Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life after Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) Closure in Patients with Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack of Undetermined Cause and Other PFO-Associated Clinical Conditions: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, R.H.; Webb, S.; Brown, N.A.; Lamers, W.; Moorman, A. Development of the heart: (2) Septation of the atriums and ventricles. Heart 2003, 89, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, H.; Virmani, R.; Ladich, E.; Mackey-Bojack, S.; Titus, J.; Reisman, M.; Gray, W.; Nakamura, M.; Mooney, M.; Poulose, A.; et al. Patent foramen ovale: Current pathology, pathophysiology, and clinical status. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmi, A. Commentary: Patent foramen ovale is not always a benign condition. JTCVS Tech. 2020, 4, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, S.G.; Mitsias, P.D. Patent Foramen Ovale in Cryptogenic Ischemic Stroke: Direct Cause, Risk Factor, or Incidental Finding? Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanche, C.; Noble, S.; Roffi, M.; Testuz, A.; Müller, H.; Meyer, P.; Bonvini, J.M.; Bonvini, R.F. Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome in the elderly treated by percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure: A case series and literature review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turc, G.; Calvet, D.; Guerin, P.; Turc, G.; Sroussi, M.; Chatellier, G.; the CLOSE Investigators. Closure, Anticoagulation, or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke with Patent Foramen Ovale: Systematic Review of Randomized Trials, Sequential Meta-Analysis, and New Insights from the CLOSE Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirwais, S.; Mirwais, M.; Altaf, A.; Collins, J. Patent Foramen Ovale with Platypnea—Orthodeoxia Syndrome: A Case Report. Cureus 2020, 12, e10958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germonpré, P.; Lafère, P.; Portier, W.; Germonpré, F.-L.; Marroni, A.; Balestra, C. Increased Risk of Decompression Sickness When Diving with a Right-to-Left Shunt: Results of a Prospective Single-Blinded Observational Study (The “Carotid Doppler” Study). Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 763408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, A.; Proserpio, P.; Roccatagliata, D.V.; Nichelatti, M.; Gigli, G.L.; Parati, G.; Lombardi, C.; Pizza, F.; Cirignotta, F.; Santilli, I.M.; et al. Wake-up stroke and TIA due to paradoxical embolism during long obstructive sleep apnoeas: A cross-sectional study. Thorax 2013, 68, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Lee, A.; Gadallah, N.E.; Wong, J.; Gupta, D. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO), the “Perfect Storm” for a Cryptogenic Stroke? Case Series of Four Patients. Front. Stroke. 2022, 1, 916154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, C.E.; Heit, J.A.; Reeder, G.S.; Bois, M.C.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Tilbury, R.T.; Holmes, D.R. Coronary Embolus: An Underappreciated Cause of Acute Coronary Syndromes. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 72–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmshurst, P.; Nightingale, S. Relationship between migraine and cardiac and pulmonary right-to-left shunts. Clin. Sci. 2001, 100, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmshurst, P.; Nightingale, S. The role of cardiac and pulmonary pathology in migraine: A hypothesis. Headache 2006, 46, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanes, L.; Mas, J.L.; Cohen, A.; Amarenco, P.; Cabanes, P.A.; Oubary, P.; Chedru, F.; Guérin, F.; Bousser, M.G.; de Recondo, J. Atrial septal aneurysm and patent foramen ovale as risk factors for cryptogenic stroke in patients less than 55 years of age. A study using transesophageal echocardiography. Stroke 1993, 24, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Pitfalls of Using Imaging Technique in the Presence of Eustachian Valve or Chiari Network: Effects on Right-to-Left Shunt and Related Influencing Factors. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manerikar, A.; Malaisrie, C. Chiari network and patent foramen ovale associated with stroke. JTCVS Tech. 2022, 11, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onorato, E.M. Large eustachian valve fostering paradoxical thromboembolism: Passive bystander or serial partner in crime? World J. Cardiol. 2021, 13, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, J.L.; Derumeaux, G.; Guillon, B.; Massardier, E.; Hosseini, H.; Mechtouff, L.; Arquizan, C.; Béjot, Y.; Vuillier, F.; Detante, O.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelets after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Saver, J.L.; Carroll, J.D.; Thaler, D.E.; Smalling, R.W.; MacDonald, L.A.; Marks, D.S.; Tirschwell, D.L. Long-Term Outcomes of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Medical Therapy after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, L.; Kasner, S.E.; Rhodes, J.F.; Andersen, G.; Iversen, H.K.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Settergren, M.; Sjöstrand, C.; Roine, R.O.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Song, J.K.; Kim, J.S.; Heo, R.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.H.; Song, J.M.; Kang, D.H.; Kwon, S.U.; Kang, D.W.; et al. Cryptogenic Stroke and High-Risk Patent Foramen Ovale: The DEFENSE-PFO Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauss, M.; Zanette, E. Detection of right-to-left shunt with ultrasound contrast agent and transcranial Doppler sonography. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2000, 10, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giblett, J.P.; Williams, L.K.; Kyramnis, S.; Shapiro, L.M.; Calvert, P.A. Patent Foramen Ovale: State of the Art. Interv. Cardiol. Rev. 2020, 15, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanchetta, M.; Rigatelli, G.; Pedon, L.; Zennaro, M.; Dimopoulous, K.; Onorato, E.; Frescura, C.; Maiolino, P.; Thiene, G.; Angelini, A. Intracardiac echocardiography: Gross anatomy and magnetic resonance correlations and validations. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2005, 21, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onorato, E.; Casilli, F. Rotational Intracardiac Echocardiography—Imaging Modalities in the cath-lab. In Percutaneous Interventions in Structural, Valvular and Congenital Heart Disease, 2nd ed.; Sievert, H., Qureshi, S.A., Wilson, N., Hijazi, Z., Eds.; Informa Healthcare: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wafa, H.A.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Emmett, E.; Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Wang, Y. Burden of Stroke in Europe. Stroke 2020, 51, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, N.D.; Hellenbrand, W.; Latson, L.; Filiano, J.; Newburger, J.W.; Lock, J.E. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale after presumed paradoxical embolism. Circulation 1992, 86, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.L.; Derex, L.; Guérin, P.; Guillon, B.; Habib, G.; Juliard, J.M.; Marijon, E.; Massardier, E.; Meneveau, N.; Vuillier, F. Reprint of: Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale to prevent stroke recurrence in patients with otherwise unexplained ischaemic stroke: Expert consensus of the French Neurovascular Society and the French Society of Cardiology. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 176, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Towfighi, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cockroft, K.M.; Gutierrez, J.; Lombardi-Hill, D.; Kamel, H.; Kernan, W.N.; Kittner, S.J.; Leira, E.C.; et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2021, 52, e364–e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xie, H.; Shao, H.; Cheng, G.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Lan, B.; He, L.; Zhang, Y. A Prospective, Single-Center, Phase I Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Value of Transesophageal Echocardiography in the Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale with a Novel Biodegradable Occluder. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 849459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspardone, A.; De Marco, F.; Sgueglia, G.A.; De Santis, A.; Iamele, M.; D’Ascoli, E.; Tusa, M.; Corciu, A.; Mullen, M.; Nobles, A.; et al. Novel percutaneous suture-mediated patent foramen ovale closure technique: Early results of the NobleStitch EL Italian Registry. EuroIntervention 2018, 14, e272–e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, D.M.; Ruthazer, R.; Weimar, C.; Mas, J.L.; Serena, J.; Homma, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Di Tullio, M.R.; Lutz, J.S.; Elkind, M.S.; et al. An index to identify stroke-related vs incidental patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke. Neurology 2013, 81, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristipino, C.; Sievert, H.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Mas, J.L.; Meier, B.; Scacciatella, P.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Gaita, F.; Toni, D.; Kyrle, P.; et al. European position paper on the management of patients with patent foramen ovale. General approach and left circulation thromboembolism. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristipino, C.; Germonpré, P.; Toni, D.; Sievert, H.; Meier, B.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Berti, S.; Onorato, E.M.; Bedogni, F.; Mas, J.-L.; et al. European position paper on the management of patients with patent foramen ovale. Part II—Decompression sickness, migraine, arterial deoxygenation syndromes, surgery in the sitting position and miscellaneous. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavinsky, C.J.; Szerlip, M.; Goldsweig, A.M.; Amin, Z.; Boudoulas, K.D.; Carroll, J.D.; Coylewright, M.; Elmariah, S.; MacDonald, L.A.; Shah, A.P.; et al. SCAI Guidelines for the Management of Patent Foramen Ovale. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2022, 1, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messé, S.R.; Gronseth, G.S.; Kent, D.M.; Kizer, J.R.; Homma, S.; Rosterman, L.; Carroll, J.D.; Ishida, K.; Sangha, N.; Kasner, S.E. Practice advisory update summary: Patent foramen ovale and secondary stroke prevention. Neurology 2020, 94, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirschwell, D.L.; Turner, M.; Thaler, D.; Choulerton, J.; Marks, D.; Carroll, J.; MacDonald, L.; Smalling, R.W.; Koullick, M.; Gu, N.Y.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure as secondary stroke prevention. J. Med. Econ. 2018, 21, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppert, M.H.; Poisson, S.N.; Carroll, J.D.; Thaler, D.E.; Kim, C.H.; Orjuela, K.D.; Ho, P.M.; Burke, J.F.; Campbell, J.D. Cost-effectiveness of patent foramen ovale closure versus medical therapy for secondary stroke prevention. Stroke 2018, 49, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, C.A.; Villines, T.C.; Resar, J.R.; Hulten, E.A. Cost effectiveness and clinical efficacy of patent foramen ovale closure as compared to medical therapy in cryptogenic stroke patients: A detailed cost analysis and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 273, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildick-Smith, D.; Turner, M.; Shaw, L.; Nakum, M.; Hartaigh, B.; Evans, R.M.; Rhodes, J.F.; Sondergaard, L.; Kasner, S.E. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of percutaneous closure of a patent foramen ovale versus medical management in patients with a cryptogenic stroke: From the UK payer perspective. J. Med. Econ. 2019, 22, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, J.J.; Ridge, J.R.; Nakum, M.; Rhodes, J.F.; Søndergaard, L.; Kasner, S.E. Cost-effectiveness of percutaneous closure of a patent foramen ovale compared with medical management in patients with a cryptogenic stroke: From the US payer perspective. J. Med. Econ. 2019, 22, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shijoh, Y.; Saito, S.; Dai, Z.; Ohde, S. Cost-effectiveness analysis of patent foramen ovale closure versus medical therapy alone after cryptogenic stroke. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzada, N.; Ladenvall, P.; Hansson, P.O.; Eriksson, P.; Taft, C.; Dellborg, M. Quality of life after percutaneous closure of patent foramen in patients after cryptogenic stroke compared to a normative sample. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 257, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willits, I.; Keltie, K.; Henderson, R.; de Belder, M.; Linker, N.; Patrick, H.; Powell, H.; Berry, L.; Urwin, S.; Cole, H.; et al. Patent foramen ovale closure: A prospective UK registry linked to hospital episode statistics. PLoS ONE 2021, 17, e0271117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smitherman, T.A.; Burch, R.; Sheikh, H.; Loder, E. The Prevalence, Impact, and Treatment of Migraine and Severe Headaches in the United States: A Review of Statistics from National Surveillance Studies. Headache 2013, 53, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwedt, T.J.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Dodick, D.W. Patent foramen ovale and migraine: A quantitative systematic review. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.C.; Loder, S.; Loder, E.; Smitherman, T.A. The prevalence and burden of migraine and severe headache in the United States: Updated statistics from government health surveillance studies. Headache 2015, 55, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputi, L.; Usai, S.; Carriero, M.R.; Grazzi, L.; D’Amico, D.; Falcone, C. Microembolic Air Load During Contrast-Transcranial Doppler: A Trigger for Migraine with Aura? Headache 2010, 50, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.J.; Nazif, T.; Privitera, L.; Robbins, B.T. Retrospective review of thienopyridine therapy in migraineurs with patent foramen ovale. Neurology 2018, 91, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Z.; Li, F. Platelet P2Y12 Inhibitor in the Treatment and Prevention of Migraine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Behav. Neurol. 2022, 2022, 2118740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, A.; Mullen, M.J.; Peatfield, R.; Muir, K.; Khan, A.A.; Wells, C.; Lipscombe, S.L.; Rees, T.; De Giovanni, J.V.; Morrison, W.L.; et al. Migraine intervention with STARFlex technology (MIST) trial: A prospective, multicenter, double-blind, sham controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness of patent foramen ovale closure with STARFlex septal repair implant to resolve refractory migraine headache. Circulation 2008, 117, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Tobis, J.M.; Charles, A.; Silberstein, S.D.; Sorensen, S.; Maini, B.; Horwitz, P.A.; Gurley, J.C. Percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale in patients with migraine: The PREMIUM trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbadawi, A.; Barssoum, K.; Abuzaid, A.S.; Rezq, A.; Biniwale, N.; Alotaki, E.; Mohamed, A.H.; Vuyyala, S.; Ogunbayo, G.O.; Saad, M. Meta-analysis of randomized trials on percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure for prevention of migraine. Acta Cardiol. 2019, 74, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Clinical and anatomical characteristics | ||
| No. | 106 | |
| Age, y (range; mean ± SD) | 16–62 | (41.77 ± 10.78) |
| Sex, female/male | 1.86 | |
| Smoking | 72 | |
| Diabetes | 19 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 27 | |
| Hypertension | 20 | |
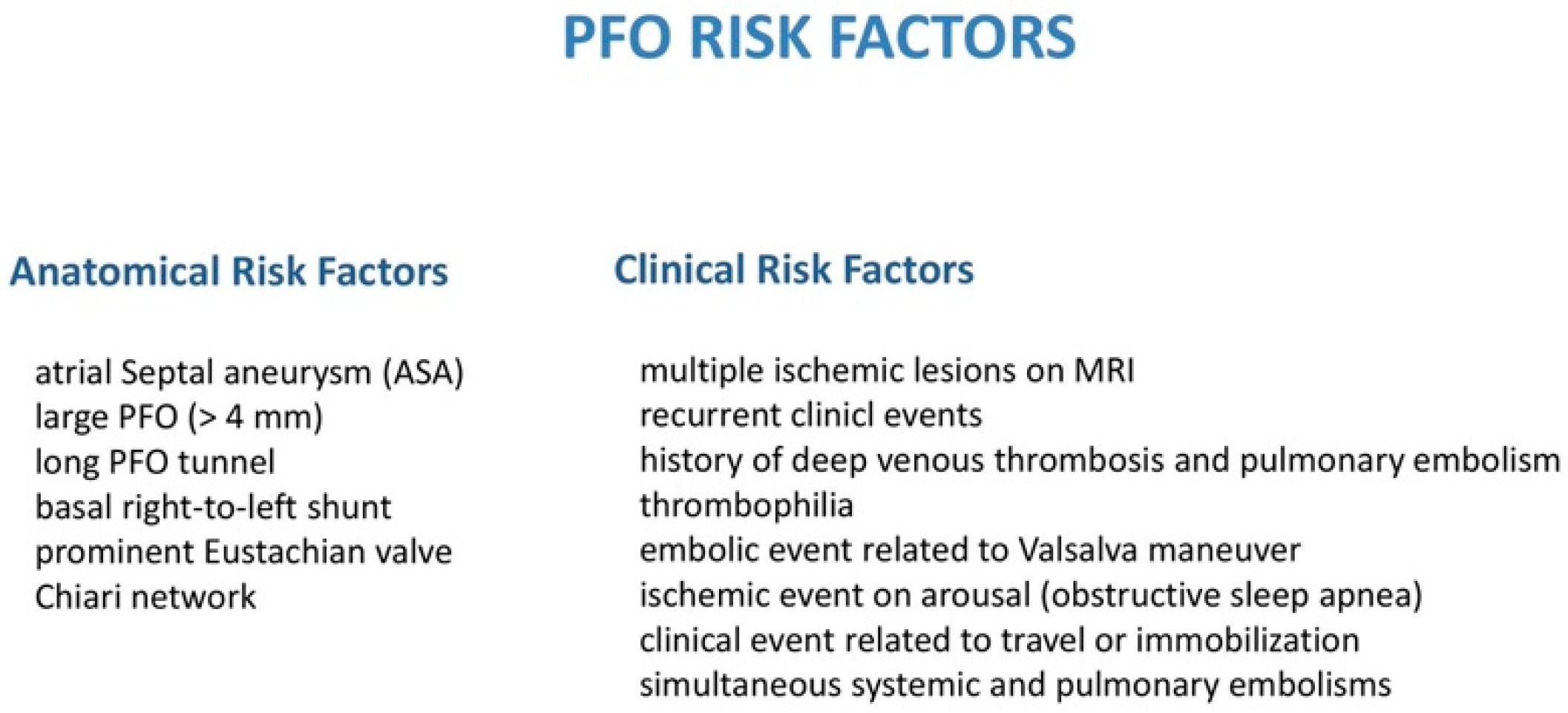
| Atrial septal anatomy, n (%) | ||
| PFO only | 20 | (18) |
| PFO and ASA | 86 | (82) |
| Fenestrated ASA | 6 | (6) |
| Eustachian valve | 83 | (78) |
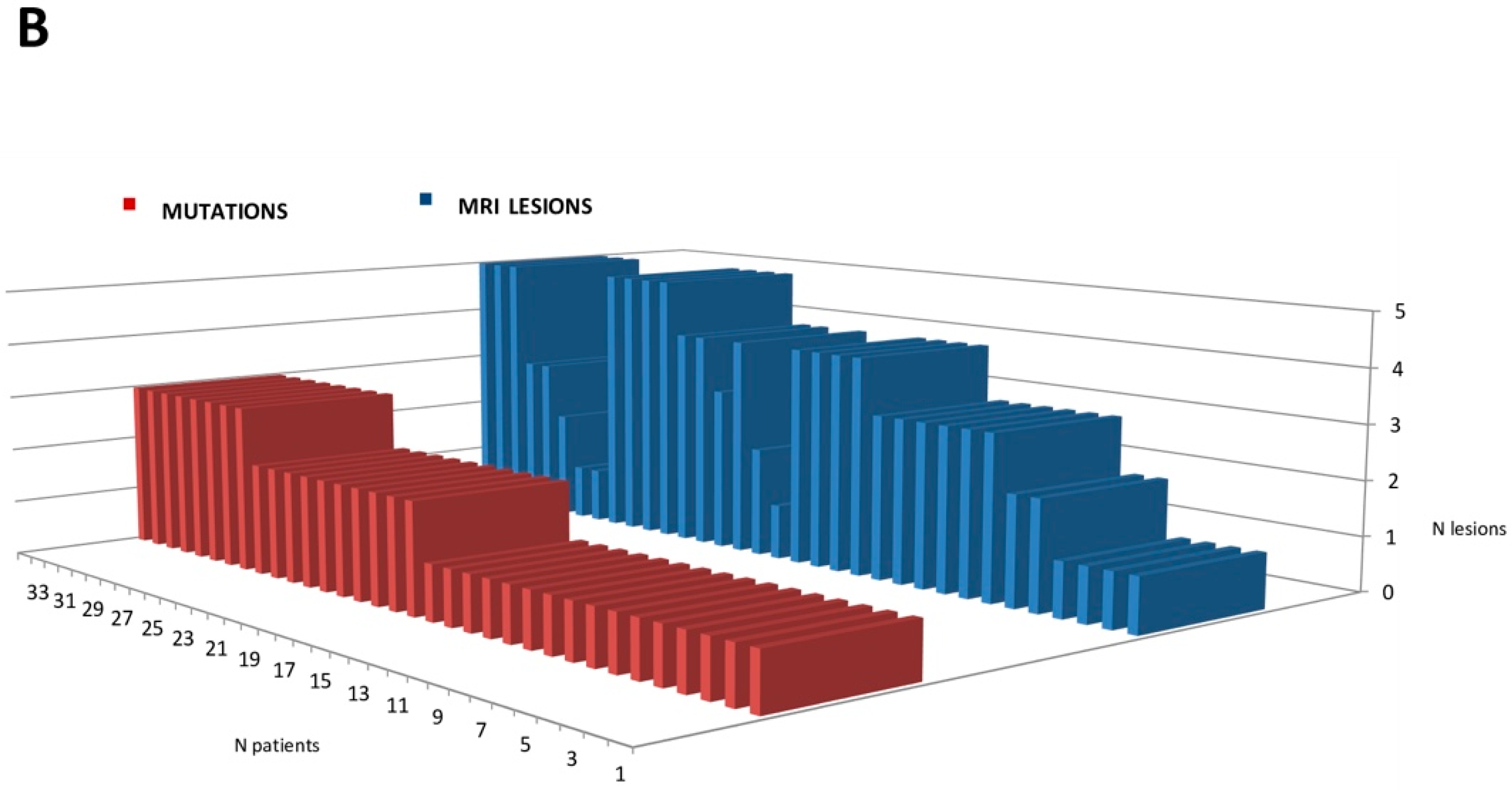
| Thromboembolic Events, n (%) | 100 | (94.4) |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke | 23 | (21.8) |
| TIA | 22 | (20.8) |
| Brain MRI lesions without TIA/Stroke | 53 | (50) |
| Coronary embolism | 1 | (0.9) |
| Brachial embolism | 1 | (0.9) |
| “Non-stroke”conditions, n (%) | 6 | (5.6) |
| Decompression sickness | 1 | (0.9) |
| Platypnea-orthodeoxia | 1 | (0.9) |
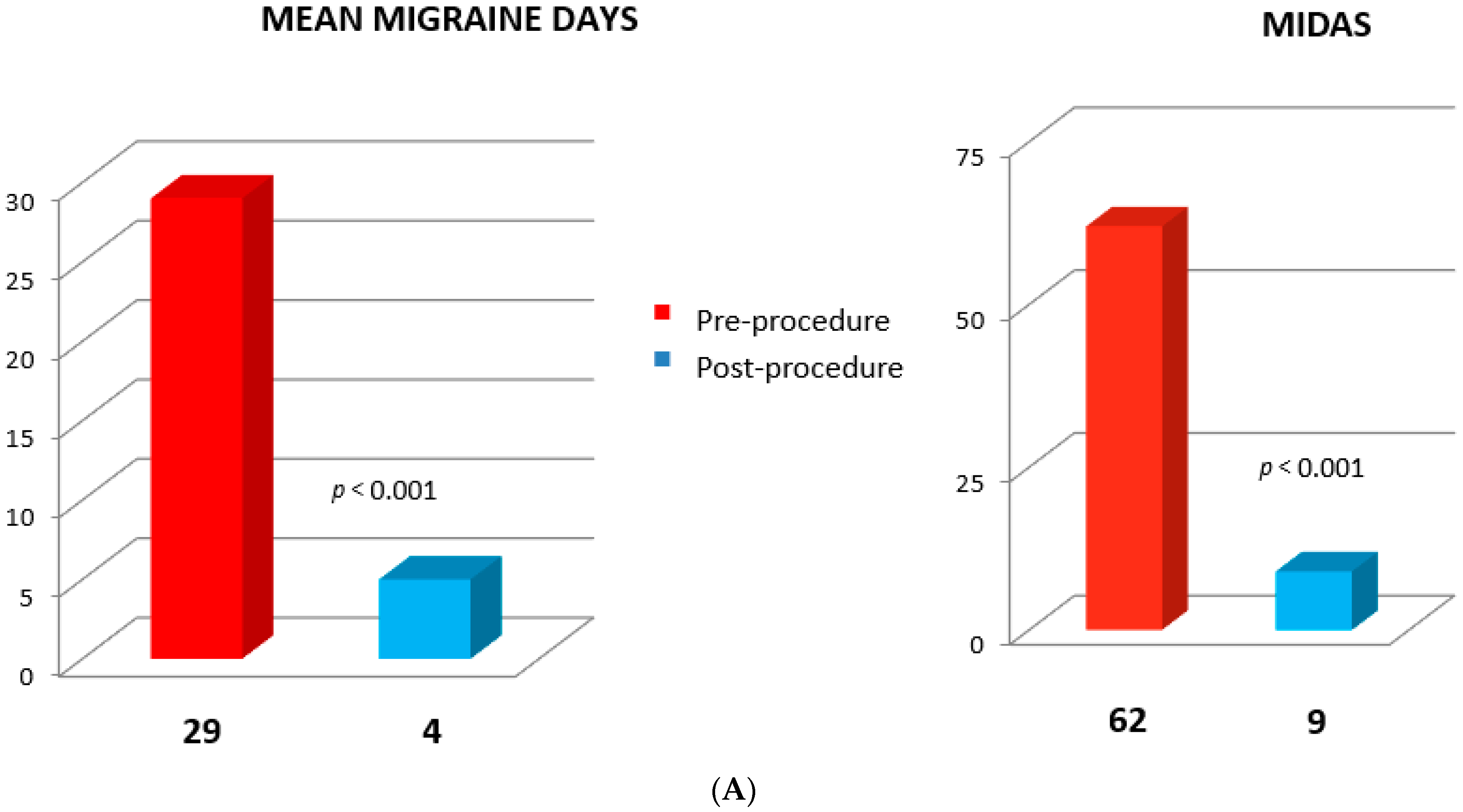
| Refractory chronic migraine | 4 | (3.8) |
| Procedural Success, n (%) | 106 | (100) |
|---|---|---|
| Procedural Characteristics | ||
| Fluoroscopy time, min (mean) | 10–45 | (15) |
| Procedural time, min (mean) | 35–90 | (55) |
| Periprocedural complications, n (%) | ||
| Arteriovenous fistula | 12 | (11.3) |
| Venous perforation | 1 | (0.9) |
| Retroperitoneal Hematoma | 1 | (0.9) |
| Femoral hematoma | 5 | (4.7) |
| Post-procedural complications, n (%) | ||
| Atrial Fibrillation | 1 | (1) |
| Follow-up outcomes, n (%) | ||
| Migraine progression | 2 | (1.8) |
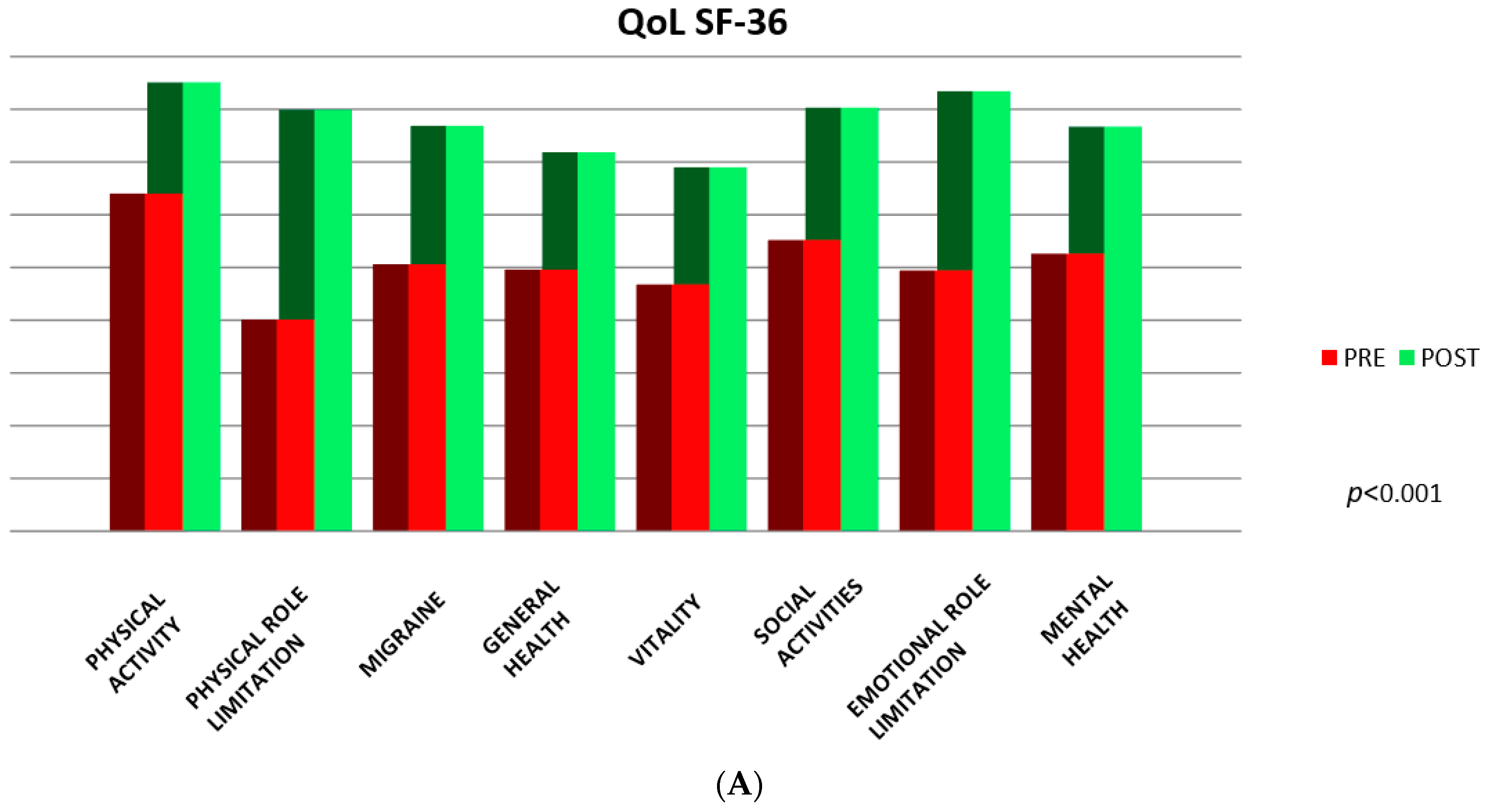
| Mean Pre-Treatment | Mean Post-Treatment | Standard Dev. Pre-treatment | Standard Dev. Post-treatment | Paired Probability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical activity | 64.04 | 85.1 | 31.32 | 19.46 | p < 0.001 |
| Physical role limitation | 40.14 | 79.9 | 40.65 | 31.05 | p < 0.001 |
| Migraine | 50.64 | 76.89 | 33.32 | 25.88 | p < 0.001 |
| General health | 49.59 | 71.89 | 25.25 | 22.61 | p < 0.001 |
| Vitality | 46.8 | 69.02 | 25.25 | 22.51 | p < 0.001 |
| Social activities | 55.22 | 80.31 | 28.95 | 20.83 | p < 0.001 |
| Emotional role limitation | 49.44 | 83.42 | 42.78 | 31.01 | p < 0.001 |
| Mental health | 52.61 | 76.72 | 26.73 | 18 | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evola, S.; Camarda, E.A.; Triolo, O.F.; Adorno, D.; D’Agostino, A.; Novo, G.; Onorato, E.M. Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life after Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) Closure in Patients with Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack of Undetermined Cause and Other PFO-Associated Clinical Conditions: A Single-Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185788
Evola S, Camarda EA, Triolo OF, Adorno D, D’Agostino A, Novo G, Onorato EM. Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life after Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) Closure in Patients with Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack of Undetermined Cause and Other PFO-Associated Clinical Conditions: A Single-Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):5788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185788
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvola, Salvatore, Emmanuele Antonio Camarda, Oreste Fabio Triolo, Daniele Adorno, Alessandro D’Agostino, Giuseppina Novo, and Eustaquio Maria Onorato. 2023. "Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life after Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) Closure in Patients with Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack of Undetermined Cause and Other PFO-Associated Clinical Conditions: A Single-Center Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 5788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185788
APA StyleEvola, S., Camarda, E. A., Triolo, O. F., Adorno, D., D’Agostino, A., Novo, G., & Onorato, E. M. (2023). Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life after Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) Closure in Patients with Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack of Undetermined Cause and Other PFO-Associated Clinical Conditions: A Single-Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 5788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185788





