Clinical Characteristics of Eyes with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Tears
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gass, D. Pathogenesis of tears of the retinal pigment epithelium. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1984, 65, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagiel, A.; Freund, K.B.; Spaide, R.F.; Munch, I.C.; Larsen, M.; Sarraf, D. Mechanism of retinal pigment epithelium tear formation following intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy revealed by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 156, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.; Rodríguez, F.J.; Joussen, A.M.; Koh, A.; Eter, N.; Wong, D.T.; Korobelnik, J.F.; Okada, A.A. Management of retinal pigment epithelium tear during anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Retina 2021, 41, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarraf, D.; Reddy, S.; Chiang, A.; Yu, F.; Jain, A. A new grading system for retinal pigment epithelial tears. Retina 2010, 30, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarraf, D.; Chan, C.; Rahimy, E.; Abraham, P. Prospective evaluation of the incidence and risk factors for the development of RPE tears after high-and low-dose ranibizumab therapy. Retina 2013, 33, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, A.; Chang, L.K.; Yu, F.; Sarraf, D. Predictors of anti-VEGF-associated retinal pigment epithelial tear using FA and OCT analysis. Retina 2008, 28, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.K.; Meyer, C.H.; Gross, J.G.; Abraham, P.; Nuthi, A.S.D.D.; Kokame, G.T.; Lin, S.G.; Rauser, M.E.; Kaiser, P.K. Retinal pigment epithelial tears after intravitreal bevacizumab injection for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2007, 27, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronan, S.M.; Yoganathan, P.; Chien, F.Y.; Corcóstegui, I.A.; Blumenkranz, M.S.; Deramo, V.A.; Elner, S.G.; Fastenberg, D.A.; Johnson, M.W.; López, M.; et al. Retinal pigment epithelium tears after intravitreal injections of bevacizumab (Avastin) for neovascular age related macular degeneration. Retina 2007, 27, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xia, J.; Yuan, M.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Bergunder, S.J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, K.; et al. Hypertension affects the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 99, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Japanese Society of Hypertension. Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension 2019; Life Science: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Yoo, S.G.; Han, J.I.; Lew, Y.J.; Cho, S.W.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, J.W. Retinal pigment epithelial tear after intravitreal ranibizumab treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2016, 36, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimy, E.; Freund, K.B.; Larsen, M.; Spaide, R.F.; Costa, R.A.; Hoang, Q.; Christakopoulos, C.; Munch, I.C.; Sarraf, D. Multilayered pigment epithelial detachment in neovascular age related macular degeneration. Retina 2014, 34, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, R.; Sato, T.; Kishi, S. A hyporeflective space between hyperreflective materials in pigment epithelial detachment and Bruch’s membrane in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014, 14, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Age (years) | Sex | Affected Eye | Hypertension | Diabetes Mellitus | Smoking | Anticoagulant Agent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 97 | Male | L | + | + | - | + |
| Case 2 | 74 | Male | R | + | - | - | - |
| Case 3 | 81 | Male | L | + | - | + | - |
| Case 4 | 91 | Female | L | + | - | - | + |
| Case 5 | 69 | Female | R | + | - | - | + |
| Case 6 | 64 | Male | R | - | + | + | + |
| Case 7 | 82 | Male | L | + | + | + | + |
| Case 8 | 84 | Male | L | + | - | - | - |
| Case 9 | 93 | Female | L | + | - | - | - |
| Case 10 | 78 | Female | L | + | - | - | - |
| Case 11 | 77 | Male | R | - | - | - | - |
| Case 12 | 93 | Male | R | - | - | + | - |
| Case 13 | 82 | Male | L | + | - | + | + |
| Case 14 | 76 | Female | R | + | - | - | - |
| Case 15 | 90 | Female | L | + | - | - | - |
| Case 16 | 76 | Male | R | + | - | + | - |
| Lesion | PED Type | PED Height before Treatment (µm) | PED Area (mm2) | Cleft | Anti-VEGF Agent | Injections before RPE Tear (n) | Time from First Treatment to RPE Tear (days) | Tear Grade | Fovea Involvement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 820 | 8.22 | - | Aflibercept | 3 | 98 | 3 | - |
| Case 2 | AMD occult | Serous vascular | 820 | 20.18 | + | None | 0 | 6 | 3 | - |
| Case 3 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 550 | unmeasurable | + | Ranibizumab →aflibercept | 17→1 | 1235 | 4 | + |
| Case 4 | AMD occult | Hemorrhagic + Fibrovascular | 450 | 11.68 | + | Aflibercept | 1 | 35 | 3 | - |
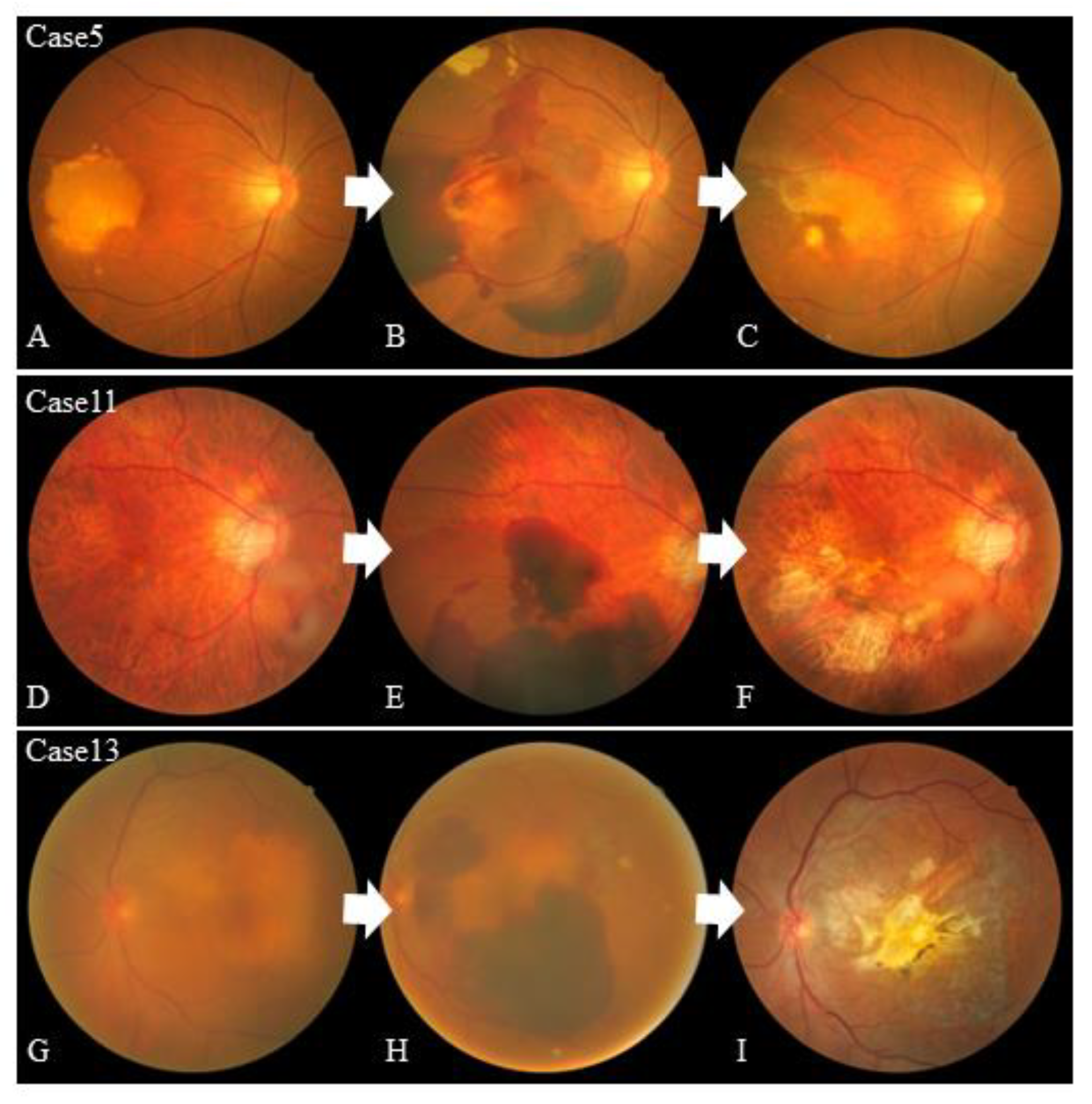
| Case 5 | AMD occult | Hemorrhagic | 405 | 32.3 | + | Aflibercept | 11 | 658 | 4 | + |
| Case 6 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 609 | 33.23 | + | Aflibercept | 1 | 15 | 4 | + |
| Case 7 | AMD classic | Fibrovascular | 720 | 21.07 | - | Ranibizumab | 2 | 41 | 3 | - |
| Case 8 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 582 | 26.45 | + | Aflibercept | 7 | 217 | 4 | + |
| Case 9 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 483 | 19.31 | + | Aflibercept | 2 | 63 | 4 | + |
| Case 10 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 905 | 18.14 | - | Aflibercept | 1 | 28 | 4 | + |
| Case 11 | PCV | Hemorrhagic | 424 | Unmeasurable | - | Ranibizumab | 5 | 434 | 3 | - |
| Case 12 | AMD occult | Hemorrhagic | 660 | Unmeasurable | + | Aflibercept | 7 | 325 | 4 | + |
| Case 13 | AMD occult | Hemorrhagic | 681 | Unmeasurable | + | Aflibercept | 10 | 490 | 4 | + |
| Case 14 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 274 | 20.26 | - | Ranibizumab | 1 | 21 | 3 | - |
| Case 15 | AMD occult | Fibrovascular | 738 | 18.86 | + | Ranibizumab | 3 | 102 | 3 | - |
| Case 16 | AMD occult | Serous vascular | 730 | 21.85 | - | Aflibercept | 8 | 448 | 4 | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagata, J.; Shiose, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Fukui, T.; Kano, K.; Mori, K.; Nakama, T.; Notomi, S.; Sonoda, K.-H. Clinical Characteristics of Eyes with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Tears. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175496
Nagata J, Shiose S, Ishikawa K, Fukui T, Kano K, Mori K, Nakama T, Notomi S, Sonoda K-H. Clinical Characteristics of Eyes with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Tears. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175496
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagata, Junya, Satomi Shiose, Keijiro Ishikawa, Takuma Fukui, Kumiko Kano, Kenichiro Mori, Takahito Nakama, Shoji Notomi, and Koh-Hei Sonoda. 2023. "Clinical Characteristics of Eyes with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Tears" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175496
APA StyleNagata, J., Shiose, S., Ishikawa, K., Fukui, T., Kano, K., Mori, K., Nakama, T., Notomi, S., & Sonoda, K. -H. (2023). Clinical Characteristics of Eyes with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Tears. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175496






