Intensive Care: A Prospective Pharmacoepidemiologic Cohort Study in 30 French NICUs From 2014 to 2020. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 939869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprairie, J.L.; Johns, M.E.; Murphy, A.Z. Preemptive Morphine Analgesia Attenuates the Long-Term Consequences of Neonatal Inflammation in Male and Female Rats. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dührsen, L.; Simons, S.H.P.; Dzietko, M.; Genz, K.; Bendix, I.; Boos, V.; Sifringer, M.; Tibboel, D.; Felderhoff-Mueser, U. Effects of Repetitive Exposure to Pain and Morphine Treatment on the Neonatal Rat Brain. Neonatology 2012, 103, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbauer, P.; Monje, F.J.; Kothgassner, O.; Goreis, A.; Eva, C.; Wildner, B.; Schned, H.; Deindl, P.; Seki, D.; Berger, A.; et al. The consequences of neonatal pain, stress and opiate administration in animal models: An extensive meta-analysis concerning neuronal cell death, motor and behavioral outcomes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 137, 104661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, G.E.; Dijk, M.V.; Tibboel, D.; de Graaff, J.C. Long-term Effects of Early Exposure to Stress, Pain, Opioids and Anaesthetics on Pain Sensitivity and Neurocognition. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 5879–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bosch, G.; Tibboel, D.; Graaff, J.; El Marroun, H.; Lugt, A.; White, T.; van Dijk, M. Neonatal Pain, Opioid, and Anesthetic Exposure; What Remains in the Human Brain After the Wheels of Time? Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 825725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verriotis, M.; Chang, P.; Fitzgerald, M.; Fabrizi, L. The development of the nociceptive brain. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giedd, J.N.; Rapoport, J.L. Structural MRI of pediatric brain development: What have we learned and where are we going? Neuron 2010, 67, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowell, E.R.; Peterson, B.S.; Thompson, P.M.; Welcome, S.E.; Henkenius, A.L.; Toga, A.W. Mapping cortical change across the human life span. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinall, J.; Miller, S.P.; Bjornson, B.H.; Fitzpatrick, K.P.; Poskitt, K.J.; Brant, R.; Synnes, A.R.; Cepeda, I.L.; Grunau, R.E. Invasive procedures in preterm children: Brain and cognitive development at school age. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmeister, J.; Kroll, A.; Wollgarten-Hadamek, I.; Zohsel, K.; Demirakça, S.; Flor, H.; Hermann, C. Cerebral processing of pain in school-aged children with neonatal nociceptive input: An exploratory fMRI study. Pain 2010, 150, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, M.; Chau, C.M.; Garg, A.; Woodward, T.S.; Beg, M.F.; Bjornson, B.; Poskitt, K.; Fitzpatrick, K.; Synnes, A.R.; Miller, S.P.; et al. Neonatal pain-related stress predicts cortical thickness at age 7 years in children born very preterm. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, R.; Fabrizi, L.; Worley, A.; Meek, J.; Boyd, S.; Fitzgerald, M. Premature infants display increased noxious-evoked neuronal activity in the brain compared to healthy age-matched term-born infants. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Fabrizi, L.; Laudiano-Dray, M.; Whitehead, K.; Meek, J.; Verriotis, M.; Fitzgerald, M. Nociceptive Cortical Activity Is Dissociated from Nociceptive Behavior in Newborn Human Infants under Stress. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 3846–3851.e3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crettaz, B.; Marziniak, M.; Willeke, P.; Young, P.; Hellhammer, D.; Stumpf, A.; Burgmer, M. Stress-induced allodynia—Evidence of increased pain sensitivity in healthy humans and patients with chronic pain after experimentally induced psychosocial stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, M.; Kanda, K.; Hirata, M.; Kusakawa, I.; Suzuki, C. Influence of repeated painful procedures on prefrontal cortical pain responses in newborns. Acta Paediatr. 2011, 100, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.C.; Stevens, B.J. Experience in a neonatal intensive care unit affects pain response. Pediatrics 1996, 98, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddio, A.; Shah, V.; Gilbert-MacLeod, C.; Katz, J. Conditioning and hyperalgesia in newborns exposed to repeated heel lances. JAMA 2002, 288, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddio, A.; Shah, V.; Hancock, R.; Smith, R.W.; Stephens, D.; Atenafu, E.; Beyene, J.; Koren, G.; Stevens, B.; Katz, J. Effectiveness of sucrose analgesia in newborns undergoing painful medical procedures. CMAJ 2008, 179, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.; Campbell-Yeo, M.; Fernandes, A.; Inglis, D.; Streiner, D.; Zee, R. Skin-to-skin care for procedural pain in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, Cd008435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmeister, J.; Demirakca, S.; Zohsel, K.; Flor, H.; Hermann, C. Responses to pain in school-aged children with experience in a neonatal intensive care unit: Cognitive aspects and maternal influences. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doesburg, S.M.; Chau, C.M.; Cheung, T.P.L.; Moiseev, A.; Ribary, U.; Herdman, A.T.; Miller, S.P.; Cepeda, I.L.; Synnes, A.; Grunau, R.E. Neonatal pain-related stress, functional cortical activity and visual-perceptual abilities in school-age children born at extremely low gestational age. Pain 2013, 154, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, A.; Doesburg, S.M.; Herdman, A.T.; Ribary, U.; Grunau, R.E. Altered Network Oscillations and Functional Connectivity Dynamics in Children Born Very Preterm. Brain Topogr. 2015, 28, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnthein, J.; Stern, J.; Aufenberg, C.; Rousson, V.; Jeanmonod, D. Increased EEG power and slowed dominant frequency in patients with neurogenic pain. Brain 2006, 129, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinas, R.R.; Ribary, U.; Jeanmonod, D.; Kronberg, E.; Mitra, P.P. Thalamocortical dysrhythmia: A neurological and neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by magnetoencephalography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 15222–15227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, A.; Shehzad, Z.; Kelly, C.; Roy, A.K.; Gee, D.G.; Uddin, L.Q.; Gotimer, K.; Klein, D.F.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. Relationship Between Cingulo-Insular Functional Connectivity and Autistic Traits in Neurotypical Adults. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victoria, N.C.; Murphy, A.Z. Exposure to Early Life Pain: Long Term Consequences and Contributing Mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 7, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbauer, P.; Deindl, P.; Fuiko, R.; Unterasinger, L.; Cardona, F.; Wagner, M.; Edobor, J.; Werther, T.; Berger, A.; Olischar, M.; et al. Long-term impact of systematic pain and sedation management on cognitive, motor, and behavioral outcomes of extremely preterm infants at preschool age. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzi, L.; Guida, E.; Montirosso, R. Preterm behavioral epigenetics: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 84, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggini, T.; Pozzoli, S.; Schiavolin, P.; Erario, R.; Mosca, F.; Brambilla, P.; Fumagalli, M. Cumulative procedural pain and brain development in very preterm infants: A systematic review of clinical and preclinical studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 123, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
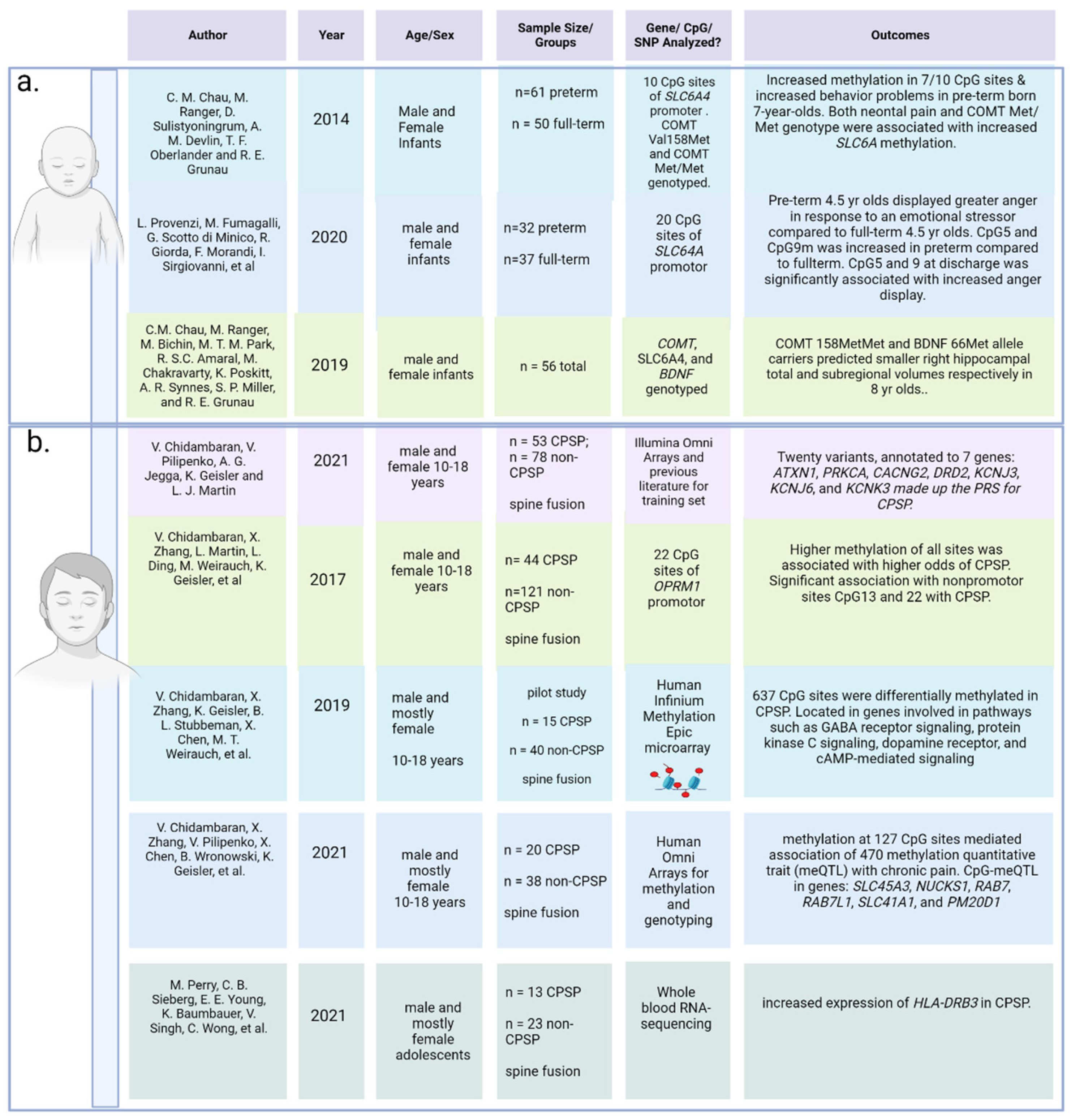
- Provenzi, L.; Fumagalli, M.; Scotto di Minico, G.; Giorda, R.; Morandi, F.; Sirgiovanni, I.; Schiavolin, P.; Mosca, F.; Borgatti, R.; Montirosso, R. Pain-related increase in serotonin transporter gene methylation associates with emotional regulation in 4.5-year-old preterm-born children. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.M.; Ranger, M.; Sulistyoningrum, D.; Devlin, A.M.; Oberlander, T.F.; Grunau, R.E. Neonatal pain and COMT Val158Met genotype in relation to serotonin transporter (SLC6A4) promoter methylation in very preterm children at school age. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.M.Y.; Ranger, M.; Bichin, M.; Park, M.T.M.; Amaral, R.S.C.; Chakravarty, M.; Poskitt, K.; Synnes, A.R.; Miller, S.P.; Grunau, R.E. Hippocampus, Amygdala, and Thalamus Volumes in Very Preterm Children at 8 Years: Neonatal Pain and Genetic Variation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaran, V.; Zhang, X.; Geisler, K.; Stubbeman, B.L.; Chen, X.; Weirauch, M.T.; Meller, J.; Ji, H. Enrichment of Genomic Pathways Based on Differential DNA Methylation Associated with Chronic Postsurgical Pain and Anxiety in Children: A Prospective, Pilot Study. Pain 2019, 20, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaran, V.; Zhang, X.; Pilipenko, V.; Chen, X.; Wronowski, B.; Geisler, K.; Martin, L.J.; Barski, A.; Weirauch, M.T.; Ji, H. Methylation quantitative trait locus analysis of chronic postsurgical pain uncovers epigenetic mediators of genetic risk. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M.; Sieberg, C.B.; Young, E.E.; Baumbauer, K.; Singh, V.; Wong, C.; Starkweather, A. The Potential Role of Preoperative Pain, Catastrophizing, and Differential Gene Expression on Pain Outcomes after Pediatric Spinal Fusion. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2021, 22, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzi, L.; Fumagalli, M.; Sirgiovanni, I.; Giorda, R.; Pozzoli, U.; Morandi, F.; Beri, S.; Menozzi, G.; Mosca, F.; Borgatti, R.; et al. Pain-related stress during the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit stay and SLC6A4 methylation in very preterm infants. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzi, L.; Fumagalli, M.; Giorda, R.; Morandi, F.; Sirgiovanni, I.; Pozzoli, U.; Mosca, F.; Borgatti, R.; Montirosso, R. Maternal Sensitivity Buffers the Association between SLC6A4 Methylation and Socio-Emotional Stress Response in 3-Month-Old Full Term, but not very Preterm Infants. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzi, L.; Giorda, R.; Fumagalli, M.; Brambilla, M.; Mosca, F.; Borgatti, R.; Montirosso, R. Telomere length and salivary cortisol stress reactivity in very preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 129, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzi, L.; Giorda, R.; Fumagalli, M.; Pozzoli, U.; Morandi, F.; Scotto di Minico, G.; Mosca, F.; Borgatti, R.; Montirosso, R. Pain exposure associates with telomere length erosion in very preterm infants. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 89, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani Wigley, I.L.C.; Mascheroni, E.; Fontana, C.; Giorda, R.; Morandi, F.; Bonichini, S.; McGlone, F.; Fumagalli, M.; Montirosso, R. The role of maternal touch in the association between SLC6A4 methylation and stress response in very preterm infants. Dev. Psychobiol. 2021, 63, e22218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunau, R.E.; Cepeda, I.L.; Chau, C.M.; Brummelte, S.; Weinberg, J.; Lavoie, P.M.; Ladd, M.; Hirschfeld, A.F.; Russell, E.; Koren, G.; et al. Neonatal pain-related stress and NFKBIA genotype are associated with altered cortisol levels in preterm boys at school age. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, P.G.; Doheny, K.K.; Klick, L.; Britcher, S.; Rebstock, S.; Bezinover, D.; Palmer, C.; Berlin, C.; Postula, M.; Kong, L.; et al. Analysis of acute pain scores and skin conductance measurements in infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2013, 89, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, L.A.; Hoffman, R.K.; Polomano, R.C.; Conley, Y. Epigenetic Modifications Following Noxious Stimuli in Infants. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2018, 20, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbi, I.; Ciantelli, M.; Farinella, R.; Tuoni, C.; Gentiluomo, M.; Moscuzza, F.; Rizzato, C.; Bedini, A.; Faraoni, M.; Giusfredi, S.; et al. Role of OPRM1, clinical and anthropometric variants in neonatal pain reduction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.; Seckl, J. Glucocorticoids, prenatal stress and the programming of disease. Horm. Behav. 2011, 59, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, S.A.; Diorio, J.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal separation leads to persistent reductions in pain sensitivity in female rats. J. Pain 2007, 8, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, S.V.; Plotsky, P.M.; Sablad, M.; Miller, J.C.; Zhou, H.; Bayati, A.I.; McRoberts, J.A.; Mayer, E.A. Neonatal maternal separation alters stress-induced responses to viscerosomatic nociceptive stimuli in rat. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G307–G316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.G.; Chen, X.; Alvarez, P.; Ferrari, L.F.; Levine, J.D. Early-life stress produces muscle hyperalgesia and nociceptor sensitization in the adult rat. Pain 2011, 152, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, P.; Green, P.G.; Levine, J.D. Stress in the Adult Rat Exacerbates Muscle Pain Induced by Early-Life Stress. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.K.; Finn, D.P. Stress-induced analgesia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 88, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunau, R.E.; Holsti, L.; Haley, D.W.; Oberlander, T.; Weinberg, J.; Solimano, A.; Whitfield, M.F.; Fitzgerald, C.; Yu, W. Neonatal procedural pain exposure predicts lower cortisol and behavioral reactivity in preterm infants in the NICU. Pain 2005, 113, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasar, S.G.; Dina, O.A.; Green, P.G.; Levine, J.D. Sound stress-induced long-term enhancement of mechanical hyperalgesia in rats is maintained by sympathoadrenal catecholamines. J. Pain 2009, 10, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.F.; Araldi, D.; Green, P.; Levine, J.D. Age-Dependent Sexual Dimorphism in Susceptibility to Develop Chronic Pain in the Rat. Neuroscience 2018, 387, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, A.; Kim, J.; Cahalan, C.M.; Loggia, M.L.; Franceschelli, O.; Berna, C.; Schur, P.; Napadow, V.; Edwards, R.R. Effects of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) on Brain Connectivity Supporting Catastrophizing in Fibromyalgia. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, D.W.; Dhandapani, K.; Wakade, C.; Mahesh, V.B.; Khan, M.M. Neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions of estrogen: Basic mechanisms and clinical implications. Steroids 2007, 72, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.F.; Araldi, D.; Levine, J.D. Regulation of Expression of Hyperalgesic Priming by Estrogen Receptor α in the Rat. J. Pain 2017, 18, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, A.L.; Handa, R.J. Sex differences in the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis’ response to stress: An important role for gonadal hormones. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbitts, J.A.; Groenewald, C.B. Epidemiology of Pediatric Surgery in the United States. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2020, 30, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieberg, C.B.; Simons, L.E.; Edelstein, M.R.; DeAngelis, M.R.; Pielech, M.; Sethna, N.; Hresko, M.T. Pain prevalence and trajectories following pediatric spinal fusion surgery. J. Pain 2013, 14, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Morales, A.M.; Holley, A.L.; Wilson, A.C.; Nagel, B.J. Default mode network connectivity is related to pain frequency and intensity in adolescents. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 27, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliki, M.N.; Geha, P.Y.; Fields, H.L.; Apkarian, A.V. Predicting value of pain and analgesia: Nucleus accumbens response to noxious stimuli changes in the presence of chronic pain. Neuron 2010, 66, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F. Neural mechanisms of drug reinforcement. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 654, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Baliki, M.N.; Farmer, M.A. Predicting transition to chronic pain. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.R.; Baliki, M.N.; Huang, L.; Torbey, S.; Herrmann, K.M.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Apkarian, V.A. Brain white matter structural properties predict transition to chronic pain. Pain 2013, 154, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, M.; Jorgenson, K.; Kong, J. Neurochemical changes in patients with chronic low back pain detected by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: A systematic review. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 13, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Kang, D.H. Abnormal neurometabolites in fibromyalgia patients: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 1744806921990946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Mun, C.W. Evaluation of the effectiveness of pregabalin in alleviating pain associated with fibromyalgia: Using functional magnetic resonance imaging study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresima, V.; Bisconti, S.; Ferrari, M. A brief review on the use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) for language imaging studies in human newborns and adults. Brain Lang. 2012, 121, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, K.D.; Peng, K.; Berry, D.; Green, S.; Labadie, R.; Kussman, B.; Borsook, D. NIRS measures in pain and analgesia: Fundamentals, features, and function. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ta Dinh, S.; Nickel, M.M.; Tiemann, L.; May, E.S.; Heitmann, H.; Hohn, V.D.; Edenharter, G.; Utpadel-Fischler, D.; Tölle, T.R.; Sauseng, P.; et al. Brain dysfunction in chronic pain patients assessed by resting-state electroencephalography. Pain 2019, 160, 2751–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocay, D.D.; Teel, E.F.; Luo, O.D.; Savignac, C.; Mahdid, Y.; Blain-Moraes, S.; Ferland, C.E. Electroencephalographic characteristics of children and adolescents with chronic musculoskeletal pain. Pain Rep. 2022, 7, e1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teel, E.F.; Ocay, D.D.; Blain-Moraes, S.; Ferland, C.E. Accurate classification of pain experiences using wearable electroencephalography in adolescents with and without chronic musculoskeletal pain. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 991793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploner, M.; May, E.S. Electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography in pain research-current state and future perspectives. Pain 2018, 159, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertz, M.; Whitlock, P.; Yang, F.; Ding, L.; Uchtman, M.; Mecoli, M.; Olbrecht, V.; Moore, D.; McCarthy, J.; Chidambaran, V. Pragmatic comparative effectiveness study of multimodal fascia iliaca nerve block and continuous lumbar epidural-based protocols for periacetabular osteotomy. J. Hip Preserv. Surg. 2020, 7, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geronimus, A.T.; Hicken, M.; Keene, D.; Bound, J. “Weathering” and age patterns of allostatic load scores among blacks and whites in the United States. Am. J. Public Health 2006, 96, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, T.E.; McEwen, B.S.; Rowe, J.W.; Singer, B.H. Allostatic load as a marker of cumulative biological risk: MacArthur studies of successful aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4770–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, T.; Epel, E.; Gruenewald, T.; Karlamangla, A.; McEwen, B.S. Socio-economic differentials in peripheral biology: Cumulative allostatic load. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1186, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.; Bento, S.; Enlow, M.B. Biomarkers of Allostatic Load as Correlates of Impairment in Youth with Chronic Pain: An Initial Investigation. Children 2021, 8, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallden, M.; Nijs, J. Before & beyond the pain—Allostatic load, central sensitivity and their role in health and function. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2021, 27, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, A.; McEwen, B.S. Adverse childhood experiences, allostasis, allostatic load, and age-related disease. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, J.; Lucente, M.; Sonino, N.; Fava, G.A. Allostatic Load and Its Impact on Health: A Systematic Review. Psychother. Psychosom. 2021, 90, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewald, C.B.; Murray, C.B.; Palermo, T.M. Adverse childhood experiences and chronic pain among children and adolescents in the United States. Pain Rep. 2020, 5, e839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.; Beveridge, J.K.; Mychasiuk, R.; Noel, M. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and Internalizing Mental Health, Pain, and Quality of Life in Youth With Chronic Pain: A Longitudinal Examination. J. Pain 2021, 22, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidmarsh, L.V.; Harrison, R.; Ravindran, D.; Matthews, S.L.; Finlay, K.A. The Influence of Adverse Childhood Experiences in Pain Management: Mechanisms, Processes, and Trauma-Informed Care. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 923866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achenbach, J.; Rhein, M.; Gombert, S.; Meyer-Bockenkamp, F.; Buhck, M.; Eberhardt, M.; Leffler, A.; Frieling, H.; Karst, M. Childhood traumatization is associated with differences in TRPA1 promoter methylation in female patients with multisomatoform disorder with pain as the leading bodily symptom. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, J.J.; Ayoub, L.J.; Moayedi, M.; Linnstaedt, S.D. Hippocampal volume, FKBP5 genetic risk alleles, and childhood trauma interact to increase vulnerability to chronic multisite musculoskeletal pain. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.; Beveridge, J.K.; Wang, M.; Orr, S.L.; Noel, M.; Mychasiuk, R. A Pilot Study Investigating the Role of Gender in the Intergenerational Relationships between Gene Expression, Chronic Pain, and Adverse Childhood Experiences in a Clinical Sample of Youth with Chronic Pain. Epigenomes 2021, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generaal, E.; Milaneschi, Y.; Jansen, R.; Elzinga, B.M.; Dekker, J.; Penninx, B.W. The brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway, life stress, and chronic multi-site musculoskeletal pain. Mol. Pain 2016, 12, 1744806916646783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, N.N.; Finn, D.P.; McGuire, B.E.; Roche, M. Psychological stress in early life as a predisposing factor for the development of chronic pain: Clinical and preclinical evidence and neurobiological mechanisms. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinall, J.; Pavlova, M.; Asmundson, G.J.; Rasic, N.; Noel, M. Mental Health Comorbidities in Pediatric Chronic Pain: A Narrative Review of Epidemiology, Models, Neurobiological Mechanisms and Treatment. Children 2016, 3, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Sex-Specific Associations Between Preoperative Chronic Pain and Moderate to Severe Chronic Postoperative Pain in Patients 2 Years After Cardiac Surgery. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 4007–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, P.J.; Le-Wendling, L.T.; Patel, A.; Zou, B.; Fillingim, R.B. Clinically derived early postoperative pain trajectories differ by age, sex, and type of surgery. Pain 2015, 156, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilopoulos, T.; Wardhan, R.; Rashidi, P.; Fillingim, R.B.; Wallace, M.R.; Crispen, P.L.; Parvataneni, H.K.; Prieto, H.A.; Machuca, T.N.; Hughes, S.J.; et al. Patient and Procedural Determinants of Postoperative Pain Trajectories. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.L.; McGrath, P.A.; Brown, S.C.; Katz, J. Children with chronic pain: Impact of sex and age on long-term outcomes. Pain 2007, 128, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.; Chambers, C.T.; Huguet, A.; MacNevin, R.C.; McGrath, P.J.; Parker, L.; MacDonald, A.J. The epidemiology of chronic pain in children and adolescents revisited: A systematic review. Pain 2011, 152, 2729–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.G.; Stinson, J.; Campbell, F.; Isaac, L.; Katz, J. Identification of pain-related psychological risk factors for the development and maintenance of pediatric chronic postsurgical pain. J. Pain Res. 2013, 6, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, M.; Fulmer, R.D.; Prohaska, J.; Anson, L.; Dryer, L.; Thomas, V.; Ariagno, J.E.; Price, N.; Schwend, R. Predictors of postoperative pain trajectories in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2014, 39, E174–E181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanasamy, S.; Yang, F.; Ding, L.; Geisler, K.; Glynn, S.; Ganesh, A.; Sathyamoorthy, M.; Garcia, V.; Sturm, P.; Chidambaran, V. Pediatric Pain Screening Tool: A Simple 9-Item Questionnaire Predicts Functional and Chronic Postsurgical Pain Outcomes After Major Musculoskeletal Surgeries. J. Pain 2021, 23, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazisaeidi, S.; Muley, M.M.; Salter, M.W. Neuropathic Pain: Mechanisms, Sex Differences, and Potential Therapies for a Global Problem. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musey, P.I., Jr.; Linnstaedt, S.D.; Platts-Mills, T.F.; Miner, J.R.; Bortsov, A.V.; Safdar, B.; Bijur, P.; Rosenau, A.; Tsze, D.S.; Chang, A.K.; et al. Gender differences in acute and chronic pain in the emergency department: Results of the 2014 Academic Emergency Medicine consensus conference pain section. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2014, 21, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, A.L.; Wilson, A.C.; Palermo, T.M. Predictors of the transition from acute to persistent musculoskeletal pain in children and adolescents: A prospective study. Pain 2017, 158, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Fillingim, R.B. Can Quantitative Sensory Testing Move Us Closer to Mechanism-Based Pain Management? Pain Med. 2014, 15, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenburg, M.; Boekens, H.; Hechler, T.; Maier, C.; Krumova, E.; Scherens, A.; Magerl, W.; Aksu, F.; Zernikow, B. Reference values for quantitative sensory testing in children and adolescents: Developmental and gender differences of somatosensory perception. Pain 2010, 149, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beland, B.; Fitzgerald, M. Influence of peripheral inflammation on the postnatal maturation of primary sensory neuron phenotype in rats. J. Pain 2001, 2, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, S.; Currie, G.; Salter, M.W.; Fitzgerald, M.; Walker, S.M. Priming of adult pain responses by neonatal pain experience: Maintenance by central neuroimmune activity. Brain 2012, 135, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathway, G.J.; Vega-Avelaira, D.; Fitzgerald, M. A critical period in the supraspinal control of pain: Opioid-dependent changes in brainstem rostroventral medulla function in preadolescence. Pain 2012, 153, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.; McKelvey, R. Nerve injury and neuropathic pain—A question of age. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 275 Pt 2, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsook, D.; Becerra, L.; Hargreaves, R. Biomarkers for chronic pain and analgesia. Part 1: The need, reality, challenges, and solutions. Discov. Med. 2011, 11, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, Y.P.; Price, N.; Namdari, R.; Cohen, C.J.; Lamers, M.H.; Winters, C.; Price, J.; Young, C.E.; Verschoof, H.; Sherrington, R.; et al. Treatment of Na(v)1.7-mediated pain in inherited erythromelalgia using a novel sodium channel blocker. Pain 2012, 153, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantoulas, C.; McMahon, S.B. Opening paths to novel analgesics: The role of potassium channels in chronic pain. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.Z.; Roche, A.M.; Berdan, C.A.; Louie, S.M.; Roberts, A.J.; Svensson, K.J.; Dou, F.Y.; Bateman, L.A.; Mina, A.I.; Deng, Z.; et al. Ablation of PM20D1 reveals N-acyl amino acid control of metabolism and nociception. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6937–E6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markman, J.D.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Perrot, S.; Beydoun, S.R.; Ohtori, S.; Viktrup, L.; Yang, R.; Bramson, C.; West, C.R.; Verburg, K.M. Clinical Meaningfulness of Response to Tanezumab in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: Analysis From a 56-Week, Randomized, Placebo- and Tramadol-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Pain Ther. 2022, 11, 1267–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, A.-P.; Belvisi, M.G.; Gaudet, R.; Szallasi, A. Advances in TRP channel drug discovery: From target validation to clinical studies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.S.; La, J.H.; Scheff, N.N.; Davis, B.M.; Albers, K.M.; Gebhart, G.F. TRPV1 and TRPA1 antagonists prevent the transition of acute to chronic inflammation and pain in chronic pancreatitis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5603–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirvanie-Persaud, L.; Millis, R.M. Epigenetics and Pain: New Insights to an Old Problem. Cureus 2022, 14, e29353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, F.; McMahon, S.B. Chronic pain: Emerging evidence for the involvement of epigenetics. Neuron 2012, 73, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doehring, A.; Geisslinger, G.; Lotsch, J. Epigenetics in pain and analgesia: An imminent research field. Eur. J. Pain 2011, 15, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanherkar, R.R.; Stair, S.E.; Bhatia-Dey, N.; Mills, P.J.; Chopra, D.; Csoka, A.B. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Integrative Medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederberger, E.; Resch, E.; Parnham, M.J.; Geisslinger, G. Drugging the pain epigenome. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.K.; Yim, H. CRISPR-mediated promoter de/methylation technologies for gene regulation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Muñoz, E.; Mejía-Terrazas, G.E. Epigenetics and Postsurgical Pain: A Scoping Review. Pain Med. 2021, 23, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachau, J.; Appel, C.; Reimer, M.; Sendel, M.; Vollert, J.; Hüllemann, P.; Baron, R. Test–retest reliability of a simple bedside-quantitative sensory testing battery for chronic neuropathic pain. Pain Rep. 2023, 8, e1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, M.; Sachau, J.; Forstenpointner, J.; Baron, R. Bedside testing for precision pain medicine. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2021, 15, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Turk, D.C.; Angst, M.S.; Dionne, R.; Freeman, R.; Hansson, P.; Haroutounian, S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Attal, N.; et al. Patient phenotyping in clinical trials of chronic pain treatments: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain 2016, 157, 1851–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, E.; Midbari, A.; Haddad, M.; Pud, D. Predicting the analgesic effect to oxycodone by ‘static’ and ‘dynamic’ quantitative sensory testing in healthy subjects. Pain 2010, 151, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, H.; Katz, J.; Flor, H.; Rietschel, M.; Diehl, S.R.; Seltzer, Z. Genetics of chronic post-surgical pain: A crucial step toward personal pain medicine. Can. J. Anaesth. 2015, 62, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B.E.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Costello, J.F.; Ren, B.; Milosavljevic, A.; Meissner, A.; Kellis, M.; Marra, M.A.; Beaudet, A.L.; Ecker, J.R.; et al. The NIH Roadmap Epigenomics Mapping Consortium. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudle, K.E.; Sangkuhl, K.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Swen, J.J.; Haidar, C.E.; Klein, T.E.; Gammal, R.S.; Relling, M.V.; Scott, S.A.; Hertz, D.L.; et al. Standardizing CYP2D6 Genotype to Phenotype Translation: Consensus Recommendations from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium and Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, K.R.; Monte, A.A.; Huddart, R.; Caudle, K.E.; Kharasch, E.D.; Gaedigk, A.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Leeder, J.S.; Callaghan, J.T.; Samer, C.F.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2D6, OPRM1, and COMT Genotypes and Select Opioid Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaran, V.; Simpson, B.; Brower, L.; Hanke, R.; Mecoli, M.; Lane, B.; Williams, S.; McKenna, E.; Bates, C.; Kraemer, A.; et al. Design and implementation of a novel patient-centered empowerment approach for pain optimisation in children undergoing major surgery. BMJ Open Qual. 2022, 11, e001874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Mansikka, H.; Staahl, C.; Rees, H.; Tan, K.; Smart, T.S.; Monhemius, R.; Suzuki, R.; Drewes, A.M. A translational study of the effects of ketamine and pregabalin on temporal summation of experimental pain. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2011, 36, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.; Armstrong-Brown, A.; Burstal, R. Perioperative intravenous ketamine infusion for the prevention of persistent post-amputation pain: A randomized, controlled trial. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2004, 32, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.; Bonin, R.P.; Orser, B.A.; Englesakis, M.; Wijeysundera, D.N.; Katz, J. The prevention of chronic postsurgical pain using gabapentin and pregabalin: A combined systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyaert, A.; Lavand’homme, P. Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Postsurgical Pain: A Narrative Review. Drugs 2018, 78, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, P.; Euasobhon, P. Chronic postsurgical pain: Current evidence for prevention and management. Korean J. Pain 2018, 31, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, L.E.; Smith, S.A.; Moore, R.A.; Wiffen, P.J.; Gilron, I. Pharmacotherapy for the prevention of chronic pain after surgery in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, Cd008307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.; Poon, M.; Weinrib, A.; Katznelson, R.; Wentlandt, K.; Katz, J. Preventive analgesia and novel strategies for the prevention of chronic post-surgical pain. Drugs 2015, 75, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, A.; Carrié, S.; Moscaritolo, L.; Ingelmo, P. Mechanism-Based Pharmacological Treatment for Chronic Non-cancer Pain in Adolescents: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Pediatr. Drugs 2022, 24, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzari, A.H.; Bazzari, F.H. Advances in targeting central sensitization and brain plasticity in chronic pain. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2022, 58, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Ridgell, S.; Alpaugh, E.S.; Mouhaffel, A.; Kaye, A.J.; Cornett, E.M.; Chami, A.A.; Shah, R.; Dixon, B.M.; Viswanath, O.; et al. Peripheral Nerve Stimulation: A Review of Techniques and Clinical Efficacy. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisset, X.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Fontaine, D. Neurostimulation methods in the treatment of chronic pain. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilfeld, B.M.; Plunkett, A.; Vijjeswarapu, A.M.; Hackworth, R.; Dhanjal, S.; Turan, A.; Cohen, S.P.; Eisenach, J.C.; Griffith, S.; Hanling, S.; et al. Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation (Neuromodulation) for Postoperative Pain: A Randomized, Sham-controlled Pilot Study. Anesthesiology 2021, 135, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Collado, A.; Valera-Calero, J.A.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Arias-Buría, J.L. Effects of Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Stimulation Targeting Peripheral Nerve Tissue on Pain and Function: A Scoping Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotkova, H.; Hamani, C.; Sivanesan, E.; Le Beuffe, M.F.E.; Moon, J.Y.; Cohen, S.P.; Huntoon, M.A. Neuromodulation for chronic pain. Lancet 2021, 397, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, T.J.; Jupudi, R.; Lenz, F.A.; Greenspan, J.D. New Developments in Non-invasive Brain Stimulation in Chronic Pain. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2020, 8, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.H.; Kluger, B.M.; Buard, I. Safety of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Children: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 68, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, A.S.; Bailey, J.; Bailenson, J.; Tataru, C.; Yoon, I.A.; Golianu, B. Immersive Virtual Reality for Pediatric Pain. Children 2017, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakpo, N.; Vieux, U.; Castro-Nuñez, C. Case Report: Virtual Reality Neurofeedback Therapy as a Novel Modality for Sustained Analgesia in Centralized Pain Syndromes. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 660105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryanton, C.; Bossé, J.; Brien, M.; McLean, J.; McCormick, A.; Sveistrup, H. Feasibility, motivation, and selective motor control: Virtual reality compared to conventional home exercise in children with cerebral palsy. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, T.; Speck, D.; Wettstein, D.; Masnari, O.; Beeli, G.; Jäncke, L. Feeling present in arousing virtual reality worlds: Prefrontal brain regions differentially orchestrate presence experience in adults and children. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2008, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpaner, M.; Kelly, C.; Lieberman, G.; Perelman, H.; Davis, M.; Keefe, F.J.; Naylor, M.R. Unlearning chronic pain: A randomized controlled trial to investigate changes in intrinsic brain connectivity following Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 5, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.; Law, E.; Dudeney, J.; Palermo, T.M.; Stewart, G.; Eccleston, C. Psychological therapies for the management of chronic and recurrent pain in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, Cd003968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, S.; Luberto, C.M.; Bogenschutz, L.H.; Pelley, T.J.; Dusek, J. Integrative care therapies and pain in hospitalized children and adolescents: A retrospective database review. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2014, 20, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, E.; D’Amico, S.; Goldstein, L.; Gardiner, P. Integrative Approaches to Pediatric Chronic Pain in an Urban Safety-Net Hospital: Cost Savings, Clinical Benefits, and Safety. J. Integr. Complement. Med. 2022, 28, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, B.; Tsai, C.L.; Hsu, W.T.; Shen, M.L.; Tseng, P.T.; Chen, D.T.; Su, K.P.; Jingling, L. Music Intervention for Pain Control in the Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jotwani, M.L.; Wu, Z.; Lunde, C.E.; Sieberg, C.B. The missing mechanistic link: Improving behavioral treatment efficacy for pediatric chronic pain. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 1022699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Targeted Mechanisms | Pharmacological Interventions * (Examples) | Non-Pharmacological Interventions (Examples) Neuromodulation and Behavioral Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peripheral sensitization | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, celecoxib | Peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) Vagal nerve stimulation | |
| Regional analgesia techniques including peripheral nerve blocks and neuraxial analgesia | |||
| Capsaicin cream | |||
| Topical application/infiltration of local anesthetics such as lidocaine | |||
| In phases of trials: anti-NGF antibody (phase 3); TrkA receptor antagonist (phase 2) | |||
| Potential: TNF blockers such as adalimumab | |||
| Central sensitization/pain facilitation | Agonists at α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels: gabapentin and pregabalin | Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) | |
| NMDA antagonists (ketamine, methadone, dextromethorphan) | |||
| Descending pain inhibition | Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline) | ||
| Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (duloxetine) | |||
| Clonidine/dexmedetomidine | |||
| Cortical modulation of pain | Anxiety medications such as benzodiazepines | Invasive neurostimulation: deep brain stimulation (DBS) | Virtual reality immersive therapy; distraction cognitive behavioral approaches; mindfulness integrative care relaxation, music, etc. |
| Noninvasive brain stimulation: transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duff, I.T.; Krolick, K.N.; Mahmoud, H.M.; Chidambaran, V. Current Evidence for Biological Biomarkers and Mechanisms Underlying Acute to Chronic Pain Transition across the Pediatric Age Spectrum. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165176
Duff IT, Krolick KN, Mahmoud HM, Chidambaran V. Current Evidence for Biological Biomarkers and Mechanisms Underlying Acute to Chronic Pain Transition across the Pediatric Age Spectrum. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(16):5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165176
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuff, Irina T., Kristen N. Krolick, Hana Mohamed Mahmoud, and Vidya Chidambaran. 2023. "Current Evidence for Biological Biomarkers and Mechanisms Underlying Acute to Chronic Pain Transition across the Pediatric Age Spectrum" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 16: 5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165176
APA StyleDuff, I. T., Krolick, K. N., Mahmoud, H. M., & Chidambaran, V. (2023). Current Evidence for Biological Biomarkers and Mechanisms Underlying Acute to Chronic Pain Transition across the Pediatric Age Spectrum. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(16), 5176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165176