Real-World Retrospective Study into the Effects of Oral Semaglutide (As a Switchover or Add-On Therapy) in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
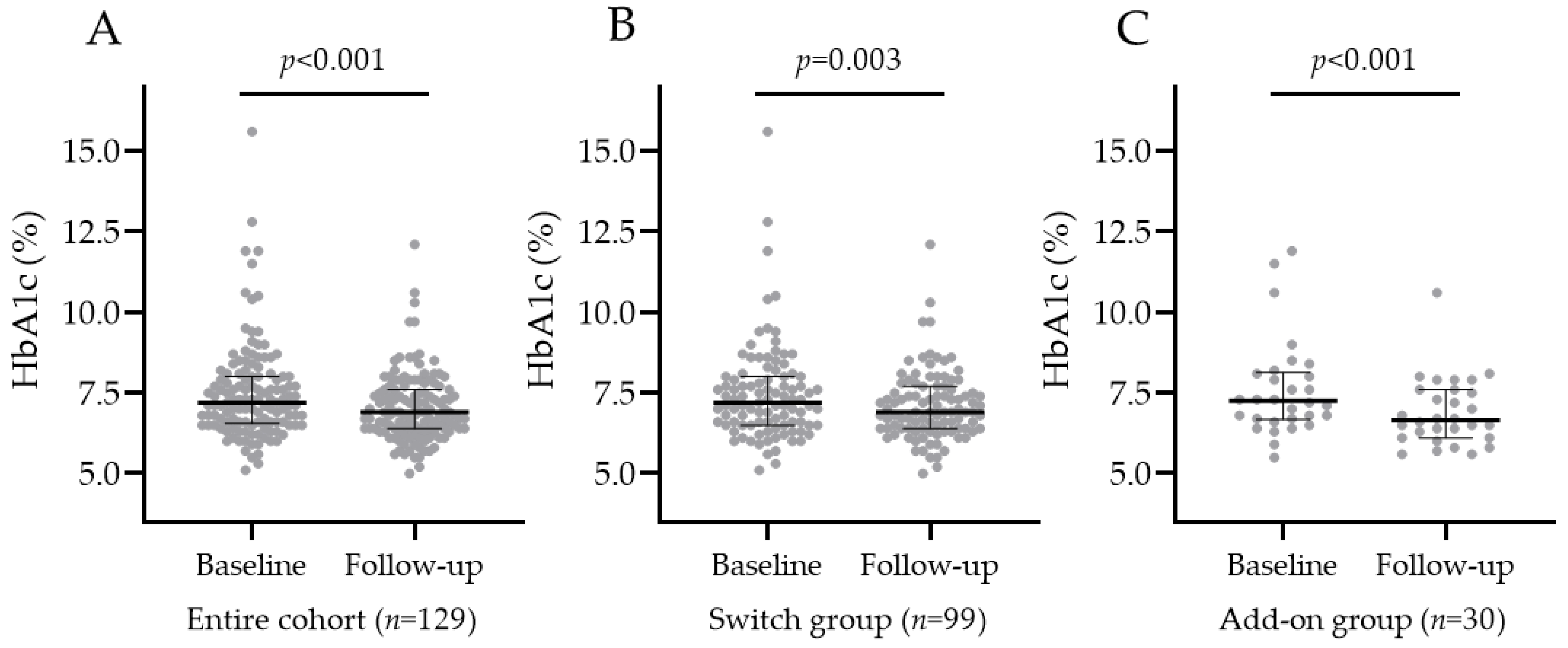
3.2. HbA1c Change after Oral Semaglutide Introduction
3.2.1. HbA1c Change in the Entire Population, SWITCH, and ADD-ON Groups
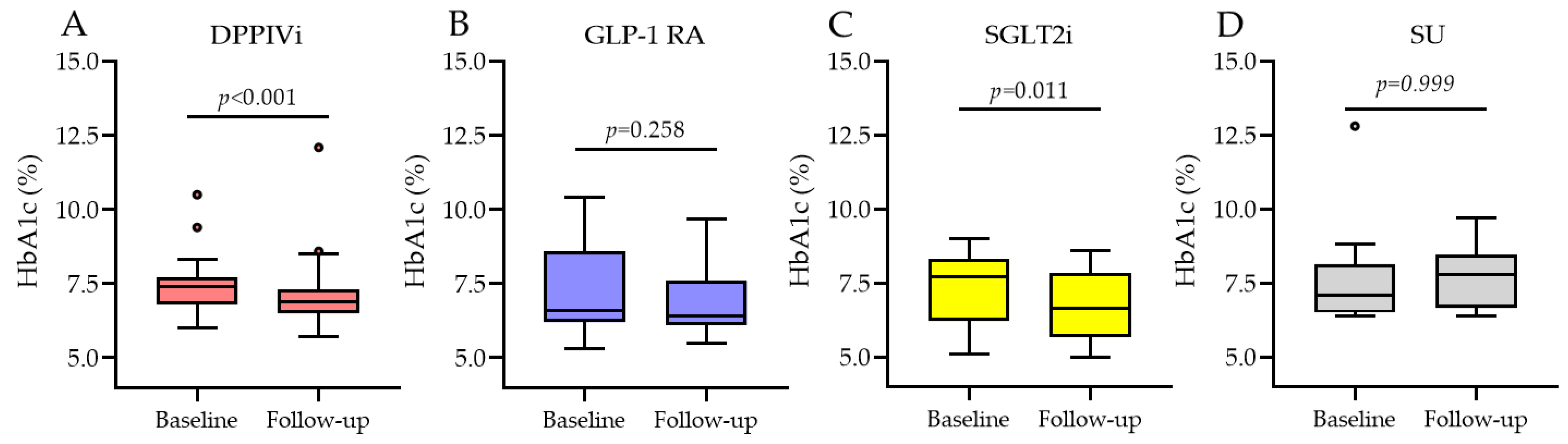
3.2.2. HbA1c Change Based on the Type of Medication Switchover
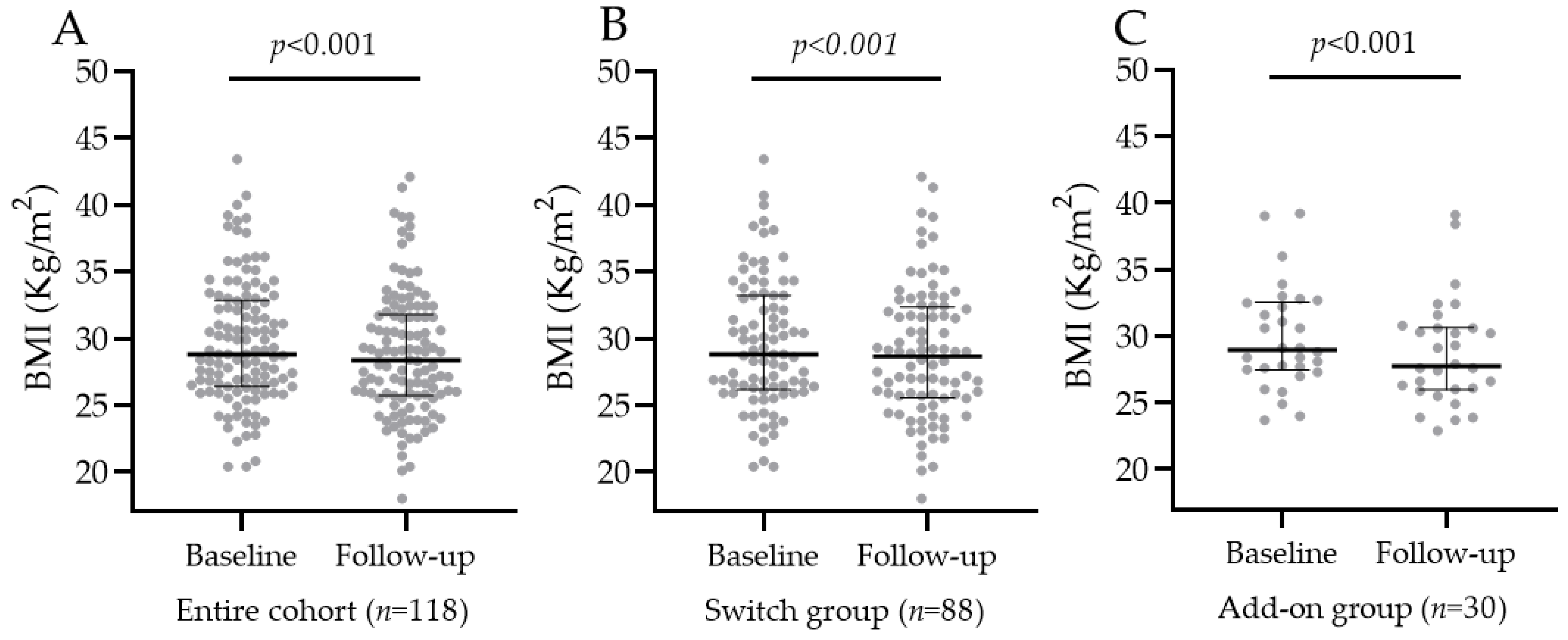
3.3. BMI and Body Weight Change after Oral Semaglutide Introduction
3.3.1. BMI Change in the Entire Population, SWITCH, and ADD-ON Groups
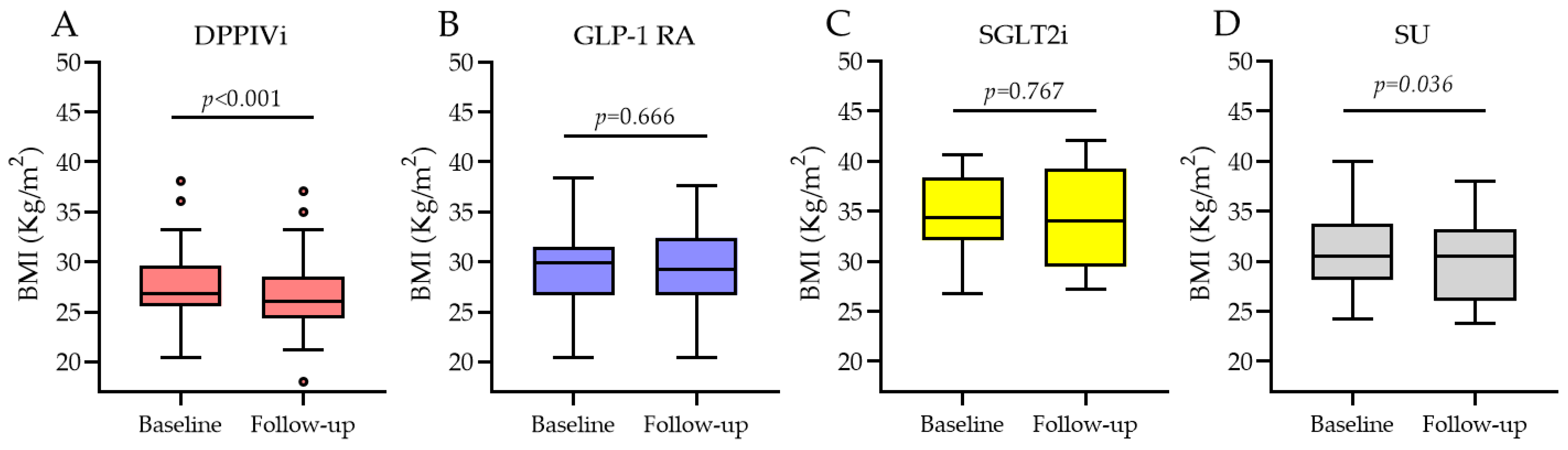
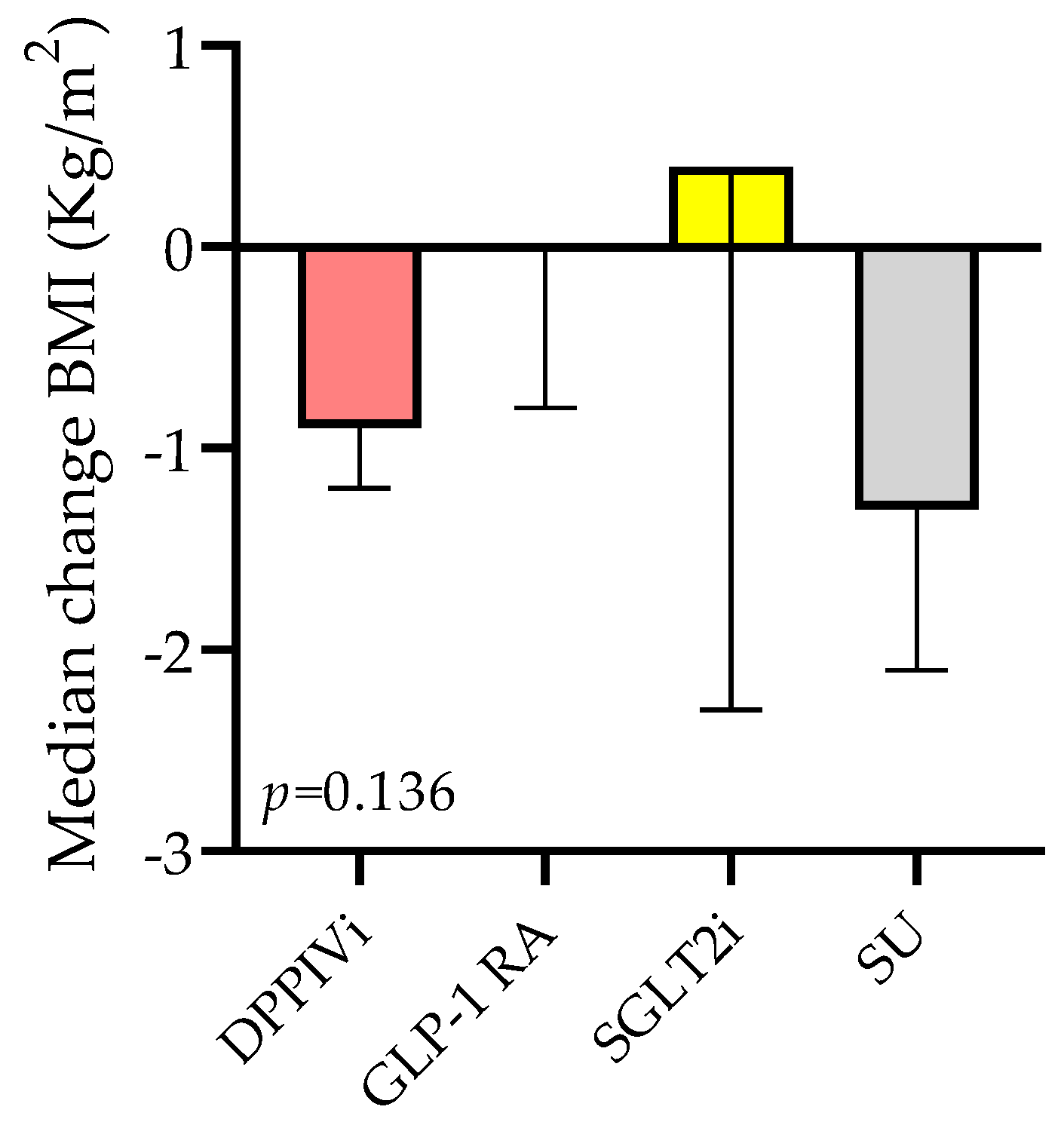
3.3.2. BMI Change Based on the Type of Medication Switchover
3.3.3. Body Weight Change after Oral Semaglutide Introduction
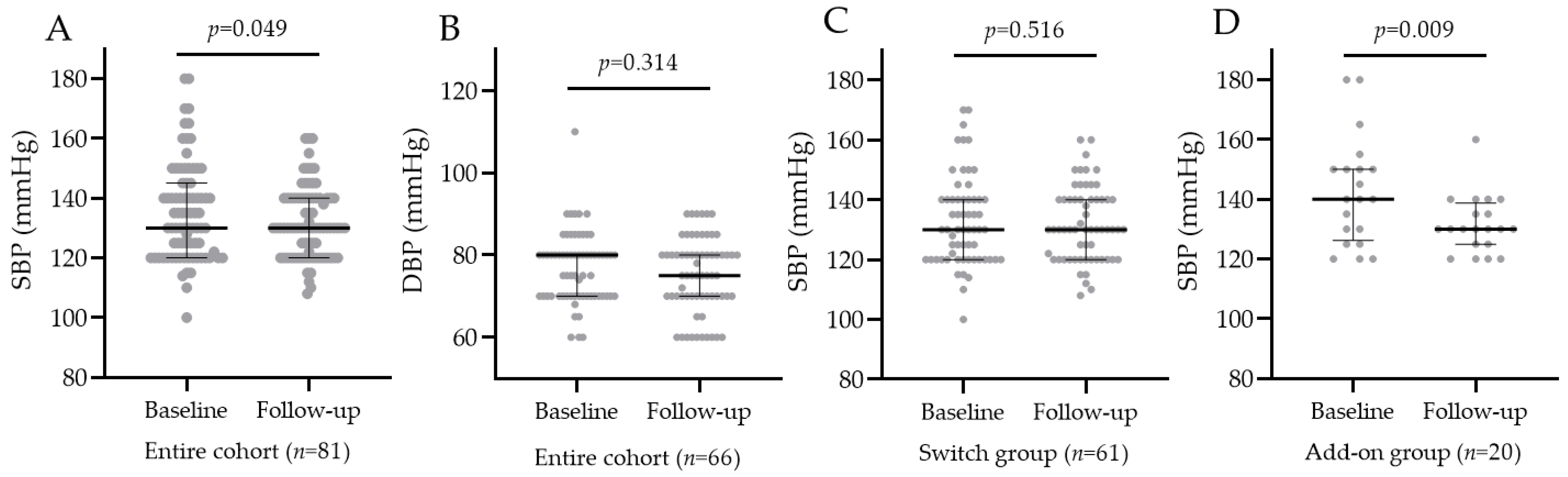
3.4. Blood Pressure Change after Oral Semaglutide Introduction
3.5. Multivariate Linear Regression Analyses
3.6. Oral Semaglutide Discontinuation and Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avogaro, A.; de Kreutzenberg, S.V.; Morieri, M.L.; Fadini, G.P.; Del Prato, S. Glucose-lowering drugs with cardiovascular benefits as modifiers of critical elements of the human life history. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, A.E.; Gaoatswe, G.; Lynch, L.; Corrigan, M.A.; Woods, C.; O’Connell, J.; O’Shea, D. Glucagon-like peptide 1 analogue therapy directly modulates innate immune-mediated inflammation in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.; Frid, A.; Hermansen, K.; Shah, N.S.; Tankova, T.; Mitha, I.H.; Zdravkovic, M.; During, M.; Matthews, D.R.; Group, L.-S. Efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide, glimepiride, and placebo, all in combination with metformin, in type 2 diabetes: The LEAD (liraglutide effect and action in diabetes)-2 study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Gerich, J.; Buse, J.B.; Lewin, A.; Schwartz, S.; Raskin, P.; Hale, P.M.; Zdravkovic, M.; Blonde, L.; LEAD-4 Study Investigators. Efficacy and safety of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide in combination with metformin and thiazolidinedione in patients with type 2 diabetes (LEAD-4 Met+TZD). Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Rosenstock, J.; Sesti, G.; Schmidt, W.E.; Montanya, E.; Brett, J.H.; Zychma, M.; Blonde, L.; Group, L.-S. Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: A 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet 2009, 374, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, A.; Oyama, J.; Komoda, H.; Asaka, M.; Komatsu, A.; Sakuma, M.; Kodama, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kotooka, N.; Hirase, T.; et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces TNF-alpha-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Capehorn, M.; De Remigis, A.; Rasmussen, S.; Weimers, P.; Mosenzon, O. Semaglutide Reduces High-Sensitivity Crp Levels across Different Treatment Formulations: Exploratory Analyses of Sustain 3 and Pioneer 1, 2 and 5 Trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, S.T.; Baekdal, T.A.; Vegge, A.; Maarbjerg, S.J.; Pyke, C.; Ahnfelt-Ronne, J.; Madsen, K.G.; Scheele, S.G.; Alanentalo, T.; Kirk, R.K.; et al. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallwitz, B.; Giorgino, F. Clinical Perspectives on the Use of Subcutaneous and Oral Formulations of Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. Lausanne 2021, 12, 645507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Rosenstock, J.; Terauchi, Y.; Altuntas, Y.; Lalic, N.M.; Morales Villegas, E.C.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Christiansen, E.; Hertz, C.L.; Haluzik, M.; et al. PIONEER 1: Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Oral Semaglutide Monotherapy in Comparison with Placebo in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Rosenstock, J.; Terauchi, Y.; Altuntas, Y.; Lalic, N.M.; Morales Villegas, E.C.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Christiansen, E.; Hertz, C.L.; Haluzik, M.; et al. Oral Semaglutide Versus Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Uncontrolled on Metformin: The PIONEER 2 Trial. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2272–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Allison, D.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Blicher, T.M.; Deenadayalan, S.; Jacobsen, J.B.; Serusclat, P.; Violante, R.; Watada, H.; Davies, M.; et al. Effect of Additional Oral Semaglutide vs. Sitagliptin on Glycated Hemoglobin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Uncontrolled with Metformin Alone or with Sulfonylurea: The PIONEER 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 1466–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratley, R.; Amod, A.; Hoff, S.T.; Kadowaki, T.; Lingvay, I.; Nauck, M.; Pedersen, K.B.; Saugstrup, T.; Meier, J.J.; PIONEER 4 Investigators. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3a trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosenzon, O.; Blicher, T.M.; Rosenlund, S.; Eriksson, J.W.; Heller, S.; Hels, O.H.; Pratley, R.; Sathyapalan, T.; Desouza, C.; PIONEER 5 Investigators. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (PIONEER 5): A placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieber, T.R.; Bode, B.; Mertens, A.; Cho, Y.M.; Christiansen, E.; Hertz, C.L.; Wallenstein, S.O.R.; Buse, J.B.; PIONEER 7 Investigators. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide with flexible dose adjustment versus sitagliptin in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 7): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Aroda, V.R.; Buse, J.B.; Cariou, B.; Harris, S.B.; Hoff, S.T.; Pedersen, K.B.; Tarp-Johansen, M.J.; Araki, E.; PIONEER 8 Investigators. Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Oral Semaglutide Versus Placebo Added to Insulin with or without Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The PIONEER 8 Trial. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Katagiri, H.; Hamamoto, Y.; Deenadayalan, S.; Navarria, A.; Nishijima, K.; Seino, Y.; PIONEER 9 Investigators. Dose-response, efficacy, and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 9): A 52-week, phase 2/3a, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, D.; Nakamura, J.; Kaneto, H.; Deenadayalan, S.; Navarria, A.; Gislum, M.; Inagaki, N.; PIONEER 10 Investigators. Safety and efficacy of oral semaglutide versus dulaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 10): An open-label, randomised, active-controlled, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroda, V.R.; Faurby, M.; Lophaven, S.; Noone, J.; Wolden, M.L.; Lingvay, I. Insights into the early use of oral semaglutide in routine clinical practice: The IGNITE study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Adachi, H.; Katsuyama, H. A Significant Effect of Oral Semaglutide on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Cardiol. Res. 2022, 13, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobučar, S.; Belančić, A.; Bukša, I.; Morić, N.; Rahelić, D. Effectiveness of Oral Versus Injectable Semaglutide in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: Results from a Retrospective Observational Study in Croatia. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2023090030. [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci, E.; Candido, R.; Monache, L.D.; Gallo, M.; Giaccari, A.; Masini, M.L.; Mazzone, A.; Medea, G.; Pintaudi, B.; Targher, G.; et al. Italian guidelines for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 579–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, E.; Candido, R.; Monache, L.D.; Gallo, M.; Giaccari, A.; Masini, M.L.; Mazzone, A.; Medea, G.; Pintaudi, B.; Targher, G.; et al. 2023 update on Italian guidelines for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 1119–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Wexler, D.J.; Tsapas, A.; Rossing, P.; Mingrone, G.; Mathieu, C.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Davies, M.J. 2019 Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. S1), S140–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Muller, T.D. Incretin hormones and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1780–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. Sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 556–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Bode, B.W.; Mertens, A.; Cho, Y.M.; Christiansen, E.; Hertz, C.L.; Nielsen, M.A.; Pieber, T.R.; PIONEER 7 Investigators. Long-term efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide and the effect of switching from sitagliptin to oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 52-week, randomized, open-label extension of the PIONEER 7 trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bowe, B.; Xian, H.; Loux, T.; McGill, J.B.; Al-Aly, Z. Comparative effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors, and sulfonylureas on risk of major adverse cardiovascular events: Emulation of a randomised target trial using electronic health records. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caparrotta, T.M.; Dear, J.W.; Colhoun, H.M.; Webb, D.J. Pharmacoepidemiology: Using randomised control trials and observational studies in clinical decision-making. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1907–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All Patients (n = 129) | SWITCH Group (n = 99) | ADD-ON Group (n = 30) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 72 (66; 79) | 73 (66.5; 79) | 69.5 (62; 79) | 0.31 | |
| Sex | M | 74 (57%) | 57 (58%) | 17 (57%) | 0.92 |
| F | 55 (43%) | 42 (42%) | 13 (43%) | ||
| Diabetes duration (years) | 11 (6; 22) | 12 (6; 22.5) | 8 (6; 12) | 0.12 | |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) | 7.2 (6.6; 8) | 7.2 (6.5; 8) | 7.3 (6.7; 8.1) | 0.75 | |
| Baseline BMI (kg/m2) | 28.8 (26.3; 32.8) | 28.8 (26.3; 33.2) | 29 (27.5; 32.4) | 0.55 | |
| Dose of oral semaglutide (mg) | 7 (7; 14) | 7 (7; 14) | 7 (7; 14) | 0.28 | |
| 3 mg | 14 (11%) | 13 (13%) | 1 (3%) | 0.31 | |
| 7 mg | 77 (60%) | 58 (59%) | 19 (63%) | ||
| 14 mg | 38 (29%) | 28 (28%) | 10 (33%) | ||
| Last follow-up (months) | 6 (6; 12) | 6.9 (6.5; 8) | 6.65 (6.7; 8.1) | 0.27 | |
| Monotherapy | Yes | 7 (5%) | 7 (7%) | 0 (0%) | 0.13 |
| No | 122 (95%) | 92 (93%) | 30 (100%) | ||
| Therapy w metformin | Yes | 84 (65%) | 64 (65%) | 20 (67%) | 0.83 |
| No | 45 (35%) | 35 (35%) | 10 (33%) | ||
| Therapy w SGLT2i | Yes | 68 (53%) | 48 (48.5%) | 20 (67%) | 0.08 |
| No | 61 (47%) | 51 (51.5%) | 10 (33%) | ||
| Therapy w insulin | Yes | 36 (28%) | 24 (24%) | 12 (40%) | 0.09 |
| No | 93 (72%) | 75 (76%) | 18 (60%) | ||
| Therapy w sulphonylureas | Yes | 17 (13%) | 15 (15%) | 2 (7%) | 0.23 |
| No | 112 (87%) | 84 (85%) | 28 (93%) | ||
| Therapy w pioglitazone | Yes | 11 (8.5%) | 10 (10%) | 1 (3%) | 0.24 |
| No | 118 (91.5%) | 89 (90%) | 29 (97%) |
| Body Weight Loss | Entire Cohort (n = 98) | SWITCH Group (n = 74) | ADD-ON Group (n = 24) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median absolute change (IQR) | −2.0 (−4.4, 0) | −2.0 (−3.0, 0) | −3.5 (−6.1, −1.9) | 0.007 a |
| ≥5% | 27 (27.6%) | 17 (22.9%) | 10 (41.4%) | 0.074 b |
| ≥10% | 6 (6.1%) | 2 (2.7%) | 4 (16.7%) | 0.013 b |
| Variable | Beta | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.00 | −0.02, 0.02 | 0.98 |
| Sex: male vs. female | −0.07 | −0.40, 0.26 | 0.67 |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) | −0.70 | −0.82, −0.58 | <0.001 |
| Baseline BMI (kg/m2) | −0.04 | −0.08, −0.01 | 0.02 |
| T2DM duration | 0.02 | 0.00, 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Dose of oral semaglutide (mg) | 0.02 | −0.03, 0.06 | 0.49 |
| Last follow-up (months) | −0.02 | −0.08, 0.03 | 0.44 |
| Monotherapy vs. association | −0.30 | −1.1, 0.50 | 0.56 |
| SWITCH vs. ADD-ON group | 0.25 | −0.14, 0.65 | 0.21 |
| Insulin (yes vs. no) | 0.21 | −0.22, 0.63 | 0.33 |
| SGLT2 (yes vs. no) | 0.12 | −0.23, 0.47 | 0.51 |
| R2 = 0.625 |
| Variable | Beta | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | −0.02 | −0.04, 0.01 | 0.16 |
| Sex: male vs. female | 0.31 | −0.19, 0.80 | 0.22 |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) | −0.06 | −0.23, 0.11 | 0.50 |
| Baseline BMI (kg/m2) | −0.05 | −0.11, 0.01 | 0.085 |
| T2DM duration | −0.01 | −0.04, 0.01 | 0.24 |
| Dose of oral semaglutide (mg) | −0.03 | −0.09, 0.04 | 0.42 |
| Last follow-up (months) | −0.07 | −0.16, 0.02 | 0.11 |
| Monotherapy vs. association | 0.02 | −1.23, 1.28 | 0.97 |
| SWITCH vs. ADD-ON group | 0.53 | −0.03, 1.08 | 0.06 |
| Insulin (yes vs. no) | 0.55 | −0.07, 1.17 | 0.08 |
| SGLT2 (yes vs. no) | −0.17 | −0.70, 0.36 | 0.52 |
| R2 = 0.149; AIC = 407 |
| Variable | Beta | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.07 | −0.28, 0.42 | 0.695 |
| Sex: male vs. female | 3.2 | −4.0, 10 | 0.38 |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) | −0.70 | −3.3, 1.9 | 0.59 |
| Baseline BMI (kg/m2) | −0.63 | −1.6, 0.30 | 0.18 |
| T2DM duration | 0.38 | 0.04, 0.72 | 0.03 |
| Dose of oral semaglutide (mg) | 0.17 | −0.79, 1.1 | 0.72 |
| Last follow-up (months) | 0.54 | −0.81, 1.9 | 0.43 |
| Monotherapy vs. association | 23 | 5.5, 40 | 0.01 |
| SWITCH vs. ADD-ON group | 5.8 | −2.5, 14 | 0.17 |
| Insulin (yes vs. no) | −0.78 | −9.8, 8.2 | 0.86 |
| SGLT2 (yes vs. no) | 1.4 | −6.0, 8.8 | 0.71 |
| R2 = 0.268; AIC = 680 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Candido, R.; Gaiotti, S.; Giudici, F.; Toffoli, B.; De Luca, F.; Velardi, V.; Petrucco, A.; Gottardi, C.; Manca, E.; Buda, I.; et al. Real-World Retrospective Study into the Effects of Oral Semaglutide (As a Switchover or Add-On Therapy) in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186052
Candido R, Gaiotti S, Giudici F, Toffoli B, De Luca F, Velardi V, Petrucco A, Gottardi C, Manca E, Buda I, et al. Real-World Retrospective Study into the Effects of Oral Semaglutide (As a Switchover or Add-On Therapy) in Type 2 Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186052
Chicago/Turabian StyleCandido, Riccardo, Sara Gaiotti, Fabiola Giudici, Barbara Toffoli, Federica De Luca, Valerio Velardi, Alessandra Petrucco, Chiara Gottardi, Elena Manca, Iris Buda, and et al. 2023. "Real-World Retrospective Study into the Effects of Oral Semaglutide (As a Switchover or Add-On Therapy) in Type 2 Diabetes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186052
APA StyleCandido, R., Gaiotti, S., Giudici, F., Toffoli, B., De Luca, F., Velardi, V., Petrucco, A., Gottardi, C., Manca, E., Buda, I., Fabris, B., & Bernardi, S. (2023). Real-World Retrospective Study into the Effects of Oral Semaglutide (As a Switchover or Add-On Therapy) in Type 2 Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186052







