Exploring the Genetic Causes for Postnatal Growth Failure in Children Born Non-Small for Gestational Age
Abstract
:1. Introduction
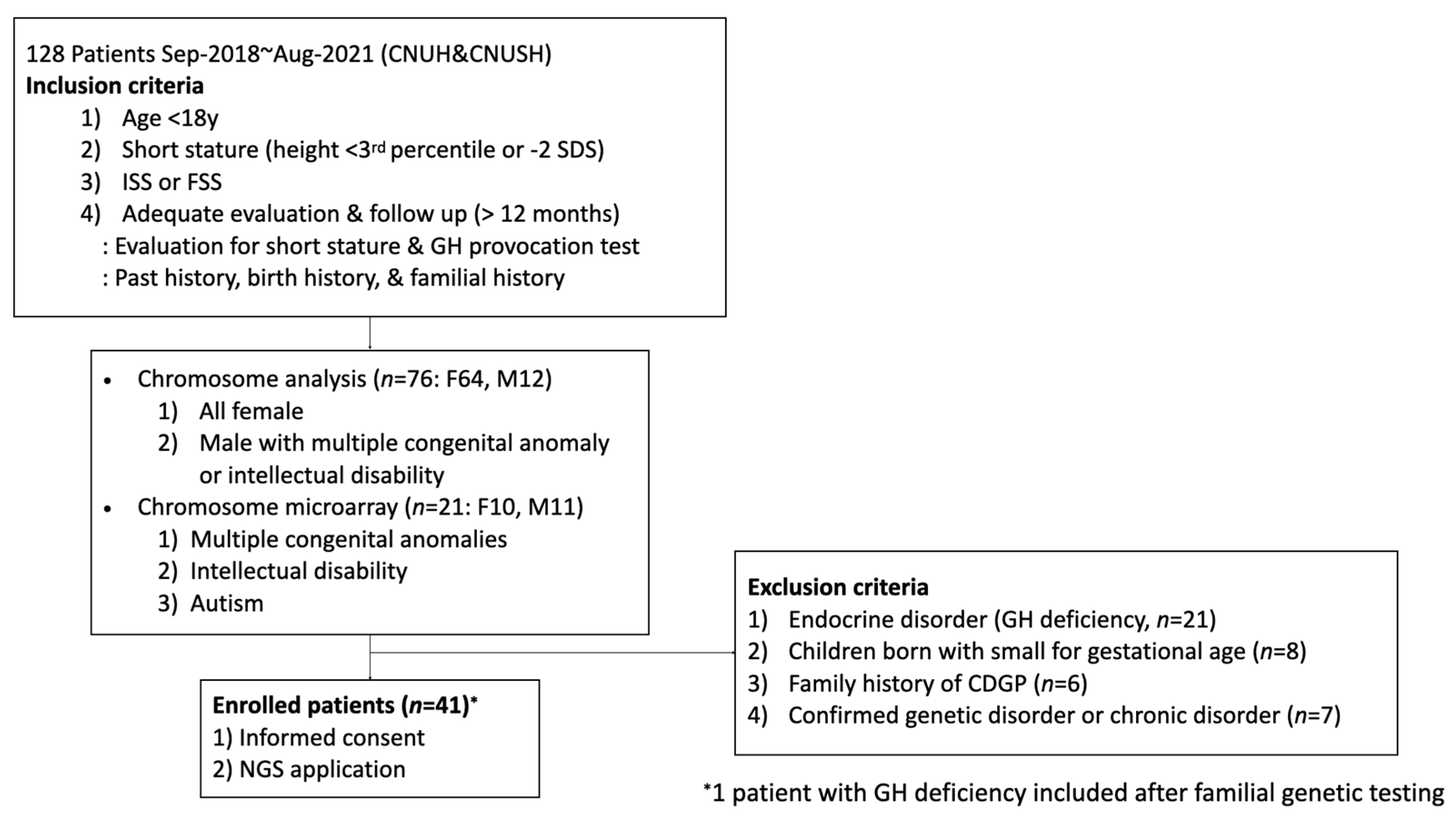
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Materials
2.3. Statistical Analysis
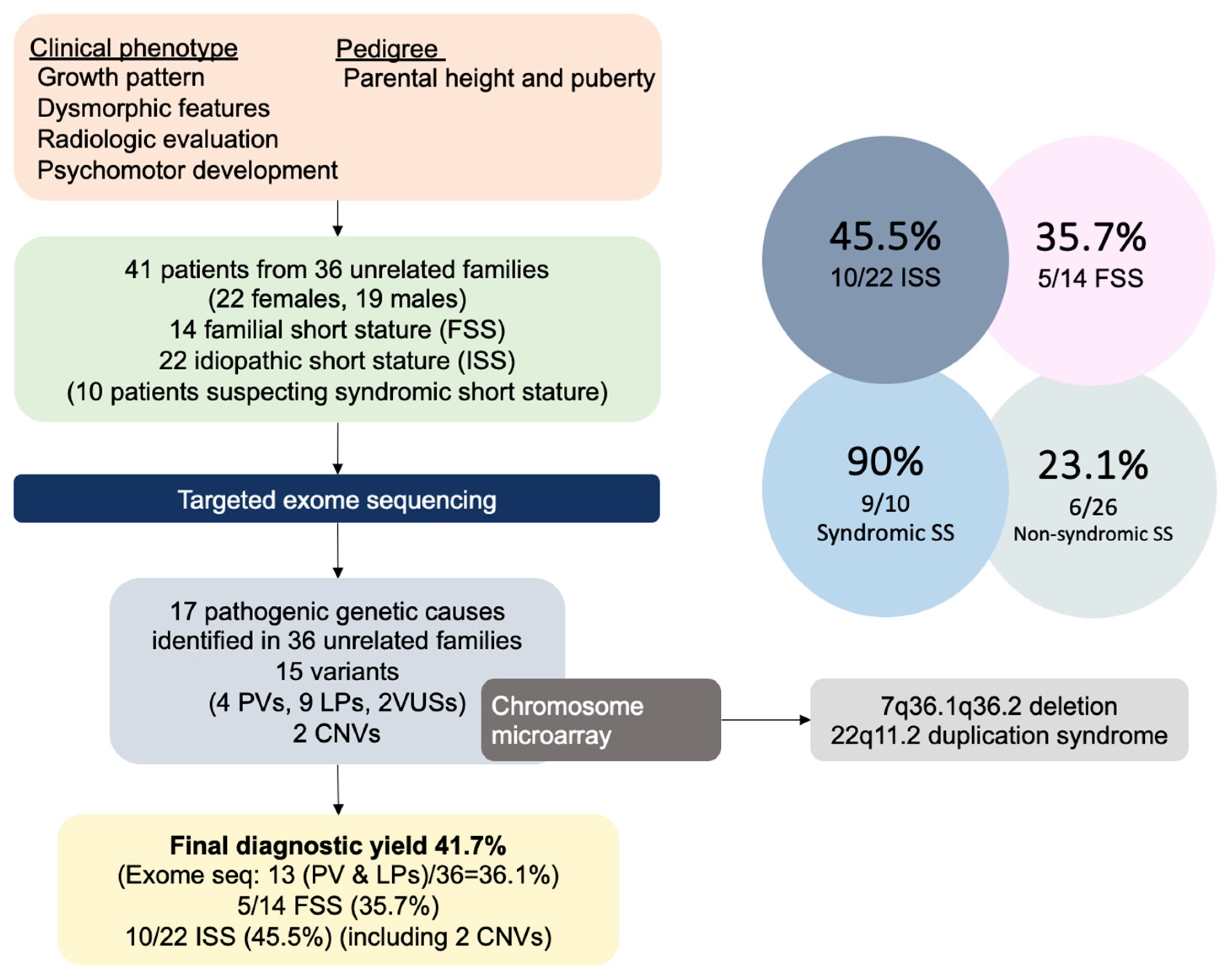
3. Results
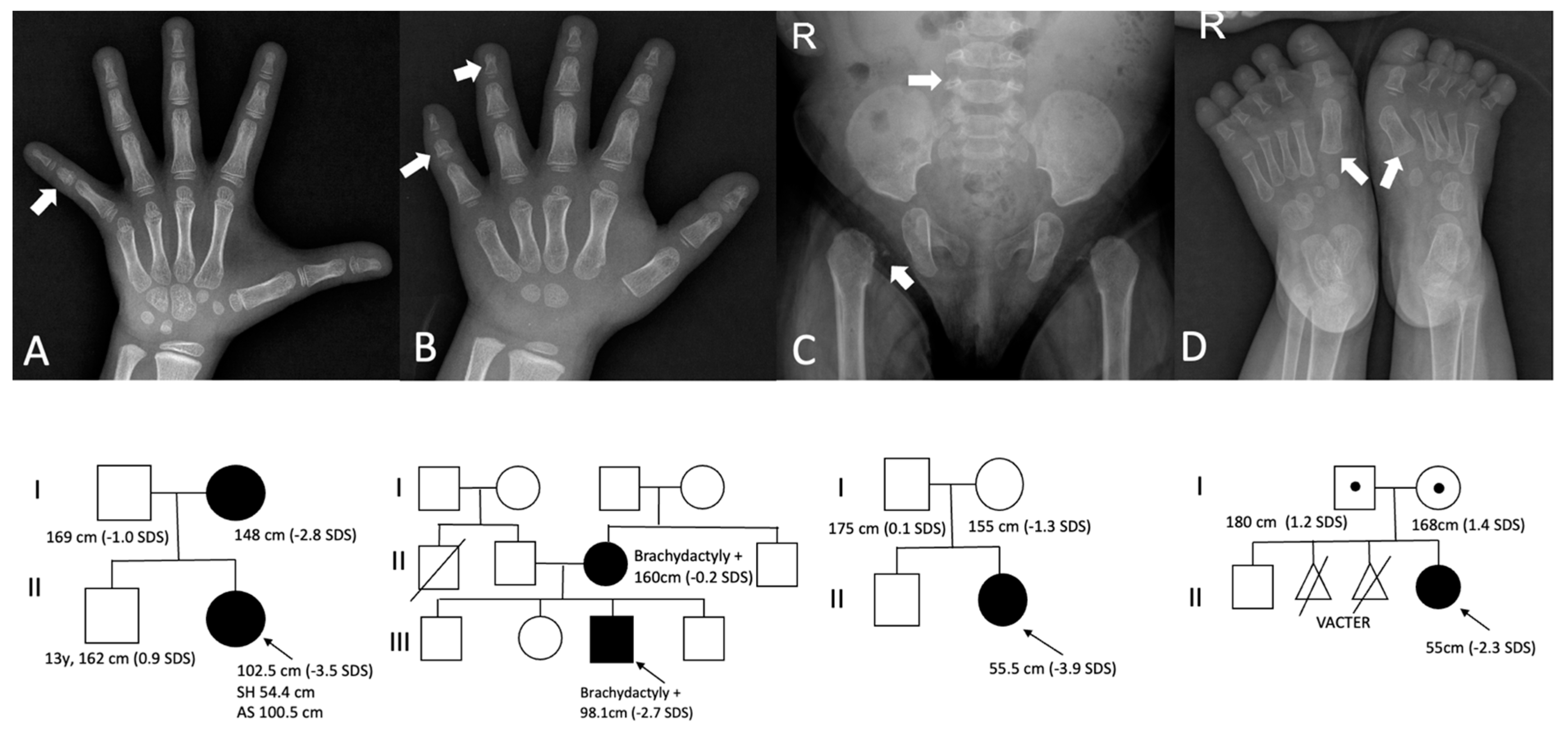
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Genetic Results
3.3. Paracrine Signaling Defects
3.4. Extracellular Matrix Defects
3.5. Fundamental Cellular Process
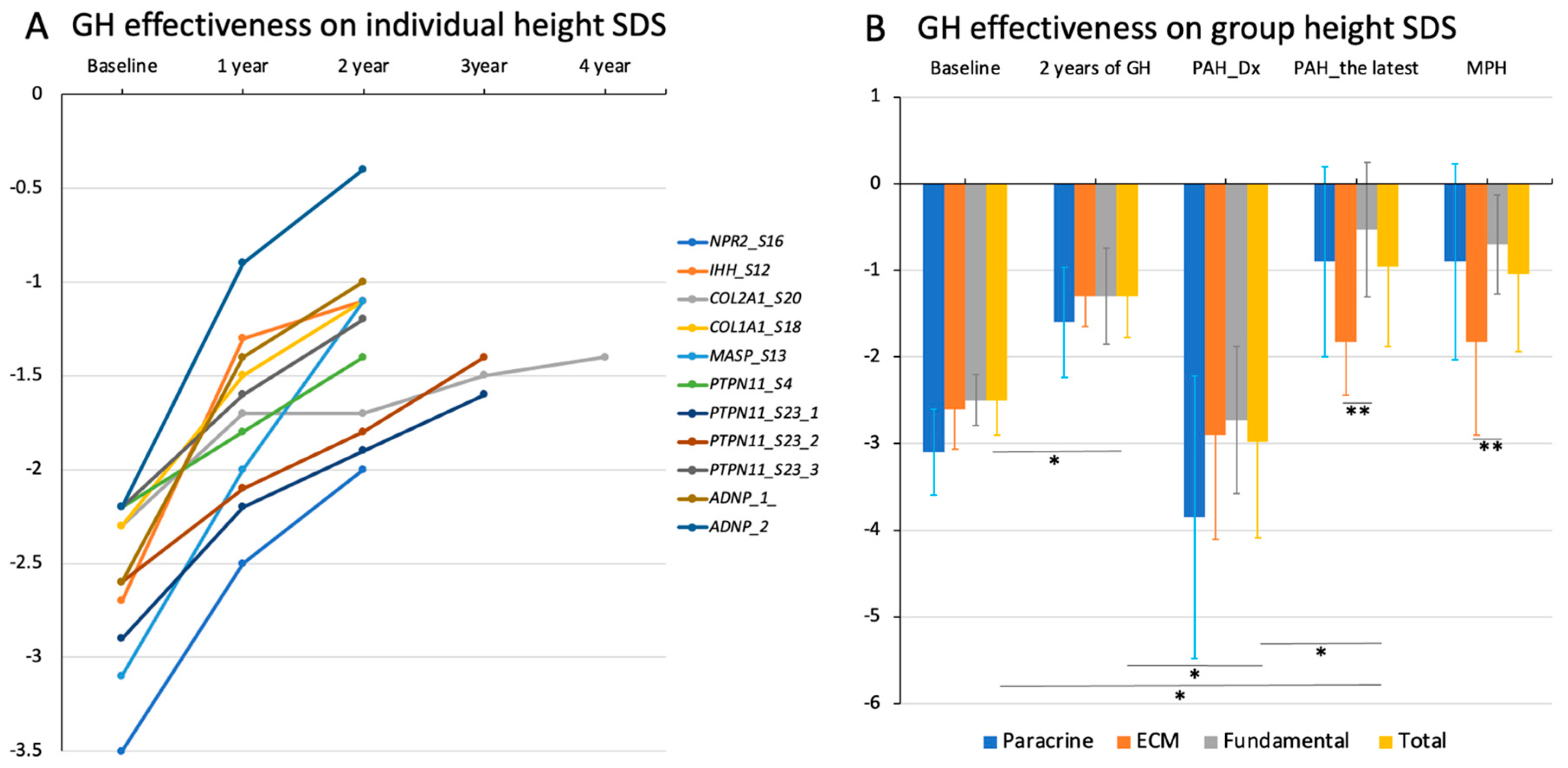
3.6. Growth Response to rhGH Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baron, J.; Sävendahl, L.; De Luca, F.; Dauber, A.; Phillip, M.; Wit, J.M.; Nilsson, O. Short and tall stature: A new paradigm emerges. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, S.A.; Ono, W.; Ono, N. Growth Plate Chondrocytes: Skeletal Development, Growth and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.J.; Mehta, L.; Rapaport, R. Genetic techniques in the evaluation of short stature. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.H.; Shen, Y.; Walvoord, E.C.; Miller, T.C.; Moon, J.E.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Dauber, A. Whole exome sequencing to identify genetic causes of short stature. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2014, 82, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.R.; Carmichael, H.; Andrew, S.F.; Miller, T.C.; Moon, J.E.; Derr, M.A.; Hwa, V.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Dauber, A. Large-scale pooled next generation sequencing of 1077 genes to identify genetic causes of short stature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1428–E1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flechtner, I.; Lambot-Juhan, K.; Teissier, R.; Colmenares, A.; Baujat, G.; Beltrand, J.; Ajaltouni, Z.; Pauwels, C.; Pinto, G.; Samara-Boustani, D.; et al. Unexpected high frequency of skeletal dysplasia in idiopathic short stature and small for gestational age patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, A.; Katoh-Fukui, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Matsubara, K.; Kamimaki, T.; Tanaka, H.; Dateki, S.; Adachi, M.; Muroya, K.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Next generation sequencing-based mutation screening of 86 patients with idiopathic short stature. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltarelli, M.A.; Quarta, A.; Chiarelli, F. Growth plate extracellular matrix defects and short stature in children. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 27, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, H.D.; Cheon, C.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Yoo, H.W. High diagnostic yield of clinically unidentifiable syndromic growth disorders by targeted exome sequencing. Clin. Genet. 2017, 92, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, A.C.; Jee, Y.H.; Nilsson, O. New Genetic Diagnoses of Short Stature Provide Insights into Local Regulation of Childhood Growth. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 88, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachy, L.; Strakova, V.; Elblova, L.; Obermannova, B.; Kolouskova, S.; Snajderova, M.; Zemkova, D.; Dusatkova, P.; Sumnik, Z.; Lebl, J.; et al. High Prevalence of Growth Plate Gene Variants in Children With Familial Short Stature Treated With GH. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.G.; Clayton, P.E.; Chernausek, S.D. A genetic approach to evaluation of short stature of undetermined cause. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faienza, M.F.; Chiarito, M.; Brunetti, G.; D’Amato, G. Growth plate gene involvement and isolated short stature. Endocrine 2021, 71, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasques, G.A.; Andrade, N.L.M.; Jorge, A.A.L. Genetic causes of isolated short stature. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 63, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, N.L.M.; Funari, M.F.A.; Malaquias, A.C.; Collett-Solberg, P.F.; Gomes, N.L.R.A.; Scalco, R.; Dantas, N.C.B.; Rezende, R.C.; Tiburcio, A.M.F.P.; Souza, M.A.R.; et al. Diagnostic yield of a multigene sequencing approach in children classified as idiopathic short stature. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e220214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plachy, L.; Amaratunga, S.A.; Dusatkova, P.; Maratova, K.; Neuman, V.; Petruzelkova, L.; Zemkova, D.; Obermannova, B.; Snajderova, M.; Kolouskova, S.; et al. Isolated growth hormone deficiency in children with vertically transmitted short stature: What do the genes tell us? Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1102968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, C.S.; Seaver, L.H.; Irons, M.; Grimberg, A.; Lozano, R.; ACMG Professional Practice and Guidelines Committee. Focused Revision: ACMG practice resource: Genetic evaluation of short stature. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, P.E.; Cianfarani, S.; Czernichow, P.; Johannsson, G.; Rapaport, R.; Rogol, A. Management of the child born small for gestational age through to adulthood: A consensus statement of the International Societies of Pediatric Endocrinology and the Growth Hormone Research Society. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokken-Koelega, A.C.S.; van der Steen, M.; Boguszewski, M.C.S.; Cianfarani, S.; Dahlgren, J.; Horikawa, R.; Mericq, V.; Rapaport, R.; Alherbish, A.; Braslavsky, D.; et al. International Consensus Guideline on Small for Gestational Age (SGA): Etiology and Management from Infancy to Early Adulthood. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yun, S.; Hwang, S.S.; Shim, J.O.; Chae, H.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.C.; Lim, D.; Yang, S.W.; et al. The 2017 Korean National Growth Charts for children and adolescents: Development, improvement, and prospects. Korean J. Pediatr. 2018, 61, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S.; Lim, S.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Song, B.S.; Shim, K.S.; Hwang, I.T. New Korean reference for birth weight by gestational age and sex: Data from the Korean Statistical Information Service (2008–2012). Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 19, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Ke, Y.H.; Yue, H.; Xiao, W.J.; Yu, J.B.; Gu, J.M.; Hu, W.W.; Wang, C.; He, J.W.; et al. The identification of novel mutations in COL1A1, COL1A2, and LEPRE1 genes in Chinese patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2012, 30, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijck, A.; Vulto-van Silfhout, A.T.; Cappuyns, E.; van der Werf, I.M.; Mancini, G.M.; Tzschach, A.; Bernier, R.; Gozes, I.; Eichler, E.E.; Romano, C.; et al. Clinical Presentation of a Complex Neurodevelopmental Disorder Caused by Mutations in ADNP. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintz, E.; Węgrzyn, G.; Fujii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Molecular mechanism of induction of bone growth by the C-type natriuretic peptide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M. A new era of genetic diagnosis for short stature children: A review. Precis. Future Med. 2022, 6, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, N.; Mukai, T.; Ito, Y.; Narumi, S.; Tanaka, T.; Yokoya, S.; Ogata, T.; Hasegawa, T. Identification and functional characterization of two novel NPR2 mutations in Japanese patients with short stature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E713–E718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasques, G.A.; Amano, N.; Docko, A.J.; Funari, M.F.; Quedas, E.P.; Nishi, M.Y.; Arnhold, I.J.; Hasegawa, T.; Jorge, A.A. Heterozygous mutations in natriuretic peptide receptor-B (NPR2) gene as a cause of short stature in patients initially classified as idiopathic short stature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1636–E1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.R.; Jacobsen, C.M.; Carmichael, H.; Edmund, A.B.; Robinson, J.W.; Olney, R.C.; Miller, T.C.; Moon, J.E.; Mericq, V.; Potter, L.R.; et al. Heterozygous mutations in natriuretic peptide receptor-B (NPR2) gene as a cause of short stature. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Liang, H.; Miao, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, F.; Pan, H.; Zhu, H. Clinical Characteristics of Short-Stature Patients With an NPR2 Mutation and the Therapeutic Response to rhGH. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lin, X.; Chen, R. Novel pathogenic NPR2 variants in short stature patients and the therapeutic response to rhGH. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentchordi-Montané, L.; Benito-Sanz, S.; Aza-Carmona, M.; Díaz-González, F.; Modamio-Høybjør, S.; de la Torre, C.; Nevado, J.; Ruiz-Ocaña, P.; Bezanilla-López, C.; Prieto, P.; et al. High prevalence of variants in skeletal dysplasia associated genes in individuals with short stature and minor skeletal anomalies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 185, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasques, G.A.; Funari, M.F.A.; Ferreira, F.M.; Aza-Carmona, M.; Sentchordi-Montané, L.; Barraza-García, J.; Lerario, A.M.; Yamamoto, G.L.; Naslavsky, M.S.; Duarte, Y.A.O.; et al. IHH gene mutations causing short stature with nonspecific skeletal abnormalities and response to growth hormone therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Gong, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, Q.; Yuan, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Functional mechanisms of TRPS1 in disease progression and its potential role in personalized medicine. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 237, 154022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuelling, M.; Kaiser, F.J.; Buelens, L.A.; Braunholz, D.; Shivdasani, R.A.; Depping, R.; Vortkamp, A. Trps1, a regulator of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation, interacts with the activator form of Gli3. Dev. Biol. 2009, 328, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmaci, A.; Walsh, T.; Akay, H.; Spiliopoulos, M.; Sakalar, Y.B.; Hasanefendioğlu-Bayrak, A.; Duman, D.; Farooq, A.; King, M.C.; Tekin, M. MASP1 mutations in patients with facial, umbilical, coccygeal, and auditory findings of Carnevale, Malpuech, OSA, and Michels syndromes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, J.; Roberts, R.; de Silva, D.; Shalev, S.; Chervinsky, E.; Nampoothiri, S.; Sznajer, Y.; Revencu, N.; Gunasekera, R.; Suri, M.; et al. Exploring the genetic basis of 3MC syndrome: Findings in 12 further families. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170A, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaoglu, N.B.; Akgun Dogan, O. Further Expansion of the Mutational Spectrum of 3MC Syndrome: A Novel MASP1 Pathogenic Variant in a Male Patient. Mol. Syndromol. 2021, 12, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, C.D.; Altıner, Ş. MASP1-related 3MC syndrome in a patient from Turkey. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2021, 185, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelli, A.M.G.; Peixoto, J.O.; Zanella, R.; Gouveia, J.J.S.; Cantão, M.E.; Coutinho, L.L.; Marchesi, J.A.P.; Pizzol, M.S.D.; Marcelino, D.E.P.; Ledur, M.C. Downregulation of growth plate genes involved with the onset of femoral head separation in young broilers. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 941134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, T.W.; Gerety, S.S.; Jones, W.D.; Van Kogelenberg, M.; King, D.A.; McRae, J.; Morley, K.I.; Parthiban, V.; Al-Turki, S.; Ambridge, K.; et al. The Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study. Large-scale discovery of novel genetic causes of developmental disorders. Nature 2015, 519, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, N.; Sakai, S.; Martorell, L.; Colomé, R.; Mizuike, A.; Goto, A.; Ortigoza-Escobar, J.D.; Hanada, K. Intellectual-disability-associated mutations in the ceramide transport protein gene CERT1 lead to aberrant function and subcellular distribution. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szot, J.O.; Slavotinek, A.; Chong, K.; Brandau, O.; Nezarati, M.; Cueto-González, A.M.; Patel, M.S.; Devine, W.P.; Rego, S.; Acyinena, A.P.; et al. New cases that expand the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of Congenital NAD Deficiency Disorder. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortbawi, H.; Ames, E.; Pritchard, A.; Devine, P.; van Ziffle, J.; Slavotinek, A. Further description of two patients with biallelic variants in NADSYN1 in association with cardiac and vertebral anomalies. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert-Mucca, M.; Janel, C.; Porquet-Bordes, V.; Patat, O.; Touraine, R.; Edouard, T.; Michot, C.; Tessier, A.; Cormier-Daire, V.; Attie-Bitach, T.; et al. Clinical heterogeneity of NADSYN1-associated VCRL syndrome. Clin. Genet. 2023, 104, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, G.L.; Aguena, M.; Gos, M.; Hung, C.; Pilch, J.; Fahiminiya, S.; Abramowicz, A.; Cristian, I.; Buscarilli, M.; Naslavsky, M.S.; et al. Rare variants in SOS2 and LZTR1 are associated with Noonan syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchelochkov, O.A.; Patel, A.; Weissenberger, G.M.; Chinault, A.C.; Wiszniewska, J.; Fernandes, P.H.; Eng, C.; Kukolich, M.K.; Sutton, V.R. Duplication of chromosome band 12q24.11q24.23 results in apparent Noonan syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2008, 146A, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, T.L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.F.; Tan, Z.P. Rare copy number variations containing genes involved in RASopathies: Deletion of SHOC2 and duplication of PTPN11. Mol. Cytogenet 2014, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.M., Jr.; Kramer, N.; Bejjani, B.A.; Thiel, C.T.; Carta, C.; Neri, G.; Tartaglia, M.; Zenker, M. Genomic duplication of PTPN11 is an uncommon cause of Noonan syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 149A, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Yang, Y.F.; Yin, B.L.; Chen, J.L.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.F.; Tan, Z.P. Microduplication of 3p25.2 encompassing RAF1 associated with congenital heart disease suggestive of Noonan syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2012, 158A, 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siano, M.A.; De Maggio, I.; Petillo, R.; Cocciadiferro, D.; Agolini, E.; Majolo, M.; Novelli, A.; Della Monica, M.; Piscopo, C. De Novo Mutation in KMT2C Manifesting as Kleefstra Syndrome 2: Case Report and Literature Review. Pediatr. Rep. 2022, 14, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, K.; Fan, X.; Gong, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, T.J.; Wu, N. Molecular Diagnostic Yield of Exome Sequencing and Chromosomal Microarray in Short Stature: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2023, e233566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toni, L.; Plachy, L.; Dusatkova, P.; Amaratunga, S.A.; Elblova, L.; Sumnik, Z.; Kolouskova, S.; Snajderova, M.; Obermannova, B.; Pruhova, S.; et al. The genetic landscape of children born small for gestational age with persistent short stature (SGA-SS). Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara-Isono, K.; Nakamura, A.; Fuke, T.; Inoue, T.; Kawashima, S.; Matsubara, K.; Sano, S.; Yamazawa, K.; Fukami, M.; Ogata, T.; et al. Pathogenic Copy Number and Sequence Variants in Children Born SGA With Short Stature Without Imprinting Disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3121–e3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Miao, H.; Liang, H.; Ke, X.; Yang, H.; Gong, F.; Wang, L.; Duan, L.; Chen, S.; Pan, H.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Short-Stature Patients With Collagen Gene Mutation and the Therapeutic Response to rhGH. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 820001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachy, L.; Dusatkova, P.; Maratova, K.; Petruzelkova, L.; Elblova, L.; Kolouskova, S.; Snajderova, M.; Obermannova, B.; Zemkova, D.; Sumnik, Z.; et al. Familial Short Stature-A Novel Phenotype of Growth Plate Collagenopathies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Kou, S.; Yang, W.; Zhang, M.; Ban, B. Clinical and genetic evaluation of children with short stature of unknown origin. BMC. Med. Genom. 2023, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No | Sex | Age | GA Week | BW kg | Mode of Delivery | Ht cm (SDS) | Wt kg (SDS) | Pat. Ht cm (SDS) | Mat. Ht cm (SDS) | MPH cm (SDS) | Psychomotor Issue | Dysmorphism | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 5 m CA 3 m | 29 + 2 | 1.15 | C/sec | 55 (−2.3) | 4.9 (−1.4) | 180 (1.2) | 168 (1.4) | 167.5 (1.3) | Gross motor delay | Prominent forehead, bulbous nose, low nasal bridge, short limb | ISS, R/O SD |
| 2 | F | 5 m | 37 + 5 | 3.16 | NSVD | 55.5 (−3.9) | 6.0 (−1.1) | 175 (0.1) | 155 (−1.3) | 156 (−1.0) | Gross motor delay | Prominent forehead, brachydactyly, short limb | ISS, R/O SD |
| 3 | M | 13 m | 40 | 3.51 | C/sec | 72.2 (−2.0) | 9.1 (−0.7) | 170 (−0.8) | 155 (−1.3) | 169 (−1.0) | None (4.6 y: IQ 120) | Macrocephaly, s/p VSD closure, resemble facial features with NS | ISS, R/O SD |
| 4 | F | 15 m | 35 + 5 | 2.57 | C/sec (twin) | 70.0 (−2.7) | 7.9 (−1.6) | 174 (−0.1) | 158 (−0.6) | 159.5 (−0.3) | None | FTT, sparse hair & eyebrows, long philtrum, down-slanting palpebral fissure, high forehead | ISS, R/O SD |
| 5 | M | 31 m | 38 | 2.9 | C/sec | 82.5 (−2.9) | 10.3 (−2.3) | 167 (−1.4) | 161 (0.0) | 170.5 (−0.7) | None | - | ISS |
| 6 | M | 3 y 10 m | 38 | 3.1 | C/sec | 91.6 (−2.6) | 13.1 (−1.7) | 178 (0.6) | 153 (−1.7) | 172 (−0.4) | None | - | ISS |
| 7 | F | 3 y 11 m | 40 + 6 | 3.5 | C/sec | 92.6 (−2.1) | 12.8 (−2.0) | 166 (−1.6) | 148 (−2.8) | 150.5 (−2.2) | None | Triangular face, prominent forehead, macrocephaly | FSS, R/O SD |
| 8 | M | 4 y 4 m | 40 | 3.6 | NSVD | 96.5 (−2.0) | 14.6 (−1.7) | 176 (0.3) | 153 (−1.7) | 171 (−0.6) | None | Blue sclerae | ISS |
| 9 | M | 4 y 10 m | 40 | 3 | NSVD | 96.7 (−2.7) | 14.3 (−2.4) | 169 (−1.0) | 153 (−1.7) | 167.5 (−1.3) | None | - | ISS |
| 10 | F | 4 y 11 m | 38 + 5 | 2.9 | NSVD | 98.2 (−2.3) | 13.2 (−2.9) | 160 (−2.7) | 165 (0.8) | 156 (−1.0) | None | - | FSS |
| 11 | F | 4 y 11 m | 40 + 6 | 4 | NSVD | 97.9 (−2.4) | 15.4 (−1.4) | 168 (−1.2) | 155 (−1.3) | 155 (−1.3) | None | - | ISS |
| 12 | M | 5 y | 40 | 3.1 | NSVD | 98.1 (−2.7) | 18.1 (−0.4) | 176 (0.3) | 160 (−0.2) | 175 (0.1) | None | Brachydactyly | ISS |
| 13 | F | 5 y 2 m | 38 | 2.9 | C/sec | 96.9 (−3.1) | 14.2 (−3.7) | 164 (−1.9) | 158 (−0.6) | 155 (−1.3) | None | - | ISS |
| 14 | M | 6 y 4 m | 35 + 4 | 2.1 | NSVD | 104.6 (−2.8) | 18.2 (−1.5) | 170 (−0.8) | 160 (−0.2) | 171.5 (−0.5) | None | - | ISS |
| 15 | M | 6 y 5 m | 39 + 5 | 3.9 | C/sec | 107.7 (−2.2) | 18.5 (−1.4) | 167 (−1.4) | 153 (−1.7) | 166.5 (−1.5) | None | - | ISS |
| 16 | F | 6 y 6 m | 37 + 2 | 2.6 | C/sec | 102.5 (−3.5) | 16.7 (−2.1) | 169 (−1.0) | 148 (−2.8) | 152 (−1.9) | None | Triangular face, down-slanting palpebral fissure, prominent philtrum, relative macrocephaly | FSS, R/O SD |
| 17-1 | M | 6 y 8 m | 40 | 3 | C/sec | 109.8 (−2.1) | 17.7 (−2.1) | 161 (−2.5) | 148 (−2.8) | 161 (−2.5) | None | - | FSS |
| 17-2 | F | 7 y 7 m | 40 | 3.03 | C/sec | 108.9 (−3.3) | 20.8 (−1.2) | 161 (−2.5) | 148 (−2.8) | 149 (−2.6) | None | - | FSS |
| 18 | F | 6 y 11 m | 38 | 2.7 | C/sec | 107.8 (−2.7) | 20.2 (−0.9) | 165 (−1.8) | 149 (−2.6) | 150.5 (−2.2) | None | Blue sclerae, triangular face, delayed eruption | FSS |
| 19 | M | 7 y | 39 | 2.8 | NSVD (IVF) | 105.5 (−3.6) | 18.0 (−2.3) | 170 (−0.8) | 158 (−0.6) | 170.5 (−0.7) | None | - | ISS |
| 20 | M | 8 y 6 m | 39 + 5 | 3.2 | NSVD | 118.1 (−2.5) | 25.8 (−0.8) | 153 (−4.1) | 153 (−1.7) | 159.5 (−2.8) | None | - | FSS |
| 21 | F | 8 y 2 m | 40 | 2.8 | NSVD | 111.1 (−3.5) | 17.7 (−2.9) | 170 (−0.8) | 148 (−2.8) | 152.5 (−1.8) | None | - | FSS |
| 22 | M | 8 y 10 m | 39 + 1 | 2.8 | NSVD | 113.0 (−3.8) | 22.0 (−2.0) | 170 (−0.8) | 160 (−0.2) | 171.5 (−0.5) | None | - | ISS |
| 23 | F | 8 y 9 m | 37 | 2.32 | C/sec (Twin) | 118.0 (−2.5) | 21.0 (−2.1) | 176 (0.3) | 150 (−2.4) | 156.5 (−0.9) | None | - | FSS |
| 24-1 | M | 8 y 8 m | 37 + 3 | 2.6 | NSVD | 119.2 (−2.3) | 19.7 (−2.7) | 176 (0.3) | 154 (−1.5) | 171.5 (−0.5) | Mild ID (IQ 64) | - | FSS |
| 24-2 | M | 10 y 8 m | 36 + 6 | 2.9 | NSVD | 126.8 (−2.7) | 25.8 (−2.0) | 176 (0.3) | 154 (−1.5) | 171.5 (−0.5) | None (IQ 94) | - | FSS |
| 24-3 | F | 7 y 10 m | 39 + 5 | 3.1 | NSVD | 117.3 (−1.6)* | 16.6 (−3.2) | 176 (0.3) | 154 (−1.5) | 158.5 (−0.5) | None (IQ 82) | - | FSS |
| 25 | F | 10 y | 40 | 3 | NSVD | 126 (−2.3) | 32.8 (−0.3) | 173 (−0.3) | 160 (−0.2) | 160 (−0.2) | None | - | ISS |
| 26 | M | 10 y 10 m | 40 | 3.2 | NSVD | 128.4 (−2.5) | 23.0 (−2.7) | 165 (−1.8) | 149 (−2.6) | 163.5 (−2.0) | Speech delay | Triangular face, narrow palpebral fissure, low nasal bridge | FSS, R/O SD |
| 27 | M | 10 y 11 m | 40 | 3.2 | NSVD | 126.7 (−2.9) | 25.0 (−2.3) | 164 (−1.9) | 154 (−1.5) | 165.5 (−1.7) | None | - | ISS |
| 28 | M | 10 y 11 m | 37 + 6 | 2.86 | NSVD | 130.1 (−2.3) | 23.4 (−2.7) | 164 (−1.9) | 154 (−1.5) | 165.5 (−1.7) | None | - | ISS |
| 29 | M | 11 y 8 m | 41 | 3 | NSVD | 126.5 (−3.4) | 23.8 (−2.9) | 170 (−0.8) | 160 (−0.2) | 171.5 (−0.5) | None | - | ISS |
| 30 | F | 11 y | 40 | 2.9 | NSVD | 122.2 (−3.7) | 22.5 (−3.0) | 170 (−0.8) | 160 (−0.2) | 158.5 (−0.5) | ADHD | s/p PDA ligation, ASD closure | ISS |
| 31 | M | 11 y 11 m | 38 + 2 | 3.3 | C/sec | 135.8 (−2.1) | 37.3 (−0.9) | 160 (−2.7) | 164 (0.6) | 168.5 (−1.1) | ADHD, mild ID (IQ 69) | Sparse hair and eyebrows, pear like nose | FSS, R/O SD |
| 32-1 | F | 6 y | 40 | 3.6 | C/sec | 103.8 (−2.6) | 15.4 (−2.5) | 161 (−2.5) | 162 (0.2) | 155 (−1.3) | None | FSS | |
| 32-2 | F | 10 y 1 m | 40 | 2.8 | C/sec | 122.9 (−2.9) | 26.8 (−1.5) | 161 (−2.5) | 162 (0.2) | 155 (−1.3) | None | FSS (GHD) | |
| 32-3 | F | 11 y 10 m | 38 | 3.3 | C/sec | 135.4 (−2.3) | 36.6 (−0.8) | 161 (−2.5) | 162 (0.2) | 155 (−1.3) | None | FSS | |
| 33 | F | 12 y | 40 | 3.1 | NSVD | 134.2 (−2.6) | 49.6 (0.7) | 170 (−0.8) | 150 (−2.4) | 156 (−1.0) | None | - | FSS |
| 34 | F | 12 y 6 m | 37 | 2.64 | NSVD | 134 (−3.1) | 27.3 (−2.9) | 171 (−0.6) | 151 (−2.1) | 154.5 (−1.4) | None | - | FSS |
| 35 | F | 14 y | 36 | 2.2 | C/sec | 129.3 (−4.9) | 21.2 (−6.1) | 173 (−0.3) | 163 (0.4) | 161.5 (0.1) | Severe ID, wide gait, stereotypic behavior | Microcephaly, widely spaced teeth, hypertelorism | ISS, R/O SD |
| 36 | F | 17 y | 41 | 3.99 | C/sec | 151.5 (−2.0) | 79.1 (2.7) | 166 (−1.5) | 161 (0.0) | 158 (−0.6) | Moderate ID | s/p TOF, polydactyly, and ectopic anus, obesity | ISS, R/O SD |
| Pt. No. | Category | Disease | Gene | cDNA Variant | Protein Variant | MAF a | In Silico Analysis b | Inheritance | ACMG Classification [22] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paracrine signaling | |||||||||
| 16 | FSS | Short stature with nonspecific skeletal abnormalities | NPR2 | c.1099A>G | p.Lys367Glu | 0/0 | D/T/D/ | Mat | LP (PM1, PM2, PP1, PP4) |
| 12 | ISS | Brachydactyly, type A1 | IHH | c.683G>T | p.Arg228Leu | 0/0 | T/D/D | Mat | VUS (PM2, PP3, PP4) |
| 36 | ISS | Bardet–Biedl syndrome, type 1 | BBS1 | c.1285C>T c.1339G>A | p.Arg429 * p.Ala447Thr | 0.0008/0 0.00037/0 | - D/T/D | Pat Mat | PV (PVS1, PM2, PM3, PP3, PP4) LP (PM1, PM2, PM3, PP3, PP4) |
| 31 | FSS | Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome 1 | TRPS1 | c.2686dup | p.Gln896Profs *8 | 0/0 | - | Pat | PV (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP4) |
| Extracellular matrix (ECM) defects | |||||||||
| 18 | FSS | Osteogenesis imperfecta | COL1A1 | c.3766G>A | p.Ala1256Thr | 0.00134 /0.00045 | D/D/D | Mat | VUS (PM2, PP1, PP3, PP4) |
| 8 | ISS | Osteogenesis imperfecta | COL1A1 | c.757C>T | p.Arg253 * | 0/0 | - | Pat | PV (PVS1, PM2, PP1, PP3, PP4, PP5) |
| 20 | ISS | Type II collagen disorder | COL2A1 | c.889G>A | p.Gly297Ser | 0/0 | D/T/ D | De novo | LP (PM1, PM2, PM6, PP3, PP4) |
| 2 | ISS | Type II collagen disorder | COL2A1 | c.3310G>C | p.Gly1104Arg | 0/0 | D/T/D | De novo | LP (PS2, PM1, PM2, PP3, PP5) |
| 13 | ISS | 3MC syndrome 1 | MASP1 | c.851C>T c.744 + 7C>T | p.Ser284Leu splicing | 0/0 0.0000041/0.00045 | D/D/D D/D/D | Pat Mat | LP (PM3, PM2, PP2, PP3, PP4) |
| Fundamental cellular process | |||||||||
| 24-1 24-2 24-3 | FSS | Noonan syndrome | PTPN11 | c.209A>G | p.Lys70Arg | 0/0 | D/D/D | Mat | LP (PM1, PM2 PP1 PP3 PP4 PP5) |
| 4 | FSS | Noonan syndrome | PTPN11 | c.1511T>C | p.Met504Thr | 0/0 | D/D/D | Pat | LP (PM1, PM2, PP1, PP3, PP4) |
| 7 | FSS | Legius syndrome | SPRED1 | c.950C>G | p.Ser317 * | 0/0 | - | Pat | PV (PVS1 PM2 PP1 PP3 PP4) |
| 32-1 32-2 | FSS | Helsmoortel-van der Aa syndrome | ADNP | c.2992G>T | p.Asp998Tyr | 0/0 | D/D/D | Mat | LP (PM1, PM2, PP1, PP4) |
| 35 | ISS | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 34 | CERT1 (COL4A3BP) | c.779C>T | p.Ser260Leu | 0/0 | D/D/D | De novo | PV (PS1 PS2 PM1 PM2 PP4) |
| 1 | ISS | NAD synthetase deficiency disorder | NADSYN1 | c.164A>T c.1048-1G>T | p.Asp55Val splicing | 0.00081/0 0/0 | D/D/D | Pat Mat | LP (PM3, PM2, PP2, PP3, PP4) |
| 3 | ISS | 22q11.2 microduplication syndrome (Noonan syndrome 10) | LZTR1 | duplication | De novo | ||||
| 30 | ISS | 7q36 microdeletion syndrome (Kleefstra syndrome 2) | KMT2C | deletion | De novo | ||||
| Patients [Reference] (Number) | SGA [54] (n = 176) | SGA Without Imprinting Disorder [55] (n = 86) | Non-SGA (ISS) [15] (n = 102) | Non-SGA (ISS and FSS) [This Study] (n = 41, 36 Families) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic testing | Whole exome sequencing or targeted exome sequencing | Copy number analysis, targeted exome sequencing | Targeted exome sequencing | Targeted exome sequencing |
| Genetic etiology (CNVs + PV or LP) | 74/176 (42%) | 13/86 (15.1%) | 17/102 (16.7%) | 15/36 (41.7%) |
| Growth plate dysfunction | 43/176 (24.4%) | 5/86 (5.8%) | 17/102 (16.7%) | 13/36 (36.1%) |
| Paracrine signaling | 7/176 (4%) FGFR3, FGFR2, NPR2 | 1/86 (1.1%) NPR2 | 8/102 (7.8%) IHH (4), NPR2 (2), FGFR3 (2) | 3/36 (8%) NPR2, IHH(VUS), BBS1, TRPS1 |
| Extracellular matrix | 24/176 (13.6%) ACAN, various collagens, FLNB, MATN3 SHOX deficiency (7) | COL2A1(VUS), SHOX (VUS), ACAN (VUS), FGFR3 (VUS) | 4/102 (3.9%) SHOX, ACAN, ACAN/SHOX *, COL2A1/NF1 * | 4/36 (11%) COL1A1(VUS, LP), COL2A1(2), MASP1 |
| Fundamental intracellular/intranuclear processes | 12/176 (6.8%) CDC42, KMT2D, LMNA, NSD1, PTPN11, SRCAP, SON, SOS1, SOX9, TLK2 | 4/86 (4.7%) SMAD4, PTPN11, CBL, MYCN | 4/102 (3.9%) NF1, PTPN11, BRAF, CBL/SHOX * | 6/36 (17%) PTPN11(2), SPRED1, ADNP, CERT1, NADSYN1 |
| Miscellaneous chromosomal aberrations | 5/176 (2.8%) del17q24.2 del1p31.1p31.3 del22q11.2 del6q24.3q25.1 dupXq | 8/86 (9.3%) del1q21.1q21.2 del22q11.2 dupXp22.33 del19p13.12 dup5q35.2q35.3 (2) del10q26.1q26.3 delXp22.3p11.2/dupXq11.1q28 | - | 2/36 (6%) dup22q11.2 (LZTR1) del7q36 (KMT2C) |
| Pituitary development, GH-IGF-1 or IGF-2 axis, and thyroid axis | 14/176 (8%) LHX4, OTX2, PROKR2, PTCH1, POU1F1, GHSR, IGFALS, IGF1R, STAT3, HMGA2, TRHR, THRA | GHR(VUS), IGF1R(VUS) | 1/102 (0.9%) GHSR | - |
| Silver–Russell syndrome | 12/176 (6.8%) : 11p15, UPD7 | Excluded | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-M.; Lim, H.-H.; Kim, E.; Kim, G.; Kim, M.; So, H.; Lee, B.K.; Kwon, Y.; Min, J.; Lee, Y.S. Exploring the Genetic Causes for Postnatal Growth Failure in Children Born Non-Small for Gestational Age. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206508
Kim Y-M, Lim H-H, Kim E, Kim G, Kim M, So H, Lee BK, Kwon Y, Min J, Lee YS. Exploring the Genetic Causes for Postnatal Growth Failure in Children Born Non-Small for Gestational Age. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(20):6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206508
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yoo-Mi, Han-Hyuk Lim, Eunhee Kim, Geena Kim, Minji Kim, Hyejin So, Byoung Kook Lee, Yoowon Kwon, Jeesu Min, and Young Seok Lee. 2023. "Exploring the Genetic Causes for Postnatal Growth Failure in Children Born Non-Small for Gestational Age" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 20: 6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206508
APA StyleKim, Y.-M., Lim, H.-H., Kim, E., Kim, G., Kim, M., So, H., Lee, B. K., Kwon, Y., Min, J., & Lee, Y. S. (2023). Exploring the Genetic Causes for Postnatal Growth Failure in Children Born Non-Small for Gestational Age. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(20), 6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206508







