The Influence of Clinical Factors on Treatment Outcome and a Recurrence of Surgically Removed Protruded Subungual Osteochondroma and Subungual Exostosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.2.1. Preparation for the Procedure
2.2.2. Anesthesia
2.2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.2.4. After Surgery
2.3. Macroscopic Assessment
2.4. Histopathological Assessment
2.5. Clinical Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Patient Satisfaction
3.3. Recurrence
3.4. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oulehri, A.; Baybay, H.; Boularbah, S.; Douhi, Z.; Elloudi, S.; Guenoun, F.Z.; Mernissi, F.Z. Subungual exostosis and subungual osteochondromas: Diagnostic challenge in children. Our Dermatol. Online 2021, 12, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovee, J.V.M.G.; Heymann, D.; Wuyts, W. Osteochondroma. In WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 356–358. [Google Scholar]
- DaCambra, M.P.; Gupta, S.K.; Ferri-de-Barros, F. Subungual exostosis of the toes: A systematic review. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiheb, S.; Slimani, Y.; Karam, R.; Marnissi, F.; Hali, F. Subungual Exostosis: A Case Series of 48 Patients. Skin Appendage Disord. 2021, 7, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Jung, M.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Gong, H.S.; Kim, J.K.; Baek, G.H. Two distinctive subungual pathologies: Subungual exostosis and subungual osteochondroma. Foot Ankle Int. 2007, 28, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkoc, M.; Korkmaz, O.; Keskinbora, M.; Seker, A.; Oltulu, I.; Bulbul, A.M.; Say, F.; Cakir, A. Surgical treatment of nail bed subungual exostosis. Singap. Med. J. 2016, 57, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Palma, L.; Manzanares-Cespedes, M.C.; de Veciana, E.G. Subungual Exostosis Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2018, 108, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, G.P.; Rosenberg, A.E. Diagnostic Pathology: Bone; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, A.B.J.; Mertens, F. Subungual exostosis. In WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 345–347. [Google Scholar]
- Storlazzi, C.T.; Wozniak, A.; Panagopoulos, I.; Sciot, R.; Mandahl, N.; Mertens, F.; Debiec-Rychter, M. Rearrangement of the COL12A1 and COL4A5 genes in subungual exostosis: Molecular cytogenetic delineation of the tumor-specific translocationt (X; 6)(q13–14; q22). Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, M. The pathogenic roles of heparan sulfate deficiency in hereditary multiple exostoses. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneri, C.; Guarneri, F.; Risitano, G.; Lentini, M.; Vaccaro, M. Solitary asymptomatic nodule of the great toe. Int. J. Dermatol. 2005, 44, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Agrawal, N.; Verma, T.; Lal, H. Subungual osteochondroma: Nail sparing excision. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2016, 7, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundada, P.; Becker, M.; Lenoir, V.; Stefanelli, S.; Rougemont, A.L.; Beaulieu, J.Y.; Boudabbous, S. High resolution MRI of nail tumors and tumor-like conditions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 112, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goktay, F.; Atis, G.; Gunes, P.; Macit, B.; Celik, N.S.; Gurdal Kosem, E. Subungual exostosis and subungual osteochondromas: A description of 25 cases. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, C.; Aguirre, J.; Catalán, V.; Fajre, X.; Vargas, F. Subungual Exostosis: High-Resolution Ultrasound Findings. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2019, 35, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura Vergara de la Campa, Á.; González-Cantero, O.G.O.; González Cantero, J. Subungual osteochondroma: Case report and review of clinical, radiologic and ultrasound presentation versus subungual exostosis. J. Dermatol. Cosmetol. 2020, 4, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvi, L.G.; Gonzalez, M.L.; Santini-Araujo, E. Subungual Exostosis. In Tumors and Tumor-Like Lesions of Bone: For Surgical Pathologists, Orthopedic Surgeons and Radiologists; Santini-Araujo, E., Kalil, R.K., Bertoni, F., Park, Y.-K., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Flores, H.; Dominguez-Cherit, J.; Vega-Memije, M.E.; Saez-De-Ocariz, M. Subungual Osteochondroma: Clinical and Radiologic Features and Treatment. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinchcliff, K.M.; Pereira, C. Subungual Tumors: An Algorithmic Approach. J. Hand Surg. 2019, 44, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Qi, X.; Guo, D.; Cao, J.; Bai, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, X. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of subungual exostosis in children. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1075089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, M.; Litowińska, A. Recurrence and satisfaction with sutured surgical treatment of an ingrown toenail. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 56, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, M.; Litowińska, A.; Cieślak, J. Efficacy of a tip of the big toe remodeling in the distal nail embedding with bone overgrowth of the distal phalanx. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 58, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, M.H.; Coriolano, K.; Jones, S.A. Nonrandomized assessment of ingrown toenails treated with excision of skinfold rather than toenail (NAILTEST): An observational study of the Vandenbos procedure. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Sternschuss, G.; Haff, R.; van Raalte, H.; Saltz, S.; Lucente, V. Quality of life and surgical satisfaction after vaginal reconstructive vs obliterative surgery for the treatment of advanced pelvic organ prolapse. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 198, 573.e1–573.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Flores, E.; López-López, D.; Becerro-De-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Romero-Morales, C.; San Antolín-Gil, M.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Bautista-Casasnovas, A.L. Surgical Treatment on Subungual Osteochondromas in Paediatric Feet: A Case Series Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhopp-Stephens, H.; Walling, A.K. Subungual exostosis: A simple technique of excision. Foot Ankle Int. 1995, 16, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berker, D.A.R.; Langtry, J. Treatment of subungual exostoses by elective day case surgery. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 140, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokiec, F.; Ezra, E.; Krasin, E.; Keret, D.; Wientroub, S. A simple and efficient surgical technique for subungual exostosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2001, 21, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, H.; Mukouda, M. Subungual exostosis: A review of 16 cases focusing on postoperative deformity of the nail. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2005, 55, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Maruyama, H.; Fujisawa, Y.; Inoue, S.; Okiyama, N.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Fujimoto, M. Subungual exostosis with postoperative recurrence followed by spontaneous regression. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, e86–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Carmona, F.J.; Pascual Huerta, J.; Fernandez Morato, D. A proposed subungual exostosis clinical classification and treatment plan. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2009, 99, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, H.; Inanmaz, M.E.; Basar, B.; Bal, E.; Kose, K.C. Protruded and nonprotruded subungual exostosis: Differences in surgical approach. Indian. J. Orthop. 2014, 48, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jou, V.; Lehoczky, J.A. Toeing the line between regeneration and fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1217185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
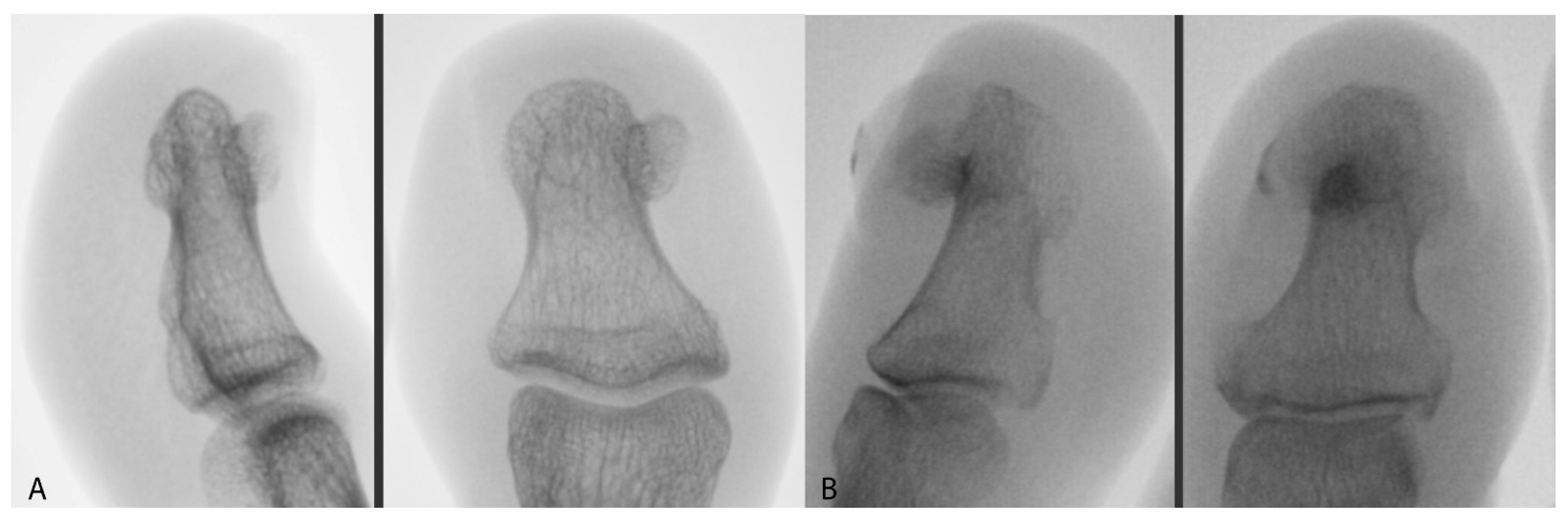




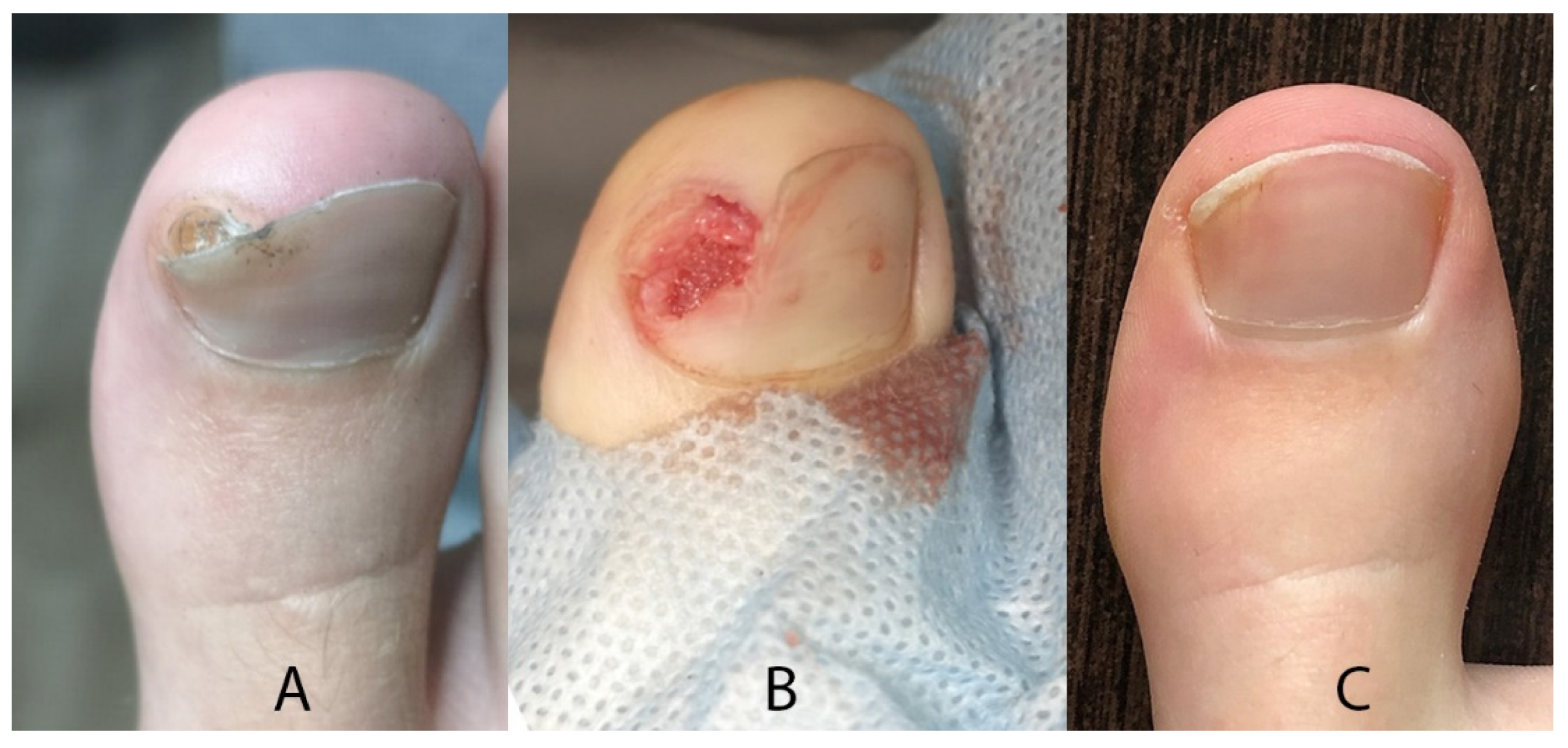
| Parameter | Results | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Mean ± SD | 29.6 ± 16.7 |
| Median (min–max) | 25 (7–74) | |
| Sex | Female | 54 (73%) |
| Male | 20 (27%) | |
| Duration of symptoms (months) | Mean ± SD | 14.1 ± 13 |
| Median (min–max) | 11 (1–60) | |
| Toes operated on | big toe | 58 (78.4%) |
| toe IV | 5 (6.8%) | |
| toe II | 4 (5.4%) | |
| toe V | 2 (2.7%) | |
| toe III | 2 (2.7%) | |
| finger IV (hand) | 2 (2.7%) | |
| finger II (hand) | 1 (1.4%) | |
| Side | Left | 46 (62.2%) |
| Right | 28 (37.8%) | |
| Localization | Lateral | 19 (25.7%) |
| Medial | 54 (73%) | |
| Central | 11 (1.4%) | |
| Localization | Distal | 42 (56.8%) |
| Proximal | 32 (43.2%) | |
| Risk factors | trauma/injury | 18 (24.3%) |
| long-term pressure | 14 (18.9%) | |
| chronic infection | 6 (8.1%) | |
| none | 41 (55.4%) | |
| Previous treatment | dermatological | 14 (18.9%) |
| Surgical removal of the nail | 14 (18.9%) | |
| antibiotic therapy | 3 (4.1%) | |
| podological/podiatrics | 8 (10.8%) | |
| biopsy | 1 (1.4%) | |
| Not treated | 38 (51.4%) | |
| Pre-operative macroscopic assessment of nail loss | Mean ± SD | 4.4 ± 2.2 |
| Median (min–max) | 4 (1–10) | |
| Intraoperative assessment of tissue loss | Mean ± SD | 6.3 ± 2.3 |
| Median (min–max) | 6 (2–12) | |
| VAS before surgery | Mean ± SD | 4.6 ± 2.8 |
| Median (min–max) | 5 (0–10) | |
| Burr usage | No | 21 (28.4%) |
| Yes | 53 (71.6%) |
| Item | Response | Participant Rating |
|---|---|---|
| 1. How satisfied are you with how your pain was controlled in the hospital after surgery? | Satisfied | 46 (92%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 4 (8%) | |
| 2. How satisfied are you with how your pain was controlled when you returned home after surgery? | Satisfied | 45 (90%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 5 (10%) | |
| 3. How satisfied are you with the amount of time it took for you to return to your daily activities, for example housework or social activities outside the home? | Satisfied | 47 (94%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 3 (6%) | |
| 4. How satisfied are you with the amount of time it took for you to return to work? | Satisfied | 47 (94%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 3 (6%) | |
| 5. How satisfied are you with the amount of time it took for you to return to your normal exercise routine? | Satisfied | 43 (86%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 7 (14%) | |
| 6. How satisfied are you with the results of your surgery? | Satisfied | 45 (90%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 5 (10%) | |
| 7. Looking back, if you “had to do it all over again” would you have the surgery again? | Yes | 42 (84%) |
| Maybe | 4 (8%) | |
| Unsure/do not think so/no | 4 (8%) | |
| 8. Would you recommend this surgery to someone else? | Yes | 47 (94%) |
| Maybe | 2 (4%) | |
| Unsure/do not think so/no | 1 (2%) | |
| 9. How satisfied are you with the esthetic results after surgery? | Satisfied | 45 (90%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 5 (10%) | |
| 10. How satisfied are you the current appearance of the problem? | Satisfied | 37 (74%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 13 (26%) | |
| 11. How satisfied are you the appearance of the postoperative scar? | Satisfied | 41 (82%) |
| Neutral/unsatisfied | 9 (18%) |
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age < 25 yo | 5.75 (1.076–30.721) | 0.041 |
| Sex: Male | 2.222 (0.512–9.647) | 0.286 |
| Duration of symptoms (months) | 1 (0.955–1.047) | 0.993 |
| Big toe | 4.5 (0.513–39.438) | 0.174 |
| Side: Right | 2.9 (0.692–12.154) | 0.145 |
| Risk factors | 1.941 (0.472–7.988) | 0.358 |
| No Previous treatment | 0.95 (0.237–3.812) | 0.942 |
| Pre-operative macroscopic assessment | 0.88 (0.641–1.207) | 0.426 |
| Intraoperative amount of tissue loss | 1.019 (0.752–1.38) | 0.906 |
| pain before surgery (VAS) | 1.113 (0.865–1.434) | 0.405 |
| pain after surgery (VAS) | 7.994 (2.12–30.141) | 0.002 |
| Observation time | 1.04 (0.986–1.097) | 0.149 |
| Recurrence | 16.286 (1.474–179.97) | 0.023 |
| No burr | 1.5 (0.357–6.308) | 0.58 |
| podological/podiatrics care after surgery | 2 (0.37–10.801) | 0.42 |
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age < 18 yo | 6.806 (1.211–38.255) | 0.03 |
| Sex: Male | 1.089 (0.194–6.121) | 0.923 |
| Duration of symptoms (months) | 0.985 (0.92–1.056) | 0.676 |
| Big toe | 1.731 (0.193–15.52) | 0.624 |
| Side: Right | 4.783 (0.86–26.593) | 0.074 |
| Risk factors | 2.903 (0.526–16.031) | 0.221 |
| No Previous treatment | 0.344 (0.062–1.902) | 0.221 |
| Pre-operative macroscopic assessment of nail loss | 0.963 (0.669–1.385) | 0.838 |
| Intraoperative amount of tissue loss | 1.175 (0.856–1.615) | 0.319 |
| pain before surgery (VAS) | 0.916 (0.635–1.323) | 0.641 |
| pain after surgery (VAS) | 1.297 (0.767–2.195) | 0.332 |
| Observation time | 1.062 (1.002–1.126) | 0.043 |
| Worse satisfaction SSQ < 80 | 16.286 (1.474–179.97) | 0.023 |
| No burr | 3.922 (0.796–19.325) | 0.093 |
| No podological/podiatrics care after surgery | 2.462 (0.313–19.377) | 0.392 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dąbrowski, M.; Rusek, D.; Dańczak-Pazdrowska, A.; Litowińska, A. The Influence of Clinical Factors on Treatment Outcome and a Recurrence of Surgically Removed Protruded Subungual Osteochondroma and Subungual Exostosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196413
Dąbrowski M, Rusek D, Dańczak-Pazdrowska A, Litowińska A. The Influence of Clinical Factors on Treatment Outcome and a Recurrence of Surgically Removed Protruded Subungual Osteochondroma and Subungual Exostosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196413
Chicago/Turabian StyleDąbrowski, Mikołaj, Damian Rusek, Aleksandra Dańczak-Pazdrowska, and Anna Litowińska. 2023. "The Influence of Clinical Factors on Treatment Outcome and a Recurrence of Surgically Removed Protruded Subungual Osteochondroma and Subungual Exostosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196413
APA StyleDąbrowski, M., Rusek, D., Dańczak-Pazdrowska, A., & Litowińska, A. (2023). The Influence of Clinical Factors on Treatment Outcome and a Recurrence of Surgically Removed Protruded Subungual Osteochondroma and Subungual Exostosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196413









