First Clinical Case Report of a Xenograft–Allograft Combination for Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Bovine Bone Substitute Material with Hyaluronate (Cerabone® Plus) Combined with Allogeneic Bone Granules (Maxgraft®)
Abstract
:1. Background
1.1. Bovine Bone Substitutes
1.2. Biofunctionalization of Bone Substitute Materials
1.3. Clinical Applications
2. Materials and Methods
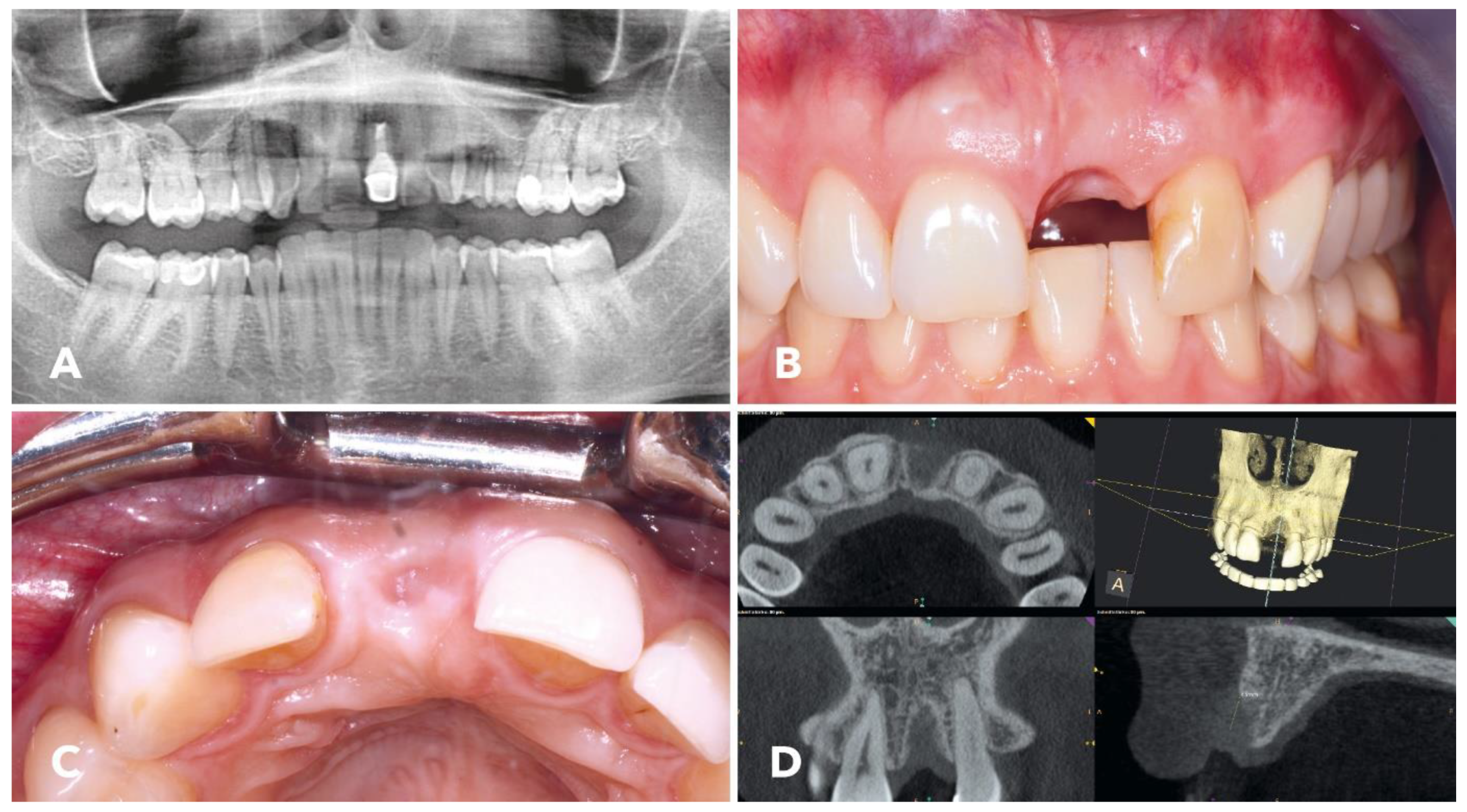
2.1. Overview of the Clinical Case
2.2. Cerabone® Plus
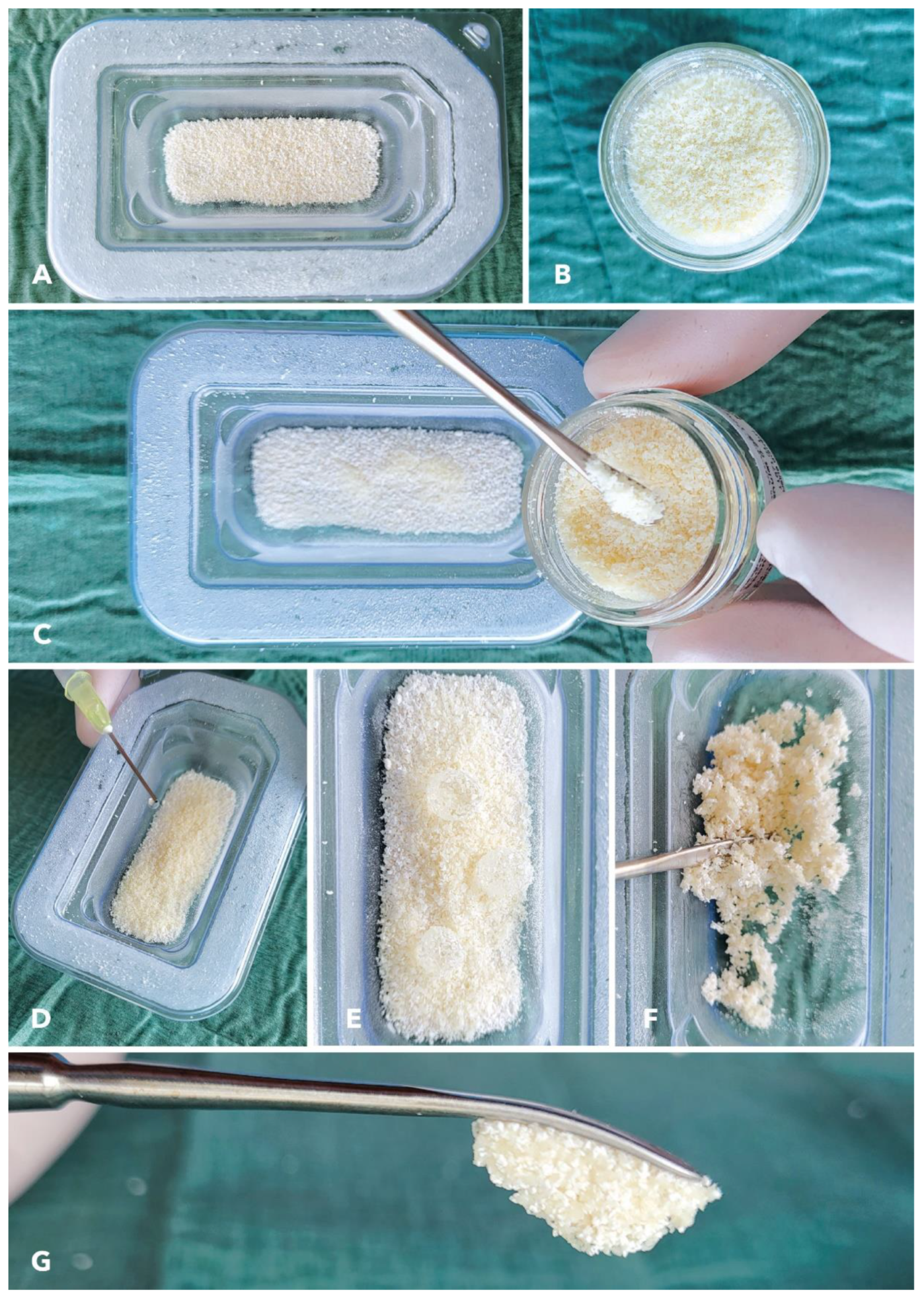
2.3. Preparation and Handling of Cerabone® Plus in Combination with Maxgraft®
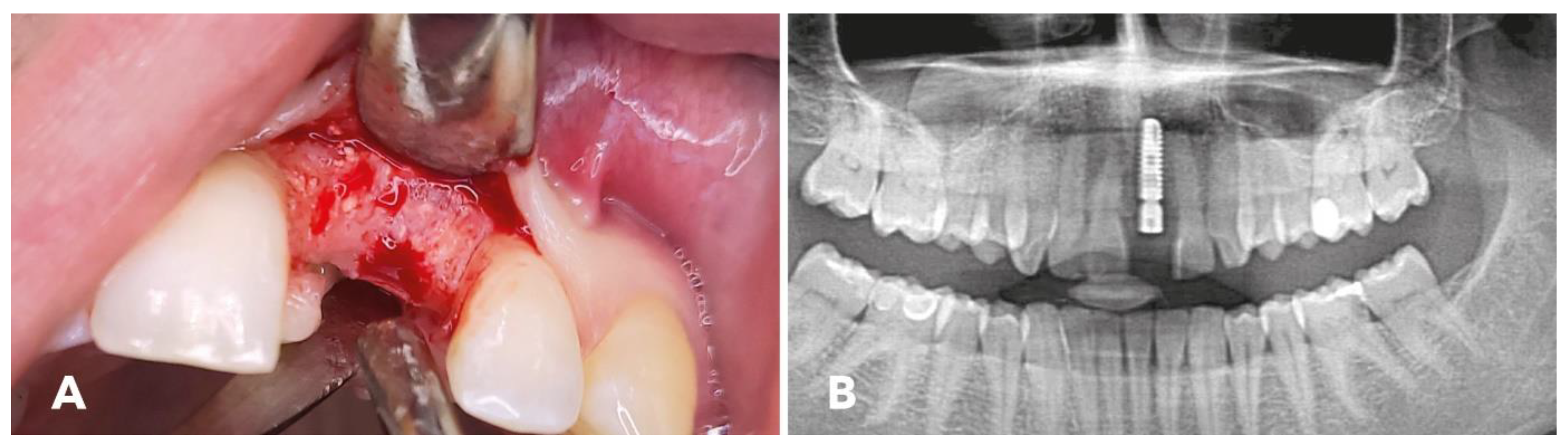
2.4. Surgical Procedure
2.5. Implantation
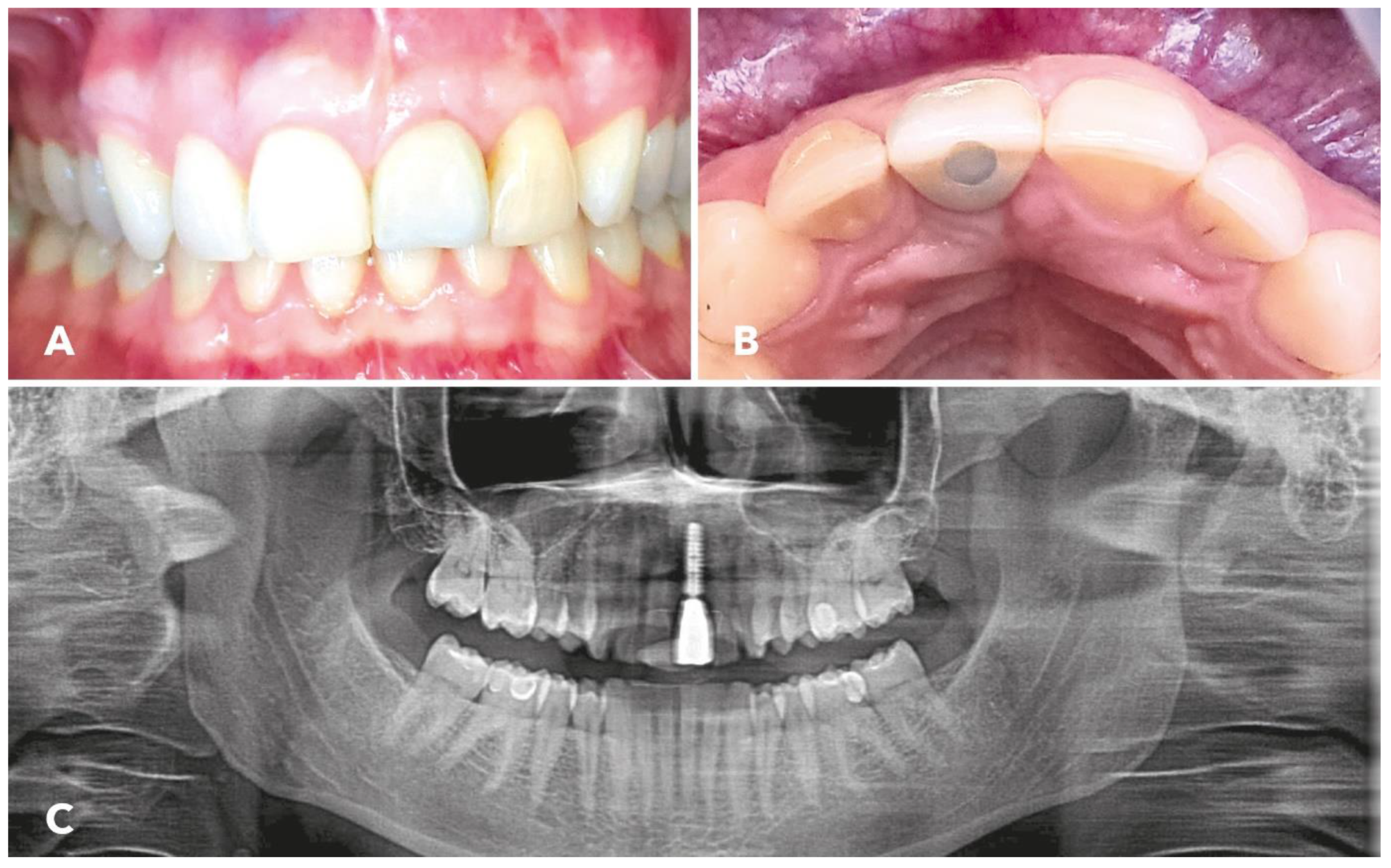
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Alveolar Ridge Augmentation
4.2. Enhanced Bone Regeneration
4.3. Promotion of Angiogenesis
4.4. Enhanced Mechanical Properties
4.5. Comparison to Previous Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kloss, F.R.; Offermanns, V.; Kloss-Brandstätter, A. Comparison of allogeneic and autogenous bone grafts for augmentation of alveolar ridge defects—A 12-month retrospective radiographic evaluation. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kämmerer, P.W.; Tunkel, J.; Götz, W.; Würdinger, R.; Kloss, F.; Pabst, A. The allogeneic shell technique for alveolar ridge augmentation: A multicenter case series and experiences of more than 300 cases. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2022, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majzoub, J.; Ravidà, A.; Starch-Jensen, T.; Tattan, M.; Del Amo, F.S.-L. The Influence of Different Grafting Materials on Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2019, 10, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloss, F.R.; Kämmerer, P.W.; Kloss-Brandstätter, A. Risk Factors for Complications Following Staged Alveolar Ridge Augmentation and Dental Implantation: A Retrospective Evaluation of 151 Cases with Allogeneic and 70 Cases with Autogenous Bone Blocks. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, F.R.; Offermanns, V.; Donkiewicz, P.; Kloss-Brandstätter, A. Customized allogeneic bone grafts for maxillary horizontal augmentation: A 5-year follow-up radiographic and histologic evaluation. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virnik, S.; Cueni, L.; Kloss-Brandstätter, A. Is one-stage lateral sinus lift and implantation safe in severely atrophic maxillae? Results of a comparative pilot study. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2023, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yang, R.; Cooper, P.R.; Khurshid, Z.; Shavandi, A.; Ratnayake, J. Bone Grafts and Substitutes in Dentistry: A Review of Current Trends and Developments. Molecules 2021, 26, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, C.; Cerri, M.; Baena, R.R.Y.; Lupi, S.M. Full-Arch Guided Restoration and Bone Regeneration: A Complete Digital Workflow Case Report. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čandrlić, M.; Tomas, M.; Karl, M.; Malešić, L.; Včev, A.; Kačarević, P.; Matijević, M. Comparison of Injectable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate and a Bovine Xenograft in Socket Preservation: Qualitative and Quantitative Histologic Study in Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, M.T.; Mahesh, L.; Mascarenhas, G.; Guirado, C.; Juneja, S. Histological evaluation of two different anorganic bovine bone matrixes in lateral wall sinus elevation procedure: A retrospective study. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 11, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedpasha, A.; Ghassemi, A.; Bijani, A.; Haghanifar, S.; Majidi, M.S.; Ghorbani, Z.M. Comparison of Bone Formation After Sinus Membrane Lifting without Graft or Using Bone Substitute “Histologic and Radiographic Evaluation”. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catros, S.; Sandgren, R.; Pippenger, B.E.; Fricain, J.C.; Herber, V.; El Chaar, E. A Novel Xenograft Bone Substitute Supports Stable Bone Formation in Circumferential Defects Around Dental Implants in Minipigs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chaar, E.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sandgren, R.; Fricain, J.-C.; Dard, M.; Pippenger, B.; Catros, S. Osseointegration of Superhydrophilic Implants Placed in Defect Grafted Bones. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, Z.; Lorean, A.; Mijiritsky, E.; Levin, L. Nasal Floor Elevation Combined with Dental Implant Placement. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawil, G.; Tawil, P.; Khairallah, A. Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Lateral Approach and Bone Window Repositioning I: Clinical and Radiographic Results in 102 Consecutively Treated Patients Followed from 1 to 5 Years. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovski, B.; Jaunich, M.; Müller, W.-D.; Beuer, F.; Zafiropoulos, G.-G.; Houshmand, A. Hydrophilicity, Viscoelastic, and Physicochemical Properties Variations in Dental Bone Grafting Substitutes. Materials 2018, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielenstein, J.; Radenković, M.; Najman, S.; Liu, L.; Ren, Y.; Cai, B.; Beuer, F.; Rimashevskiy, D.; Schnettler, R.; Alkildani, S.; et al. In Vivo Analysis of the Regeneration Capacity and Immune Response to Xenogeneic and Synthetic Bone Substitute Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargolzaie, N.; Kadkhodazadeh, M.; Ebadian, A.R.; Shafieian, R.; Pourkaveh, S.; Naghibi, N.; Ramandie, M.F. Histological Evaluation of Bone Regeneration Using Hydroxyapatite Based Bone Substitute Derived from Antler: An Animal Study. J. Long Term Eff. Med. Implants 2022, 32, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricky, M.M.C.; Gabor, A.-G.; Milutinovici, R.A.; Watz, C.G.; Avram, Ș.; Drăghici, G.; Mihali, C.V.; Moacă, E.-A.; Dehelean, C.A.; Galuscan, A.; et al. Scaffold-Type Structure Dental Ceramics with Different Compositions Evaluated through Physicochemical Characteristics and Biosecurity Profiles. Materials 2021, 14, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawil, G.; Barbeck, M.; Unger, R.; Tawil, P.; Witte, F. Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Lateral Approach and Window Repositioning and a Xenogeneic Bone Substitute as a Grafting Material: A Histologic, Histomorphometric, and Radiographic Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susin, C.; Lee, J.; Fiorini, T.; Koo, K.-T.; Schüpbach, P.; Stadler, A.F.; Wikesjö, U.M. Screening of Hydroxyapatite Biomaterials for Alveolar Augmentation Using a Rat Calvaria Critical-Size Defect Model: Bone Formation/Maturation and Biomaterials Resolution. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneru, S.; Kollati, P.; Dwarakanath, C.D.; Gottumukkala, S.N.V.S. Effectiveness of naturally derived bovine hydroxyapatite (Cerabone™) combined with platelet-rich fibrin matrix in socket preservation: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2019, 23, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyyak, S.; Blatt, S.; Wiesmann, N.; Smeets, R.; Kaemmerer, P.W. Hyaluronic Acid with Bone Substitutes Enhance Angiogenesis In Vivo. Materials 2022, 15, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyyak, S.; Pabst, A.; Heimes, D.; Kämmerer, P.W. The Influence of Hyaluronic Acid Biofunctionalization of a Bovine Bone Substitute on Osteoblast Activity In Vitro. Materials 2021, 14, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Peng, X.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, X. The application of hyaluronic acid in bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 151, 1224–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Zhou, C.; Hui, D.; Du, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Pu, X.; Gu, L.; Liu, L.; et al. Hyaluronic acid as a bioactive component for bone tissue regeneration: Fabrication, modification, properties, and biological functions. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 1059–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blašković, M.; Blašković, D.; Hangyasi, D.B.; Peloza, O.C.; Tomas, M.; Čandrlić, M.; Rider, P.; Mang, B.; Kačarević, P.; Trajkovski, B. Evaluation between Biodegradable Magnesium Metal GBR Membrane and Bovine Graft with or without Hyaluronate. Membranes 2023, 13, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pröhl, A.; Batinic, M.; Alkildani, S.; Hahn, M.; Radenkovic, M.; Najman, S.; Jung, O.; Barbeck, M. In Vivo Analysis of the Biocompatibility and Bone Healing Capacity of a Novel Bone Grafting Material Combined with Hyaluronic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkildani, S.; Ren, Y.; Liu, L.; Rimashevskiy, D.; Schnettler, R.; Radenković, M.; Najman, S.; Stojanović, S.; Jung, O.; Barbeck, M. Analyses of the Cellular Interactions between the Ossification of Collagen-Based Barrier Membranes and the Underlying Bone Defects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakašević, D.; Šćepanović, M.; Mijailović, I.; Mišić, T.; Janjić, B.; Soldatović, I.; Marković, A. Reconstructive Peri-Implantitis Therapy by Using Bovine Bone Substitute with or without Hyaluronic Acid: A Randomized Clinical Controlled Pilot Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafiropoulos, G.G.; Trajkovski, B. Socket preservation, sinus lift and lateral augmentation by using natural bovine bone substitute with hyaluronate. Int. J. Dent. Biomater. Res. 2023, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Kienle, G.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Sox, H.; Riley, D. The CARE Guidelines: Consensus-based Clinical Case Reporting Guideline Development. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2013, 2, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, D.S.; Barber, M.S.; Kienle, G.S.; Aronson, J.K.; von Schoen-Angerer, T.; Tugwell, P.; Kiene, H.; Helfand, M.; Altman, D.G.; Sox, H.; et al. CARE guidelines for case reports: Explanation and elaboration document. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 89, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.T.; Buser, D. ITI Treatment Guide Volume 3: Implants in extraction sockets. In Implants in Post-Extraction Sites: A Literature Update; Buser, D., Belser, U., Wismeijer, D., Eds.; Quintessense Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Benic, G.I.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration. Periodontol. 2000 2014, 66, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, A.; Chen, S. The SAC Classification in Implant Dentistry; Quintessense Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.K.; Ku, J.K. Ridge augmentation in implant dentistry. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 46, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhary, I.E.; El-Mekkawi, H.A.; Elsalanty, M.E. Alveolar ridge augmentation for implant fixation: Status review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 114, S179–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasson, G.; Skoglund, I.; Rythén, M. The rise and fall of the alveolar process: Dependency of teeth and metabolic aspects. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 96, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodic, F.; Hamel, L.; Lerouxel, E.; Basle, M.F.; Chappard, D. Bone loss and teeth. Jt. Bone Spine 2005, 72, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, A.; Navet, B.; Vargas, J.W.; Castaneda, B.; Lezot, F. Bone resorption: An actor of dental and periodontal development? Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, I.A.; Montero, E.; Monje, A.; Sanz-Sanchez, I. Effectiveness of vertical ridge augmentation interventions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeltzsch, M.; Troeltzsch, M.; Kauffmann, P.; Gruber, R.; Brockmeyer, P.; Moser, N.; Rau, A.; Schliephake, H. Clinical efficacy of grafting materials in alveolar ridge augmentation: A systematic review. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1618–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolin, E.; Ceccarelli, G.; Baena, R.R.Y.; D’Urso, L.; Todaro, C.; Lupi, S.M. Long-term results of autologous periosteum-derived micro-grafts with poly(lactic-go-glycolic acid) in sinus lift augmentation surgeries: A 7-years follow-up observational study. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2023, 106, 108153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Labrador, L.; Molinero-Mourelle, P.; Pérez-González, F.; Saez-Alcaide, L.M.; Brinkmann, J.C.-B.; Martínez, J.L.-Q.; Martínez-González, J.M. Clinical performance of alveolar ridge augmentation with xenogeneic bone block grafts versus autogenous bone block grafts. A systematic review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 122, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yeung, K.W.K. Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: A review. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 224–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.-S.; Oh, J.-K. Review of bone graft and bone substitutes with an emphasis on fracture surgeries. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnival, I.G.; Hirst, C. Mammographic Microcalcification in Axillary Lymph Nodes. Australas. Radiol. 1992, 36, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.T.; Rosenbaum, A.J. Bone grafts, bone substitutes and orthobiologics: The bridge between basic science and clinical advancements in fracture healing. Organogenesis 2012, 8, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, M.P.G.; Seigerman, D.A. The Clinical Use of Allografts, Demineralized Bone Matrices, Synthetic Bone Graft Substitutes and Osteoinductive Growth Factors: A Survey Study. HSS J. 2005, 1, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starch-Jensen, T.; Deluiz, D.; Tinoco, E.M.B. Horizontal Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Allogeneic Bone Block Graft Compared with Autogenous Bone Block Graft: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2020, 11, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.G.; Grønlund, G.P.; Georgi, S.R.; Starch-Jensen, T.; Bruun, N.H.; Jensen, S.S. Horizontal Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Xenogenic Block Grafts Compared with Autogenous Bone Block Grafts for Implant-retained Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2023, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, R.; Matthies, L.; Windisch, P.; Gosau, M.; Jung, R.; Brodala, N.; Stefanini, M.; Kleinheinz, J.; Payer, M.; Henningsen, A.; et al. Horizontal augmentation techniques in the mandible: A systematic review. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2022, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Hou, L.; Wang, X. The assessment of xenogeneic bone immunotoxicity and risk management study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2019, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onică, N.; Onică, C.A.; Baciu, E.-R.; Vasluianu, R.-I.; Ciofu, M.; Balan, M.; Gelețu, G.L. Advanced Techniques for Bone Restoration and Immediate Loading after Implant Failure: A Case Report. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Egusa, H. Current bone substitutes for implant dentistry. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health status | Healthy, cooperative and without immunological restriction | ||
| Tobacco use | Non-smoker | 1-10/d | >10/d |
| Patient’s claim | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of the smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Fabric strong, flat garland shape | Medium strong, average garland shape | Fabric weak, steep garland shape |
| Dental form type | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Local infection | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone level at neighboring teeth | ≤5 mm from the contact point | 5.5–6.5 mm from the contact point | ≥7 mm from the contact point |
| Restoration status of neighboring teeth | Untouched | Restored | |
| Width of the gap | 1 tooth (≥7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤7 mm) | ≥2 teeth |
| Soft tissue condition | Intact | Reduced | Defective |
| Bone volume | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kloss, F.R.; Kämmerer, P.W.; Kloss-Brandstätter, A. First Clinical Case Report of a Xenograft–Allograft Combination for Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Bovine Bone Substitute Material with Hyaluronate (Cerabone® Plus) Combined with Allogeneic Bone Granules (Maxgraft®). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196214
Kloss FR, Kämmerer PW, Kloss-Brandstätter A. First Clinical Case Report of a Xenograft–Allograft Combination for Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Bovine Bone Substitute Material with Hyaluronate (Cerabone® Plus) Combined with Allogeneic Bone Granules (Maxgraft®). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196214
Chicago/Turabian StyleKloss, Frank R., Peer W. Kämmerer, and Anita Kloss-Brandstätter. 2023. "First Clinical Case Report of a Xenograft–Allograft Combination for Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Bovine Bone Substitute Material with Hyaluronate (Cerabone® Plus) Combined with Allogeneic Bone Granules (Maxgraft®)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196214
APA StyleKloss, F. R., Kämmerer, P. W., & Kloss-Brandstätter, A. (2023). First Clinical Case Report of a Xenograft–Allograft Combination for Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Bovine Bone Substitute Material with Hyaluronate (Cerabone® Plus) Combined with Allogeneic Bone Granules (Maxgraft®). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196214







