Anterior Scleral Thickness and Other Dimensions in Nanophthalmos by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography: A Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ophthalmological Examination
2.3. Ocular Biometry
- -
- Axial Length (AXL) (mm): distance from the epithelium of the corneal apex to the inner limiting membrane (ILM) on the optical axis;
- -
- Anterior Chamber Depth (ACD) (mm): distance from the corneal endothelium to the anterior lens capsule;
- -
- Crystalline Lens Thickness (LT) (mm): distance from the anterior to the posterior pole of the lens ACD and LT were analyzed only in phakic patients in the group of nanophthalmos (n = 33);
- -
- White-to-white (WTW) (mm): horizontal corneal diameter measured from limbus to limbus;
- -
- Central Corneal Thickness (CCT) (µm): measured from the epithelium to the endothelium.
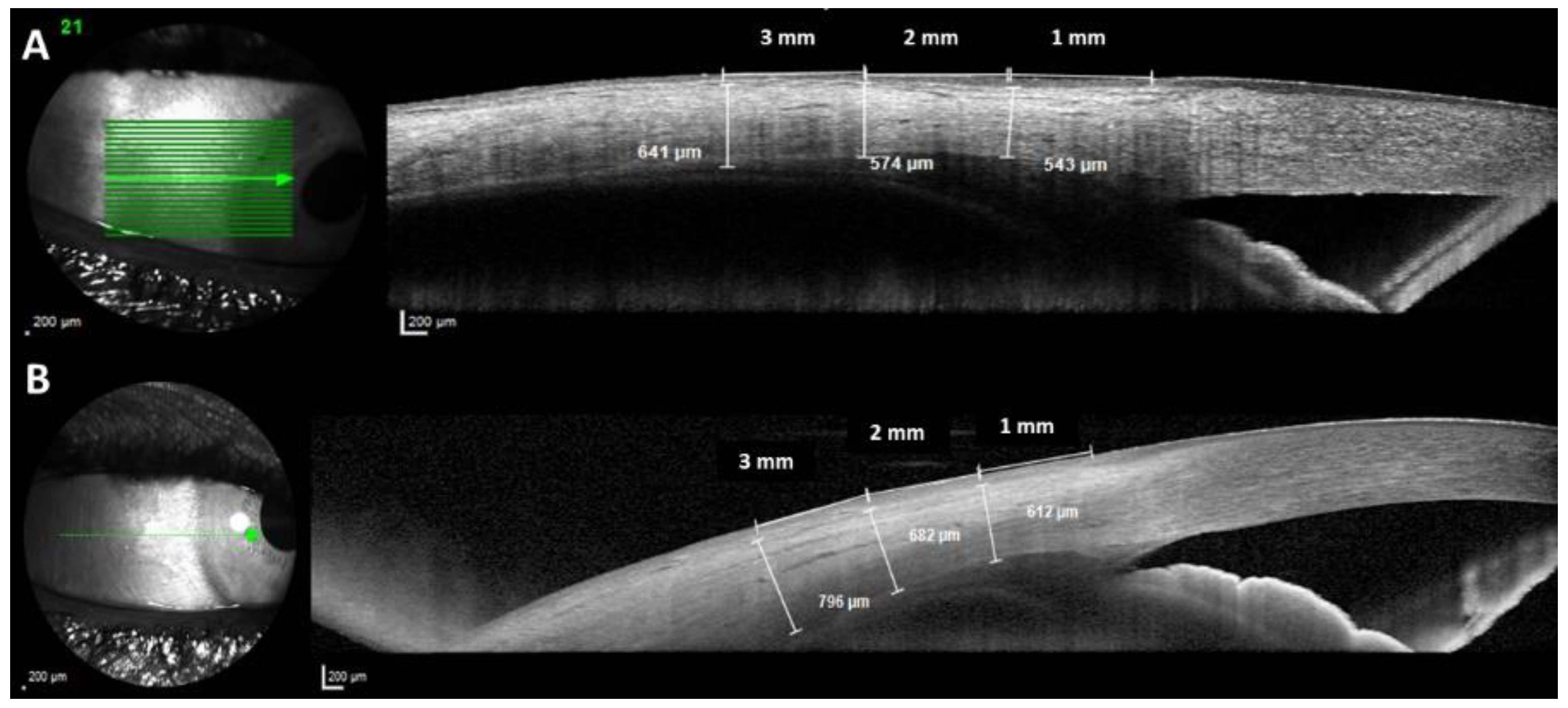
2.4. Optical Coherence Tomography
2.5. OCT Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, N.; Zhao, L.-L.; Liu, J.; Ma, L.-L.; Zhao, J.-S. Nanophthalmos: An Update on the Biological Parameters and Fundus Abnormalities. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 2021, 8853811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendrababu, S.; Shroff, S.; Uduman, M.S.; Babu, N. Clinical Spectrum and Treatment Outcomes of Patients with Nanophthalmos. Eye 2021, 35, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carricondo, P.C.; Andrade, T.; Prasov, L.; Ayres, B.M.; Moroi, S.E. Nanophthalmos: A Review of the Clinical Spectrum and Genetics. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2018, 2735465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steijns, D.; Bijlsma, W.R.; Van der Lelij, A. Cataract Surgery in Patients with Nanophthalmos. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.-Y.; Feng, J.-R.; Zhang, L. Treatment of Nanophthalmos Cataracts: Surgery and Complications. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 37, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Dawson, D.G.; Sugar, A.; Elner, S.G.; Meyer, K.A.; McKey, J.B.; Moroi, S.E. Cataract Surgery in Patients with Nanophthalmos. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2004, 30, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailor, R.; Ng, A.T.W.; Murthy, S. Cataract Surgery in Patients with Nanophthalmos. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; He, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, X. Morphological Features of Anterior Segment: Factors Influencing Intraocular Pressure after Cataract Surgery in Nanophthalmos. Eye Vis. 2020, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrababu, S.; Babu, N.; Sinha, S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Vardhan, A.; Puthuran, G.V.; Ramulu, P.Y. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Outcomes of Cataract Surgery in Nanophthalmos With and Without Prophylactic Sclerostomy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 183, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, A.C.; MacLaren, R.E.; Bunce, C.; Stevens, J.D.; Foster, P.J. Outcomes of Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation in Microphthalmos and Nanophthalmos. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2013, 39, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, R.; Vupparaboina, K.K.; Verkicharla, P.K. Anterior Sclera Undergoes Thinning with Increasing Degree of Myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.; Eom, Y.S.; Suh, Y.W.; Kim, Y.Y. Central Corneal Thickness and Anterior Scleral Thickness in Korean Patients with Open-Angle Glaucoma: An Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography Study. J. Glaucoma 2011, 20, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanaga, N.; Terao, N.; Nakamine, S.; Tamashiro, T.; Wakugawa, S.; Sawaguchi, K.; Koizumi, H. Scleral Thickness in Central Serous Chorioretinopathy. Ophthalmol. Retina 2021, 5, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Vigo, J.I.; Moreno-Morillo, F.J.; Shi, H.; Ly-Yang, F.; Burgos-Blasco, B.; Güemes-Villahoz, N.; Donate-López, J.; García-Feijóo, J. Assessment of the Anterior Scleral Thickness in Central Serous Chorioretinopathy Patients by Optical Coherence Tomography. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 65, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Vigo, J.I.; Shi, H.; Burgos-Blasco, B.; Fernández-Aragón, S.; De-Pablo-Gómez-de-Liaño, L.; Kudsieh, B.; Macarro-Merino, A.; Ángel Fernández-Vigo, J. Anterior Scleral Thickness Dimensions by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2022, 105, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhou, H.; Shi, Y.; Choe, J.; Shen, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Feuer, W.J.; Gregori, G.; et al. Interocular Asymmetry of Choroidal Thickness and Vascularity Index Measurements in Normal Eyes Assessed by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín-Moro, J.; Gutierrez-Ortiz, C. Implications of SS-OCT-Anterior Scleral Thickness Biometry on the Definition of Nanophthtalmos. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2022, 105, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Vigo, J.I.; Burgos-Blasco, B.; De-Pablo-Gómez-de-Liaño, L.; Kudsieh, B.; Fernández-Vigo, J.Á. Implications of SS-OCT-Anterior Scleral Thickness Biometry on the Definition of Nanophthtalmos. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2022, 105, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalvac, I.S.; Satana, B.; Ozkan, G.; Eksioglu, U.; Duman, S. Management of Glaucoma in Patients with Nanophthalmos. Eye 2008, 22, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewsangthong, K.; Thoongsuwan, S.; Uiprasertkul, M.; Phasukkijwatana, N. Unusual Non-Nanophthalmic Uveal Effusion Syndrome with Histologically Normal Scleral Architecture: A Case Report. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.W.; Aaberg, S.Y.; Geroski, D.H.; Edelhauser, H.F. Human Sclera: Thickness and Surface Area. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 125, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamani, A.; Wood, I.; Sugino, I.; Wanner, M.; Zarbin, M.A. Abnormal Collagen Fibrils in Nanophthalmos: A Clinical and Histologic Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 127, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trelstad, R.L.; Silbermann, N.N.; Brockhurst, R.J. Nanophthalmic Sclera. Ultrastructural, Histochemical, and Biochemical Observations. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1982, 100, 1935–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calhoun, F.P. The Management of Glaucoma in Nanophthalmos. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1975, 73, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, W.; Kunde, W. On the Origin of the Ebbinghaus Illusion: The Role of Figural Extent and Spatial Frequency of Stimuli. Vision Res. 2021, 188, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relhan, N.; Jalali, S.; Pehre, N.; Rao, H.L.; Manusani, U.; Bodduluri, L. High-Hyperopia Database, Part I: Clinical Characterisation Including Morphometric (Biometric) Differentiation of Posterior Microphthalmos from Nanophthalmos. Eye 2016, 30, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, A.; Altan, C.; Osmanbasoglu, O.A.; Celik, U.; Kara, N.; Demirok, A. Subfoveal Choroidal Thickness Measurements with Enhanced Depth Imaging Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Nanophthalmos. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, F.E.; Altan, C.; Kesim, C.; Demircan, A.; Tunç, U.; Demir, G.; Taskapılı, M. Choroidal Vascularity Index as an Indicator of Vascular Status of Choroid, in Eyes with Nanophthalmos. Eye 2020, 34, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Tsujikawa, A.; Matsumoto, A.; Hangai, M.; Ooto, S.; Yamashiro, K.; Akiba, M.; Yoshimura, N. Macular Choroidal Thickness and Volume in Normal Subjects Measured by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 4971–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Shinojima, A.; Ryusaburo, M.; Kawamura, A.; Yuzawa, M. Choroidal Thickness Findings in Two Siblings with Nanophthalmos by Swept Source-OCT: A Case Report. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variable | Nanophthalmos | Control Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AXL (mm) | 19.3 ± 1.5 (15.48–20.47) | 23.9 ± 1.1 (21.84–26.97) | <0.001 |
| CCT (µm) | 549.0 ± 35.5 (479–625) | 540.6 ± 38.4 (412–644) | 0.253 |
| WTW (mm) | 11.6 ± 0.48 (10.60–13.02) | 12.1 ± 0.40 (11.40–13.20) | <0.001 |
| ACD (mm) | 3.06 ± 0.91 (1.97–5.06) | 3.46 ± 0.48 (2.83–4.66) | <0.001 |
| LT (mm) | 4.44 ± 0.58 (3.26–5.47) | 4.12 ± 0.48 (3.25–5.42) | <0.001 |
| SFCT (µm) | 447 ± 125 (192–761) | 307 ± 90 (139–545) | <0.001 |
| Nasal 1 mm CT (µm) | 440 ± 131 (177–755) | 273 ± 87 (111–498) | <0.001 |
| Temporal 1 mm CT (µm) | 424 ± 120 (182–704) | 292 ± 82 (119–500) | <0.001 |
| CRT (µm) | 292 ± 80 (205–535) | 252 ± 51 (186–545) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Nanophthalmos | Control Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal OWT1 (µm) | 1185 ± 185 (881–1761) | 1064 ± 120 (651–1315) | <0.001 * |
| Nasal OWT2 (µm) | 1066 ± 208 (747–1757) | 948 ± 96 (715–1181) | <0.001 * |
| Nasal OWT3 (µm) | 1020 ± 222 (554–1579) | 923 ± 120 (562–1218) | 0.005 * |
| Temporal OWT1 (µm) | 1157 ± 166 (776–1594) | 1049 ± 116 (615–1303) | <0.001 * |
| Temporal OWT2 (µm) | 996 ± 190 (729–1811) | 916 ± 104 (635–1222) | 0.007 * |
| Temporal OWT3 (µm) | 981 ± 253 (560–1823) | 874 ± 121 (554–1163) | 0.005 * |
| Nasal AST1 (µm) SS-OCT | 742 ± 91 (590–983) | 687 ± 98 (505–1180) | 0.004 * |
| Nasal AST2 (µm) SS-OCT | 769 ± 137 (547–1271) | 740 ± 94 (565–1060) | 0.199 |
| Nasal AST3 (µm) SS-OCT | 755 ± 146 (400–1207) | 767 ± 120 (458–990) | 0.654 |
| Temporal AST1 (µm) SS-OCT | 693 ± 101 (523–951) | 670 ± 100 (535–1229) | 0.249 |
| Temporal AST2 (µm) SS-OCT | 695 ± 129 (400–1017) | 704 ± 89 (516–923) | 0.688 |
| Temporal AST3 (µm) SS-OCT | 705 ± 188 (358–1333) | 691 ± 118 (402–943) | 0.656 |
| Nasal AST1 (µm) SD-OCT | 705 ± 102 (547–1003) | 682 ± 99 (540–1002) | 0.238 |
| Nasal AST2 (µm) SD-OCT | 732 ± 106 (553–1008) | 707 ± 84 (547–998) | 0.194 |
| Nasal AST3 (µm) SD-OCT | 759 ± 120 (566–1042) | 719 ± 69 (562–902) | 0.039 * |
| Temporal AST1 (µm) SD-OCT | 654 ± 79 (527–841) | 691 ± 99 (518–1154) | 0.038 * |
| Temporal AST2 (µm) SD-OCT | 658 ± 83 (497–850) | 666 ± 87 (519–991) | 0.628 |
| Temporal AST3 (µm) SD-OCT | 691 ± 96 (550–956) | 691 ± 74 (577–955) | 0.994 |
| Variable | Correlation with AXL (p-Value) |
|---|---|
| ACD | R = 0.029 (p = 0.847) |
| LT | R = −0.366 (p = 0.008) |
| WTW | R = 0.150 (p = 0.319) |
| CCT | R = −0.097 (p = 0.517) |
| SFCT | R = −0.216 (p = 0.113) |
| Nasal 1 mm CT | R = −0.242 (p = 0.075) |
| Temporal 1 mm CT | R = −0.112 (p = 0.416) |
| Retinal thickness | R = 0.079 (p = 0.567) |
| Nasal OWT1 | R = 0.103 (p = 0.520) |
| Nasal OWT2 | R = −0.036 (p = 0.826) |
| Nasal OWT3 | R = −0.054 (p = 0.745) |
| Temporal OWT1 | R = −0.045 (p = 0.779) |
| Temporal OWT2 | R = −0.432 (p = 0.004) |
| Temporal OWT3 | R = −0.540 (p = 0.001) |
| Nasal AST1 SS-OCT | R = −0.018 (p = 0.911) |
| Nasal AST2 SS-OCT | R = −0.238 (p = 0.135) |
| Nasal AST3 SS-OCT | R = −0.076 (p = 0.647) |
| Temporal AST1 SS-OCT | R = −0.090 (p = 0.572) |
| Temporal AST2 SS-OCT | R = −0.322 (p = 0.038) |
| Temporal AST3 SS-OCT | R = −0.478 (p = 0.001) |
| Nasal AST1 SD-OCT | R = 0.230 (p = 0.087) |
| Nasal AST2 SD-OCT | R = −0.089 (p = 0.512) |
| Nasal AST3 SD-OCT | R = 0.147 (p = 0.280) |
| Temporal AST1 SD-OCT | R = −0.181 (p = 0.223) |
| Temporal AST2 SD-OCT | R = −0.357 (p = 0.015) |
| Temporal AST3 SD-OCT | R = −0.272 (p = 0.075) |
| Nanophthalmos | SFCT (µm) | Nasal 1 mm CT (µm) | Temporal 1 mm CT (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observer 1: First measurement | 447 ± 125 (192–761) | 440 ± 131 (177–755) | 424 ± 120 (182–704) |
| Observer 1: Second measurement | 442 ± 123 (191–723) | 442 ± 130 (181–765) | 419 ± 117 (189–711) |
| Observer 2 | 443 ± 123 (201–744) | 434 ± 125 (195–740) | 423 ± 115 (189–689) |
| Intraobserver ICC | 0.995 (0.989–0.998) | 0.997 (0.995–0.999) | 0.995 (0.989–0.998) |
| Interobserver ICC | 0.996 (0.991–0.998) | 0.991 (0.978–0.996) | 0.996 (0.993–0.998) |
| Control Group | SFCT (µm) | Nasal 1 mm CT (µm) | Temporal 1 mm CT (µm) |
| Observer 1: First measurement | 307 ± 90 (139–545) | 273 ± 87 (111–498) | 292 ± 82 (119–500) |
| Observer 1: Second measurement | 303 ± 87 (143–559) | 276 ± 85 (116–505) | 295 ± 80 (121–491) |
| Observer 2 | 305 ± 88 (142–537) | 274 ± 85 (114–503) | 293 ± 79 (123–495) |
| Intraobserver ICC | 0.993 (0.985–0.996) | 0.994 (0.990–0.997) | 0.994 (0.990–0.997) |
| Interobserver ICC | 0.995 (0.992–0.997) | 0.994 (0.990–0.997) | 0.993 (0.988–0.996) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Vigo, J.I.; Rodríguez-Quet, O.; Montolío-Marzo, E.; Burgos-Blasco, B.; Kudsieh, B.; González-Martin-Moro, J.; García-Feijóo, J. Anterior Scleral Thickness and Other Dimensions in Nanophthalmos by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography: A Comparative Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5564. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175564
Fernández-Vigo JI, Rodríguez-Quet O, Montolío-Marzo E, Burgos-Blasco B, Kudsieh B, González-Martin-Moro J, García-Feijóo J. Anterior Scleral Thickness and Other Dimensions in Nanophthalmos by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography: A Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5564. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175564
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Vigo, José Ignacio, Olivia Rodríguez-Quet, Elena Montolío-Marzo, Bárbara Burgos-Blasco, Bachar Kudsieh, Julio González-Martin-Moro, and Julián García-Feijóo. 2023. "Anterior Scleral Thickness and Other Dimensions in Nanophthalmos by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography: A Comparative Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5564. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175564
APA StyleFernández-Vigo, J. I., Rodríguez-Quet, O., Montolío-Marzo, E., Burgos-Blasco, B., Kudsieh, B., González-Martin-Moro, J., & García-Feijóo, J. (2023). Anterior Scleral Thickness and Other Dimensions in Nanophthalmos by Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography: A Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5564. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175564







