Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease, Congestive Heart Failure and Stroke—A Review and Clinical Guide for Healthcare Professionals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
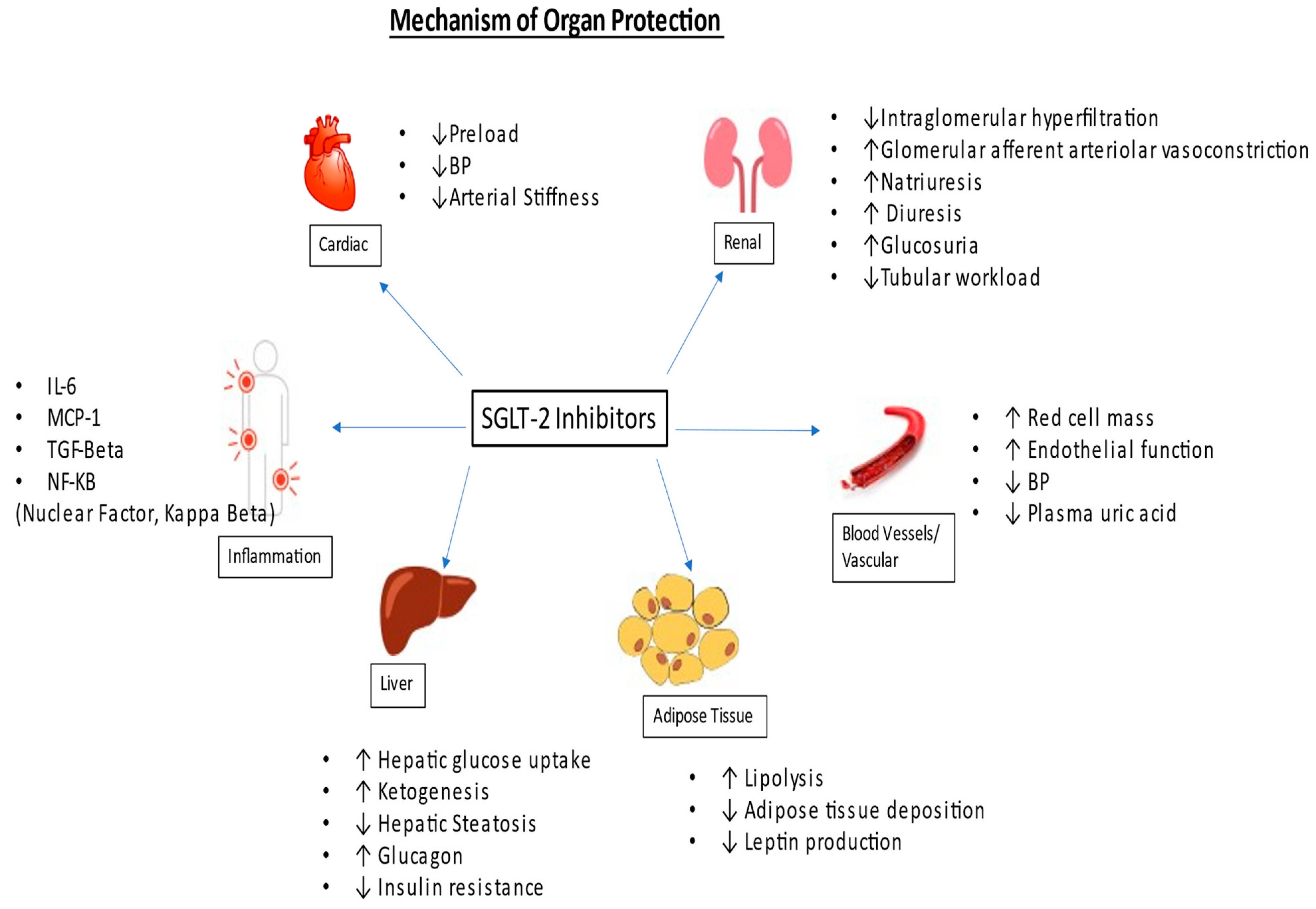
2. Mechanism of Action
3. Effectiveness
3.1. Effectiveness in CKD
3.2. Effectiveness in CHF
3.3. Effectiveness in Stroke
3.3.1. Safety Profile and Adverse Effects
3.3.2. Genital Mycotic Infections
3.3.3. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
3.3.4. Lower-Limb Amputation/Fractures
3.3.5. Volume Depletion
3.3.6. Adjustment and Interaction with Other Medications
3.3.7. GLP-1 Agonist
4. Discussion
Key Points for Clinical Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASCVD | atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| ACE-I | angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ARB | angiotensin receptor blocker |
| BMP | basic metabolic panel |
| CHF | congestive heart failure |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| DKA | diabetic ketoacidosis |
| DKD | diabetic kidney disease |
| ESKD | end-stage kidney disease |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ENaC | epithelial sodium channel |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| HTN | hypertension |
| MI | myocardial infarction |
| MR | mineralocorticoid receptor |
| MRA | mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist |
| RAAS | renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| SGLT2 | sodium-glucose transport protein 2 |
| T2DM | type II diabetes mellitus |
| UACR | urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
References
- USRDS. Annual Data Report | USRDS. Available online: https://usrds-adr.niddk.nih.gov/2022 (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional, and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; de Jong, P.E.; Coresh, J.; El Nahas, M.; Astor, B.C.; Matsushita, K.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Kasiske, B.L.; Eckardt, K.-U. The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: A KDIGO Controversies Conference report. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Bain, R.P. The Effect of Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibition on Diabetic Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; De Zeeuw, D. Effects of Losartan on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R. Renoprotective Effect of the Angiotensin-Receptor Antagonist Irbesartan in Patients with Nephropathy Due to Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigators, D. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Kosiborod, M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Cherney, D.Z. Renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Mechanisms Leading to Differential Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Signaling in the Diabetic Kidney: Modulation by SGLT2 Inhibitors and Hypoxia Mimetics. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, L.G.; Norman, J.T. Chronic hypoxia as a mechanism of progression of chronic kidney diseases: From hypothesis to novel therapeutics. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Perco, P.; Mulder, S.; Leierer, J.; Hansen, M.K.; Heinzel, A.; Mayer, G. Canagliflozin reduces inflammation and fibrosis biomarkers: A potential mechanism of action for beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, C.C.J.; Petrykiv, S.; Laverman, G.D.; Cherney, D.Z.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Effects of the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on glomerular and tubular injury markers. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Har, R.; Fagan, N.; Johansen, O.; Woerle, H.-J.; von Eynatten, M.; Broedl, U.C. The effect of empagliflozin on arterial stiffness and heart rate variability in subjects with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazer, C.D.; Hare, G.M.; Connelly, P.W.; Gilbert, R.E.; Shehata, N.; Quan, A.; Teoh, H.; Leiter, L.A.; Zinman, B.; Jüni, P.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Erythropoietin Levels, Iron Stores, and Red Blood Cell Morphology in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2020, 141, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.; Oshima, M.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Agarwal, R.; Cannon, C.P.; Capuano, G.; Charytan, D.M.; De Zeeuw, D.; Edwards, R.; Greene, T.; et al. Effects of Canagliflozin in Patients with Baseline eGFR <30 mL/min per 1.73 m2. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjöström, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on the rate of decline in kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes: A prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Docherty, K.F.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Solomon, S.D.; Verma, S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: An Exploratory Analysis From DAPA-HF. Diabetes Care 2020, 44, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner–La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Claggett, B.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; Martinez, F.; et al. Dapagliflozin in heart failure with preserved and mildly reduced ejection fraction: Rationale and design of the DELIVER trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.; Rothwell, P.M. Impact of multimorbidity on risk and outcome of stroke: Lessons from chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 16, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Bonaca, M.P.; Furtado, R.H.; Mosenzon, O.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Wilding, J.P.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2020, 141, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, H.T.; Teo, Y.N.; Syn, N.L.; Wee, C.F.; Leong, S.; Yip, A.S.Y.; See, R.M.; Ting, A.Z.H.; Chia, A.Z.; Cheong, A.J.Y.; et al. Effects of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitors on Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke: A Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jardine, M.J.; Li, Q.; Neuen, B.L.; Cannon, C.P.; de Zeeuw, D.; Edwards, R.; Levin, A.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Perkovic, V.; et al. Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Stroke 2021, 52, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Chen, J.; Huang, P.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Hwang, J.; Tsai, C. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Prevents Stroke in Patients With Diabetes and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e027764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baigent, C.; Emberson, J.; Haynes, R.; Herrington, W.G.; Judge, P.; Landray, M.J.; Mayne, K.J.; Ng, S.Y.; Preiss, D.; Roddick, A.J.; et al. Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes: Collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 2022, 400, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersoff-Matcha, S.J.; Chamberlain, C.; Cao, C.; Kortepeter, C.; Chong, W.H. Fournier Gangrene Associated With Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, N.; Billups, S.J.; Saseen, J.J.; Fixen, C.W. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and risk for genitourinary infections in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2020, 12, 204209862199770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Xu, Y.; Su, Q. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 6657380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, S.E.; Osmanska, J.; Petrie, M.C. Dapagliflozin versus metolazone in heart failure resistant to loop diuretics. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2966–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, J.M.; Fogo, A.B. The role of mineralocorticoid receptor activation in kidney inflammation and fibrosis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, F.; Caramori, M.L.; Chan, J.C. Executive summary of the KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: An update based on rapidly emerging new evidence. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Tendal, B.; Mustafa, R.A.; Vandvik, P.O.; Li, S.; Hao, Q.; Tunnicliffe, D.; Ruospo, M.; Natale, P.; Saglimbene, V.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMJ 2021, 372, m4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Lakshmanan, M.C.; Rayner, B.; Busch, R.S.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Woodward, D.B.; Botros, F.T. Dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7): A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.; Ørsted, D.D.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Rasmussen, S.; Tornøe, K.; Zinman, B.; Buse, J.B. Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, K.W.; Jardine, M.J.; Bompoint, S.; Cannon, C.P.; Neal, B.; Heerspink, H.J.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary and Secondary Cardiovascular Prevention Groups. Circulation 2019, 140, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and kidney disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, K.; Dharia, A.; Alrowiyti, I.; Cherney, D.Z. Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients With CKD: Expanding Indications and Practical Considerations. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuen, B.L.; Young, T.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Billot, L.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Charytan, D.M.; Wheeler, D.C.; Arnott, C.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trial | CREDENCE | DAPA-HF | DAPA CKD | VERTIS | EMPA KIDNEY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug dose | Canagliflozin 100 mg 100 mg | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | Ertugliflozin 5, 15 mg | Empagliflozin 10 mg |
| Year published | June 2019 | November 2019 | March 2020 | June 2020 | November 2022 |
| Median follow up | 2.6 yrs. | 18.2 months | 2.4 yrs. | 3.5 yrs. | 2 yrs. |
| eGFR on enrollment | >30, UACR 300–5000 mg/gm | >30 (40% pt had eGFR < 60) | 25–75, UACR 200–5000 mg/gm | >30 | 20–45 or >45 < 90, if UACR > 200 mg/gm |
| DM-2 on enrollment | DM-2 only | 42% had DM-2 | 30% non-diabetic | DM only | Both Diabetic and non-Diabetic 2.2% had DM-type 1 |
| CVD on enrollment | 50% participants | All participants | 37% participants | 76.3% had CAD, 23% had CHF | 26% participants |
| Primary outcome | ESKD, doubling of serum creatinine, death from renal or CV causes. | CV death, heart failure hospitalization, all-cause mortality | ESKD, >50% drop in eGFR, death from renal and CV causes | MACE (CV death, MI, stroke) | ESKD, sustained decrease in eGFR < 10, in eGFR > 40%, death due to renal or cv Causes. |
| Secondary outcome | Cardiovascular mortality, all-cause mortality, MI, stroke. | ESKD, >50% drop in eGFR lasting >28 days, death from renal causes. | Same as above. | Composite of renal death, dialysis, doubling of serum creatinine | Heart failure hospitalization, all cause mortality, all cause hospitalization |
| Results | Reduction in primary outcome by 30–35% | Reduction in - CV death, HF by 24%, - All cause mortality by 17% | Reduction in primary outcome by 35–45% | no statistically significant improvement in primary outcomes. | Reduction in primary outcome by 25–30% |
| NNT (for primary outcome) | 22 | 21 | 19 | Not available | Not available |
| CKD Staging | Stage 3b (eGFR 30–44) | Stage 4 (eGFR 15–29) | Stage 5 (eGFR < 15) | Hepatic Dysfunction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canagliflozin | 100 mg daily | Do not initiate if eGFR < 45 | Avoid in Severe impairment (Child-Pugh class C) | |
| Dapagliflozin | 10 mg daily | Do not initiate if eGFR < 25. If previously taking, may continue until dialysis | No dosage adjustment Use caution if initiating in severe impairment | |
| Empagliflozin | 10, 25 mg daily | - No dosage adjustment necessary for eGFR ≥ 20 US manufacturer does not recommend use for glycemic control for eGFR < 30 | No dosage adjustment necessary | |
| Ertugliflozin | Maximum of 15 mg daily, Do not initiate if eGFR < 45 | Not recommended | Use is not recommended with Severe impairment (Child-Pugh class C) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, P.; Goyal, L.; Mallick, D.C.; Surani, S.R.; Yashi, K. Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease, Congestive Heart Failure and Stroke—A Review and Clinical Guide for Healthcare Professionals. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196202
Singh P, Goyal L, Mallick DC, Surani SR, Yashi K. Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease, Congestive Heart Failure and Stroke—A Review and Clinical Guide for Healthcare Professionals. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196202
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Prabhat, Lokesh Goyal, Deobrat C. Mallick, Salim R. Surani, and Kanica Yashi. 2023. "Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease, Congestive Heart Failure and Stroke—A Review and Clinical Guide for Healthcare Professionals" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196202
APA StyleSingh, P., Goyal, L., Mallick, D. C., Surani, S. R., & Yashi, K. (2023). Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease, Congestive Heart Failure and Stroke—A Review and Clinical Guide for Healthcare Professionals. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196202






