Impaired Executive Functioning Associated with Alcohol-Related Neurocognitive Disorder including Korsakoff’s Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Materials
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
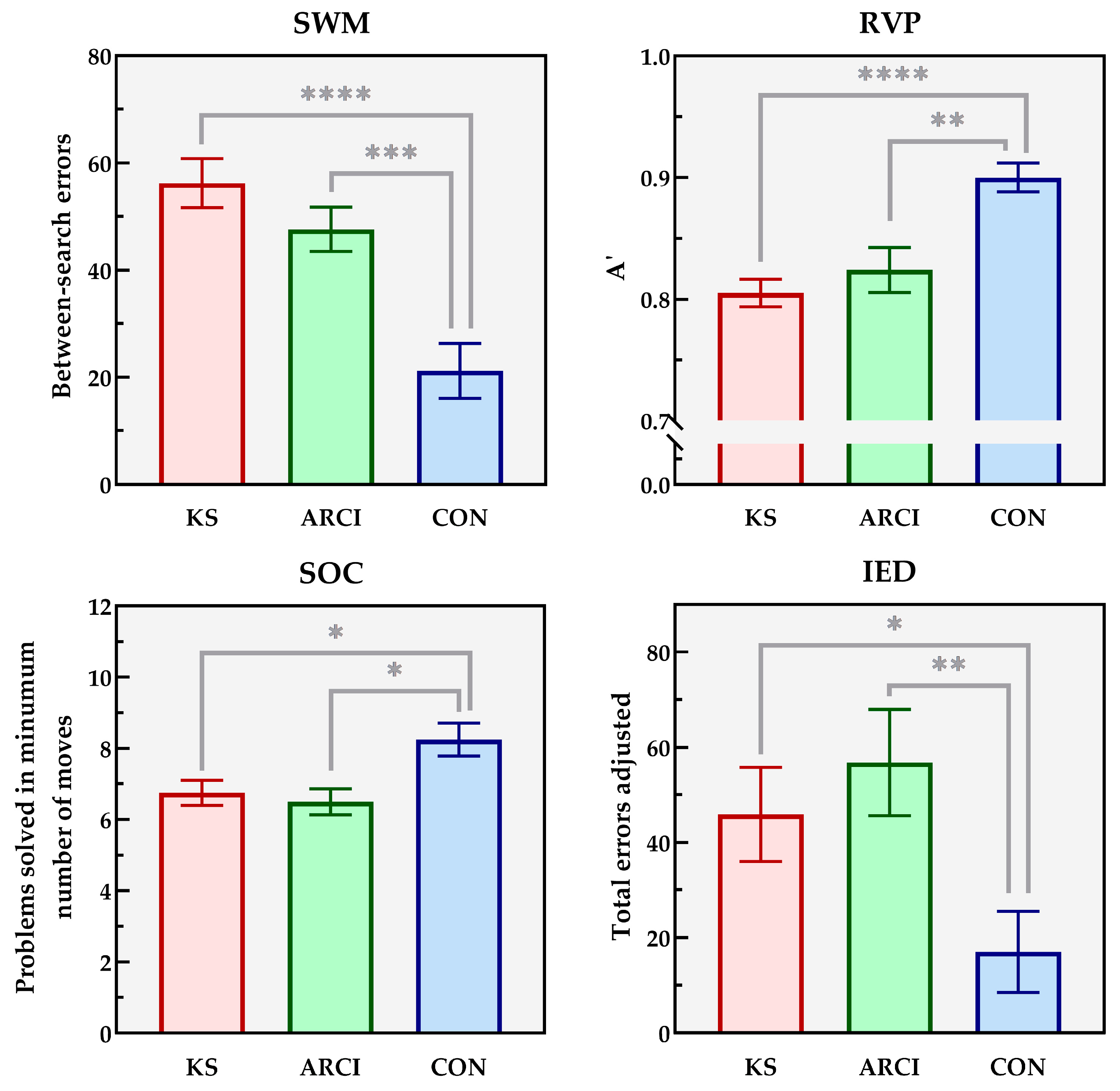
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehm, J.; Shield, K.D. Global burden of disease and the impact of mental and addictive disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heirene, R.; John, B.; Roderique-Davies, G. Identification and evaluation of neuropsychological tools used in the assessment of alcohol-related cognitive impairment. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijnen, C.J.W.H.; Dijktra, B.A.G.; Walvoort, S.J.W.; Markus, W.; Van Der Nagel, J.E.L.; Kessels, R.P.C.; De Jong, C.A.J. Prevalence of cognitive impairment in patients with substance use disorder. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2019, 38, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withall, A.; Shafiee, N. Alcohol and cognitive impairment: Considerations with the older client. In Alcohol and the Adult Brain; Svanber, J., Withall, A., Draper, D., Bowden, S., Eds.; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2015; pp. 83–107. [Google Scholar]
- Arts, N.J.M.; Walvoort, S.J.W.; Kessels, R.P.C. Korsakoff’s syndrome: A critical review. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 27, 2875–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haalboom, R.; Van Aken, L.; Walvoort, S.J.W.; Egger, J.I.M.; Kessels, R.P.C. Preserved intellectual functioning in Korsakoff’s syndrome? Actual and premorbid intelligence in patients with major or mild alcohol-related cognitive disorder. J. Subst. Use 2019, 24, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, M.E.; Bowden, S.C.; Barry, D. Neurocognitive impairment associated with alcohol use disorders: Implications for treatment. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2002, 10, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, A.; Chandra, M.; Choudhary, M.; Dayal, P.; Singh Anand, K. Alcohol-related dementia and neurocognitive impairment: A review study. High Risk Behav. Addict. 2016, 7, 27976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Berre, A.; Fama, R.; Sullivan, E.V. Executive functions, memory, and social cognitive deficits and recovery in chronic alcoholism: A critical review to inform future research. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavro, K.; Pelletier, J.; Potvin, S. Widespread and sustained cognitive deficits in alcoholism: A meta-analysis. Addict. Biol. 2012, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fein, G.; Torres, J.; Price, L.; Di Sclafani, V. Cognitive performance in long-term abstinent alcoholics. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 30, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, S.F. Widespread cognitive deficits in alcoholism persistent following prolonged abstinence: An updated meta-analysis of studies that used standardized neuropsychological assessment tools. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2019, 35, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Bigler, E.D.; Tranel, D. Neuropsychological Assessment, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, A.; Friedman, N.P.; Emerson, M.J.; Witzki, A.H.; Howerter, A.; Wager, T.D. The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contribution to complex: “Frontal lobe” tasks: A latent variable analysis. Cogn. Psychol. 2000, 41, 49–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.P.; Miyake, A. Unity and diversity of executive functions: Individual differences as a window on a cognitive structure. Cortex 2017, 86, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M.E.; Pawlak, A.P. Cognitive impairment influences drinking outcome by altering therapeutic mechanisms of change. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2006, 20, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smidt, F.; Benzerouk, F.; Barriere, S.; Henry, A.; Limosin, F.; Kaladjian, A.; Gierski, F. Heterogeneity of executive function abilities in recently detoxified patients with alcohol use disorder: Evidence from a cluster analysis. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, M.E.; Buckman, J.F.; Nguyen, T.T. A role for cognitive rehabilitation in increasing the effectiveness of treatment for alcohol use disorders. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2013, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharasingam, M.; Macniven, J.A.B.; Mason, O.J. Executive function in chronic alcoholism and Korsakoff syndrome. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2013, 35, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oort, R.; Kessles, R.P.C. Executive dysfunction in Korsakoff’s syndrome: Time to revise the DSM criteria for alcohol-induced persisting amnestic disorder? Int. J. Psychiatry. Clin. Pract. 2009, 13, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moerman-van den Brink, W.G.; van Aken, L.; Verschuur, E.M.L.; Walvoort, S.J.W.; Egger, J.I.M.; Kessels, R.P.C. Executive dysfunction in patients with Korsakoff’s syndrome: A theory-driven approach. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, N.J.M.; Pitel, A.L.; Kessels, R.P.C. The contribution of mamillary body damage to Wernicke’s encephalopathy and Korsakoff’s syndrome. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 180, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, M.D. What is the Korsakoff syndrome? A paper in tribute to prof Alwyn Lishman. Cogn. Neuropsych. 2022, 27, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brion, M.; D’Hondt, F.; Pitel, A.; Lecomte, B.; Ferauge, M.; Timary, P.; Maurage, P. Executive functions in alcohol-dependence: A theoretically grounded and integrative exploration. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 177, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Need, A.C.; Circulli, E.T.; Chiba-Falek, O.; Attix, D.K. A comparison of the Cambridge Automated Neuropsychological Test Battery (CANTAB) with traditional neuropsychological testing instruments. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2013, 35, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, M.D.; Thomson, A.D.; Guerrini, I.; Marshall, E.J. The Korsakoff syndrome: Clinical aspects, psychology and treatment. Alcohol Alcohol. 2009, 44, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessels, R.; Hendriks, M.; Gorissen, M.; Schmand, B.; Duits, A. Testselectie en testafname. In Neuropsychologische Diagnostiek; Hendriks, M., Kessels, R., Gorissen, M., Schmand, B., Duits, A., Eds.; Boom uitgevers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 91–114. [Google Scholar]
- Schmand, B.; Bakker, D.; Saan, D.; Louman, J. De Nederlandse leestest voor volwassenen: Een maat voor premorbide intelligentie. Tijdschr. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1991, 22, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bouma, A.; Mulder, J.; Lindeboom, J.; Schmand, B. Handboek Neuropsychologische Diagnostiek; Person Assessment and Information: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sahakian, B.J.; Morris, R.G.; Evenden, J.L.; Heald, A.; Levy, R.; Philpot, M. A comparative study of visuospatial memory and learning in Alzheimer-tyoe demetia and Parkinson disease. Brain 1988, 11, 695–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, T.W.; James, M.; Owen, A.M.; Sahakian, B.J.; Lawrence, A.D.; McInnes, L.; Rabbit, P.M.A. A study on tests from the CANTAB battery sensitive to frontal lobe dysfunction in a large sample of normal volunteers: Implications for theories of executive functioning and cognitive aging. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 1998, 4, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, F.; Salvadori, N.; Eusebi, P.; Lisetti, V.; Luchetti, E.; Calabresi, P.; Parnetti, L. Evidence of practice effect in CANTAB spatial working memory test in a cohort of patients with mild cognitive impairment. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2018, 25, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, M.M.; Pinho, M.S.; Simões, M.R. Test-retest reliability analysis of the Cambridge Neuropsychological Automated Tests for the assessment of dementia in older people living in retirement homes. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2016, 23, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, C.; Rabbit, P. Test/re-test reliability of the CANTAB and ISPOCD neuropsychological batteries: Theoretical and practical issues. Neuropsychologia 1998, 36, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syväoja, H.; Tammelin, T.H.; Ahonen, T.; Räsänen, P.; Tolvanen, A.; Kankaanpää, A.; Kantomaa, M. Internal consistency and stability of the CANTAB neuropsychological test battery in children. Psychol. Assess. 2015, 27, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, S.; Hassan, R.; Shahriar, M.; Akter, N.; Abass, G.; Bhuiyan, M.A. Cognitive impact after short-term exposure to different proton pump inhibitors: Assessment using CANTAB software. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2015, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, F.C.; de Oliviera, T.C.G.; de Macedo, L.D.; Tomás, A.M.; Picanco-Diniz, D.L.W.; Bent-Torres, J.; Bento-Torres, N.V.; Picanco-Diniz, C.W. CANTAB object recognition and language test to detect aging cognitive decline: An exploratory comparative study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmickienė, J.; Kaubrys, G. Cognitive results of CANTAB test and their change due to first dose of donepezil may predict treatment efficacy in Alzheimer disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Owen, A.M.; Downes, J.J.; Sahakian, B.J.; Polkey, C.E.; Robbins, T.W. Planning and spatial working memory following frontal lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia 1990, 28, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, D.A.; Berg, E. A behavioral analysis of degree of reinforcement and case of shifting to new responses in a Weigl-type card-sorting problem. J. Exp. Psychol. 1948, 38, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, R.K.; Chelune, G.J.; Talley, J.L.; Kay, G.G.; Curtiss, G. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test manual: Revised and Expanded; Psychological Assessment Resources: Lutz, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Levaux, M.N.; Potvin, S.; Sepehry, A.A.; Sablier, J.; Mendrek, A.; Stip, E. Computerized assessment of cognition in schizophrenia: Promises and pitfalls of CANTAB. Eur. Psychiatry 2007, 22, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallice, T. Specific impairments of planning. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. 1982, 298, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, B.A.; Constantine, L.J.; Hendren, R.; Rocke, D.; Ozonoff, S. Examining executive functioning in children with autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and typical development. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 166, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.R.; Mihic, A.M.; Nikkel, S.M.; Stade, B.C.; Rasmussen, C.; Munoz, D.P.; Reynolds, J.N. Executive function deficits in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) measured using the Cambridge Neuropsychological Tests Automated Battery (CANTAB). J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2009, 50, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, C.; Soleimani, M.; Pei, J. Executive functioning and working memory defictis on the CANTAB among children with prenatal alcohol exposure. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 18, e44–e53. [Google Scholar]
- Oscar-Berman, M.; Valmas, M.M.; Sawyer, K.S.; Mosher Ruiz, S.; Luhar, R.B.; Gravitz, Z.R. Profiles of impaired, spared, and recovered neuropsychological processes in alcoholism. Hanb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 125, 183–210. [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt, H.; Brokate, B.; Eling, P.; Lanz, M. Response shifting and inhibition, but not working memory, are impaired after long-term heavy alcohol consumption. Neuropsychology 2004, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Haj, M.; Nandrino, J.L. Phenomenological characteristics of autobiographical memory in Korsakoff’s syndrome. Conscious Cogn. 2017, 55, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitel, A.L.; Beaunieux, H.B.; Witkowski, T.; Vabret, F.; de la Sayette, V.; Viader, F.; Desgranges, B.; Eustache, F. Episodic and working memory deficits in alcoholic Korsakoff patients: The continuity theory revisited. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, S.; Amjad, Z.; Abaza, A.; Vasada, A.M.; Sadhu, A.; Valencia, C.; Fatima, H.; Nwankwo, I.; Anam, M.; Mohammed, L. Executive dysfunction in patients with alcohol use disorder: A systematic review. Cureus 2022, 14, 29207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Salas, S.; Díaz-Batanero, C.; Lozano-Rojas, O.M.; Verdejo-Garcia, A. Impact of general cognition and executive function deficits on addiction treatment outcomes: Systematic review and discussion of neurocognitive pathways. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 772–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, R.M.; Isquith, P.K.; Gioia, G. Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function—Adult Version (BRIEF-A): Professional Manual; Psychological Assessment Resources: Lutz, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cermak, L.S. Recall of antonyms from short-term memory. J. Exp. Psychol. 1974, 102, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butters, N.; Brandt, J. The continuity hypothesis: The relationship of long-term alcoholism to the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. In Recent Developments in Alcoholism; Galanter, M., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 207–226. [Google Scholar]
- Walvoort, S.; Wester, A. The neuropsychology of cognitive functions in alcohol abstinence. Tijdschr. Psychiatr. 2013, 55, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.; Gunther, A.; Stetter, E.; Ackermann, K. Rapid recovery from cognitive deficits in abstinent alcoholics: A controlled test-retest study. Alcohol Alcohol. 1999, 34, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerque-Duval, V.; Barre, T.; Cognat, E.; Brichet, A.L.; Geraud, C.; Azuar, J.; Michaud, P.; Lecallier, D.; Arfaoui Geffrov, S.; Hispard, E.; et al. Patients with severe alcohol-related cognitive impairment improve in flexibility when abstinence is maintained: A comparative study with Alzheimers’s disease. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 936639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudman, E.; Oey, M.J.; Batjes, D.; Van Dam, M.; Van Dorp, M.; Postma, A.; Wijnia, J.W. Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome diagnostics and rehabilitation in the post-acute phase. Addict. Neurosci. 2022, 4, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| KS (n = 20) | ARCI (n = 22) | CON (n = 22) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean + SD) | 55.3 (8.9) | 57.2 (7.4) | 48.9 (15.7) | 0.050 |
| Sex (% men) | 14 (70%) | 15 (68.2%) | 9 (40.1%) | 0.172 |
| Education level (1–7) | 3.7 (0.92) 3 | 3.75 (0.86) 4 | 5.59 (0.96) | 0.001 |
| NART 1-IQ (mean + SD) | 92.1 (16.9) | 94.5 (19.0) | 98.2 (12.5) | 0.473 |
| RAVLT T-scores 2 (mean + SD) | ||||
| Immediate recall | 28.4 (11.9) | 40.3 (16.2) | n.a. | 0.014 |
| Delayed recall | 22.1 (7.8) | 38.5 (17.4) | n.a. | <0.001 |
| Task | Outcome Measure | KS | ARCI | CON | Overall p-Value | Post-Hoc Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWM | n = 19 | n = 22 | n = 20 | |||
| Strategy measure | 37.9 (3.6) | 37.1 (8.9) | 17.9 (13.6) | < 0.0005 | CON > ARCI = KS | |
| Mean time to first response (ms) | 3481 (511) | 2446 (683) | 1200 (318) | < 0.0005 | CON > ARCI > KS | |
| Total error | 57.1 (20.1) | 48.7 (20.1) | 21.7 (23.7) | < 0.0005 | CON > ARCI = KS | |
| RVP | n = 18 | n = 22 | n = 20 | |||
| Mean latency (ms) | 540 (99) | 531 (111) | 523 (128) | 0.901 | - | |
| Number of false alarms | 5.78 (8.6) | 15.1 (29.9) | 2.55 (3.1) | 0.074 | - | |
| SOC | n = 20 | n = 22 | n = 20 | |||
| Mean planning time 2-step problems (ms) | 2233 (2482) | 1463 (1220) | 1759 (1788) | 0.426 | - | |
| Mean planning time 5-step problems (ms) | 3970 (2573) | 3154 (1460) | 8912 (4894) | 0.507 | - | |
| IED | n = 20 | n = 22 | n = 20 | |||
| Intra-dimensional set shifting (blocks 2, 5, 7, 9) | 12.1 (9.5) | 9.1 (7.4) | 6.4 (4.2) | 0.047 | ARCI = CON; CON > KS | |
| Extra-dimensional set shifting (blocks 6, 8) | 9.5 (9.3) | 13.7 (11.0) | 11.8 (10.0) | 0.402 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janssen, G.T.L.; Egger, J.I.M.; Kessels, R.P.C. Impaired Executive Functioning Associated with Alcohol-Related Neurocognitive Disorder including Korsakoff’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206477
Janssen GTL, Egger JIM, Kessels RPC. Impaired Executive Functioning Associated with Alcohol-Related Neurocognitive Disorder including Korsakoff’s Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(20):6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206477
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanssen, Gwenny T. L., Jos I. M. Egger, and Roy P. C. Kessels. 2023. "Impaired Executive Functioning Associated with Alcohol-Related Neurocognitive Disorder including Korsakoff’s Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 20: 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206477
APA StyleJanssen, G. T. L., Egger, J. I. M., & Kessels, R. P. C. (2023). Impaired Executive Functioning Associated with Alcohol-Related Neurocognitive Disorder including Korsakoff’s Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(20), 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206477






