Semi-Automatic Measurement of Fetal Cardiac Axis in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
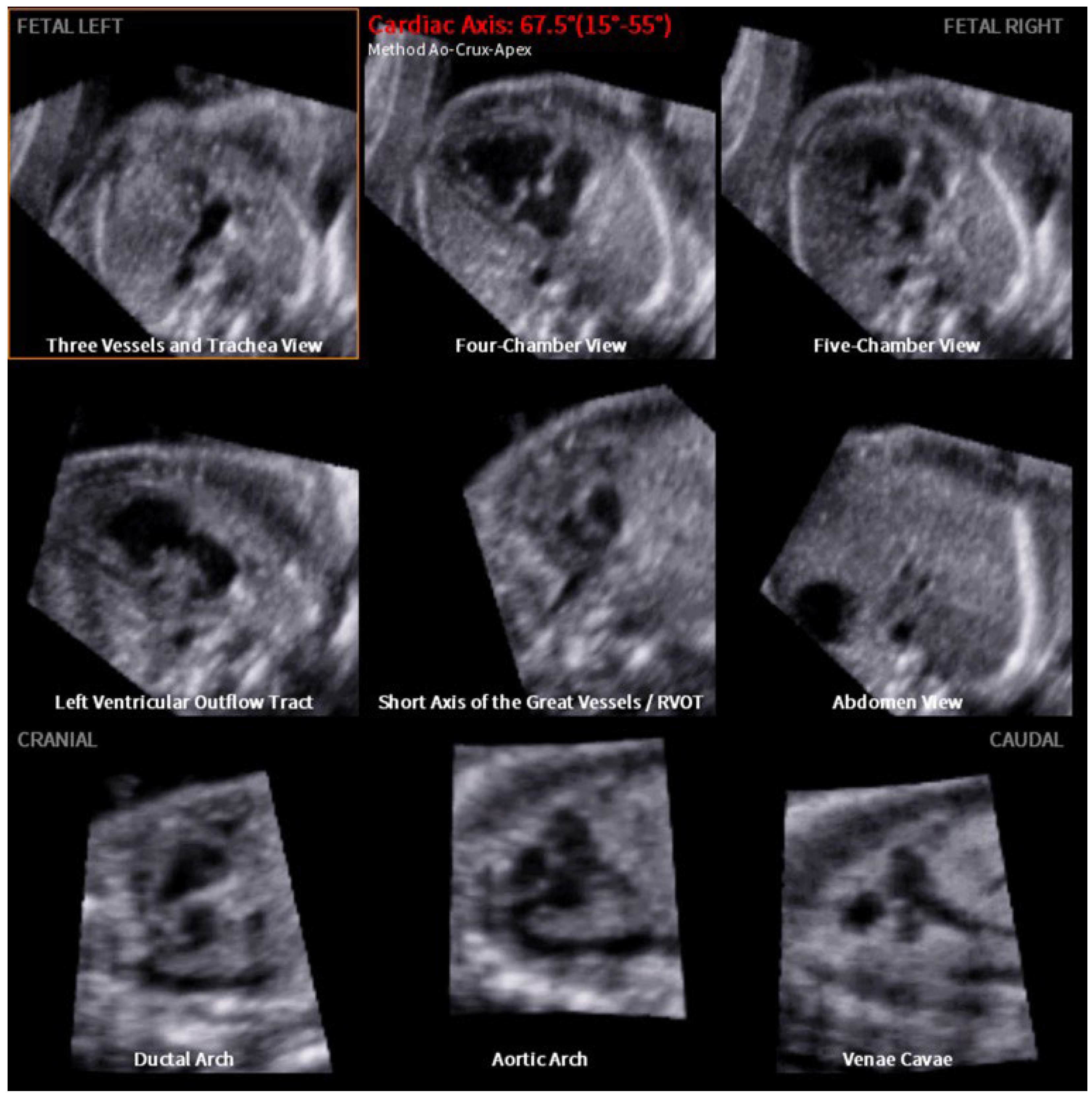
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffman, J.I.; Kaplan, S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, P.; Sluysmans, T.; De Wolf, D.; Massin, M.; Suys, B.; Benatar, A.; Gewillig, M. Congenital heart disease in 111 225 births in Belgium: Birth prevalence, treatment and survival in the 21st century. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Seo, S.R.; Moon, J.R.; Cho, E.J.; Kim, E.; Chang, S.A.; Song, J.; Huh, J.; Kang, I.S.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Prevalence and mortality of congenital heart disease in Korean adults. Medicine 2018, 97, e11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.K. Supporting Optimal Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Infants and Children with Congenital Heart Disease. Crit. Care Nurse 2018, 38, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, J.V.B.; Guimaraes, A.L.S.; Sobral Filho, D.C.; Santos, A. Mortality due to congenital heart disease in Pernambuco from 1996 to 2016. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2020, 66, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, P.T.; Thomas, A.R.; Wethall, A.; Perez, D.; Steurer, M.; Ball, M.K. Rethinking Congenital Heart Disease in Preterm Neonates. Neoreviews 2022, 23, e373–e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilboa, S.M.; Salemi, J.L.; Nembhard, W.N.; Fixler, D.E.; Correa, A. Mortality resulting from congenital heart disease among children and adults in the United States, 1999 to 2006. Circulation 2010, 122, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donofrio, M.T. Predicting the Future: Delivery Room Planning of Congenital Heart Disease Diagnosed by Fetal Echocardiography. Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edler, I.; Hertz, C.H. The use of ultrasonic reflectoscope for the continuous recording of the movements of heart walls. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2004, 24, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramiak, R.; Nanda, N.C.; Shah, P.M. Echocardiographic detection of the pulmonary valve. Radiology 1972, 102, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, C.S.; Hobbins, J.C.; Jaffe, C.C.; Lynch, D.C.; Talner, N.S. Echocardiographic studies of the human fetus: Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease and cardiac dysrhythmias. Pediatrics 1980, 65, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulik, D.; Nanda, N.C.; Maulik, D.; Vilchez, G. A brief history of fetal echocardiography and its impact on the management of congenital heart disease. Echocardiography 2017, 34, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.S.; Axt-Fliedner, R.; Chaoui, R.; Copel, J.A.; Cuneo, B.F.; Goff, D.; Gordin Kopylov, L.; Hecher, K.; Lee, W.; Moon-Grady, A.J.; et al. ISUOG Practice Guidelines (updated): Fetal cardiac screening. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 61, 788–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itsukaichi, M.; Serikawa, T.; Yoshihara, K.; Suzuki, H.; Haino, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Enomoto, T.; Niigata Fetal Cardiac Screening Study Group; Takakuwa, K.; Aida, H.; et al. Effectiveness of fetal cardiac screening for congenital heart disease using a combination of the four-chamber view and three-vessel view during the second trimester scan. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 44, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, J.S.; Comstock, C.H.; Lee, W.; Smith, R.S.; Riggs, T.W.; Weinhouse, E. Fetal cardiac asymmetry: A marker for congenital heart disease. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 93, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svirsky, R.; Brabbing-Goldstein, D.; Rozovski, U.; Kapusta, L.; Reches, A.; Yaron, Y. The genetic and clinical outcome of isolated fetal muscular ventricular septal defect (VSD). J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 32, 2837–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeggi, E.; Ohman, A. Fetal and Neonatal Arrhythmias. Clin. Perinatol. 2016, 43, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkovskaya, E.S.; Chaoui, R.; Karl, K.; Andreeva, E.; Zhuchenko, L.; Abuhamad, A.Z. Fetal cardiac axis and congenital heart defects in early gestation. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesrouani, A.; Abdallah, W.; Kharrat, R.; Choueiry, E.; Daou, L.; Nasr, B. Normal values of cardiac axis (CA) measurements in healthy fetuses during the first trimester screening ultrasound. J. Perinat. Med. 2021, 49, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembicki, M.; Scharf, J.L.; Dracopoulos, C.; Welp, A.; Weichert, J. Maximal Reduction of STIC Acquisition Time for Volumetric Assessment of the Fetal Heart-Benefits and Limitations of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Static Mode. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, L.J.; Dong, S.Z. Utility of fetal cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in assessing the cardiac axis in fetuses with congenital heart disease. Pediatr. Radiol. 2023, 53, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gembicki, M.; Hartge, D.R.; Dracopoulos, C.; Weichert, J. Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography Has the Potential to Aid Cardiac Evaluations Even in Less Experienced Hands. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Velzen, C.L.; Ket, J.C.F.; van de Ven, P.M.; Blom, N.A.; Haak, M.C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the performance of second-trimester screening for prenatal detection of congenital heart defects. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2018, 140, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Hornberger, L.K.; Fruitman, D.; Ngwezi, D.; Eckersley, L.G. Impact of rural residence and low socioeconomic status on rate and timing of prenatal detection of major congenital heart disease in a jurisdiction of universal health coverage. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 60, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nisselrooij, A.E.L.; Teunissen, A.K.K.; Clur, S.A.; Rozendaal, L.; Pajkrt, E.; Linskens, I.H.; Rammeloo, L.; Van Lith, J.M.; Blom, N.A.; Haak, M.C. Why are congenital heart defects being missed? Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 55, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaanse, B.M.; van Vugt, J.M.; Haak, M.C. Three- and four-dimensional ultrasound in fetal echocardiography: An up-to-date overview. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichert, J.; Weichert, A. A ‘holistic’ sonographic view on congenital heart disease—How automatic reconstruction using fetal intelligent navigation echocardiography (FINE) eases the unveiling of abnormal cardiac anatomy part I: Right heart anomalies. Echocardiography 2021, 38, 1430–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichert, J.; Weichert, A. A “holistic” sonographic view on congenital heart disease: How automatic reconstruction using fetal intelligent navigation echocardiography eases unveiling of abnormal cardiac anatomy part II—Left heart anomalies. Echocardiography 2021, 38, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusanovic, J.P.; Nien, J.K.; Goncalves, L.F.; Espinoza, J.; Lee, W.; Balasubramaniam, M.; Soto, E.; Erez, O.; Romero, R. The use of inversion mode and 3D manual segmentation in volume measurement of fetal fluid-filled structures: Comparison with Virtual Organ Computer-aided AnaLysis (VOCAL). Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 31, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simioni, C.; Nardozza, L.M.; Araujo Junior, E.; Rolo, L.C.; Zamith, M.; Caetano, A.C.; Moron, A.F. Heart stroke volume, cardiac output, and ejection fraction in 265 normal fetus in the second half of gestation assessed by 4D ultrasound using spatio-temporal image correlation. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 24, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Capponi, A.; Pietrolucci, M.E.; Arduini, D. Role of sonographic automatic volume calculation in measuring fetal cardiac ventricular volumes using 4-dimensional sonography: Comparison with virtual organ computer-aided analysis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2010, 29, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, B.; Gilboa, Y.; Lipschuetz, M.; Valsky, D.V.; Cohen, S.M.; Yagel, S. Fetal tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (f-TAPSE): Evaluation of fetal right heart systolic function with conventional M-mode ultrasound and spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC) M-mode. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 42, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasina, F.; Bellussi, F.; Morganelli, G.; Salsi, G.; Pilu, G.; Simonazzi, G. Electronic spatiotemporal image correlation improves four-dimensional fetal echocardiography. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 51, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalache, K.D.; Bamberg, C.; Proquitte, H.; Sarioglu, N.; Lebek, H.; Esser, T. Three-dimensional multi-slice view: New prospects for evaluation of congenital anomalies in the fetus. J. Ultrasound Med. 2006, 25, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.C.; Shyu, M.K.; Su, Y.N.; Chiang, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, C.N. “Big-eyed frog” sign on spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC) in the antenatal diagnosis of transposition of the great arteries. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 32, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE): A novel method for rapid, simple, and automatic examination of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 42, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Color and power Doppler combined with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) to evaluate the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembicki, M.; Welp, A.; Scharf, J.L.; Dracopoulos, C.; Weichert, J. Application of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) in Twin Pregnancies: Half the Work or Twice the Effort? Cureus 2023, 15, e38052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swor, K.; Yeo, L.; Tarca, A.L.; Jung, E.; Romero, R. Fetal intelligent navigation echocardiography (FINE) has superior performance compared to manual navigation of the fetal heart by non-expert sonologists. J. Perinat. Med. 2023, 51, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Luewan, S.; Markush, D.; Gill, N.; Romero, R. Prenatal Diagnosis of Dextrocardia with Complex Congenital Heart Disease Using Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) and a Literature Review. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2018, 43, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Luewan, S.; Romero, R. Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Detects 98% of Congenital Heart Disease. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 2577–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. New and advanced features of fetal intelligent navigation echocardiography (FINE) or 5D heart. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 1498–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo Junior, E.; Rocha, L.A.; Nardozza, L.M. Sonocubic fine: New three-dimensional ultrasound software to the screening of congenital heart diseases. Rev. Bras. Cir. Cardiovasc. 2014, 29, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comstock, C.H. Normal fetal heart axis and position. Obstet. Gynecol. 1987, 70, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolter, A.; Kawecki, A.; Stressig, R.; Ritgen, J.; Degenhardt, J.; Enzensberger, C.; Axt-Fliedner, R. Fetal Cardiac Axis in Fetuses with Conotruncal Anomalies. Ultraschall Med. 2017, 38, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Edington, S.; Fleenor, J.; Sinkovskaya, E.; Porche, L.; Abuhamad, A. Fetal cardiac axis in tetralogy of Fallot: Associations with prenatal findings, genetic anomalies and postnatal outcome. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, G.J. Efficacy of fetal cardiac axis evaluation in the first trimester as a screening tool for congenital heart defect or aneuploidy. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2020, 63, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CHD/Thoracic Mass | n | Axis Mean (Range) | Axis Median |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absent pulmonary valve ** | 7 | 64.0° (38.5–76.2°) | 68.6° |
| Aortic stenosis | 5 | 49.4° (34.2–60.1°) | 50.3° |
| ASD | 5 | 50.6° (45.3–57.4°) | 48.9° |
| AVSD | 75 | 40.0° (19.5–66.9°) | 40.5° |
| Coarctation aortae | 20 | 39.2° (30.7–55.0°) | 38.8° |
| Complex CHD | 8 | 47.1° (22.9–78.2°) | 48.1° |
| DAA | 2 | 39.2° (36.8–41.7°) | 39.2° |
| DORV ** | 87 | 45.9° (8.7–105.4°) | 43.2° |
| HLHS **** | 157 | 45.1° (10.2–87.2°) | 45.8° |
| HRHS | 27 | 32.1° (−54.8–65.7°) | 49.6° |
| IAA | 1 | 45.6° | 45.6° |
| Others | 13 | 34.8° (19.9–46.2°) | 37.3° |
| Pulmonary Atresia **** | 19 | 60.2° (26.6–97.0°) | 61.5° |
| RAA *** | 12 | 24.1° (15.3–39.0°) | 23.8° |
| Rhabdomyoma | 5 | 37.7° (28.3–58.5°) | 34.2° |
| Situs ambiguus | 15 | −8.0° (−31.4–36.7) | −16.8 |
| TAC *** | 30 | 50.3° (24.4–65.7°) | 51.6° |
| TGA | 21 | 34.6° (−3.7–69.6°) | 34.8° |
| TOF **** | 25 | 56.6° (29.4–86.9°) | 58.9° |
| Thoracic masses | 11 | 23.3° (13.4–48.9°) | 21.8° |
| Total | 545 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weichert, A.; Gembicki, M.; Weichert, J.; Weber, S.C.; Koenigbauer, J. Semi-Automatic Measurement of Fetal Cardiac Axis in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196371
Weichert A, Gembicki M, Weichert J, Weber SC, Koenigbauer J. Semi-Automatic Measurement of Fetal Cardiac Axis in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196371
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeichert, Alexander, Michael Gembicki, Jan Weichert, Sven Christian Weber, and Josefine Koenigbauer. 2023. "Semi-Automatic Measurement of Fetal Cardiac Axis in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196371
APA StyleWeichert, A., Gembicki, M., Weichert, J., Weber, S. C., & Koenigbauer, J. (2023). Semi-Automatic Measurement of Fetal Cardiac Axis in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196371







