Evaluation of Artifact Appearance and Burden in Pediatric Brain Tumor MR Imaging with Compressed Sensing in Comparison to Conventional Parallel Imaging Acceleration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fink, J.R.; Muzi, M.; Peck, M.; Krohn, K.A. Multimodality Brain Tumor Imaging: MR Imaging, PET, and PET/MR Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Mabray, M.C.; Cha, S. Current Clinical Brain Tumor Imaging. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartoretti, E.; Sartoretti, T.; Binkert, C.; Najafi, A.; Schwenk, Á.; Hinnen, M.; van Smoorenburg, L.; Eichenberger, B.; Sartoretti-Schefer, S. Reduction of procedure times in routine clinical practice with Compressed SENSE magnetic resonance imaging technique. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, K.G. Reducing acquisition time in clinical MRI by data undersampling and compressed sensing reconstruction. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, R297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranic, J.E.; Cross, N.M.; Wang, Y.; Hippe, D.S.; de Weerdt, E.; Mossa-Basha, M. Compressed Sensing-Sensitivity Encoding (CS-SENSE) Accelerated Brain Imaging: Reduced Scan Time without Reduced Image Quality. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkovich, M.J.; Li, Y.; Desikan, R.S.; Barkovich, A.J.; Xu, D. Challenges in pediatric neuroimaging. Neuroimage 2019, 185, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machata, A.M.; Willschke, H.; Kabon, B.; Prayer, D.; Marhofer, P. Effect of brain magnetic resonance imaging on body core temperature in sedated infants and children. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salerno, S.; Granata, C.; Trapenese, M.; Cannata, V.; Curione, D.; Espagnet, M.C.R.; Magistrelli, A.; Tomà, P. Is MRI imaging in pediatric age totally safe? A critical reprisal. Radiol. Med. 2018, 123, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serai, S.D.; Hu, H.H.; Ahmad, R.; White, S.; Pednekar, A.; Anupindi, S.A.; Lee, E.Y. Newly Developed Methods for Reducing Motion Artifacts in Pediatric Abdominal MRI: Tips and Pearls. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Hu, H.H.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Krishnamurthy, R. Reducing sedation for pediatric body MRI using accelerated and abbreviated imaging protocols. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanawala, S.S.; Alley, M.T.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Barth, R.A.; Pauly, J.M.; Lustig, M. Improved pediatric MR imaging with compressed sensing. Radiology 2010, 256, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, J.Y.; Potnick, A.G.; Barth, R.A.; Alley, M.T.; Uecker, M.; Lustig, M.; Pauly, J.M.; Vasanawala, S.S. Fast pediatric 3D free-breathing abdominal dynamic contrast enhanced MRI with high spatiotemporal resolution. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, R.L.; Groth, M.; Jurgens, J.H.W.; Zhang, S.; Buhk, J.H.; Herrmann, J. Compressed SENSE in Pediatric Brain Tumor MR Imaging: Assessment of Image Quality, Examination Time and Energy Release. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2022, 32, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, B.M.; Jaimes, C.; Kirsch, J.; Gee, M.S. MRI Techniques to Decrease Imaging Times in Children. Radiographics 2020, 40, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartoretti, T.; Reischauer, C.; Sartoretti, E.; Binkert, C.; Najafi, A.; Sartoretti-Schefer, S. Common artefacts encountered on images acquired with combined compressed sensing and SENSE. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thust, S.C.; Heiland, S.; Falini, A.; Jäger, H.R.; Waldman, A.D.; Sundgren, P.C.; Godi, C.; Katsaros, V.K.; Ramos, A.; Bargallo, N.; et al. Glioma imaging in Europe: A survey of 220 centres and recommendations for best clinical practice. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3306–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiland, S. From A as in Aliasing to Z as in Zipper: Artifacts in MRI. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2008, 18, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisanti, C.; Carlin, C.; Banks, K.P.; Wang, D. Normal MRI appearance and motion-related phenomena of CSF. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, O.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. Artifacts in 3-T MRI: Physical background and reduction strategies. Eur. J. Radiol. 2008, 65, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.; Gullapalli, R.P. AAPM/RSNA physics tutorial for residents: MR artifacts, safety, and quality control. In Radiographics; 2006; Volume 26, pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.R.; Broadbent, D.A.; Fent, G.J.; Garg, P.; Brown, L.A.; Chew, P.G.; Dobson, L.E.; Swoboda, P.P.; Plein, S.; Higgins, D.M.; et al. Clinical evaluation of two dark blood methods of late gadolinium quantification of ischemic scar. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chowdhury, S.; Lustig, M.; Barth, R.A.; Alley, M.T.; Grafendorfer, T.; Calderon, P.D.; Robb, F.J.; Pauly, J.M.; Vasanawala, S.S. Clinical performance of contrast enhanced abdominal pediatric MRI with fast combined parallel imaging compressed sensing reconstruction. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, M.I.; Delavelle, J.; Kohler, R.; Becker, C.D.; Lovblad, K. Brain and spine MRI artifacts at 3Tesla. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 36, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.D.; Fong, C.L.; Tzung, B.S.; Law, M.; Nayak, K.S. Clinical image quality assessment of accelerated magnetic resonance neuroimaging using compressed sensing. Investig. Radiol. 2013, 48, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes, C.; Kirsch, J.E.; Gee, M.S. Fast, free-breathing and motion-minimized techniques for pediatric body magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaskis, C.; Neyns, B.; Michotte, A.; De Ridder, M.; Everaert, H. Pseudoprogression after radiotherapy with concurrent temozolomide for high-grade glioma: Clinical observations and working recommendations. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualetti, F.; Malfatti, G.; Cantarella, M.; Gonnelli, A.; Montrone, S.; Montemurro, N.; Gadducci, G.; Giannini, N.; Pesaresi, I.; Perrini, P.; et al. Role of magnetic resonance imaging following postoperative radiotherapy in clinical decision-making of patients with high-grade glioma. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreha-Kulaczewski, S.; Konopka, M.; Joseph, A.A.; Kollmeier, J.; Merboldt, K.-D.; Ludwig, H.-C.; Gärtner, J.; Frahm, J. Respiration and the watershed of spinal CSF flow in humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, H.; Tithof, J.; Du, T.; Song, W.; Peng, W.; Sweeney, A.M.; Olveda, G.; Thomas, J.H.; Nedergaard, M.; Kelley, D.H. Flow of cerebrospinal fluid is driven by arterial pulsations and is reduced in hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.; Pauly, J.M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.L.; Santos, J.M.; Pauly, J.M. Compressed Sensing MRI. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Ying, L. Accelerating SENSE using compressed sensing. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruessmann, K.P.; Weiger, M.; Scheidegger, M.B. SENSE: Sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanath, S.; Reddy, R.; Konar, A.S.; Imam, S.; Sundaresan, R.; DR, R.B.; Venkatesan, R. Compressed sensing MRI: A review. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspan, O.N.; Fleysher, R.; Lipton, M.L. Compressed sensing MRI: A review of the clinical literature. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.K.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S. Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging for Double Hepatic Arterial Phase Acquisition in Gadoxetate-Enhanced Dynamic Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano-Massiah, S.; Sayadi, A.; de Boer, R.; Gelderblom, J.; Mahdjoub, R.; Gerber, S.; Zuber, M.; Zins, M.; Hodel, J. Accuracy of the Compressed Sensing Accelerated 3D-FLAIR Sequence for the Detection of MS Plaques at 3T. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xu, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Feng, F.; Xue, H.; Jin, Z. Comparison and evaluation of the efficacy of compressed SENSE (CS) and gradient- and spin-echo (GRASE) in breath-hold (BH) magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfield, J.; Kealey, S. Magnetic resonance imaging acquisition techniques intended to decrease movement artefact in paediatric brain imaging: A systematic review. Pediatr. Radiol. 2015, 45, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

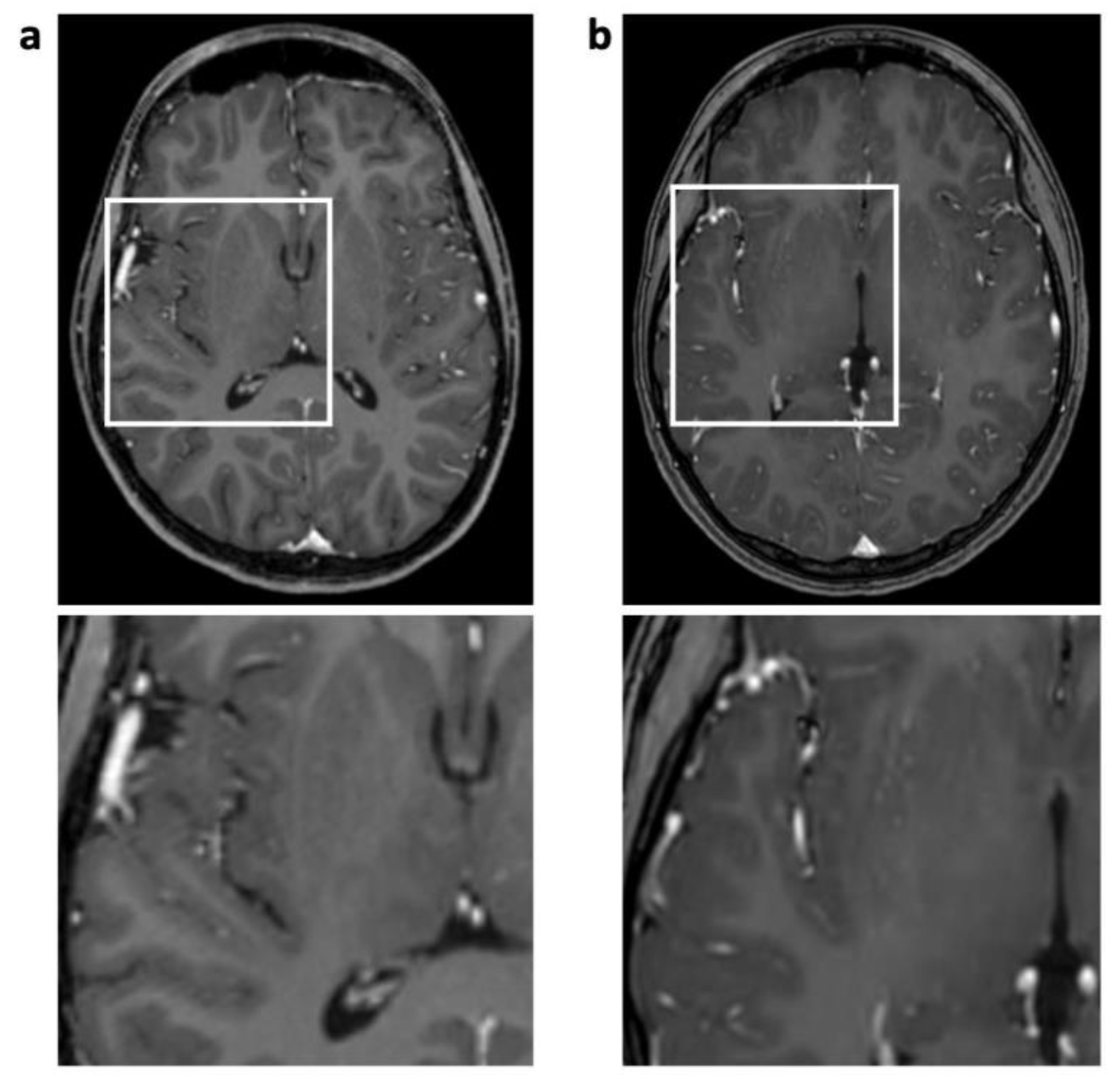
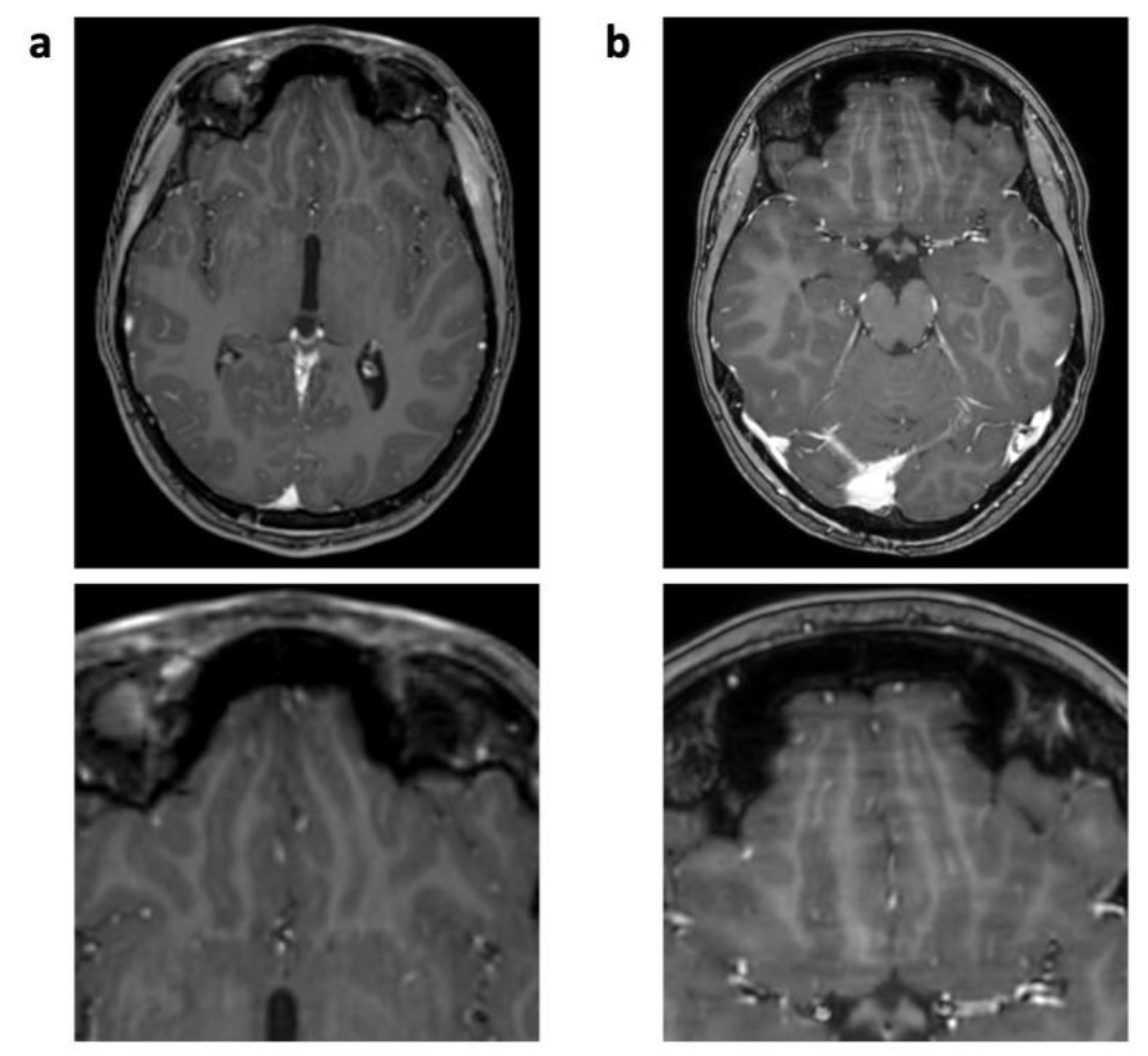
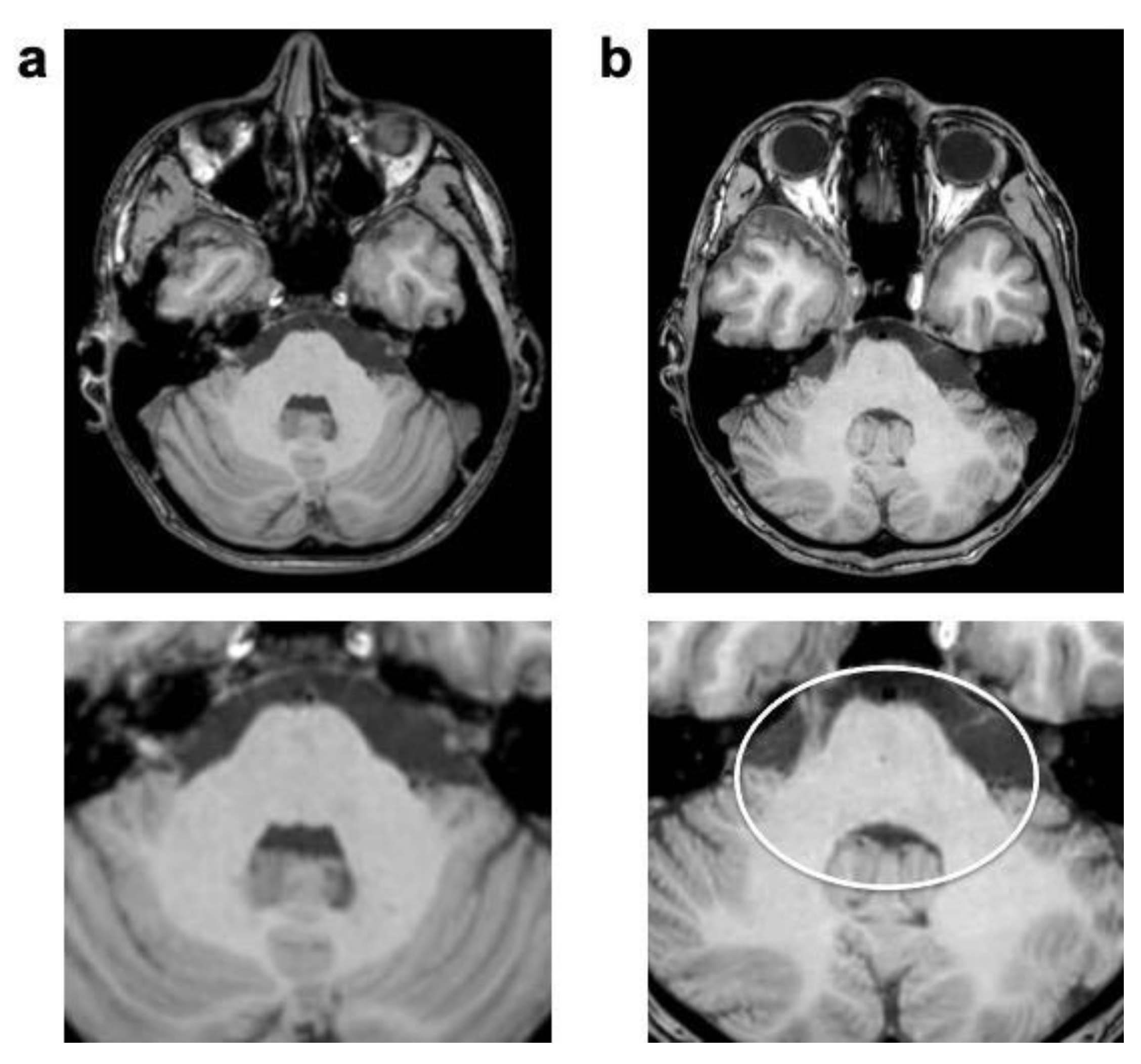
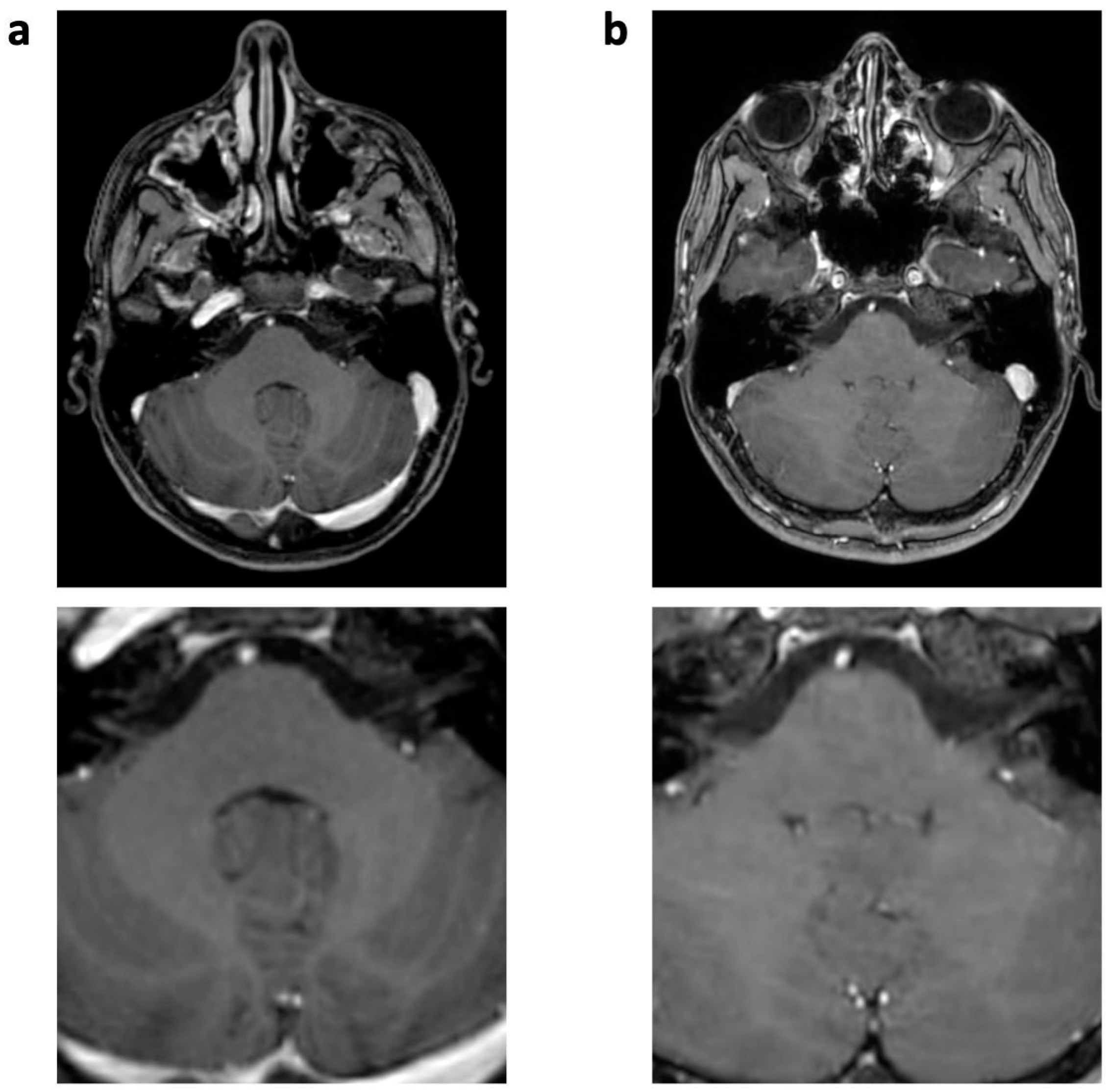
| 3D T1 TFE | T2 TSE | FLAIR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SENSE | CS | SENSE | CS | SENSE | CS | |
| Scan time (min:sec) | 03:38 | 03:00 | 03:36 | 02:07 | 03:51 | 02:38 |
| Acceleration | SENSE 1.2 × 2.2 | 3.3 | - | 1.3 | SENSE 1.8 × 1.3 | 4.5 |
| TR/TE (ms) | 8.3/3.8 | 8.6/4.0 | 3000/80 | 3954/80 | 11,000/125 | 4800/396 |
| TI delay (ms) | 956.8 | 989.9 | - | - | 2800 | 1650 |
| SNRa (arbitrary) | 167.0 | 145.7 | 155.3 | 189.3 | 205.3 | 222.3 |
| FOV (mm3) | 240 × 240 × 175 | 240 × 240 × 175 | 230 × 182 × 152 | 230 × 182 × 152 | 230 × 183 × 138 | 230 × 179 × 152 |
| Voxel size [ACQ] (mm3) | 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 | 0.85 × 0.85 × 0.85 | 0.55 × 0.65 × 3.0 | 0.55 × 0.65 × 3.0 | 0.65 × 0.87 × 3.0 | 0.75 × 0.75 × 3.3 |
| Voxel size [REC] (mm3) | 0.9 × 0.9 × 1.0 | 0.43 × 0.43 × 0.43 | 0.4 × 0.4 × 3.0 | 0.4 × 0.4 × 3.0 | 0.34 × 0.34 × 3.0 | 0.34 × 0.34 × 3.3 |
| Artifact Category | Type of Artifact | SENSE | Compressed Sensing (CS) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | |||
| Physiology-related | Motion | 2 (9%) | 2 (0.09 ± 0.29) | 0 | 0 | 0.180 |
| Ringing | 11 (50%) | 14 (0.64 ± 0.73) | 10 (45%) | 10 (0.45 ± 0.61) | 0.010 | |
| CSF flow | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pulsation/ghosting | 12 (55%) | 15 (0.68 ± 0.72) | 0 | 0 | 0.002 | |
| Physics-related | Chemical shift | 22 (100%) | 30 (1.36 ± 0.49) | 22 (100%) | 36 (1.64 ± 0.49) | 0.030 |
| Susceptibility effects | 21 (95%) | 35 (1.59 ± 0.59) | 21 (95%) | 34 (1.55 ± 0.60) | 0.285 | |
| Technique-related | Straight bands | 10 (45%) | 10 (0.45 ± 0.51) | 1 (5%) | 1 (0.05 ± 0.21) | 0.008 |
| Starry sky | 0 | 0 | 22 (100%) | 33 (1.50 ± 0.51) | ||
| Wax layer | 0 | 0 | 1 (5%) | 1 (0.05 ± 0.21) | ||
| Wavy lines | 0 | 0 | 1 (5%) | 1 (0.05 ± 0.21) | ||
| Overall | 4.82 ± 1.50 | 3.68 ± 1.04 * | <0.001 | |||
| Artifact Category | Type of Artifact | SENSE | Compressed Sensing (CS) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | |||
| Physiology-related | Motion | 4 (18%) | 6 (0.27 ± 0.63) | 1 (5%) | 1 (0.05 ± 0.21) | 0.066 |
| Ringing | 14 (64%) | 19 (0.64 ± 0.73) | 11 (55%) | 14 (0.45 ± 0.51) | 0.060 | |
| CSF flow | 0 | 0 | 1 (5%) | 2 (0.09 ± 0.43) | 0.317 | |
| Pulsation/ghosting | 17 (77%) | 23 (1.05 ± 0.72) | 0 | 0 | <0.001 | |
| Physics-related | Chemical shift | 22 (100%) | 31 (1.41 ± 0.50) | 22 (100%) | 31 (1.41 ± 0.50) | 0.354 |
| Susceptibility effects | 21 (95%) | 37 (1.68 ± 0.57) | 21 (95%) | 35 (1.59 ± 0.59) | 0.180 | |
| Technique-related | Straight bands | 9 (41%) | 10 (0.45 ± 0.60) | 2 (9%) | 2 (0.09 ± 0.29) | 0.029 |
| Starry sky | 0 | 0 | 12 (55%) | 14 (0.45 ± 0.51) | ||
| Wax layer | 0 | 0 | 11 (50%) | 11 (0.50 ± 0.51) | ||
| Wavy lines | 0 | 0 | 2 (9%) | 2 (0.09 ± 0.43) | ||
| Overall | 5.73 ± 1.72 | 3.86 ± 1.21 * | <0.001 | |||
| Artifact Category | Type of Artifact | SENSE | Compressed Sensing (CS) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | |||
| Physiology-related | Motion | 3 (14%) | 4 (0.18 ± 0.50) | 3 (14%) | 3 (0.14 ± 0.35) | 0.423 |
| Ringing | 9 (41%) | 12 (0.55 ± 0.74) | 10 (45%) | 12 (0.55 ± 0.67) | 0.192 | |
| CSF flow | 22 (100%) | 38 (1.73 ± 0.46) | 22 (100%) | 41 (1.86 ± 0.35) | 0.080 | |
| Pulsation/ghosting | 17 (77% | 22 (1.00 ± 0.69) | 20 (91%) | 26 (1.18 ± 0.59) | 0.041 | |
| Physics-related | Chemical shift | 1 (5%) | 1 (0.05 ± 0.21) | 1 (5%) | 1 (0.05 ± 0.21) | 0 |
| Susceptibility effects | 19 (86%) | 23 (1.05 ± 0.58) | 19 (86%) | 23 (1.05 ± 0.58) | 0 | |
| Technique-related | Straight bands | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Starry sky | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Wax layer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Wavy lines | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Overall | 4.55 ± 1.53 | 4.82 ± 1.10 * | 0.018 | |||
| Artifact Category | Type of Artifact | SENSE | Compressed Sensing (CS) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | Scans Affected n (%) | Artifact Strength Sum Score (Mean ± SD) | |||
| Physiology-related | Motion | 10 (45%) | 11 (0.50 ± 0.60) | 0 | 0 | 0.005 |
| Ringing | 21 (95%) | 24 (1.09 ± 0.43) | 6 (27%) | 6 (0.27 ± 0.46) | <0.001 | |
| CSF flow | 22 (100%) | 43 (1.95 ± 0.21) | 8 (36%) | 8 (0.36 ± 0.49) | <0.001 | |
| Pulsation/ghosting | 18 (82%) | 30 (1.36 ± 0.79) | 0 | 0 | <0.001 | |
| Physics-related | Chemical shift | 6 (27%) | (0.27 ± 0.46) | 0 | 0 | 0.028 |
| Susceptibility effects | 19 (86%) | 20 (0.91 ± 0.43) | 19 (86%) | 23 (1.05 ± 0.58) | 0.109 | |
| Technique-related | Straight bands | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Starry sky | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Wax layer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Wavy lines | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Overall | 6.09 ± 1.72 | 1.68 ± 0.72 * | <0.001 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meister, R.L.; Groth, M.; Zhang, S.; Buhk, J.-H.; Herrmann, J. Evaluation of Artifact Appearance and Burden in Pediatric Brain Tumor MR Imaging with Compressed Sensing in Comparison to Conventional Parallel Imaging Acceleration. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175732
Meister RL, Groth M, Zhang S, Buhk J-H, Herrmann J. Evaluation of Artifact Appearance and Burden in Pediatric Brain Tumor MR Imaging with Compressed Sensing in Comparison to Conventional Parallel Imaging Acceleration. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175732
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeister, Rieke Lisa, Michael Groth, Shuo Zhang, Jan-Hendrik Buhk, and Jochen Herrmann. 2023. "Evaluation of Artifact Appearance and Burden in Pediatric Brain Tumor MR Imaging with Compressed Sensing in Comparison to Conventional Parallel Imaging Acceleration" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175732
APA StyleMeister, R. L., Groth, M., Zhang, S., Buhk, J.-H., & Herrmann, J. (2023). Evaluation of Artifact Appearance and Burden in Pediatric Brain Tumor MR Imaging with Compressed Sensing in Comparison to Conventional Parallel Imaging Acceleration. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175732






