Does Ramadan Intermittent Fasting Affect the Fasting Blood Glucose Level among Type II Diabetic Patients?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Participants
2.2. Demographic Data
2.3. Attitude toward Ramadan Intermittent Fasting
2.4. Fasting Blood Glucose Level
2.5. Medication Adherence
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Types of Medicines and Adherence before and during Ramadan
3.3. FBG Values, Attitude, and Practice toward Ramadan Fasting among Diabetic Patients
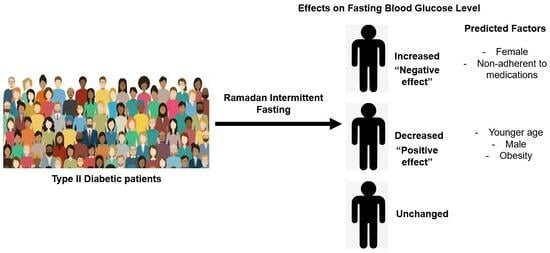
3.4. Effects of Fasting for Ramadan on FBG Value
3.5. Factors Affecting FBG Levels during the Fasting of Ramadan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Visioli, F.; Mucignat-Caretta, C.; Anile, F.; Panaite, S.A. Traditional and Medical Applications of Fasting. Nutrients 2022, 14, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cabo, R.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Bernier, M.; Hall, M.N.; Madeo, F. The search for antiaging interventions: From elixirs to fasting regimens. Cell 2014, 157, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos-Vatopaidinos, I.E.; Papagiannopoulou, M.; Sideris, V. Dry Fasting Physiology: Responses to Hypovolemia and Hypertonicity. Complement. Med. Res. 2020, 27, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkour, M.; Giddey, A.D.; Soares, N.C.; Semreen, M.H.; Bustanji, Y.; Zeb, F.; Halwani, R.; Faris, M.E. Ramadan diurnal intermittent fasting is associated with significant plasma metabolomics changes in subjects with overweight and obesity: A prospective cohort study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1008730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Jung, J.Y.; Oh, C.M.; Choi, J.M.; Kim, M.H.; Ha, E.; Ryoo, J.H. Fasting glucose level and the risk of incident osteoporosis in the Koreans. Bone 2021, 142, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A.D.; Souza, E.C.F.; Echazu Boschemeier, A.G.; Costa, C.; Bezerra, H.S.; Feitosa, E. Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and living with a chronic condition: Participatory study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Ali, M.; Zehra, T.; Haider Zaidi, S.A.; Tariq, R. Intermittent Fasting: A User-Friendly Method for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus 2021, 13, e19348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Hong, D.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. Effect of Intermittent Fasting Diet on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Impaired Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 6999907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M. Role of intermittent fasting on improving health and reducing diseases. Int. J. Health Sci. 2014, 8, V–VI. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, A.; Abdulle, A.; El Issa, A.; Al Suwaidi, J.; Nagelkerke, N. Favorable changes in lipid profile: The effects of fasting after Ramadan. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salti, I.; Benard, E.; Detournay, B.; Bianchi-Biscay, M.; Le Brigand, C.; Voinet, C.; Jabbar, A. A population-based study of diabetes and its characteristics during the fasting month of Ramadan in 13 countries: Results of the epidemiology of diabetes and Ramadan 1422/2001 (EPIDIAR) study. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2306–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Arouj, M.; Assaad-Khalil, S.; Buse, J.; Fahdil, I.; Fahmy, M.; Hafez, S.; Hassanein, M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Kendall, D.; Kishawi, S.; et al. Recommendations for management of diabetes during Ramadan: Update 2010. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Abu Al Magd, M.; Annabi, F.A.; Assaad-Khalil, S.; Ba-Essa, E.M.; Fahdil, I.; Karadeniz, S.; Meriden, T.; Misha’l, A.A.; Pozzilli, P.; et al. Recommendations for management of diabetes during Ramadan: Update 2015. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2015, 3, e000108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Peng, C.; Yan, C.; Yan, D. Metabolite biomarkers of type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes, A. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin. Diabetes 2021, 39, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, A.M.; Alrahbeni, T.; Qarni, A.A.; Qarni, H.M.A. Adherence to diabetes medication among diabetic patients in the Bisha governorate of Saudi Arabia—A cross-sectional survey. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2019, 13, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashur, S.T.; Shamsuddin, K.; Shah, S.A.; Bosseri, S.; Morisky, D.E. Reliability and known-group validity of the Arabic version of the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. East Mediterr. Health J. 2015, 21, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, S.I.; Khan, H.A.; Ekhzaimy, A.; Masood, A.; Sakharkar, M.K. Significance of HbA1c Test in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Diabetic Patients. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbuwono, D.S.; Sazli, B.I.; Kurniawan, F.; Darmowidjojo, B.; Koesnoe, S.; Tahapary, D.L. The impact of Ramadan fasting on Fetuin-A level in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assy, M.H.; Awd, M.; Elshabrawy, A.M.; Gharieb, M. Effect of Ramadan fasting on incidence of cerebrovascular stroke in Egyptian patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 151, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bener, A.; Yousafzai, M.T. Effect of Ramadan fasting on diabetes mellitus: A population-based study in Qatar. J. Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2014, 89, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, H.; Al-Nassr, N.; Mohammed, I.; Khan, A.; MacDonald, R.; Mussleman, P.; Malik, R.A. Effect of Ramadan fasting in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.; Rosenberg, I. Nutrition and aging: Changes in the regulation of energy metabolism with aging. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, J.M.; Santos, I.; Pezarat-Correia, P.; Silva, A.M.; Mendonca, G.V. Effects of Ramadan and Non-ramadan Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 26, 625240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasmeh, R.; Jarrar, Y.; Al-Sheikh, I.; Alshaiah, H.; Jarrar, Q.; Alani, R.; Abudahab, S. Effects of Fasting and Phoenix dactylifera on the Expression of Major Drug- Metabolizing Enzymes in the Mouse Livers. Curr. Drug Metab. 2022, 23, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Whim, M.D. Fasting induces a form of autonomic synaptic plasticity that prevents hypoglycemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3029–E3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, M.A.; Hussein, R.N.; Al-Kurd, R.A.; Al-Fararjeh, M.A.; Bustanji, Y.K.; Mohammad, M.K. Impact of ramadan intermittent fasting on oxidative stress measured by urinary 15-f(2t)-isoprostane. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 802924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrar, Y. Pharmaceutical practice and selling of drugs during Ramadan. Libyan J. Med. 2011, 6, 5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brockman, N.K.; Sigal, R.J.; Kenny, G.P.; Riddell, M.C.; Perkins, B.A.; Yardley, J.E. Sex-Related Differences in Blood Glucose Responses to Resistance Exercise in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Secondary Data Analysis. Can. J. Diabetes 2020, 44, 267–273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Perez, L.E.; Alvarez, M.; Dilla, T.; Gil-Guillen, V.; Orozco-Beltran, D. Adherence to therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2013, 4, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wabe, N.T.; Angamo, M.T.; Hussein, S. Medication adherence in diabetes mellitus and self management practices among type-2 diabetics in Ethiopia. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 3, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Demographic or Clinical | Frequency n (%) |
|---|---|
| Residency Location | |
| Large City | 80 (44.2) |
| Village | 97 (55.6) |
| Palestinian Refugee Camp | 4 (2.2) |
| Age | |
| <40 Years old | 45 (24.9) |
| 40–50 Years old | 33 (18.2) |
| 51–60 Years old | 52 (28.7) |
| 61–70 Years old | 35 (19.3) |
| >70 Years old | 16 (8.8) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 96 (53.0) |
| Female | 85 (47.0) |
| Number of Family Members | |
| Living alone | 8 (4.4) |
| 1–3 Family Members | 73 (40.3) |
| 4–5 Family Members | 54 (29.8) |
| >5 Family Members | 46 (25.4) |
| Weight (depending on the BMI value) | |
| Under Weight | 14 (7.7) |
| Normal Weight | 74 (40.9) |
| Overweight | 76 (42.0) |
| Obese | 17 (9.4) |
| Other Diseases? | |
| Yes | 100 (55.2) |
| No | 81 (44.8) |
| Respiratory Diseases? | |
| Yes | 11 (6.1) |
| No | 170 (93.9) |
| Cardiovascular Diseases? | |
| Yes | 64 (35.4) |
| No | 117 (64.6) |
| Musculoskeletal Diseases? | |
| Yes | 25 (13.8) |
| No | 156 (86.2) |
| Digestive Diseases? | |
| Yes | 13 (7.2) |
| No | 168 (92.8) |
| Endocrine Diseases? | |
| Yes | 10 (5.5) |
| No | 171 (94.5) |
| Psychological Diseases? | |
| Yes | 11 (6.1) |
| No | 170 (93.9) |
| Medications | Frequency n (%) |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | |
| Yes | 3 (1.7) |
| No | 178 (98.3) |
| Aspirin | |
| Yes | 14 (7.7) |
| No | 167 (92.3) |
| Anti-hyperlipidemic | |
| Yes | 21 (11.6) |
| No | 160 (88.4) |
| Anti-hypertensive | |
| Yes | 15 (8.3) |
| No | 166 (91.7) |
| Anti-Diabetic Treatment Modalities | |
| None | 8 (4.4) |
| Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs (OHDs) | 101 (55.8) |
| Combination of OHDs and Insulin | 18 (9.9) |
| Insulin | 54 (29.8) |
| Anti-Diabetic Treatment Regimen | |
| None | 9 (5.0) |
| Metformin | 58 (32.0) |
| Metformin + SUs and/or DPP4 Inhibitors | 41 (22.7) |
| Insulin | 54 (29.8) |
| Insulin + Metformin | 11 (6.1) |
| Insulin + Metformin and/or DPP4 Inhibitors | 8 (4.4) |
| Medication Adherence before Ramadan | |
| Yes | 169 (93.4) |
| No | 12 (6.6) |
| Medication Adherence during Ramadan | |
| Yes | 169 (93.4) |
| No | 12 (6.6) |
| Variable | Frequency n (%) |
|---|---|
| Did you fast the whole Ramadan month? | |
| Yes | 126 (69.6) |
| No | 55 (30.4) |
| Is fasting easy during Ramadan? | |
| Yes | 102 (56.4) |
| No | 79 (43.6) |
| Do you think that RIF has a negative effect on diabetic patients? | |
| Yes | 73 (40.3) |
| No | 108 (59.7) |
| Variables: (Socio-Demographic and Clinical Characteristics) | Unchanged FBG Level (Yes) N = 58 | p Value | Negative Effects (Yes) N = 43 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residency Location | 0.165 | 0.364 | ||
| Large Cities | 26 (44.8) | 17 (39.5) | ||
| Small Cities | 29 (50.0) | 26 (60.5) | ||
| Palestinian Refugee Camp | 3 (5.2) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Age | 0.170 | 0.840 | ||
| <40 Years old | 10 (17.2) | 10 (23.3) | ||
| 40–50 Years old | 13 (22.4) | 6 (14.0) | ||
| 51–60 Years old | 15 (25.9) | 14 (32.6) | ||
| 61–70 Years old | 16 (27.6) | 8 (18.6) | ||
| >60 Years old | 4 (6.9) | 5 (11.6) | ||
| Sex | 0.475 | 0.001 | ||
| Male | 33 (56.9) | 13 (30.2) | ||
| Female | 25 (43.1) | 30 (69.8) | ||
| Number of Family Members | 0.324 | 0.699 | ||
| Living alone | 3 (5.2) | 3 (7.0) | ||
| 1–3 Family members | 27 (46.6) | 17 (39.5) | ||
| 4–5 family members | 12 (20.7) | 14 (32.6) | ||
| >5 family members | 16 (27.6) | 9 (20.9) | ||
| Weight (Depending on BMI) | 0.093 | 0.774 | ||
| Under weight | 8 (13.8) | 3 (7.0) | ||
| Normal weight | 19 (32.8) | 15 (34.9) | ||
| Over weight | 27 (46.6) | 20 (46.5) | ||
| Obese | 4 (6.9) | 5 (11.6) | ||
| Other Diseases? | 0.989 | 0.095 | ||
| Yes | 32 (55.2) | 19 (44.2) | ||
| No | 26 (44.8) | 57 (41.3) | ||
| Respiratory Diseases? | 0.325 | 0.654 | ||
| Yes | 5 (8.6) | 2 (4.7) | ||
| No | 53 (91.4) | 41 (95.3) | ||
| Cardiovascular Diseases? | 0.866 | 0.023 | ||
| Yes | 20 (34.5) | 9 (20.9) | ||
| No | 38 (65.5) | 34 (79.1) | ||
| Musculoskeletal Diseases? | 0.641 | 0.975 | ||
| Yes | 7 (12.1) | 6 (14.0) | ||
| No | 51 (87.9) | 37 (86) | ||
| Digestive Diseases? | 0.051 | 0.196 | ||
| Yes | 1 (1.7) | 5 (11.6) | ||
| No | 57 (98.3) | 38 (88.4) | ||
| Endocrine Diseases | 0.579 | 0.774 | ||
| Yes | 4 (6.9) | 2 (4.7) | ||
| No | 54 (93.1) | 41 (95.3) | ||
| Psychological Diseases | 0.726 | 0.238 | ||
| Yes | 3 (5.2) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| No | 55 (94.8) | 42 (97.7) | ||
| Aspirin | 0.376 | 0.080 | ||
| Yes | 3 (5.2) | 6 (14.0) | ||
| No | 55 (94.8) | 37 (86.0) | ||
| Anti-Hyperlipidemic | 0.717 | 0.101 | ||
| Yes | 6 (10.3) | 8 (18.6) | ||
| No | 52 (89.7) | 35 (81.4) | ||
| Anti-Hypertensive | 0.105 | 0.721 | ||
| Yes | 2 (3.4) | 3 (7.0) | ||
| No | 56 (96.6) | 40 (93.0) | ||
| Anti-Diabetic Treatment Modalities | 0.740 | 0.365 | ||
| None | 3 (5.2) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| OHDs | 29 (50.0) | 24 (55.8) | ||
| Combines OHDs and Insulin | 7 (12.1) | 7 (16.3) | ||
| Insulin alone | 19 (32.8) | 11 (25.6) | ||
| Anti-Diabetic Treatment Regimen | 0.760 | 0.078 | ||
| None | 3 (5.2) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| Metformin | 17 (29.3) | 9 (20.9) | ||
| Metformin + SUs and/or DPP4Is | 13 (22.4) | 15 (34.9) | ||
| Insulin | 19 (32.8) | 11 (25.6) | ||
| Insulin + Metformin | 2 (3.4) | 5 (11.6) | ||
| Insulin + Metformin and/or DPP4Is | 4 (6.9) | 2 (4.7) | ||
| Medication Adherence before Ramadan | 0.167 | 0.194 | ||
| Yes | 6 (10.3) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| No | 52 (89.7) | 42 (97.7) | ||
| Medication Adherence during Ramadan | 0.087 | 0.035 | ||
| Yes | 7 (12.1) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| No | 51 (87.9) | 43 (100.0) |
| Variable | Odds Ratio with 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Residency Location | 0.29 | |
| Large Cities | Reference | |
| Small Cities | 1.006 (0.462–2.192) | 0.998 |
| Palestinian Refugee Camp | 0.068 (0.002–1.994) | 0.119 |
| Age | 0.043 | |
| <40 Years old | Reference | |
| 40–50 Years old | 0.358 (0.106–1.216) | 0.1 |
| 51–60 Years old | 0.224 (0.066–0.762) | 0.017 |
| 61–70 Years old | 0.133 (0.032–0.556) | 0.006 |
| >70 Years old | 0.082 (0.012–0.573) | 0.012 |
| Weight | 0.023 | |
| Underweight | Reference | |
| Normal Weight | 18.020 (2.309–140.621) | 0.006 |
| Overweight | 8.778 (1.117–68.958) | 0.039 |
| Obese | 20.932 (1.959–223.663) | 0.012 |
| Sex | 0.028 | |
| Male | Reference | |
| Female | 0.383 (0.163–0.900) | |
| Number of Family Members | 0.573 | |
| Living alone | Reference | |
| 1–3 Family Members | 2.962 (0.320–27.405) | 0.339 |
| 4–5 Family Members | 4.655 (0.463–46.764) | 0.191 |
| >5 Family Members | 3.740 (0.367–38.136) | 0.266 |
| Fasting the whole Ramadan? | ||
| Yes | 0.583 (0.177–1.918) | 0.375 |
| No | Reference | |
| Positive attitude toward RIF | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.009 |
| No | 0.001 (0.000–0.187) | |
| Other Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.315 |
| No | 2.152 (0.482–9.599) | |
| Cardiovascular Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.088 |
| No | 0.221 (0.058–0.847) | |
| Respiratory Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.178 |
| No | 0.236 (0.029–1.926) | |
| Musculoskeletal Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.331 |
| No | 0.550 (0.165–1.835) | |
| Digestive Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.224 |
| No | 0.369 (0.074–1.840) | |
| Endocrine Diseases? | 0.802 | |
| Yes | Reference | |
| No | 0.800 (0.139–4.598) | |
| Psychological Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.054 |
| No | 0.166 (0.029–0.955) | |
| Aspirin? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.396 |
| No | 2.913 (0.247–34.346) | |
| Anti-Hyperlipidemic? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.734 |
| No | 1.299 (0.287–5.889) | |
| Antihypertensive? | ||
| Yes | Reference | 0.078 |
| No | 0.058 (0.007–0.476) | |
| Anti-Diabetic Treatment Modalities: | 0.998 | |
| None | Reference | |
| Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs (OHDs) | 216.3 (0.000) | 1 |
| Combination of OHDs and Insulin | 2.922 (0.000) | 1 |
| Insulin alone | 1.204 (0.196–7.406) | 0.842 |
| Anti-Diabetic Treatment Regimen: | 0.224 | |
| None | Reference | |
| Metformin | 0.000 (0.000) | 1 |
| Metformin + SUs and/or DPP4 Inhibitors | 0.000 (0.000) | 1 |
| Insulin | 0.000 (0.000) | 1 |
| Insulin + Metformin | 0.748 (0.000) | 1 |
| Insulin + Metformin and/or DPP4 Inhibitors | 0.103 (0.000) | 1 |
| Medication Adherence before Ramadan | ||
| Yes | 1.503 (0.182–12.421) | 0.705 |
| No | Reference | |
| Medication Adherence during Ramadan | ||
| Yes | 2.970 (0.330–26.772) | |
| No | Reference | 0.332 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio with 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.067 | |
| <40 Years old | Reference | |
| 40–50 Years old | 0.491 (0.181–1.328) | 0.161 |
| 51–60 Years old | 0.407 (0.160–1.038) | 0.060 |
| 61–70 Years old | 0.195 (0.063–0.608) | 0.005 |
| >70 Years old | 0.215 (0.050–0.930) | 0.040 |
| Weight | 0.087 | |
| Underweight | Reference | |
| Normal Weight | 5.683 (1.214–26.609) | 0.027 |
| Overweight | 3.263 (0.700–15.204) | 0.132 |
| Obese | 6.403 (1.033–39.700) | 0.046 |
| Sex | 0.031 | |
| Male | Reference | |
| Female | 0.469 (0.235–0.935) | |
| Positive attitude toward RIF | ||
| Yes | Reference | |
| No | 0.732 (0.362–1.480) | 0.385 |
| Cardiovascular Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | |
| No | 0.472 (0.274–0.896) | 0.071 |
| Psychological Diseases? | ||
| Yes | Reference | |
| No | 0.283 (0.066–1.219) | 0.090 |
| Antihypertensive? | ||
| Yes | Reference | |
| No | 0.328 (0.062–0.837) | 0.056 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jarrar, Y.; Abdul-Wahab, G.; Mosleh, R.; Abudahab, S.; Jarrar, Q.; Hamdan, A.; Qadous, S.G.; Balasmeh, R.; Abed, A.F.; Ibrahim, Y.; et al. Does Ramadan Intermittent Fasting Affect the Fasting Blood Glucose Level among Type II Diabetic Patients? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206604
Jarrar Y, Abdul-Wahab G, Mosleh R, Abudahab S, Jarrar Q, Hamdan A, Qadous SG, Balasmeh R, Abed AF, Ibrahim Y, et al. Does Ramadan Intermittent Fasting Affect the Fasting Blood Glucose Level among Type II Diabetic Patients? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(20):6604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206604
Chicago/Turabian StyleJarrar, Yazun, Ghasaq Abdul-Wahab, Rami Mosleh, Sara Abudahab, Qais Jarrar, Anas Hamdan, Shurouq Ghalib Qadous, Ruba Balasmeh, Abdulqader Fadhil Abed, Yasmeen Ibrahim, and et al. 2023. "Does Ramadan Intermittent Fasting Affect the Fasting Blood Glucose Level among Type II Diabetic Patients?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 20: 6604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206604
APA StyleJarrar, Y., Abdul-Wahab, G., Mosleh, R., Abudahab, S., Jarrar, Q., Hamdan, A., Qadous, S. G., Balasmeh, R., Abed, A. F., Ibrahim, Y., Al-Doaiss, A. A., & AlShehri, M. A. (2023). Does Ramadan Intermittent Fasting Affect the Fasting Blood Glucose Level among Type II Diabetic Patients? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(20), 6604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206604