Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice
Abstract
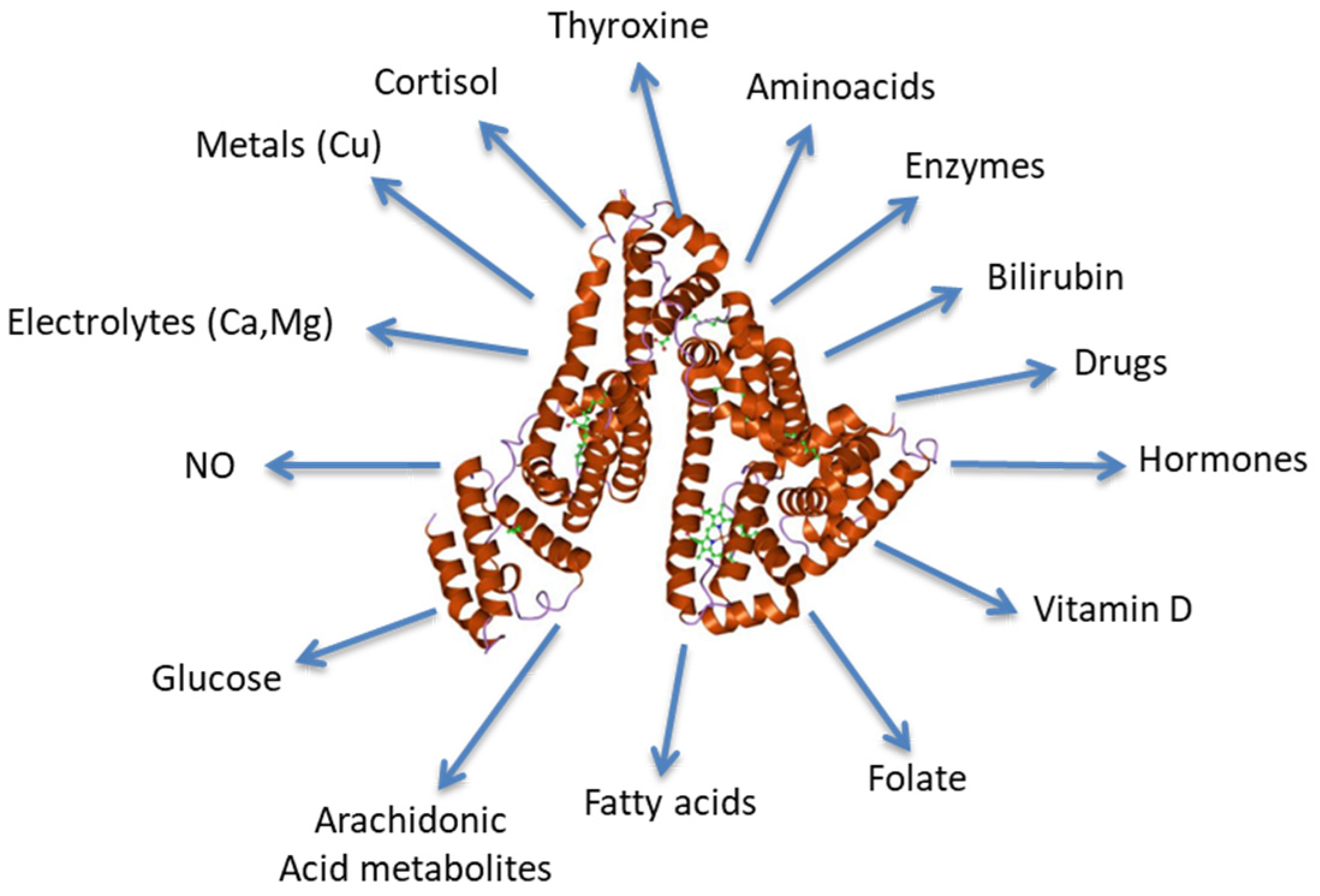
:1. Introduction
2. Albumin Synthesis and Physiology
3. Critical Levels of Albumin in Hospitalized and Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Patients
4. Albumin and Cardiovascular Disease
5. Albumin and COVID-19
6. Albumin in Nephrology
7. Albumin in Oncology
8. Albumin in Rheumatologic Autoimmune Diseases
9. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levitt, D.G.; Levitt, M.D. Human serum albumin homeostasis: A new look at the roles of synthesis, catabolism, renal and gastrointestinal excretion, and the clinical value of serum albumin measurements. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2016, 9, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, T., Jr. All about Albumin: Biochemistry, Genetics, and Medical Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Spada, A.; Emami, J.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Lavasanifar, A. The Uniqueness of Albumin as a Carrier in Nanodrug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 1862–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaving, G.; Batstone, G.F.; Jones, R.G. Age and sex variation in serum albumin concentration: An observational study. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 53 Pt 1, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmer, P.E. Causes and mechanisms of hypoalbuminaemia. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2001, 20, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyl, C.; Van Zyl-Smit, R. Mechanisms of oedema formation: The minor role of hypoalbuminaemia. S. Afr. Med. J. Suid-Afr. Tydskr. Vir Geneeskd. 2009, 99, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Taverna, M.; Marie, A.-L.; Mira, J.-P.; Guidet, B. Specific antioxidant properties of human serum albumin. Ann. Intensive Care 2013, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravifarsani, M.; Monfared, A.S.; Pouramir, M.; Zabihi, E. Effects of Fenton Reaction on Human Serum Albumin: An In Vitro Study. Electron. Physician 2016, 8, 2970–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginter, E.; Simko, V.; Panakova, V. Antioxidants in health and disease. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2014, 115, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambanelli, U.; Spisni, A.; Ferraccioli, G.F. Serum antioxidant activity and related variables in rheumatoid arthritis. Behaviour during sulphydrylant treatment. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1982, 11, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Albumin—An important extracellular antioxidant? Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feo, P.; Horber, F.F.; Haymond, M.W. Meal stimulation of albumin synthesis: A significant contributor to whole body protein synthesis in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263 Pt 1, E794–E799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballmer, P.E.; McNurlan, M.A.; Hulter, H.N.; Anderson, S.E.; Garlick, P.J.; Krapf, R. Chronic metabolic acidosis decreases albumin synthesis and induces negative nitrogen balance in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U. Nutritional Laboratory Markers in Malnutrition. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.K.; Rosenthal, T.C. Prealbumin: A marker for nutritional evaluation. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, L.; Bachman, T.E.; Meguid, M.; Ament, M.; Baumgartner, T.; Kinosian, B.; Martindale, R.; Spiekerman, M. Measurement of visceral protein status in assessing protein and energy malnutrition: Standard of care. Prealbumin in Nutritional Care Consensus Group. Nutr. Burbank Los Angel. Cty. Calif 1995, 11, 169–171. [Google Scholar]
- De Feo, P.; Gaisano, M.G.; Haymond, M.W. Differential effects of insulin deficiency on albumin and fibrinogen synthesis in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, R.; Mateu, X.; Maseda, E.; Yébenes, J.C.; Aldecoa, C.; De Haro, C.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, J.C.; Garnacho-Montero, J. Non-oncotic properties of albumin. A multidisciplinary vision about the implications for critically ill patients. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufoni, M.; Baldassarre, M.; Zaccherini, G.; Antognoli, A.; Caraceni, P. Hemodynamic and Systemic Effects of Albumin in Patients with Advanced Liver Disease. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2020, 19, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, M.; Rondeau, P.; Singh, N.R.; Tarnus, E.; Bourdon, E. The antioxidant properties of serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.-L.; Dubois, M.-J.; Navickis, R.J.; Wilkes, M.M. Hypoalbuminemia in Acute Illness: Is There a Rationale for Intervention? A meta-analysis of cohort studies and controlled trials. Ann Surg. 2003, 237, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, F.; Bettinelli, L.A.; Dobner, T.; Stobbe, J.C.; Pomatti, G.; Telles, C.T. Prevalence of hypoalbuminemia and nutritional issues in hospitalized elders. Rev. Lat. Am. Enfermagem 2016, 24, e2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, M.A.; Oratz, M.; Schreiber, S.S. Serum albumin. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 1988, 8, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.; Johnson, R. Malabsorption Syndromes. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 53, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodner, C. Diagnosis and Management of Nephrotic Syndrome in Adults. Am. Fam. Physician 2016, 93, 479–485. [Google Scholar]
- Sakr, Y.; Bauer, M.; Nierhaus, A.; Kluge, S.; Schumacher, U.; Putensen, C.; Fichtner, F.; Petros, S.; Scheer, C.; Jaschinski, U.; et al. Randomized controlled multicentre study of albumin replacement therapy in septic shock (ARISS): Protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2020, 21, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckart, A.; Struja, T.; Kutz, A.; Baumgartner, A.; Baumgartner, T.; Zurfluh, S.; Neeser, O.; Huber, A.; Stanga, Z.; Mueller, B.; et al. Relationship of Nutritional Status, Inflammation, and Serum Albumin Levels During Acute Illness: A Prospective Study. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 713–722.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roytblat, L.; Rachinsky, M.; Fisher, A.; Greemberg, L.; Shapira, Y.; Douvdevani, A.; Gelman, S. Raised interleukin-6 levels in obese patients. Obes. Res. 2000, 8, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Arner, P.; Caro, J.F.; Atkinson, R.L.; Spiegelman, B.M. Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straczkowski, M.; Dzienis-Straczkowska, S.; Stêpieñ, A.; Kowalska, I.; Szelachowska, M.; Kinalska, I. Plasma interleukin-8 concentrations are increased in obese subjects and related to fat mass and tumor necrosis factor-alpha system. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 4602–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Bouter, L.M.; McQuillan, G.M.; Wener, M.H.; Harris, T.B. Elevated C-reactive protein levels in overweight and obese adults. JAMA 1999, 282, 2131–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Castell, J.V.; Andus, T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem. J. 1990, 265, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood 1991, 77, 1627–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadori, G.; Van Damme, J.; Rieder, H.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H. Interleukin 6, the third mediator of acute-phase reaction, modulates hepatic protein synthesis in human and mouse. Comparison with interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988, 18, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronit, A.; Kirkegaard-Klitbo, D.M.; Dohlmann, T.L.; Lundgren, J.; Sabin, C.A.; Phillips, A.N.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Afzal, S. Plasma Albumin and Incident Cardiovascular Disease: Results From the CGPS and an Updated Meta-Analysis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arques, S. Serum albumin and cardiovascular disease: State-of-the-art review. Ann. Cardiol. Angeiol. 2020, 69, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalk, B.W.M.; Visser, M.; Bremmer, M.A.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Bouter, L.M.; Deeg, D.J.H. Change of serum albumin and risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Iskandarani, M.; El Kurdi, B.; Murtaza, G.; Paul, T.K.; Refaat, M.M. Prognostic role of albumin level in heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e24785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwich, T.B.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; MacLellan, R.W.; Fonarow, G.C. Albumin levels predict survival in patients with systolic heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2008, 155, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chan, C.-P.; Yan, B.P.; Zhang, Q.; Lam, Y.-Y.; Li, R.-J.; Sanderson, J.E.; Coats, A.J.S.; Sun, J.-P.; Yip, G.W.-K.; et al. Albumin levels predict survival in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, S.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Leu, H.-B.; Su, C.-H.; Yin, W.-H.; Tseng, W.-K.; Wu, Y.-W.; Lin, T.-H.; Chang, K.-C.; Wang, J.-H.; et al. Association of low serum albumin concentration and adverse cardiovascular events in stable coronary heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 241, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtul, A.; Murat, S.N.; Yarlioglues, M.; Duran, M.; Ocek, A.H.; Koseoglu, C.; Celık, I.E.; Kilic, A.; Aksoy, O. Usefulness of Serum Albumin Concentration to Predict High Coronary SYNTAX Score and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome. Angiology 2016, 67, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kates, R.E.; Yee, Y.G.; Hill, I. Effect of albumin on the electrophysiologic stability of isolated perfused rabbit hearts. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1989, 13, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Jiao, H.; Zhao, D.; Teng, J.; Yang, M. A Retrospective Study to Determine the Association Between Serum Albumin Levels and Atrial Fibrillation by Sex in 950 Patients from a Single Center in China. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2022, 28, e935347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, A.; Meng, X.; Lin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jing, J.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; et al. Low serum albumin levels predict poor outcome in patients with acute ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2021, 6, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahrour, M.A.; Kharroubi, H.; Al Tannir, A.H.; Assi, S.; Habib, J.R.; Hoballah, J.J. Hypoalbuminemia is Associated with Mortality in Patients Undergoing Lower Extremity Amputation. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 77, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charokopos, A.; Griffin, M.; Rao, V.S.; Inker, L.; Sury, K.; Asher, J.; Turner, J.; Mahoney, D.; Cox, Z.L.; Wilson, F.P.; et al. Serum and Urine Albumin and Response to Loop Diuretics in Heart Failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2019, 14, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, C.E.; Ha, J.S.; Theriault, A.G.; Bhagavan, N.V. Effects of statins on the secretion of human serum albumin in cultured HepG2 cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantis, E.; Kyriakos, G.; Quiles-Sanchez, L.V.; Farmaki, P.; Troupis, T. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Statins on Coronary Artery Disease: An Updated Review of the Literature. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2017, 13, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Bai, T.; Zeng, J.; Niu, Z.; Fan, D.; Xu, X.; Luo, M.; Wang, P.; Zou, Q.; Dai, X. Combined Administration of Metformin and Atorvastatin Attenuates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Inhibiting Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 634900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagyas, M.; Úri, K.; Siket, I.M.; Fülöp, G.Á.; Csató, V.; Daragó, A.; Boczán, J.; Bányai, E.; Szentkirályi, I.E.; Maros, T.M.; et al. New perspectives in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) II: Albumin suppresses angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity in human. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iles, J.; Zmuidinaite, R.; Sadee, C.; Gardiner, A.; Lacey, J.; Harding, S.; Ule, J.; Roblett, D.; Heeney, J.; Baxendale, H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding of Glycated Serum Albumin-Its Potential Role in the Pathogenesis of the COVID-19 Clinical Syndromes and Bias towards Individuals with Pre-Diabetes/Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, J.U.; Hansson, L.O.; Ortqvist, A.B. Hypoalbuminemia in hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Arch. Intern. Med. 1995, 155, 1438–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Jo, Y.H.; Rhee, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Na, S.H.; Hwang, S.S. Albumin and C-reactive protein have prognostic significance in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viasus, D.; Garcia-Vidal, C.; Simonetti, A.; Manresa, F.; Dorca, J.; Gudiol, F.; Carratalà, J. Prognostic value of serum albumin levels in hospitalized adults with community-acquired pneumonia. J. Infect. 2013, 66, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violi, F.; Cangemi, R.; Romiti, G.F.; Ceccarelli, G.; Oliva, A.; Alessandri, F.; Pirro, M.; Pignatelli, P.; Lichtner, M.; Carraro, A.; et al. Is Albumin Predictor of Mortality in COVID-19? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosato, M.; Calvani, R.; Ciciarello, F.; Galluzzo, V.; Martone, A.M.; Zazzara, M.B.; Pais, C.; Savera, G.; Robles, M.C.; Ramirez, M.; et al. Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Team. Malnutrition in COVID-19 survivors: Prevalence and risk factors. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violi, F.; Ceccarelli, G.; Loffredo, L.; Alessandri, F.; Cipollone, F.; D’ardes, D.; D’Ettorre, G.; Pignatelli, P.; Venditti, M.; Mastroianni, C.M.; et al. Albumin Supplementation Dampens Hypercoagulability in COVID-19: A Preliminary Report. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnau-Barrés, I.; Pascual-Dapena, A.; López-Montesinos, I.; Gómez-Zorrilla, S.; Sorlí, L.; Herrero, M.; Nogués, X.; Navarro-Valls, C.; Ibarra, B.; Canchucaja, L.; et al. Severe Hypoalbuminemia at Admission Is Strongly Associated with Worse Prognosis in Older Adults with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcato, G.; Zaboli, A.; Kostic, I.; Melchioretto, B.; Ciccariello, L.; Zaccaria, E.; Olivato, A.; Maccagnani, A.; Pfeifer, N.; Bonora, A. Severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection and albumin levels recorded at the first emergency department evaluation: A multicentre retrospective observational study. Emerg. Med. J. EMJ 2022, 39, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shabrawy, M.; Alsadik, M.E.; El-Shafei, M.; Abdelmoaty, A.A.; Alazzouni, A.S.; Esawy, M.M.; Shabana, M.A. Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as predictors of COVID-19 severity and mortality. Egypt J. Bronchol. 2021, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşkin, Ö.; Yilmaz, A.; Soylu, V.G.; Demir, U.; Çatan Inan, F. Ferritin/albumin ratio could be a new indicator of COVID-19 disease mortality. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2023, 17, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, B.; Acar, T. The relationship between albumin and its proportion to other markers in predicting mortality in severe COVID-19 patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 6429–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.C.N.; Silva, M.L.; Mantovani, M.D.S.; Silva, J.M.D.; Domingues, M.F.P.; Tanni, S.É.; Azevedo, P.S.; Minicucci, M.F.; Buffarah, M.N.B.; Pereira, A.G.; et al. Higher urea-to-albumin ratio is associated with mortality risk in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 56, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovska Jovičić, B.; Raković, I.; Gavrilović, J.; Sekulić Marković, S.; Petrović, S.; Marković, V.; Pavković, A.; Čanović, P.; Radojević Marjanović, R.; Irić-Čupić, V.; et al. Vitamin D, Albumin, and D-Dimer as Significant Prognostic Markers in Early Hospitalization in Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Scherzer, R.; Weekley, C.C.; Tien, P.C.; Grunfeld, C.; Shlipak, M.G. Serum albumin and short-term risk for mortality and cardiovascular disease among HIV-infected veterans. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2013, 27, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, Y.; Qader, H.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Latest consensus and update on protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanami, D.; Takashi, Y.; Tanabe, M. Significance of Metformin Use in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.R.; Morrison, V.L.; Levin, D.; Mohan, M.; Forteath, C.; Beall, C.; McNeilly, A.D.; Balfour, D.J.; Savinko, T.; Wong, A.K.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Metformin Irrespective of Diabetes Status. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minatoguchi, S.; Nomura, A.; Imaizumi, T.; Sasaki, S.; Ozeki, T.; Uchida, D.; Kawarazaki, H.; Sasai, F.; Tomita, K.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Low serum albumin as a risk factor for infection-related in-hospital death among hemodialysis patients hospitalized on suspicion of infectious disease: A Japanese multicenter retrospective cohort study. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2018, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ficociello, L.H.; Bazzanella, J.; Mullon, C.; Anger, M.S. Slipping Through the Pores: Hypoalbuminemia and Albumin Loss During Hemodialysis. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2021, 14, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amdur, R.L.; Feldman, H.I.; Dominic, E.A.; Anderson, A.H.; Beddhu, S.; Rahman, M.; Wolf, M.; Reilly, M.; Ojo, A.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Use of Measures of Inflammation and Kidney Function for Prediction of Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Events and Death in Patients With CKD: Findings From the CRIC Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2019, 73, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Masutani, K.; Torisu, K.; Katafuchi, R.; Tanaka, S.; Tsuchimoto, A.; Mitsuiki, K.; Tsuruya, K.; Kitazono, T. Association between serum albumin level and incidence of end-stage renal disease in patients with Immunoglobulin A nephropathy: A possible role of albumin as an antioxidant agent. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q. J. Med. 1987, 64, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camilla, R.; Suzuki, H.; Daprà, V.; Loiacono, E.; Peruzzi, L.; Amore, A.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Mazzucco, G.; Scolari, F.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. Oxidative stress and galactose-deficient IgA1 as markers of progression in IgA nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2011, 6, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Chung, Y.; Poulton, C.J.; Derebail, V.K.; Hogan, S.L.; Reich, H.N.; Falk, R.J.; Nachman, P.H. Serum Albumin at Partial Remission Predicts Outcomes in Membranous Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Hao, J.; Hu, H.; Hao, L. The level of serum albumin is associated with renal prognosis and renal function decline in patients with chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Meyenfeldt, M. Cancer-associated malnutrition: An introduction. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. Off. J. Eur. Oncol. Nurs. Soc. 2005, 9 (Suppl. S2), S35–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, G.L.; Thornton, P.A. Nutritional assessment of the hospitalized patient. Med. Clin. North Am. 1979, 63, 11103–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, M.; Nagata, H.; Takagi, K.; Kubota, K. Influence of inflammation-based prognostic score on mortality of patients undergoing chemotherapy for far advanced or recurrent unresectable colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, C.-M.; Kim, K.-S.; Choi, J.-S.; Lee, W.-J.; Kim, B.-R. Prognostic factors and optimal treatment strategy for intrahepatic nodular recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, T.; Sharples, L.; Groves, A.M.; Ritchie, A.J.; Wells, F.C.; Laroche, C.M. Predicting survival in potentially curable lung cancer patients. Lung 2008, 186, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, V.; Lee, J.; Bali, A. Preoperative serum albumin is an independent prognostic predictor of survival in ovarian cancer. Med. Oncol. Northwood Lond. Engl. 2012, 29, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Tokuda, S.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kurozumi, S.; Obayashi, S.; Yajima, R.; Shirabe, K. Implications of Low Serum Albumin as a Prognostic Factor of Long-term Outcomes in Patients With Breast Cancer. Vivo Athens Greece 2020, 34, 2033–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.-K.; Chowell, D.; Valero, C.; Morris, L.G.T.; Chan, T.A. Pre-treatment serum albumin and mutational burden as biomarkers of response to immune checkpoint blockade. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka Herrán, C.; Jané-Salas, E.; Estrugo Devesa, A.; López-López, J. Protective effects of metformin, statins and anti-inflammatory drugs on head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Oral Oncol. 2018, 85, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeb, S.; Egaila, S.; Hamed, A.; Hassan, W. Significance of serum albumin and derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio score in assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabil. 2020, 47, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, Y.; Ebina, K.; Tsuboi, H.; Hirao, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Yoshikawa, H.; Okada, S.; Nakata, K. Low serum albumin concentration is associated with increased risk of osteoporosis in postmenopausal patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Orthop. Sci. Off. J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 2022, 27, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madda, R.; Lin, S.-C.; Sun, W.-H.; Huang, S.-L. Differential expressions of plasma proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus patients identified by proteomic analysis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi 2019, 52, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sule, S.D.; Fadrowski, J.J.; Fivush, B.A.; Gorman, G.; Furth, S.L. Reduced albumin levels and utilization of arteriovenous access in pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2007, 22, 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-T.; Chen, G.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-D. Effect of disease activity and position on autonomic nervous modulation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 27, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, J.; Aghdassi, E.; Su, J.; Lou, W.; Reich, H.; Bargman, J.; Scholey, J.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B.; Fortin, P.R. Serum albumin as a marker for disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, V.; Levinson, B.A.; Bornkamp, N.; Goldberg, J.D.; Buyon, J.; Belmont, H.M. Serum albumin at 1 year predicts long-term renal outcome in lupus nephritis. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.S.; Yoon, T.; Song, J.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Serum albumin, prealbumin, and ischemia-modified albumin levels in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchiotti, L.; Galliano, M.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Peters, T., Jr. Mutations and polymorphisms of the gene of the major human blood protein, serum albumin. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsova, A.; Gordiienko, I.; Tkachenko, V.; Ushakova, G. Ischemia-Modified Albumin: Origins and Clinical Implications. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 9945424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Tian, L.; Wang, Z. Correlation between ischemia-modified albumin level and coronary collateral circulation. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.; Yuksel, M.; Ates, I.; Kilic, Z.M.Y.; Kilic, H.; Kuzu, U.B.; Kayacetin, E. Is ischemia modified albumin a disease activity marker for inflammatory bowel diseases? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capkin, E.; Karkucak, M.; Kola, M.; Karaca, A.; Aydin Capkin, A.; Caner Karahan, S. Ischemia-modified albumin (IMA): A novel marker of vascular involvement in Behçet’s disease? Joint Bone Spine 2015, 82, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertpoyraz, F.M.; Colak, A.; Dikici, A.; Gunduz, N.E.; Aksit, M.Z. The relationship of ischemia-modified albumin levels to disease activity scores and HLA-B27 in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. North. Clin. Istanb. 2021, 8, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Yasuda, K.; Takeda, N.; Sakata, S.; Era, S.; Kuwata, K.; Sogami, M.; Miura, K. Increased oxidized form of human serum albumin in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1992, 18, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingolani, F.; Czaja, M.J. Oxidized Albumin-A Trojan Horse for p38 MAPK-Mediated Inflammation in Decompensated Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1678–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Suda, K.; Matsuyama, Y.; Era, S.; Soejima, A. Close relationship between redox state of human serum albumin and serum cysteine levels in non-diabetic CKD patients with various degrees of renal function. Clin. Nephrol. 2014, 82, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Prealbumin Levels | Risk |
|---|---|
| 15.0 to 35.0 mg/dL | Normality |
| 11.0 to 15.0 mg/dL | Below the normality, increased risk |
| 5.0–10.9 mg/dL | Malnutrition, severe risk |
| <5.0 mg/dL | Poor prognosis |
| Clinical Setting | ALB Levels | Risk | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emergency Department (ED) | <3.4 g/dL | 30 days mortality, OR: 2.87 | [27] |
| Hospital Discharge | <3.4 g/dL | 3 months mortality, 2.5 fold higher | [22] |
| CKD hospitalized | <2.5 g/dL | Mortality, 4.9 fold higher risk | [70] |
| Diffuse large B cell lymphoma | <3.5 g/dL | In-hospital death, 2.0 fold higher | [80] |
| HFPEF hospitalized | <3.4 g/dL | 30 days death, 2.4 fold higher risk | [40] |
| CAP hospitalized | <3.0 g/dL | 30 days mortality, OR: 2.11 | [55] |
| COVID-19 pneumonitis at ED | <3.5 g/dL | 30 days mortality, OR: 2.92 | [60] |
| CICU (Cardiologic-ICU) | <3.4 g/dL | In-hospital mortality, 2.3 fold higher | [27] |
| Nephritic SLE | >3.7 g/dL | At 1 year follow-up post biopsy, HR 0.14 | [95] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gremese, E.; Bruno, D.; Varriano, V.; Perniola, S.; Petricca, L.; Ferraccioli, G. Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186017
Gremese E, Bruno D, Varriano V, Perniola S, Petricca L, Ferraccioli G. Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186017
Chicago/Turabian StyleGremese, Elisa, Dario Bruno, Valentina Varriano, Simone Perniola, Luca Petricca, and Gianfranco Ferraccioli. 2023. "Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186017
APA StyleGremese, E., Bruno, D., Varriano, V., Perniola, S., Petricca, L., & Ferraccioli, G. (2023). Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186017







