Minimally Invasive Cervical Styloidectomy in Stylohyoid Syndrome (Eagle Syndrome)
Abstract
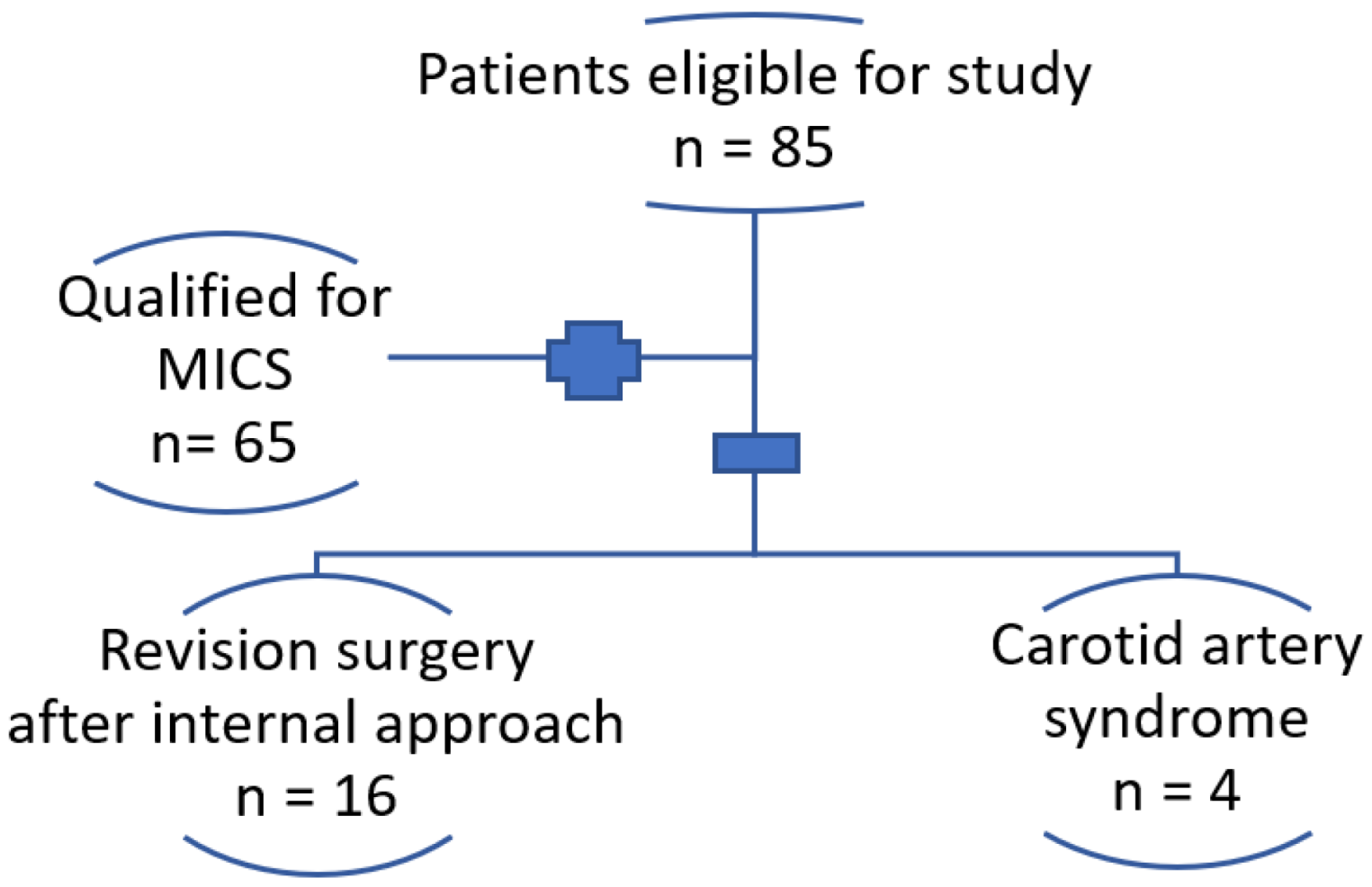
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Surgery Planning
2.3. Surgical Technique
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. History
4.2. Symptoms
4.3. Diagnostic Imaging
4.4. Treatment Options
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kış, H.C.; Çabuk, D.S. Evaluation of styloid chain calcification related to temporomandibular joint disc displacement: A retrospective cohort study. Oral Radiol. 2020, 37, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glogoff, M.R.; Baum, S.M.; Cheifetz, I. Diagnosis and treatment of Eagle’s syndrome. J. Oral. Surg. 1981, 39, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thoenissen, P.; Bittermann, G.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Oshima, T.; Fretwurst, T. Eagle’s syndrome—A non-perceived differential diagnosis of temporomandibular disorder. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2015, 15, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossman, J.R., Jr.; Tarsitano, J.J. The styloid-stylohyoid syndrome. J. Oral. Surg. 1977, 35, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, S.M.; Elzay, R.P.; Irish, E.F. Styloid Process Variation: Radiologic and Clinical Study. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1970, 91, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keur, J.; Campbell, J.; McCarthy, J.; Ralph, W. The clinical significance of the elongated styloid process. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1986, 61, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Sigurta, D.; Daddona, A.; Dalloca, L.; Miani, A.; Tafuro, F.; Sforza, C. Calcification of the stylohyoid ligament: Incidence and morphoquantitative evaluations. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1990, 69, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsour, P.A.; Young, W.G. Variability of the styloid process and stylohyoid ligament in panoramic radiographs. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1986, 61, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbuena, L.; Hayes, D.; Ramirez, S.G.; Johnson, R. Eagle’s Syndrome (Elongated Styloid Process). South. Med. J. 1997, 90, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, W.W. Elongated Styloid Processes: Report of Two Cases. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1937, 25, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisan, Q.; Rubin, F.; Werner, A.; Guiquerro, S.; Bonfils, P.; Laccourreye, O. Management of stylohyoid syndrome: A systematic review following PRISMA guidelines. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2019, 136, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesalius, A. Ex off. Ioannis Oporini. In De Humani Corporis Fabrica; Liber Septum: Basileae, Switzerland, 1543. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, P. Anatomia. Patavii 1652, 13, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Stirling, A. On bony growths invading the tonsil. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1896, 27, 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwight, T. Stylo-Hyoid Ossification. Ann. Surg. 1907, 46, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garel, M. Angine styloidienne chronique. Lyon Med. 1927, 9, 654–661. [Google Scholar]
- Bernfeld, K. Fur Begriffsbestimmung und Pathogenese eines neuen Krankheitsbildes, des sog. Styloideus-Komplexes. Z. Laryngol. Rhinol. 1932, 23, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Czako, L.; Simko, K.; Thurzo, A.; Galis, B.; Varga, I. The Syndrome of Elongated Styloid Process, the Eagle’s Syndrome—From Anatomical, Evolutionary and Embryological Backgrounds to 3D Printing and Personalized Surgery Planning. Report of Five Cases. Medicina 2020, 56, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, E.; Voljevica, A.; Šahinović, M.; Šahinović, A.; Arapović, A. Styloid Process Length Variations: An Osteological Study. Acta Medica Acad. 2022, 51, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, W.W. Symptomatic Elongated Styloid Process Report of Two Cases of Styloid Process-Carotid Artery Syndrome with Operation. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1949, 49, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, W.W. Elongated Styloid Process: Symptoms and Treatment. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1958, 67, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, W.W. The symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of the elongated styloid process. Am. Surg. 1962, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malik, J.N.; Monga, S.; Sharma, A.P.; Nabi, N.; Naseeruddin, K. Stylalgia Revisited: Clinical Profile and Management. Iran. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 30, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Usseglio, J.; Montoro, F.M.; Martin, S.; Lerat, J.; Laloze, J.; Taibi, A.; Brie, J. Accident ischémique transitoire, une manifestation rare du syndrome d’Eagle [Transcient ischemic attack, a rare manifestation of Eagle syndrome]. Rev. Stomatol. Chir. Maxillofac. Chir. Orale. 2016, 117, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, A.O.; de Tejada, E.C.S.; Peña, C.L.; Góngora, M.S.; Delgado, A.B. Eagle’s syndrome as a cause of oropharyngeal dysphagia. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2023, 115, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, D.R.; Pujary, K.; Aggarwal, M.; Punnoose, S.E.; Chaly, V.A. Role of three-dimensional computed tomography reconstruction in the management of elongated styloid process: A preliminary study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 121, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcioglu, H.A.; Kilic, C.; Akyol, M.; Ozan, H.; Kokten, G. Length of the styloid process and anatomical implications for Eagle’s syndrome. Folia Morphol. 2009, 68, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Bin Wang, Z.; Yan, K.S. Intraoral and extraoral approach for surgical treatment of Eagle’s syndrome: A retrospective study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2022, 279, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.N.; Browske, L.K.M.; Rosenthal, C.M.D. Elongated Styloid Processes and Calcified Stylohyoid Ligaments in a Patient With Neck Pain: Implications for Manual Therapy Practice. J. Chiropr. Med. 2014, 13, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunachak, S. Anterior cervical pain syndromes: Hyoid, thyroid and cricoid cartilage syndromes and their treatment with triamcinolone acetonide. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1995, 109, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Hatashima, S.; Matsuda, T. Non-surgical therapy for bilateral glossopharyngeal neuralgia caused by Eagle’s syndrome, diagnosed by three-dimensional computed tomography: A case report. J. Anesth. 2012, 26, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Y.; Dar, J.A.; Almadani, A.A.R. Seizures with an atypical aetiology in an elderly patient: Eagle’s syndrome—How does one treat it? BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2014206136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supsic, B.; Minzola, D. Anesthetic Management of a Patient with Eagle’s Syndrome: A Case Study. AANA J. 2023, 91, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singhania, A.A.; Chauhan, N.V.; George, A.; Rathwala, K. Lidocine Infiltration Test: An Useful Test in the Prediction of Results of Styloidectomy for Eagle’s Syndrome. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 65, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T.D.; Iida, M.D.; Sugiyama, S.D.; Mitsudo, K.D. Intraoral Styloidectomy Using an Endoscope with Tissue Retractor. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2021, 33, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, Y.; Cha, D.; Kim, S. Transoral robotic surgery in Eagle’s syndrome: Our experience on four patients. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czajka, M.; Szuta, M.; Zapała, J.; Janecka, I. Assessment of surgical treatment of Eagle’s syndrome. Otolaryngol. Polska 2019, 73, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Dou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zong, C.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y. Application of surgical navigation in styloidectomy for treating Eagle’s syndrome. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.C.; Kamath, M.; Reddy, K.M.; Raju, K.; Agarwal, S. Elongated styloid process (Eagle’s syndrome): A clinical study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 60, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambor, D.V.; Shetgaunkar, R.R.; De Sa, C. Stylalgia: Our Experience of 101 Cases Treated by Intraoral Styloidectomy. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Custódio, A.L.N.; de Oliveira, D.R.F. An intraoral surgical approach to the styloid process in Eagle’s syndrome. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 13, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.; Jindal, G.; Garg, S. Eagle’s Syndrome: A New Surgical Technique for Styloidectomy. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2015, 14, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamin, O.S.; Arif, A.T.; Razha, A.B.C.; Aziz, J.M.M.A.; Rashid, M.J.M.; Rasheed, M.K.M.; Abdullah, L.L.B.; Mustafa, S.A.; Ghafoor, R.A.B.; Qutbadeen, N.B.; et al. Chronically misdiagnosed Eagle’s syndrome, treated through transoral styloidectomy: A rare case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 3611–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, F.M.; Xiao, R.; Burkey, B.B. Surgical management of patients with Eagle syndrome. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| PATIENT (n = 65) | |
|---|---|
| AGE IN YEARS (MEAN) | 16–70 (38) |
| GENDER, N (%) | |
| male | 18 (27.7%) |
| female | 47 (72.3%) |
| SITE, N (%) | |
| right | 28 (43.1%) |
| left | 37 (56.9%) |
| BILATERAL STYLALGIA, N (%) | 9 (13.8%) |
| LENGTH OF STYLOID (MEAN) | 2.6–8 cm (42.5 cm) |
| PATIENTS (n = 65) | |
|---|---|
| OPERATIVE TIME IN MINUTES (MEAN) | 15–65 (36) |
| LENGTH OF REMOVED STYLOID IN CM (MEAN) | 2–7 (43) |
| COMPLICATIONS | No. of patients (%) |
| Ipsilateral temporary facial nerve weakness | 1 (1.5%) |
| OUTCOMES | No. of patients (%) |
| Complete remission of symptoms | 56 (86.2%) |
| Significant improvement with partial remission of symptoms | 7 (10.8%) |
| Partial relapse without the need for surgical treatment | 1 (1.5%) |
| No improvement | 1 (1.5%) |
| OVERALL SUCCESS RATE | 63 (97.0%) |
| SATISFACTION WITH THE AESTHETIC RESULT | 65 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bargiel, J.; Gontarz, M.; Marecik, T.; Szczurowski, P.; Gąsiorowski, K.; Zapała, J.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. Minimally Invasive Cervical Styloidectomy in Stylohyoid Syndrome (Eagle Syndrome). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216763
Bargiel J, Gontarz M, Marecik T, Szczurowski P, Gąsiorowski K, Zapała J, Wyszyńska-Pawelec G. Minimally Invasive Cervical Styloidectomy in Stylohyoid Syndrome (Eagle Syndrome). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(21):6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216763
Chicago/Turabian StyleBargiel, Jakub, Michał Gontarz, Tomasz Marecik, Paweł Szczurowski, Krzysztof Gąsiorowski, Jan Zapała, and Grażyna Wyszyńska-Pawelec. 2023. "Minimally Invasive Cervical Styloidectomy in Stylohyoid Syndrome (Eagle Syndrome)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 21: 6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216763
APA StyleBargiel, J., Gontarz, M., Marecik, T., Szczurowski, P., Gąsiorowski, K., Zapała, J., & Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. (2023). Minimally Invasive Cervical Styloidectomy in Stylohyoid Syndrome (Eagle Syndrome). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(21), 6763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216763






