Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss on Periapical Radiographs—A Diagnostic Study Using Different Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Periapical Radiographs
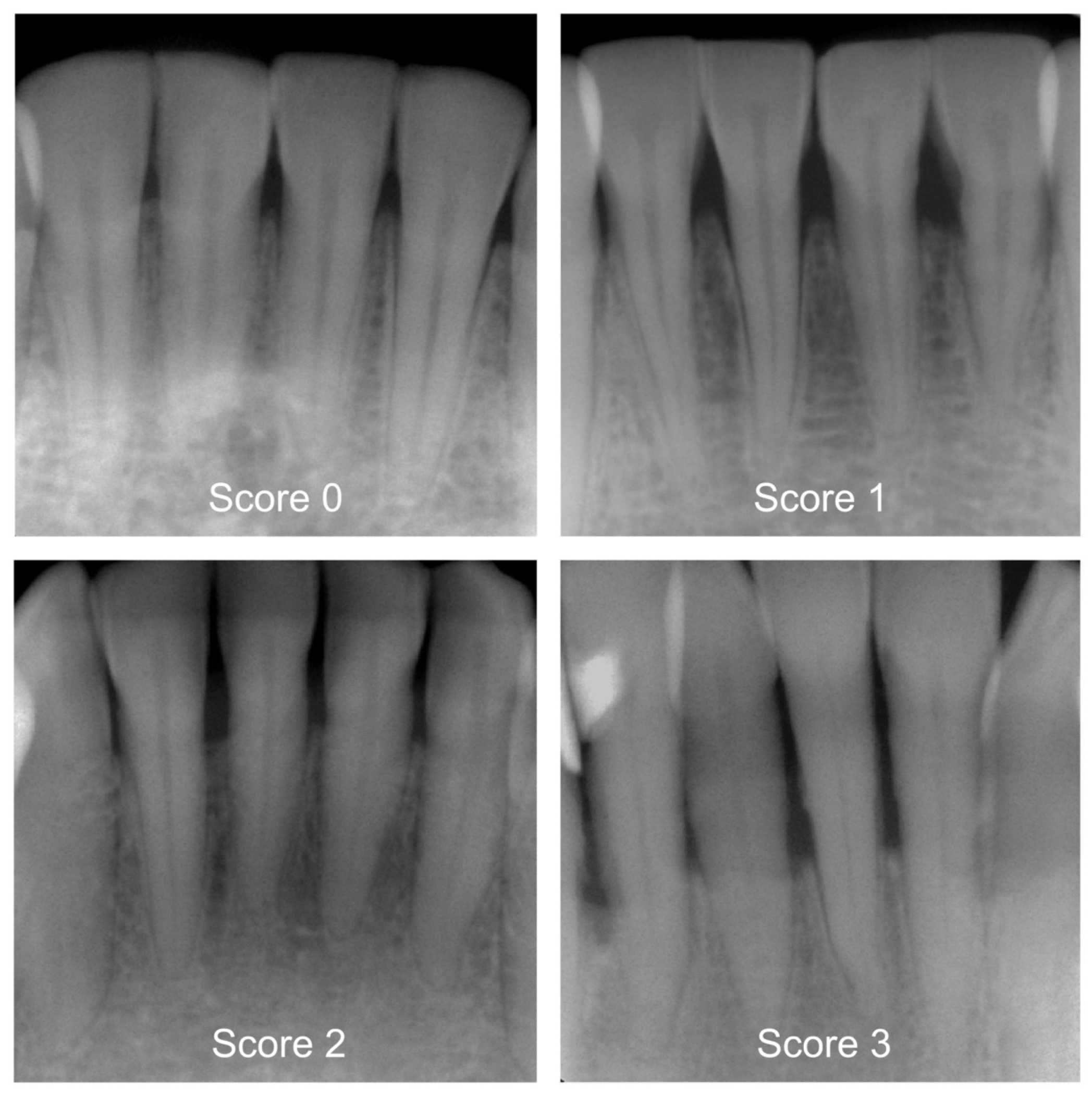
2.3. Categorization of Periodontal Bone Loss (Reference Standard)
2.4. Training of the Deep-Learning-Based CNNs (Test Method)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Bernabe, E.; Dahiya, M.; Bhandari, B.; Murray, C.J.; Marcenes, W. Global burden of severe periodontitis in 1990–2010: A systematic review and meta-regression. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frencken, J.E.; Sharma, P.; Stenhouse, L.; Green, D.; Laverty, D.; Dietrich, T. Global epidemiology of dental caries and severe periodontitis—A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44 (Suppl. S18), S94–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, M.A. Prevalence of periodontal disease, its association with systemic diseases and prevention. Int. J. Health Sci. 2017, 11, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Damgaard, C.; Holmstrup, P.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Nielsen, C.H. The complement system and its role in the pathogenesis of periodontitis: Current concepts. J. Periodontal. Res. 2015, 50, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, A.A.; Al-Taweel, F.B.; Al-Sharqi, A.J.B.; Gul, S.S.; Sha, A.; Chapple, I.L.C. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of periodontitis: From symbiosis to dysbiosis. J. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2197779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könönen, E.; Gursoy, M.; Gursoy, U.K. Periodontitis: A Multifaceted Disease of Tooth-Supporting Tissues. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelman, D.; Petersen, P.E.; Ueda, H. Oral health, general health, and quality of life in older people. Spec. Care Dent. 2008, 28, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Jepsen, S.; Jin, L.; Otomo-Corgel, J. Impact of the global burden of periodontal diseases on health, nutrition and wellbeing of mankind: A call for global action. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Links between atherosclerotic and periodontal disease. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgnakke, W.S.; Ylöstalo, P.V.; Taylor, G.W.; Genco, R.J. Effect of periodontal disease on diabetes: Systematic review of epidemiologic observational evidence. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84 (Suppl. S4), S135–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes-Filho, I.S.; Cruz, S.S.D.; Trindade, S.C.; Passos-Soares, J.S.; Carvalho-Filho, P.C.; Figueiredo, A.; Lyrio, A.O.; Hintz, A.M.; Pereira, M.G.; Scannapieco, F. Periodontitis and respiratory diseases: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preshaw, P.M. Detection and diagnosis of periodontal conditions amenable to prevention. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15 (Suppl. S1), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnick, J.J.; Silverstein, L. Periodontal probing: Probe tip diameter. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, R.; Eaton, K.A.; Savage, A. Methodological issues in epidemiological studies of periodontitis—How can it be improved? BMC Oral Health 2010, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusburger, T.; Wulk, A.; Kessler, A.; Heck, K.; Hickel, R.; Dujic, H.; Kuhnisch, J. The Detection of Dental Pathologies on Periapical Radiographs-Results from a Reliability Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Cao, Y.; Huang, T.; Ahn, E.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H. Automated periodontitis bone loss diagnosis in panoramic radiographs using a bespoke two-stage detector. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, R.P.; Bano, S.; Orishko, A.; Tan, H.J.; Moreno Sancho, F.; D’Aiuto, F.; Stoyanov, D. Automating Periodontal bone loss measurement via dental landmark localization. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, G.; Awawdeh, M.; Farook, F.F.; Aljohani, M.; Aldhafiri, R.M.; Aldhoayan, M. Artificial intelligence (AI) diagnostic tools: Utilizing a convolutional neural network (CNN) to assess periodontal bone level radiographically a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Chang, M.F.; Angelov, N.; Hsu, C.Y.; Meng, H.W.; Sheng, S.; Glick, A.; Chang, K.; He, Y.R.; Lin, Y.B.; et al. Application of deep machine learning for the radiographic diagnosis of periodontitis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 6629–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, T.; Lee, C.T.; Chen, L.; Jiang, X.; Shams, S. A comprehensive artificial intelligence framework for dental diagnosis and charting. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.T.; Kabir, T.; Nelson, J.; Sheng, S.; Meng, H.W.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Walji, M.F.; Jiang, X.; Shams, S. Use of the deep learning approach to measure alveolar bone level. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoromokos, N.; Parinussa, S.; Claessen, F.; Moin, D.A.; Loos, B.G. Estimation of Alveolar Bone Loss in Periodontitis Using Machine Learning. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y. Dental disease detection on periapical radiographs based on deep convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.-h.; Jeong, S.-N.; Choi, S.-H. Diagnosis and prediction of periodontally compromised teeth using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2018, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.L.; Huang, P.Y.; Huang, P.W. Automatic methods for alveolar bone loss degree measurement in periodontitis periapical radiographs. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 148, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.L.; Huang, P.W.; Huang, P.Y.; Hsu, H.C. Alveolar bone-loss area localization in periodontitis radiographs based on threshold segmentation with a hybrid feature fused of intensity and the H-value of fractional Brownian motion model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2015, 121, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Wu, Y.F.; Aung, L.M.; Lin, J.C.; Ngo, S.T.; Su, J.N.; Lin, Y.M.; Chang, W.J. Automatic recognition of teeth and periodontal bone loss measurement in digital radiographs using deep-learning artificial intelligence. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, D.; Cao, Z.; Wu, F.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, F. A two-stage deep learning architecture for radiographic staging of periodontal bone loss. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertas, K.; Pence, I.; Cesmeli, M.S.; Ay, Z.Y. Determination of the stage and grade of periodontitis according to the current classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions (2018) using machine learning algorithms. J. Periodontal. Implant Sci. 2023, 53, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widyaningrum, R.; Candradewi, I.; Aji, N.; Aulianisa, R. Comparison of Multi-Label U-Net and Mask R-CNN for panoramic radiograph segmentation to detect periodontitis. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2022, 52, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadrozny, L.; Regulski, P.; Brus-Sawczuk, K.; Czajkowska, M.; Parkanyi, L.; Ganz, S.; Mijiritsky, E. Artificial Intelligence Application in Assessment of Panoramic Radiographs. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.; She, Y.; Gao, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, X. An Interpretable Computer-Aided Diagnosis Method for Periodontitis from Panoramic Radiographs. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 655556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Yong, T.H.; Shin, N.Y.; Jang, B.G.; Kim, J.E.; Huh, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Heo, M.S.; Choi, S.C.; et al. Deep Learning Hybrid Method to Automatically Diagnose Periodontal Bone Loss and Stage Periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanathornwong, B.; Suebnukarn, S. Automatic detection of periodontal compromised teeth in digital panoramic radiographs using faster regional convolutional neural networks. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2020, 50, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.S.; Song, I.S.; Jung, K.H. DeNTNet: Deep Neural Transfer Network for the detection of periodontal bone loss using panoramic dental radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krois, J.; Ekert, T.; Meinhold, L.; Golla, T.; Kharbot, B.; Wittemeier, A.; Dorfer, C.; Schwendicke, F. Deep Learning for the Radiographic Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, F.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Tang, X.; Deng, L.; Song, L. Deep learning for the early identification of periodontitis: A retrospective, multicentre study. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, e985–e992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, K.; Aktuna Belgin, C.; Manulis, D.; Golitsyna, M.; Bayrak, S.; Aksoy, S.; Sanders, A.; Onder, M.; Ezhov, M.; Shamshiev, M.; et al. Determining the reliability of diagnosis and treatment using artificial intelligence software with panoramic radiographs. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2023, 53, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Biancardi, A.M.; Jones, O.; Andrew, D. Artificial Intelligence in Periodontology: A Scoping Review. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Joda, T.; Soffe, B.; Awan, K.H.; Fageeh, H.N.; Tovani-Palone, M.R.; Licari, F.W. Efficacy of artificial intelligence in the detection of periodontal bone loss and classification of periodontal diseases: A systematic review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2023, 154, 795–804.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turosz, N.; Checinska, K.; Checinski, M.; Brzozowska, A.; Nowak, Z.; Sikora, M. Applications of artificial intelligence in the analysis of dental panoramic radiographs: An overview of systematic reviews. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2023, 52, 20230284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.; et al. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendicke, F.; Singh, T.; Lee, J.H.; Gaudin, R.; Chaurasia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Uribe, S.; Krois, J.; on behalf of the IADR E-oral Health Network and the ITU WHO Focus Group AI for Health. Artificial intelligence in dental research: Checklist for authors, reviewers, readers. J. Dent. 2021, 107, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1801.04381. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.03545. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.E.; Farewell, V.T. Using and Understanding Medical Statistics; S.Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.E.; Nam, N.E.; Shim, J.S.; Jung, Y.H.; Cho, B.H.; Hwang, J.J. Transfer Learning via Deep Neural Networks for Implant Fixture System Classification Using Periapical Radiographs. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, V.P.; Yansane, A.M.; Brandon, R.G.; Vaderhobli, R.; Lin, G.H.; Hekmatian, H.; Deng, W.; Joshi, N.; Bhandari, H.; Sadat, A.S.; et al. A generative adversarial inpainting network to enhance prediction of periodontal clinical attachment level. J. Dent. 2022, 123, 104211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepelassi, E.A.; Tsiklakis, K.; Diamanti-Kipioti, A. Radiographic detection and assessment of the periodontal endosseous defects. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2000, 27, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorellini, J.P.; Sourvanos, D.; Sarimento, H.; Karimbux, N.; Luan, K.W. Periodontal and Implant Radiology. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 65, 447–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Examiner | Inter-Examiner | Intra-Examiner |
|---|---|---|
| P.H. | 0.601–0.650 | 0.889 |
| T.M. | 0.620–0.658 | 0.554 |
| A.W. | 0.762–0.796 | 0.779 |
| L.M. | 0.516–0.565 | 0.797 |
| U.W. | 0.658–0.699 | 0.455 |
| J.K. | 0.706–0.748 | 0.579 |
| H.D. | 0.529–0.534 | 0.767 |
| Expert Classification | Healthy Periodontium (Score 0) | Mild PBL (Score 1) | Moderate PBL (Score 2) | Severe PBL (Score 3) | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| Upper jaw | Anteriors | 653 | 3.0 | 661 | 3.0 | 433 | 2.0 | 197 | 0.9 | 1944 | 8.9 |
| 1st Quadrant | 1701 | 7.8 | 1826 | 8.4 | 851 | 3.9 | 367 | 1.7 | 4745 | 21.8 | |
| 2nd Quadrant | 1231 | 5.6 | 2080 | 9.5 | 1093 | 5.0 | 312 | 1.5 | 4716 | 21.6 | |
| Lower jaw | Anteriors | 202 | 0.9 | 676 | 3.1 | 786 | 3.6 | 325 | 1.5 | 1989 | 9.1 |
| 3rd Quadrant | 1477 | 6.8 | 2033 | 9.3 | 593 | 2.7 | 157 | 0.7 | 4260 | 19.5 | |
| 4th Quadrant | 1282 | 5.9 | 2027 | 9.3 | 713 | 3.3 | 143 | 0.6 | 4165 | 19.1 | |
| Total | 6546 | 30.0 | 9303 | 42.6 | 4469 | 20.5 | 1501 | 6.9 | 21,819 | 100 | |
| CNN | True Positive (TP) | True Negative (TN) | False Positive (FP) | False Negative (FN) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| ResNet-18 | 1876 | 62.5 | 609 | 20.3 | 294 | 9.8 | 221 | 7.4 |
| MobileNetV2 | 1863 | 62.1 | 598 | 19.9 | 305 | 10.2 | 234 | 7.8 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 1877 | 62.6 | 639 | 21.3 | 264 | 8.8 | 220 | 7.3 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 1901 | 63.4 | 643 | 21.4 | 260 | 8.7 | 196 | 6.5 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 1890 | 63.0 | 637 | 21.2 | 266 | 8.9 | 207 | 6.9 |
| CNN | Diagnostic Performance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | SE | SP | NPV | PPV | AUC | |
| ResNet-18 | 82.8 | 89.5 | 67.4 | 73.4 | 86.5 | 0.884 |
| MobileNetV2 | 82.0 | 88.8 | 66.2 | 71.9 | 85.9 | 0.884 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 83.9 | 89.5 | 70.8 | 74.4 | 87.7 | 0.903 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 84.8 | 90.7 | 71.2 | 76.6 | 88.0 | 0.911 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 84.2 | 90.1 | 70.5 | 75.5 | 87.7 | 0.913 |
| CNN | True Positive (TP) | True Negative (TN) | False Positive (FP) | False Negative (FN) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| Radiographs with maxillary anterior teeth | ||||||||
| ResNet-18 | 155 | 58.7 | 72 | 27.3 | 27 | 10.2 | 10 | 3.8 |
| MobileNetV2 | 154 | 58.3 | 79 | 29.9 | 20 | 7.6 | 11 | 4.2 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 155 | 58.7 | 79 | 29.9 | 20 | 7.6 | 10 | 3.8 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 157 | 59.5 | 77 | 29.2 | 22 | 8.3 | 8 | 3.0 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 158 | 59.8 | 74 | 28.0 | 25 | 9.5 | 7 | 2.7 |
| Radiographs with maxillary posterior teeth | ||||||||
| ResNet-18 | 786 | 59.1 | 263 | 19.8 | 151 | 11.4 | 129 | 9.7 |
| MobileNetV2 | 798 | 60.0 | 239 | 18.0 | 175 | 13.2 | 117 | 8.8 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 783 | 58.9 | 275 | 20.7 | 139 | 10.5 | 132 | 9.9 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 794 | 59.7 | 278 | 20.9 | 136 | 10.2 | 121 | 9.1 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 794 | 59.8 | 266 | 20.0 | 148 | 11.1 | 121 | 9.1 |
| Radiographs with mandibular anterior teeth | ||||||||
| ResNet-18 | 244 | 89.7 | 14 | 5.2 | 11 | 4.0 | 3 | 1.1 |
| MobileNetV2 | 239 | 87.9 | 19 | 7.0 | 6 | 2.2 | 8 | 2.9 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 242 | 89.0 | 19 | 7.0 | 6 | 2.2 | 5 | 1.8 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 244 | 89.7 | 17 | 6.3 | 8 | 2.9 | 3 | 1.1 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 243 | 89.3 | 18 | 6.6 | 7 | 2.6 | 4 | 1.5 |
| Radiographs with mandibular posterior teeth | ||||||||
| ResNet-18 | 691 | 60.9 | 260 | 22.9 | 105 | 9.3 | 79 | 6.9 |
| MobileNetV2 | 672 | 59.2 | 261 | 23.0 | 104 | 9.2 | 98 | 8.6 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 697 | 61.4 | 266 | 23.4 | 99 | 8.7 | 73 | 6.4 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 706 | 62.2 | 271 | 23.9 | 94 | 8.3 | 64 | 5.6 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 695 | 61.2 | 279 | 24.6 | 86 | 7.6 | 75 | 6.6 |
| Diagnostic Performance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | SE | SP | NPV | PPV | AUC | |
| Radiographs with maxillary anterior teeth | ||||||
| ResNet-18 | 86.0 | 93.9 | 72.7 | 87.8 | 85.2 | 0.925 |
| MobileNetV2 | 88.3 | 93.3 | 79.8 | 87.8 | 88.5 | 0.935 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 88.6 | 93.9 | 79.8 | 88.8 | 88.6 | 0.951 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 88.6 | 95.2 | 77.8 | 90.6 | 87.7 | 0.959 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 87.9 | 95.8 | 74.7 | 91.4 | 86.3 | 0.950 |
| Radiographs with maxillary posterior teeth | ||||||
| ResNet-18 | 78.9 | 85.9 | 63.5 | 67.1 | 83.9 | 0.844 |
| MobileNetV2 | 78.0 | 87.2 | 57.7 | 67.1 | 82.0 | 0.839 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 79.6 | 85.6 | 66.4 | 67.6 | 84.9 | 0.858 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 80.7 | 86.8 | 67.1 | 69.7 | 85.4 | 0.868 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 79.8 | 86.8 | 64.3 | 68.7 | 84.3 | 0.866 |
| Radiographs with mandibular anterior teeth | ||||||
| ResNet-18 | 94.9 | 98.8 | 56.0 | 82.4 | 95.7 | 0.942 |
| MobileNetV2 | 94.9 | 96.8 | 76.0 | 70.4 | 97.6 | 0.960 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 96.0 | 98.0 | 76.0 | 79.2 | 97.6 | 0.969 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 96.0 | 98.8 | 68.0 | 85.0 | 96.8 | 0.978 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 96.0 | 98.4 | 72.0 | 81.8 | 97.2 | 0.980 |
| Radiographs with mandibular posterior teeth | ||||||
| ResNet-18 | 83.8 | 89.7 | 71.2 | 76.7 | 86.8 | 0.895 |
| MobileNetV2 | 82.2 | 87.3 | 71.5 | 72.7 | 86.6 | 0.893 |
| ConvNeXT/s 1 | 84.8 | 90.5 | 72.9 | 78.5 | 87.6 | 0.916 |
| ConvNeXT/b 2 | 86.1 | 91.7 | 74.2 | 80.9 | 88.3 | 0.921 |
| ConvNeXT/l 3 | 85.8 | 90.3 | 76.4 | 78.8 | 89.0 | 0.930 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoss, P.; Meyer, O.; Wölfle, U.C.; Wülk, A.; Meusburger, T.; Meier, L.; Hickel, R.; Gruhn, V.; Hesenius, M.; Kühnisch, J.; et al. Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss on Periapical Radiographs—A Diagnostic Study Using Different Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227189
Hoss P, Meyer O, Wölfle UC, Wülk A, Meusburger T, Meier L, Hickel R, Gruhn V, Hesenius M, Kühnisch J, et al. Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss on Periapical Radiographs—A Diagnostic Study Using Different Convolutional Neural Networks. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(22):7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227189
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoss, Patrick, Ole Meyer, Uta Christine Wölfle, Annika Wülk, Theresa Meusburger, Leon Meier, Reinhard Hickel, Volker Gruhn, Marc Hesenius, Jan Kühnisch, and et al. 2023. "Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss on Periapical Radiographs—A Diagnostic Study Using Different Convolutional Neural Networks" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 22: 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227189
APA StyleHoss, P., Meyer, O., Wölfle, U. C., Wülk, A., Meusburger, T., Meier, L., Hickel, R., Gruhn, V., Hesenius, M., Kühnisch, J., & Dujic, H. (2023). Detection of Periodontal Bone Loss on Periapical Radiographs—A Diagnostic Study Using Different Convolutional Neural Networks. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(22), 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227189







